Custom resources are an AWS CloudFormation feature that allows you to execute custom logic during the creation, updating, and deletion of CloudFormation stacks.
Sometimes, it’s useful to execute custom logic while provisioning CloudFormation stacks. For example, what if you need to create resources that are not natively supported by CloudFormation?
In this post, I’ll demonstrate a sample project that initializes data in an Amazon DynamoDB table using a custom resource backed by AWS Lambda.
Project overview
You can find the sample source code introduced in this post in my GItHub repository.
git clone https://github.com/toru-iwasa/lambda-custom-resource-sample.git
cd lambda-custom-resource-sample
Project Structure
Here’s the project structure:
lambda-custom-resource-sample/
├── README.md
├── bin
│ └── lambda-custom-resource-sample.ts
├── cdk.json
├── lib
│ ├── lambda
│ │ ├── index.ts
│ │ └── package.json
│ └── lambda-custom-resource-sample-stack.ts
├── package.json
├── test
│ └── lambda-custom-resource-sample.test.ts
└── tsconfig.json
The key files for this project are lambda-custom-resource-sample-stack.ts and lib/lambda/index.ts.
lambda-custom-resource-sample-stack.ts
This file difines the following:
- DynamoDB Table
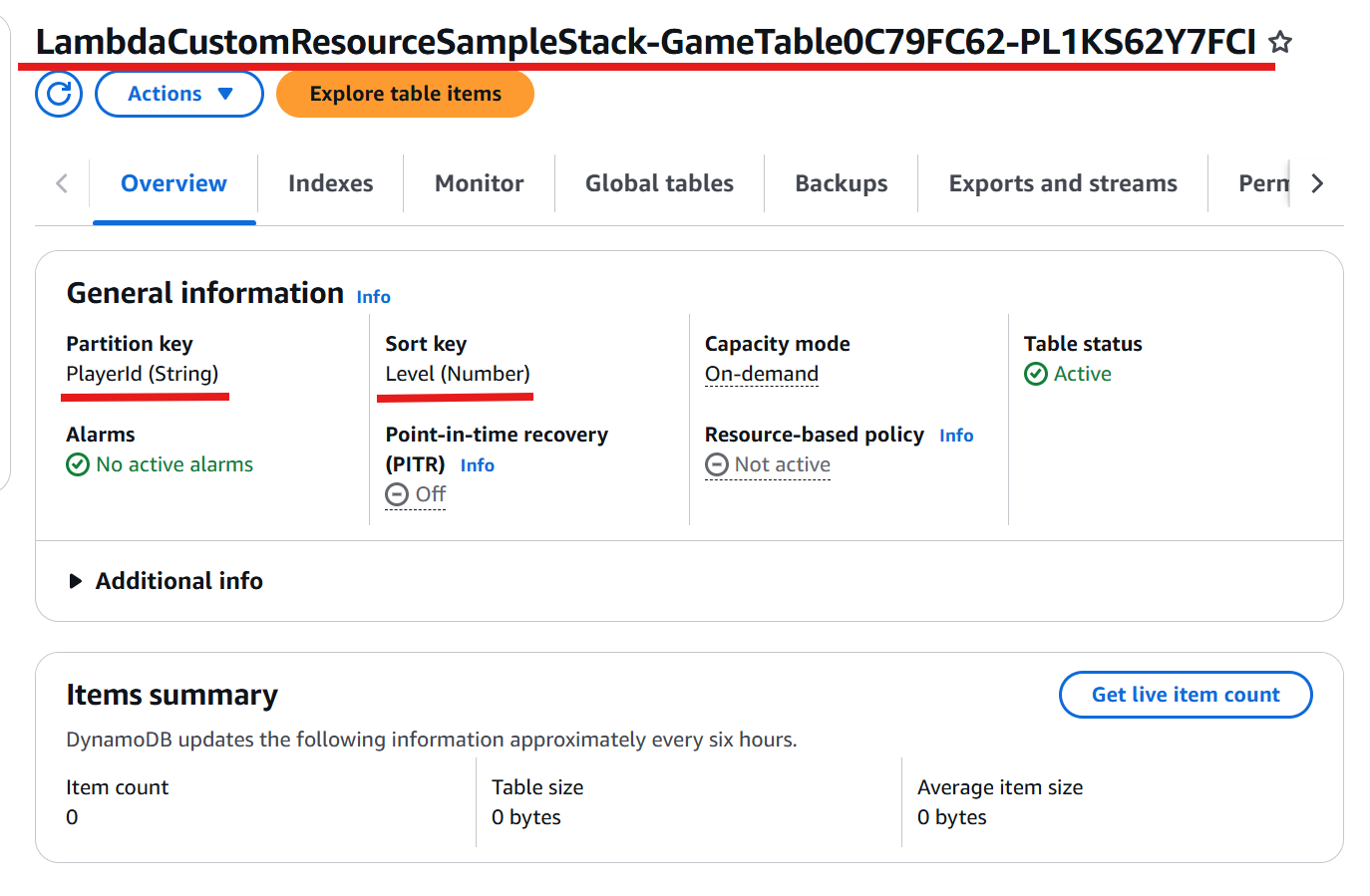
AGameTableis defined with two fields:-
PlayerId(partition key) -
Level(sort key)
-
- Lambda function
A singleton lambda function,PutItemLambda, is defined as part of the stack. - Granting Permissions
The Lambda function is granted read and write permissions for theGameTable. - Custom resource
A custom resource is defined to pass properties (tableName,playerId, andlevel) for initializing data. - Dependency Management
The custom resource ensures permissions are granted before creating other resources (even if this step may not be nessesary in this example).
