はじめに
こちらの記事ではReact Hook FormとZodの基本的な使い方をまとめました。
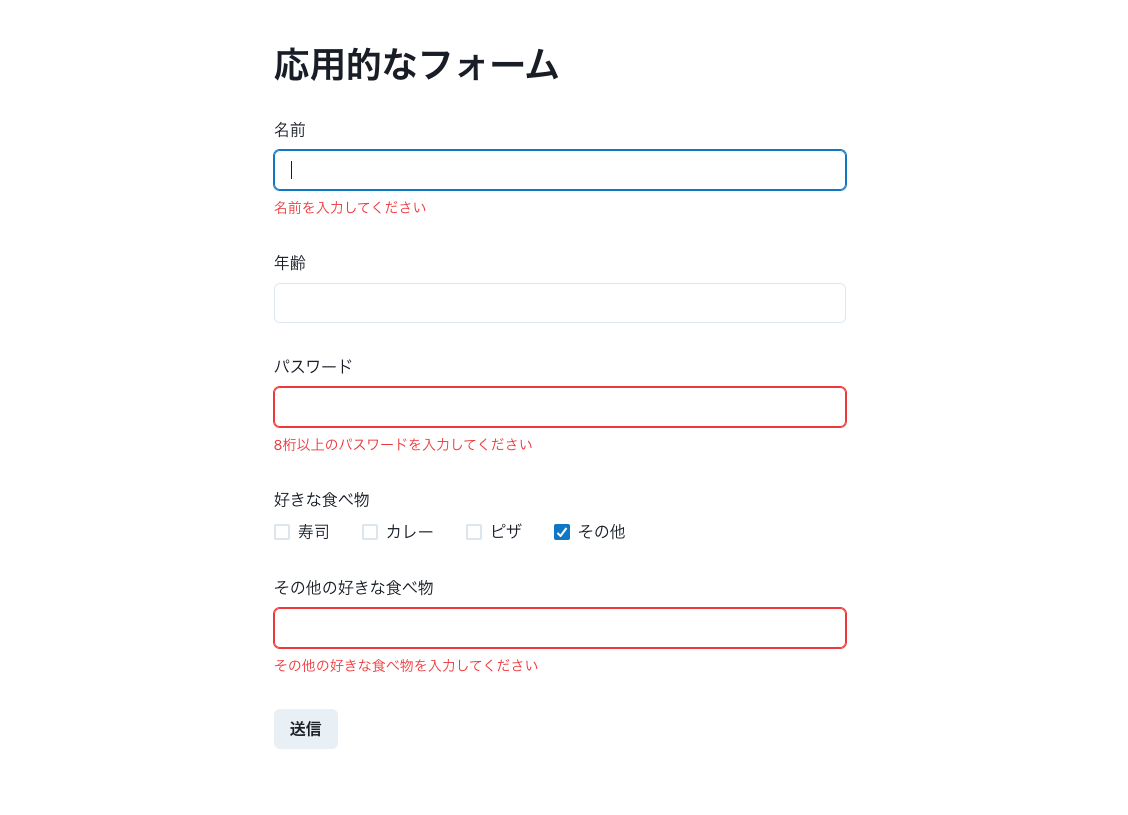
今回はもう少し応用的なフォームを作成してみます。
完成イメージと仕様、環境は以下の通りです。
- 仕様
- 「名前」は1文字以上、必須
- 「年齢」は任意
- 「パスワード」は英大文字or英小文字or数字を使って8文字以上、必須、onBlur時にバリデーションチェック
- 「好きな食べ物」はチェックボックス、任意
- 「その他の好きな食べ物」は「その他」がチェックされているときのみ必須
- バリデーションが成功したら入力値を取得できる
- 環境
- Next.js 13.3.4
- react-hook-form 7.43.9
- zod 3.21.4
- chakra-ui 2.6.0
コード例
use-applied-form-top.tsx
import { useForm } from "react-hook-form";
import {
appliedFormSchema,
AppliedFormSchemaType,
} from "@/features/applied-form/schema";
import { zodResolver } from "@hookform/resolvers/zod";
export const useAppliedFormTop = () => {
const {
register,
handleSubmit,
formState: { errors },
trigger,
control,
} = useForm<AppliedFormSchemaType>({
resolver: zodResolver(appliedFormSchema),
});
const onSubmit = (data: AppliedFormSchemaType) => {
console.log(data);
};
return {
register,
onSubmit: handleSubmit(onSubmit),
errors,
trigger,
control,
};
};
-
triggerはバリデーションのタイミングを手動で設定するために使います -
controlは後述するControllerコンポーネントを定義する際に必要です
applied-form-top.tsx
import {
Container,
Heading,
FormControl,
FormLabel,
FormErrorMessage,
Input,
Button,
CheckboxGroup,
Checkbox,
} from "@chakra-ui/react";
import { useAppliedFormTop } from "@/features/applied-form/hooks";
import { Controller } from "react-hook-form";
const foods = [
{
id: "sushi",
label: "寿司",
},
{
id: "curry",
label: "カレー",
},
{
id: "pizza",
label: "ピザ",
},
{
id: "other",
label: "その他",
},
];
export const AppliedFormTop = () => {
const { register, onSubmit, errors, trigger, control } = useAppliedFormTop();
return (
<Container mt={12}>
<Heading as={"h2"} mb={8}>
応用的なフォーム
</Heading>
<form onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<FormControl isInvalid={!!errors.name}>
<FormLabel htmlFor={"name"}>名前</FormLabel>
<Input type={"text"} id={"name"} {...register("name")} />
<FormErrorMessage>
{errors.name && errors.name.message}
</FormErrorMessage>
</FormControl>
<FormControl mt={8}>
<FormLabel htmlFor={"age"}>年齢</FormLabel>
<Input type={"text"} id={"age"} {...register("age")} />
</FormControl>
