概要
この記事では、PythonとShapelyを使用して六角形をモチーフにしたGenerative Artを作成する方法を紹介します。matplotlibとShapelyライブラリを活用して、円内に六角形のグリッドを描画し、さらに色や形を変化させて簡単なビジュアルアートを生成します。
平面充填 「テセレーション(tessellation)」 (タイル張り)
正多角形の平面充填 「テセレーション(tessellation)」 (いわゆる、タイル張り) が可能であるためには、その頂点で集まる内角の和が正確に $360^{\circ}$ でなければなりません。この条件を満たす正多角形を見つけるためには、正 $n$ 角形の内角の公式 $\frac{(n-2) \times 180^{\circ}}{n}$ を使用し、これを $k$ 倍して $360^{\circ}$ と等しくなるよう な $n, k$ の組み合わせを探します。つまり、次の方程式を満たす $n, k$ を見つける必要 があります :
k \times \frac{(n-2) \times 180^{\circ}}{n}=360^{\circ}
これを単純化すると :
\begin{gathered}
k \times(n-2) \times 180^{\circ}=360^{\circ} \times n \\
k \times(n-2)=2 n
\end{gathered}
$k, n$ は正の整数でなければならないため、この方程式を満たす $n$ の値は限られます。実際には、この方程式を満たすのは $n=3$ (正三角形) 、 $n=4$ (正方形) 、 $n=6$ (正六角形) の場合のみです。これ以外の $n$ については、方程式を満たす正の整数 $k$ が存在しないため、それらの正多角形は平面を敷き詰めることができません。この記事では六角形の例を紹介します。
必要なライブラリ
-
numpy: 数値計算のためのライブラリ -
matplotlib: 描画のためのライブラリ -
matplotlib.colors&matplotlib.cm: カラーマップを使用するためのモジュール
に加えて、多角形の演算などを簡単に操作するために、
-
Shapely: 幾何学的オブジェクトを操作するためのライブラリ
を用いています。この例では、六角形ですが、それ以外にも様々なポリゴンや、領域の結合などを簡単に扱うことができます。
Generative Artのアイディア
- カラーマップの選択: カラーマップを変更することで、異なる視覚効果を得ることができます。
plt.cmの中から、さまざまなカラーマップを試してみてください。 - 透明度の変化: 小さい正六角形の透明度を変えることで、奥行きの感じられるアートを作成できます。透明度を距離や他のパラメータに応じて変更してみてください。
- サイズと回転の変化: 小さい正六角形のサイズを徐々に変えたり、回転させたりすることで、動きのあるアートを作成できます。
- オーバーレイの使用: 複数のレイヤーを重ね合わせることで、複雑なパターンを作成することができます。
これらのアイディアを組み合わせることで、より創造的でユニークなGenerative Artを作成することができます。この記事では、基本パーツの簡単な紹介になりますが、ぜひ自由に書き換えて遊んでみてください。
コードの解説
google Colab 上で実行例を掲載しています。
コードを見ればわかる方はこちらを参照ください。
コードの概要
下記の3つの関数が、基本的な六角形の骨組みを作る部分になります。
- 六角形を変化させながら描画する関数
def hexagon_coordinates(cx, cy, r, offset_angle = 0.): - 六角形のグリッドを生成する関数
def create_hexagon_grid_in_circle(circle_radius, hex_radius): - 六角形のグリッドを描画する関数
def plot_hexagon_grid_in_circle(hexagon_grid, circle_radius):
これに加えて、六角形を変化させながら描画する関数を用意して、以下の関数群により、六角形のサイズを変化させたり、回転させたりしながら描画します。これにより、動的で興味深いビジュアルエフェクトが生まれます。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
# 六角形グリッド内に、より小さな六角形を描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_rotate(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
# さらに、六角形を回転させながら描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_move(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
# 六角形を動かしながら描画します。
関数の定義のコード部分