Here’s the code:
import {
CustomResource,
Duration,
RemovalPolicy,
Stack,
StackProps,
} from "aws-cdk-lib";
import {
AttributeType,
BillingMode,
Table,
} from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb";
import {
SingletonFunction,
Architecture,
Runtime,
Code,
} from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda";
import { Construct } from "constructs";
import path = require("path");
export class LambdaCustomResourceSampleStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const gameTable = new Table(this, "GameTable", {
partitionKey: {
name: "PlayerId",
type: AttributeType.STRING,
},
sortKey: {
name: "Level",
type: AttributeType.NUMBER,
},
billingMode: BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.RETAIN,
});
const putItemLambda = new SingletonFunction(this, "PutItemLambda", {
architecture: Architecture.ARM_64,
runtime: Runtime.NODEJS_LATEST,
handler: "index.handler",
code: Code.fromAsset(path.join(__dirname, "lambda")),
lambdaPurpose: "PutItemLambda",
timeout: Duration.minutes(10),
uuid: "7acd8116-b39b-463d-932c-2e61f824067b",
});
const grant = gameTable.grantReadWriteData(putItemLambda);
const gameTableItem = new CustomResource(this, "GameTableItem", {
serviceToken: putItemLambda.functionArn,
serviceTimeout: Duration.minutes(5),
resourceType: "Custom::GameTableItem",
properties: {
tableName: gameTable.tableName,
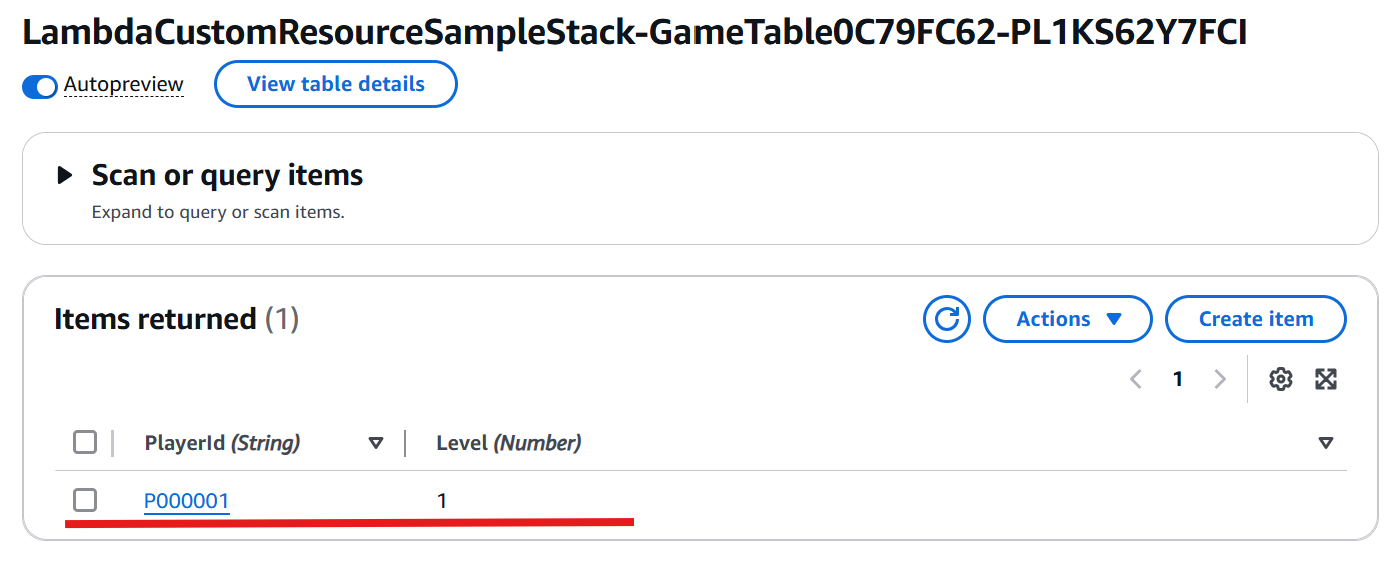
playerId: "P000001",
level: 1,
},
});
gameTableItem.node.addDependency(grant);
}
}
lib/lambda/index.ts
This file implements the Lambda function used for custom resource. Key responsibilities of the Lambda function include:
- Handling Custom Resource Requests
The Lmabda function receives and processesCreate,Update, andDeleteevents. - Executing Custom Logic
