パーセプトロンの学習
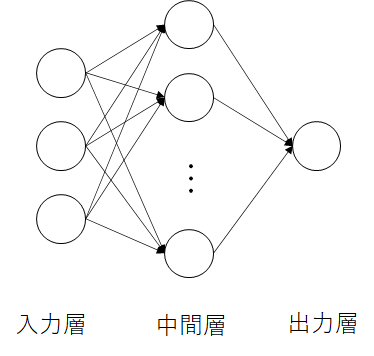
使用するネットワーク
・入力層,中間層,出力層の3層でできているネットワークです.
・層と層の間はフルで連結します.
・すべてのニューロンは$1$か$0$を出力します.
パーセプトロンの目的は中間層と出力層の間の重み(シナプス荷重)を学習し,入力パターンに対応する出力パターンを生成することです.
入力層
$M$個のニューロンがあるとします.
外部からの入力をそのまま受け取って,出力します.
$i$番目のニューロンの出力は以下の式で表します.
$$output_i = input_i$$
中間層
$N$個のニューロンがあるとします.
中間層の$j$番目のニューロンに与える入力は,すべての入力層ニューロンの出力値にシナプス荷重$w_{i,j}$をかけた値の和です.
$$input_j=\sum_{i=1}^{M}{w_{i,j}output_i}$$
そして,それぞれの中間層ニューロンに受け取った信号に閾値$\theta_j$を設定し,その分だけ減らします.
$$input_j-\theta_j$$
出力は$0$か$1$だけなので,出力関数$f(x)$を設定します.なので,中間層の$j$番目のニューロンの出力値は以下の式で表します.
$$output_j = f(input_j-\theta_j)$$
f(u) = \left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & (u \gt 0) \\
0 & (u \leq 0)
\end{array}
\right.
出力層
出力層の入力も中間層の入力と同じく,前の層のすべてのニューロンの出力値にシナプス荷重をかけたものになります.出力層のニューロン個数を$1$とします.
$$input_o=\sum_{j=1}^{N}{w_{j,o}output_j}$$
そして,出力層の出力は中間層と同じく,入力から閾値を引いた値に$f(x)$を適応した結果です.
$$output_o=f(input_o-\theta_o)$$
f(u) = \left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
1 & (u \gt 0) \\
0 & (u \leq 0)
\end{array}
\right.
学習
学習時,他のパラメータは変えず,出力層と中間層の間のシナプス荷重$w_{j,o}$だけを更新します.
$$\Delta w_{j,o}=\eta(t_o-output_o)output_j$$
$$w^{t+1}=w^{t}+\Delta w_{j,o}$$
$\eta$は学習率で,小さい正の値を設定するのが一般的です.
$t_o-output_o$は教師データの出力$t_o$と実際の出力データ$output_o$の差分です.なので,計算して出した結果と教師信号が違うときだけ,シナプス荷重が更新されることが分かります.
パーセプトロンの収束定理の説明や証明はここで割愛します.興味があったら,調べてみてください.
実装
パラメータ設定
- 入力データ
- $0$以上$15$以下の整数対$(x,y)$に対して,$x \gt y$のとき$1$,$x \leq y$のとき$0$を返す関数を想定します.
- このようなデータを$2000$個を用意しました.
- データの中の半分を学習用で,半分をテスト用にしました.
- ネットワーク構造
- 入力層
- ニューロン数:$8$個
- $16x+y$を$8$桁の二進数で表し,各桁をニューロンに渡します
- 中間層
- ニューロン数:$30$個(適当に設定した,いろいろ実験してみると楽しいです)
- 出力層
- ニューロン数:$1$個
- シナプス荷重
- $[-0.005,0.005)$の一様乱数
- 入力層
- 他のパラメータ
- 実験回数$200$回
- 学習率:$\eta = 10^{-4}$
コード
ライブラリーの導入と入力パスの設定
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
PATH_X = "./../input_x.npy"
PATH_Y = "./../input_y.npy"
入力データを$(x,y)$の形から,長さ$8$の$0$と$1$の列に変換
def to_input(data):
x = data[0]
y = data[1]
n = x * 16 + y
return np.array([int(k) for k in format(n, '08b')])
パーセプトロンクラス
注意! プログラム中の荷重計算は上で説明した式をベクトルとして考え,計算しています.