関数定義のコード部分を載せておきます。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
import matplotlib.colors as colors
import matplotlib.cm as cm
# 与えられた中心座標と半径に基づいて、六角形の頂点座標を計算します。
def hexagon_coordinates(cx, cy, r, offset_angle = 0.):
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 7)[:-1]
x_coords = cx + r * np.cos(angles + offset_angle)
y_coords = cy + r * np.sin(angles + offset_angle)
return list(zip(x_coords, y_coords))
# 与えられた半径の円内に収まるように六角形のグリッドを生成します。
def create_hexagon_grid_in_circle(circle_radius, hex_radius):
hexagon_grid = []
vertical_distance = hex_radius * np.sqrt(3)
grid_radius = int(circle_radius / vertical_distance) + 1
for row in range(-grid_radius, grid_radius + 1):
for col in range(-grid_radius, grid_radius + 1):
cx = col * 1.5 * hex_radius
cy = row * vertical_distance
if col % 2 == 1:
cy += vertical_distance / 2
# Create a hexagon
hexagon = Polygon(hexagon_coordinates(cx, cy, hex_radius))
# Check if all vertices of the hexagon are inside the circle
if all(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) <= circle_radius for x, y in hexagon.exterior.coords):
hexagon_grid.append(hexagon)
return hexagon_grid
# 生成した六角形のグリッドを描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_in_circle(hexagon_grid, circle_radius):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
circle = plt.Circle((0, 0), circle_radius, color='yellow', alpha=0.05, ec='blue')
ax.add_patch(circle)
for hexagon in hexagon_grid:
x, y = hexagon.exterior.xy
ax.plot(x, y, color='blue', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
ax.set_xlim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
ax.set_ylim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
plt.savefig("hexgon_grid_in_circle.png")
plt.show()
# 六角形グリッド内に、より小さな六角形を描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
circle = plt.Circle((0, 0), circle_radius, color='yellow', alpha=0.05, ec='blue')
ax.add_patch(circle)
current_radius = start_hex_radius
N = int(current_radius/decrement)
usercmap = plt.get_cmap(cmap)
cNorm = colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=N)
scalarMap = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=cNorm, cmap=usercmap)
