webアプリケーション開発の研修で突如出てきたこのDAOパターン。『〜だお』みたいな舐めた口の聞き方みたいな印象でよく分からなかったので、勉強がてらまとめてみます。
ちなみにデザインパターンはソフトウェア開発(Javaを含む)において、よく使用される設計や問題解決策をノウハウとしてまとめたもの。
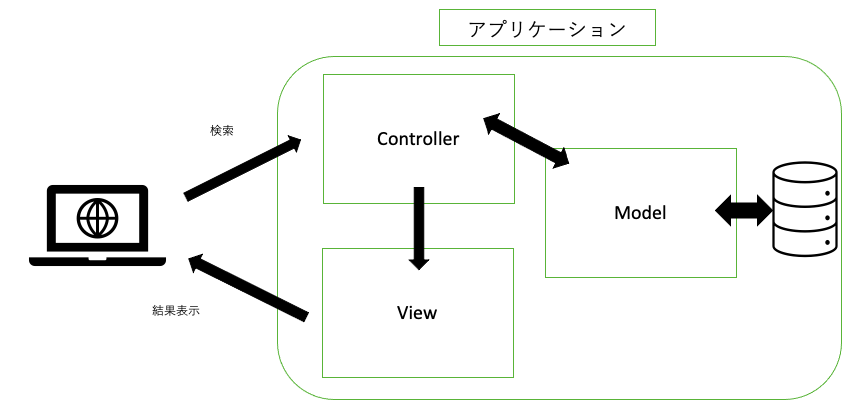
MVCモデル
まずDAOを説明するにあたって、webアプリ開発における必須事項を簡単に確認します。
| 名前 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| モデル(Model) | データベースとのやりとりなど、実際の機能の処理を担う。 |
| コントローラー(Controller) | モデルやビューに命令したり、アプリケーション全体の制御を担う。CPU的な。 |
| ビュー(View) | ユーザーが見る画面。入力処理や表示処理を担う。 |
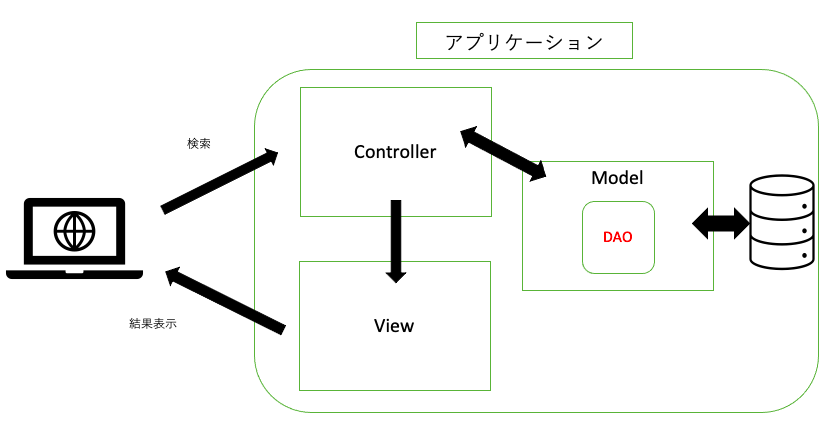
DAOとは
教科書的に言うと、「CRUD(C:作成R:参照U:更新D:削除)操作の機能をメソッドとして定義した部品」です。この説明では、ちょと分かりにくいと思います。そもそも、この「CRUD操作」っというのは、データを追加したり参照したり、、、とデータベースにアクセスして、各々のデータにアクションをしています。つまり簡潔にまとめると、DAOというのは データベース関連の処理(メソッド)をまとめたクラス です。
なので、他のクラスにおいて、データベースとのやり取りが必要になった場合、DAOを使えばわざわざデータベース処理を書く必要がないのです。保守性・可用性の面でgoodですね。
〇特徴
・ルールとして、1テーブルにつき、1つのDAOクラスを作成します。
・DAOクラスの名前は、テーブル名+DAOとすることが一般的です。
・MVCモデルにおいては、Modelに分類されます。
基本構造
○SELECT句の場合
結果が1件 → DAOオブジェクトを返す
結果が複数 → ArrayListオブジェクトで返す
○UPADATE/DELETE/INSERTの場合
成功 → true
失敗 → false
これらメソッドはデータ型が定義されているので、全てreturnで返す。
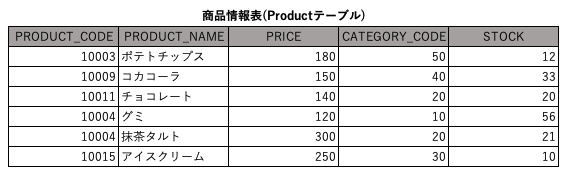
実際のコードを見てみる。
ここでは、商品情報が格納された、Productテーブル(データベース)から①②の処理を行うDAOクラスを使う。
- PRODUCT_CODEとPRODUCT_NAMEはString型、それ以外はint型
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
// DAOクラスを定義
public class ProductDAO {
// DB接続に必要なConnectionオブジェクトを宣言
private Connection con;
public ProductDAO(Connection con) {
this.con = con;
}
// ①Productテーブルから与えられた商品ID(PRODUCT_CODE)と一致する情報を全て取得する処理
public Product findItemByCode(String productCode) throws SQLException {
// ①の処理を実行するSQL文を定義
String sql = "SELECT * FROM product WHERE PRODUCT_CODE= ?";
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
Product pro = null;
try {
// PreparedStatementの作成(SQLの処理が早くなる)
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// パラメータの設定
stmt.setString(1, productCode);
// SQL文の実行(resに実行結果を格納)
res = stmt.executeQuery();
// 結果セットから情報を取り出す(もしデータがあったら、、)
if (res.next()) {
// Itemオブジェクトの生成
pro = new Product(res.getString("PRODUCT_CODE"),
res.getString("PRODUCT_NAME"), res.getInt("PRICE"),
res.getInt("CATEGORY_CODE"),res.getInt("STOCK"));
}
} finally {
// クローズ処理
if (res != null) {
res.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}
return pro;
}
// ②全ての商品をproductテーブルから検索する処理
// ArrayListを用いて全て表示できる様にする
public ArrayList<Item> findAllItem() throws SQLException {
ArrayList<Product> proList = new ArrayList<>();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM product";
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
Product pro = null;
try {
// PreparedStatementの作成
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
// SQL文の実行
res = stmt.executeQuery();
// 結果セットから情報を取り出す(データがなくなる行にたどり着くまで)
while (res.next()) {
// Productオブジェクトの生成
pro = new Product(res.getString("PRODUCT_CODE"),
res.getString("PRODUCT_NAME"),res.getInt("PRICE"),
res.getInt("CATEGORY_CODE"),res.getInt("STOCK"));
// 生成したproオブジェクトをリストに追加
proList.add(pro);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 捜査が終了したらクローズする