-
Create Event: Adds the item specified in the
propertiesfield to the DynamoDB table. - Delete Event: Deletes the item from the DynamoDB table if it exists.
-
Create Event: Adds the item specified in the
- Sending Responses
Return aSUCCESSorFAILEDresponse to theResponseURL.
Here’s the code:
import { CloudFormationCustomResourceEvent, Handler } from "aws-lambda";
import {
DynamoDBClient,
ResourceNotFoundException,
waitUntilTableExists,
} from "@aws-sdk/client-dynamodb";
import {
PutCommand,
DynamoDBDocumentClient,
PutCommandInput,
DeleteCommand,
DeleteCommandInput,
GetCommand,
GetCommandInput,
} from "@aws-sdk/lib-dynamodb";
interface PutItemLambdaProps {
tableName: string;
playerId: string;
level: number;
}
const client = new DynamoDBClient({});
const docClient = DynamoDBDocumentClient.from(client);
async function sendResponse(
event: CloudFormationCustomResourceEvent<PutItemLambdaProps>,
status: string,
reason: string | null
): Promise<void> {
console.log("sendResponse: ", event, status, reason);
const physicalResourceId = (() => {
switch (event.RequestType) {
case "Create":
return event.LogicalResourceId;
case "Update":
case "Delete": {
return event.PhysicalResourceId;
}
}
})();
const responseBody = JSON.stringify({
Status: status,
Reason: reason,
PhysicalResourceId: physicalResourceId,
StackId: event.StackId,
RequestId: event.RequestId,
LogicalResourceId: event.LogicalResourceId,
});
const result = await fetch(event.ResponseURL, {
method: "PUT",
body: responseBody,
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Content-Length": responseBody.length.toString(),
},
});
console.log(result);
}
const handleCreate = async (
event: CloudFormationCustomResourceEvent<PutItemLambdaProps>
) => {
const props = event.ResourceProperties as PutItemLambdaProps;