j = 0
while current_radius > 0:
for i, hexagon in enumerate(hexagon_grid):
# Get the center of the hexagon
center_x, center_y = hexagon.centroid.x, hexagon.centroid.y
# Create a smaller hexagon at the same center
smaller_hexagon = Polygon(hexagon_coordinates(center_x, center_y, current_radius))
x, y = smaller_hexagon.exterior.xy
c = scalarMap.to_rgba(np.random.rand()*N)
ax.plot(x, y, color=c, alpha=np.random.rand()**2)
current_radius -= decrement
j += 1
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
ax.set_xlim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
ax.set_ylim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
plt.savefig("hexgon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons.png")
plt.show()
# さらに、六角形を回転させながら描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_rotate(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
circle = plt.Circle((0, 0), circle_radius, color='yellow', alpha=0.05, ec='blue')
ax.add_patch(circle)
current_radius = start_hex_radius
N = int(current_radius/decrement)
usercmap = plt.get_cmap(cmap)
cNorm = colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=N)
scalarMap = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=cNorm, cmap=usercmap)
j = 0
while current_radius > 0:
for i, hexagon in enumerate(hexagon_grid):
# Get the center of the hexagon
center_x, center_y = hexagon.centroid.x, hexagon.centroid.y
# Create a smaller hexagon at the same center
smaller_hexagon = Polygon(hexagon_coordinates(center_x, center_y, current_radius, offset_angle = 0.1 * j))
x, y = smaller_hexagon.exterior.xy
c = scalarMap.to_rgba(np.random.rand()*N)
ax.plot(x, y, color=c, alpha=np.random.rand()**2)
current_radius -= decrement
j += 1
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
ax.set_xlim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
ax.set_ylim(-circle_radius, circle_radius)
plt.savefig("hexgon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_rotates.png")
plt.show()
# 六角形を動かしながら描画します。
def plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_move(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, start_hex_radius, decrement, cmap="hsv"):