class Perceptron:
def __init__(self, m, n, o):
# decide initial weight [-0.005,0.005)
# 1を足したのは閾値を簡単に扱うため
self.w_IM = np.random.rand(n,m+1) - 0.5
self.w_IM = self.w_IM / 100
self.w_MO = np.random.rand(o,n+1) - 0.5
self.w_MO = self.w_MO / 100
# calculate accuracy
def get_acc(self, x, y):
ok = 0
for i in range(len(x)):
# 常に1を出力するニューロンを加えています
mid_in = np.inner(np.append(x[i],1.), self.w_IM)
mid_out = np.array([int(k > 0) for k in mid_in])
# 常に1を出力するニューロンを加えています
out_in = np.inner(np.append(mid_out,1.), self.w_MO)
ok += int(int(out_in[0] > 0) == y[i])
return ok / len(x)
def learn(self, train_x, train_y, eta = 0.00001):
# 常に1を出力するニューロンを加えています
mid_in = np.inner(np.append(train_x,1.), self.w_IM)
mid_out = np.array([int(k > 0) for k in mid_in])
# 常に1を出力するニューロンを加えています
out_in = np.inner(np.append(mid_out,1.), self.w_MO)
out = int(out_in[0] > 0)
# 出力と教師データの値から荷重を更新しています
self.w_MO[0,:-1] = self.w_MO[0,:-1] + eta * (train_y - out) * mid_out
パラメータの設定と結果グラフの描画
def main():
# read datas
x = np.load(PATH_X)
y = np.load(PATH_Y)
# split datas
train_x, test_x = np.split(x, 2)
train_y, test_y = np.split(y, 2)
# preprocess - transfer data into inputs
datas = np.array([to_input(k) for k in train_x])
tests = np.array([to_input(k) for k in test_x])
# number of neurons input layer
m = 8
# number of neurons mid layer
n = 10
# number of neurons output layer
o = 1
# define the perceptron
P = Perceptron(m,n,o)
# learning time
N = 10
cnt = 0
x = np.linspace(0,200,200)
acc_train = np.copy(x)
acc_test = np.copy(x)
while True:
acc = P.get_acc(datas, train_y)
acc_train[cnt] = acc
acc = P.get_acc(tests, test_y)
acc_test[cnt] = acc
print("Try ", cnt, ": ", acc)
cnt += 1
for i in range(len(datas)):
P.learn(datas[i], train_y[i])
if cnt >= 200:
break
plt.plot(x,acc_train,label="train")
plt.plot(x,acc_test,label="test")
plt.savefig("result.png")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Githubにもアップしています.
https://github.com/xuelei7/NeuralNetwork/tree/master/Perceptron
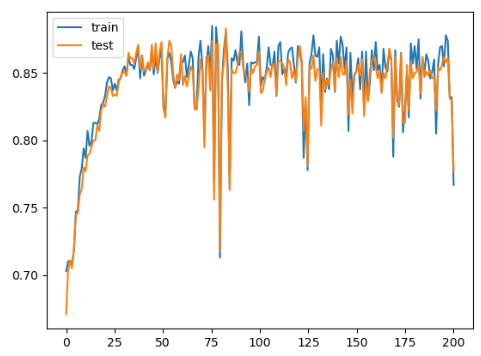
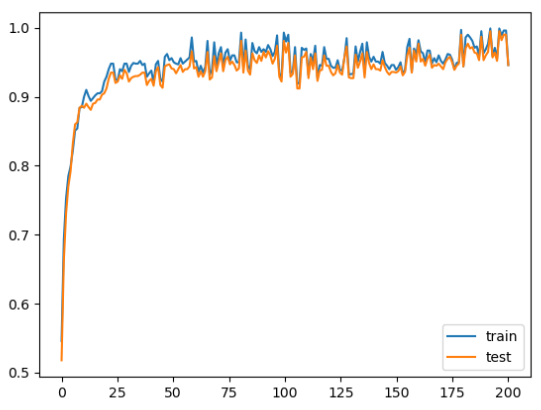
結果
※横軸が試行回数で,縦軸は正解率
おわりに
何か適切ではない点がありましたら,修正したいと思いますので,ご迷惑をお掛けしますが,作者までご連絡ください.
参考資料
「ニューラルネットワーク」,吉富康成,朝倉書店,