const waitResult = await waitUntilTableExists(
{ client: client, maxWaitTime: 60 },
{ TableName: props.tableName }
);
console.log("wait result: ", waitResult);
if (waitResult.state !== "SUCCESS") {
throw new Error(waitResult.reason);
}
const command = new PutCommand({
TableName: props.tableName,
Item: {
PlayerId: props.playerId,
Level: Number(props.level),
},
} as PutCommandInput);
await docClient.send(command);
};
const handleDelete = async (
event: CloudFormationCustomResourceEvent<PutItemLambdaProps>
) => {
const props = event.ResourceProperties as PutItemLambdaProps;
const input = {
TableName: props.tableName,
Key: {
PlayerId: props.playerId,
Level: Number(props.level),
},
};
const getCommand = new GetCommand(input as GetCommandInput);
await docClient
.send(getCommand)
.then(async () => {
const deleteCommand = new DeleteCommand(input as DeleteCommandInput);
await docClient.send(deleteCommand);
})
.catch((error: ResourceNotFoundException) => {
console.log("Item not found: ", error.message);
});
};
export const handler: Handler = async (
event: CloudFormationCustomResourceEvent<PutItemLambdaProps>
): Promise<void> => {
console.log(event);
try {
switch (event.RequestType) {
case "Create": {
console.log("RequestType: Create");
await handleCreate(event);
await sendResponse(event, "SUCCESS", "TableItem successfully created.");
break;
}
case "Update": {
console.log("RequestType: Update");
await sendResponse(event, "SUCCESS", "Update not implemented.");
break;
}
case "Delete": {
console.log("RequestType: Delete");
await handleDelete(event);
await sendResponse(event, "SUCCESS", "TableItem successfully deleted.");
break;
}
}
} catch (error: any) {
console.error("Error: ", error);
await sendResponse(event, "FAILED", error.message);
}
};
Deploy Stack
Steps to Deploy
1. Install dependencies:
npm install && npm install --prefix lib/lambda
2. Build the project:
npm run build
3. Bootstrap the CDK environment (if this is your first CDK project):
cdk bootstrap
4. Deploy the stack:
cdk deploy
Verify the DynamoDB Table
Once the deployment is complete, navigate to the DynamoDB console. Select the GameTable, click Explore table items, and verify the item have been created successfully.
Table Item Deletion
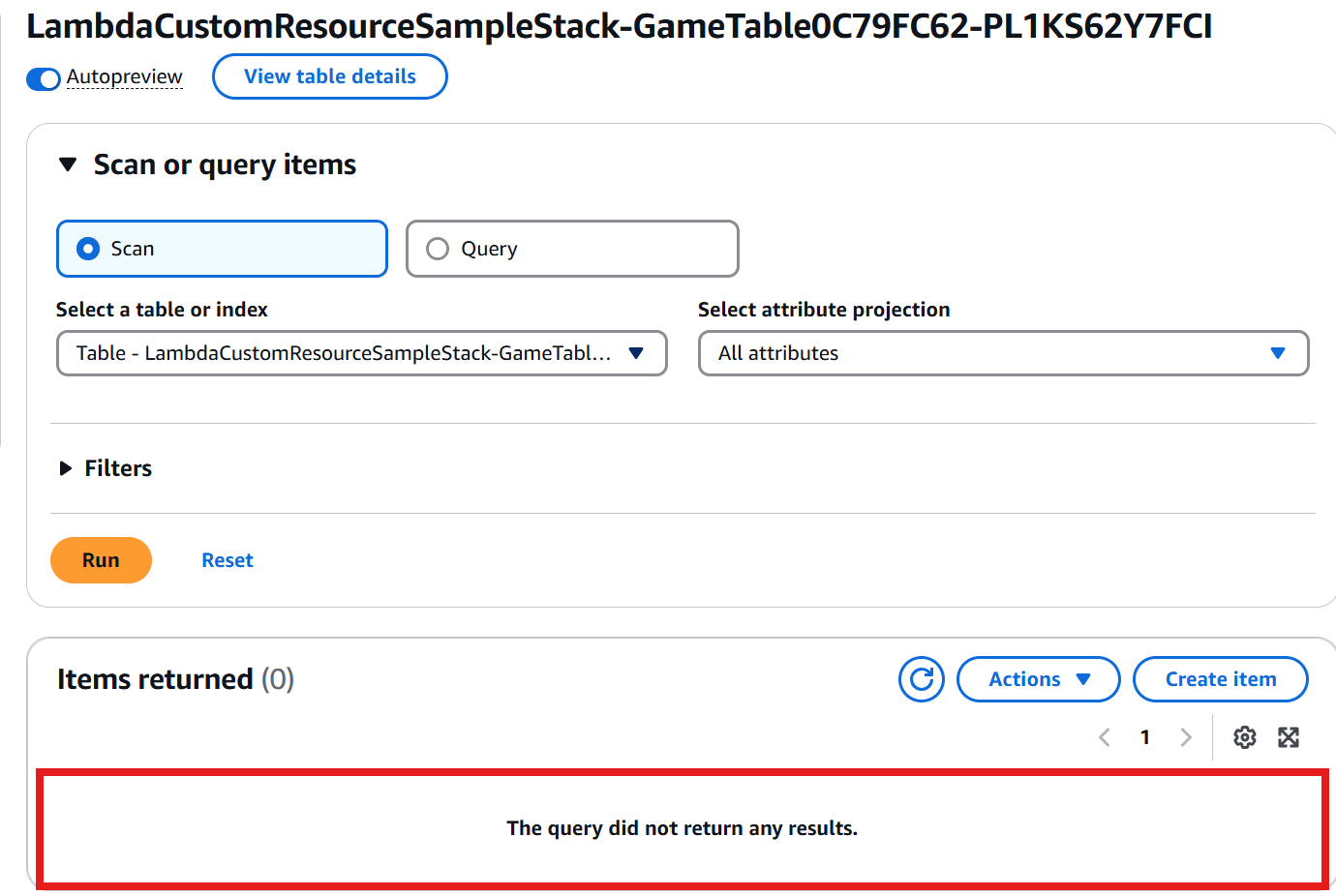
When the CDK stack destroyed, the GameTable will be retained because its removal policy is set to RETAIN. This ensures that the table is not deleted alog with the stack, allowing yout to verify that the item successfully deleted from the table.
Destroy the CDK Stack
Run the following command to destroy the stack:
cdk destroy
Once the destruction completed, go back to the GameTable of DynamoDB Console and verify the item have been successfully deleted.
Clean up
Delete the DynamoDB Table
To delete the GameTable, navigate to the DynamoDB Console, select the table, and choose Actions > Delete table. Enter confirm when prompted, and click Delete.
Delete the CloudWatch Log group
The CloudWatch Log group created for the Lambda function is not part of the stack and must be deleted manually.
- Open the CloudWatch console and navigate to Log groups
- Find the Log Group with a name starting with
/aws/lambda/LambdaCustomResourceSampl-PutItemLambda... - Select the log group, click Actions, and choose Delete log group
Wrap up
In this blog post, I demonstrated a sample project using Lambda backed custom resources with AWS CDK.
With this knowledge, you can now develop Lambda-backed CloudFormation custom resources and execute any custom logic you need. Feel free to use teh provided sample code in your own projects.
Happy coding, and enjoy developing!