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
circle = plt.Circle((0, 0), circle_radius, color='yellow', alpha=0.05, ec='blue')
ax.add_patch(circle)
current_radius = start_hex_radius
N = int(current_radius/decrement)
usercmap = plt.get_cmap(cmap)
cNorm = colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=N)
scalarMap = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=cNorm, cmap=usercmap)
j = 0
while current_radius > 0:
for i, hexagon in enumerate(hexagon_grid):
# Get the center of the hexagon
center_x, center_y = hexagon.centroid.x, hexagon.centroid.y
# Create a smaller hexagon at the same center
smaller_hexagon = Polygon(hexagon_coordinates(center_x - 0.01 * j, center_y + 0.03 * j, current_radius, offset_angle = 2 * j))
x, y = smaller_hexagon.exterior.xy
c = scalarMap.to_rgba(np.random.rand()*N)
ax.plot(x, y, color=c, alpha=np.random.rand()**2)
current_radius -= decrement
j += 1
ax.set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
ax.set_xlim(-circle_radius*1.1, circle_radius*1.1)
ax.set_ylim(-circle_radius*1.1, circle_radius*1.1)
plt.savefig("hexgon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_move.png")
plt.show()
実行例
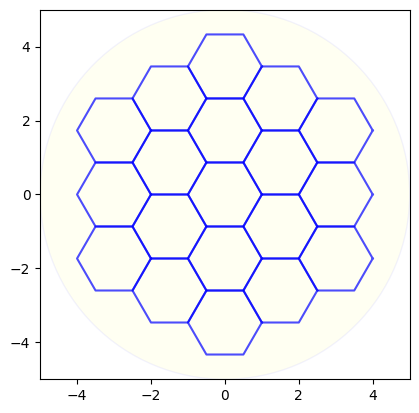
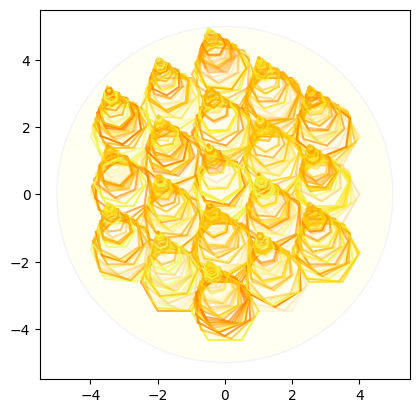
六角形の数が 19 個の場合
# Parameters for the grid in a circle
circle_radius = 5
hex_radius = 1
hexagon_grid = create_hexagon_grid_in_circle(circle_radius, hex_radius)
print("Number of hexagon = ", len(hexagon_grid)) # 19
六角形の枠組みの描画
# Plot the grid in a circle
plot_hexagon_grid_in_circle(hexagon_grid, circle_radius)
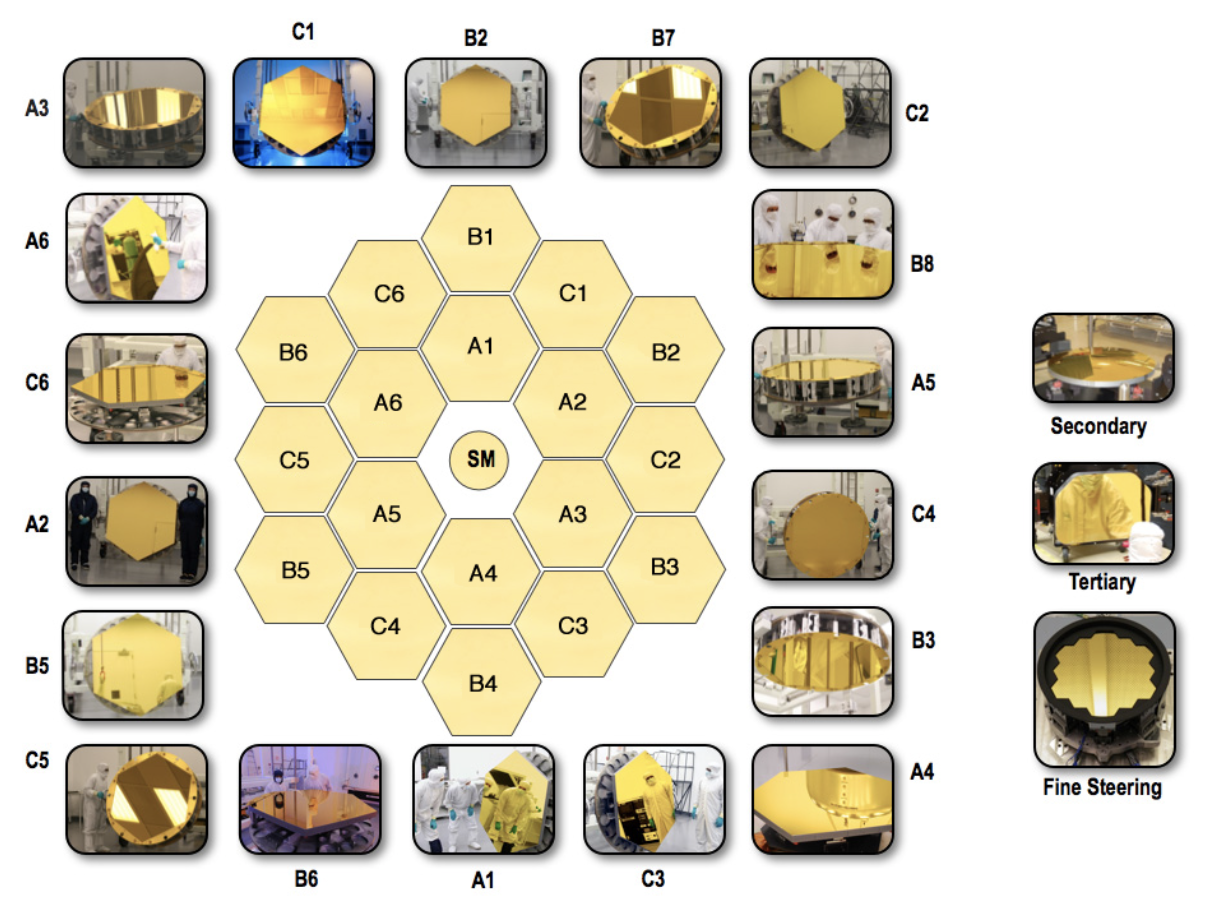
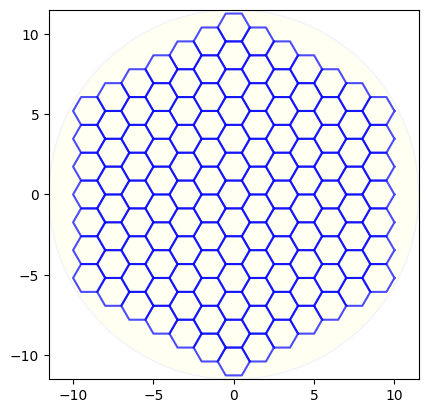
ちなみに、この形状はJWSTの鏡の配置と同じです。
JWSTは六角形の鏡を組み合わせて大きな集光系を実現してます。
自然界には、蜂の巣や柱状節理など、六角形に溢れていて、工学的にも広く応用されています。
雪の結晶や亀の甲羅など、六角形は自然界に多く存在する形状です。正六角形をぎっしりと並べた「ハニカム構造」とは、ハチの巣(Honeycomb)に由来するもの。平面上に並べた時の安定性と一方向から力を受けた場合の衝撃吸収性が高いことから、建築や航空機、サッカーのゴールネットなどにも応されています。
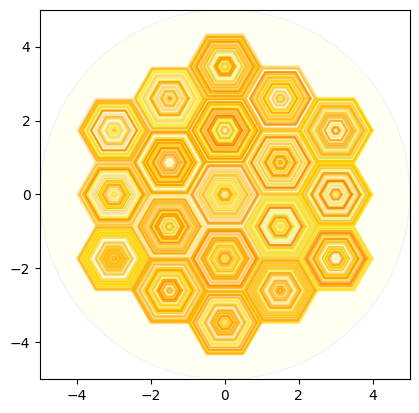
徐々に小さい六角形を入れる場合
decrement = 0.02
# Plot the grid in a circle
cmap="Wistia"
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
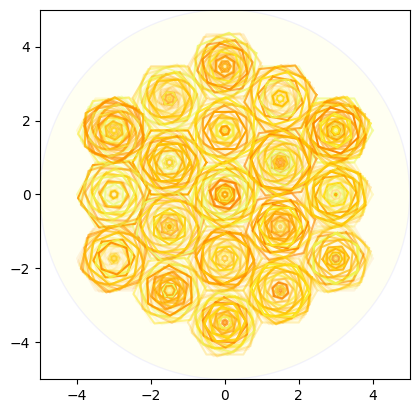
小さい六角形の角度を変えていく場合