<FormControl isInvalid={!!errors.password} mt={8}>
<FormLabel htmlFor={"password"}>パスワード</FormLabel>
<Input
type={"password"}
id={"password"}
{...register("password")}
onBlur={() => trigger("password")}
/>
<FormErrorMessage>
{errors.password && errors.password.message}
</FormErrorMessage>
</FormControl>
<FormControl mt={8}>
<FormLabel>好きな食べ物</FormLabel>
<Controller
name="foods"
control={control}
render={({ field }) => {
return (
<CheckboxGroup {...field} defaultValue={[]}>
{foods.map((food) => {
return (
<Checkbox key={food.id} value={food.id} mr={8}>
{food.label}
</Checkbox>
);
})}
</CheckboxGroup>
);
}}
/>
</FormControl>
<FormControl isInvalid={!!errors.other} mt={8}>
<FormLabel htmlFor={"other"}>その他の好きな食べ物</FormLabel>
<Input type={"text"} id={"other"} {...register("other")} />
<FormErrorMessage>
{errors.other && errors.other.message}
</FormErrorMessage>
</FormControl>
<Button type="submit" mt={8}>
送信
</Button>
</form>
</Container>
);
};
-
trigger(名前)とすることで、その入力のバリデーションをチェックできます- 今回はパスワードのinputのonBlur時に実行するようにしています
-
Controllerコンポーネントについて- 外部のライブラリやUIコンポーネントを使用して、フォームを作成、制御する際に使用します
-
nameにはフィールドの名前、controlにはuseFormから受け取ったcontrolオブジェクト、renderにはフォームフィールドを描画するためのコンポーネントを渡します - また、引数の
fieldにはフォームフィールドに関する情報が含まれています
index.ts
import { z } from "zod";
export const appliedFormSchema = z
.object({
name: z.string().min(1, { message: "名前を入力してください" }),
age: z.string().nullable(),
password: z
.string()
.min(8, { message: "8桁以上のパスワードを入力してください" })
.regex(/^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$/, {
message: "英大文字、英小文字、数字で入力してください",
}),
foods: z.array(z.string()),
other: z.string().nullable(),
})
.refine((data) => !data.foods.includes("other") || !!data.other, {
message: "その他の好きな食べ物を入力してください",
path: ["other"],
});
export type AppliedFormSchemaType = z.infer<typeof appliedFormSchema>;
-
refine()について-
refine()を使うことで独自のバリデーションロジックを設定できます - 第1引数にバリデーション関数を設定し、期待する条件を書きます
- 第2引数にいくつかのオプションを設定します(一部抜粋)
-
message:エラーメッセージ -
path:エラー扱いにするフィールド
-
-
参考記事
採用のお知らせ
株式会社Relicでは、エンジニア・デザイナーを積極的に採用中です。
またRelicでは、地方拠点がありますので、U・Iターンも大歓迎です!🙌
少しでもご興味がある方は、Relic採用サイトからエントリーください!