if (res != null) {
res.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}
return proList;
}
上記2つのメソッドの最初に共通して記述されている、
private Connection con;
public テーブル名DAO(Connection con) {
this.con = con;
}
--------------------------------------
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
Product pro = null; // オブジェクト生成
この様なコードは、DAOクラスのメソッドを実装する際に、DBにアクセスするために必要なお約束みたいなものです。以下のコードがProductクラスで値の格納先です。テーブルの要素の名前とは違う点に注意が必要です。
public class Product {
private String productCode;
private String productName;
private int price;
private int categoryCode;
private int stock;
public Product(){
}
public Item(String productCode, String productName, int price,
int categoryCode, int stock) {
this.productCode = productCode;
this.productName = productName;
this.price = price;
this.categoryCode = categoryCode;
this.stock = stock;
}
// 以下、それぞれのGetter、Setter
public String getProductCode(){
return productCode;
}
public void setProductCode(){
this.productCode = productCode;
}
public String getProductName(){
return productName;
}
public void setProductName(){
this.productName = productName;
}
public int getPrice(){
return price;
}
public void setPrice(){
this.price = price;
}
public int getCategoryCode(){
return categoryCode;
}
public void setCategoryCode(int categoryCode) {
this.categoryCode = categoryCode;
}
public int getStock(){
return stock;
}
public void setStock(int stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
}
今回はmainクラスを省略していますが、実際にはmainメソッドでDAOクラスの挙動を確認します。
クラス単位で行う、単体テストでのテストドライバとして実装されることが多いです。
最後にDELETEを実行したい場合の、DAOクラスを見てみましょう。
public boolean deleteProduct(Product pro) throws SQLException {
String sql = "DELETE FROM product WHERE PRODUCT_CODE = ?";
PreparedStatement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
boolean result = false;
try {
stmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
stmt.setString(1,pro.getProductCode());
// executeUpdate()はSQLを実行した場合の更新行数を返す
int count = stmt.executeUpdate();
if(count == 1){ // もし実行に成功したら
result = true;
}
}finally {
if(stmt != null){
stmt.close();
}
}
return result;
}
DELETE処理の場合は、メソッドのデータ型を見ると分かるとおり、Boolean型で返します。
つまり、
・削除成功 → true
・削除失敗 → false
となります。
上記のDAOクラスの処理を実行するmainメソッドが、以下になります。
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import ConnectionManager;
import ProductDAO;
import Product;
public class TestItemDAOdeleteItem01 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Connection con = null;
try {
// データベースの接続を取得する
con = ConnectionManager.getConnection();
// DAOを生成し、メソッドを呼び出す
Product pro = new Product();
pro.setProductCode("50001");
ProductDAO proDAO = new ProductDAO(con);
// 削除成功→true,削除失敗→false
boolean result = proDAO.deleteProduct(pro);
// 戻り値を表示
System.out.println("戻り値:" + result);
} catch (SQLException e) {
// データベースエラーの場合
System.out.println("SQLExceptionがスローされました。");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (con != null) {
con.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
参考文献
その他詳しいことは、以下の記事を参照。