# Plot the grid in a circle, with rotate
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_rotate(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
小さい六角形の場所を変えていく場合
# Plot the grid in a circle, with rotate and move
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_move(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
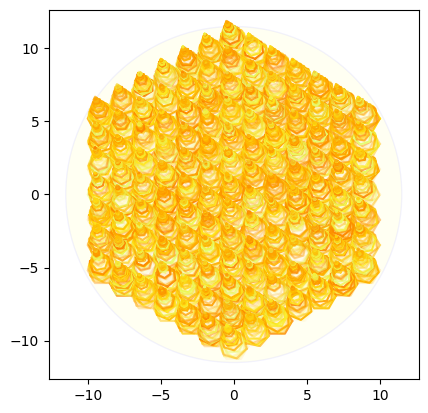
六角形の数が 127 個の場合
# Parameters for the grid in a circle
circle_radius = 11.5
hex_radius = 1
hexagon_grid = create_hexagon_grid_in_circle(circle_radius, hex_radius)
print("Number of hexagon = ", len(hexagon_grid)) # 127
六角形の枠組みの描画
# Plot the grid in a circle
plot_hexagon_grid_in_circle(hexagon_grid, circle_radius)
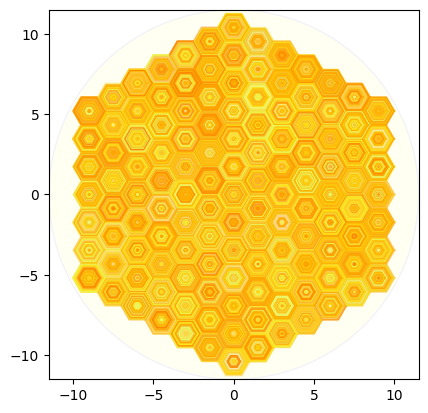
徐々に小さい六角形を入れる場合
decrement = 0.02
# Plot the grid in a circle
cmap="Wistia"
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
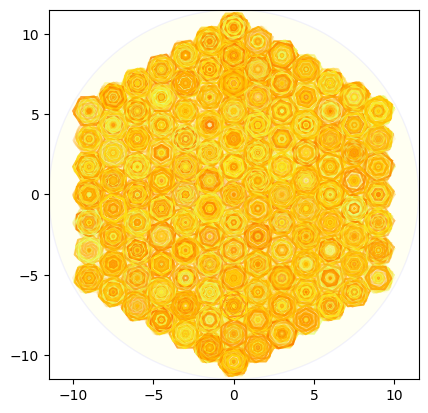
小さい六角形の角度を変えていく場合
# Plot the grid in a circle, with rotate
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_rotate(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
小さい六角形の場所を変えていく場合
# Plot the grid in a circle, with rotate and move
plot_hexagon_grid_with_smaller_hexagons_move(hexagon_grid, circle_radius, hex_radius, decrement, cmap = cmap)
コードの補足説明
all()関数の使い方
# Check if all vertices of the hexagon are inside the circle
if all(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) <= circle_radius for x, y in hexagon.exterior.coords):
は、Pythonの all() 関数で、与えられたイテラブル(リスト、タプル、辞書、セットなど)の全ての要素が True であるかどうかを判定する組み込み関数です。all() 関数に渡されたイテラブルの全ての要素が True または真と評価される場合、all() は True を返します。もしイテラブルの中に偽と評価される要素が一つでもあれば、False を返します。
all(np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) <= circle_radius for x, y in hexagon.exterior.coords) : この式は、正六角形の各頂点 (x, y) が与えられた円の半径 circle_radius 内にあるかどうかをチェックしています。ここで使用されているのはジェネレータ式で、各頂点に対して np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) <= circle_radius が True かどうかを計算し、その結果のシーケンスを all() 関数に渡しています。
ジェネレータ式の中で np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2) は各頂点の原点からの距離を計算しており、この距離が circle_radius 以下であることを確認しています。つまり、すべての頂点が円内にある場合にのみ True を返すようになっています。
まとめ
PythonとShapelyを使用して六角形をモチーフにしたGenerative Artを作成する方法を紹介しました。
このようにプログラムを使って、いろんな絵が簡単に描けるので、いろんな芸術の表現にトライしてもらえると幸いです。