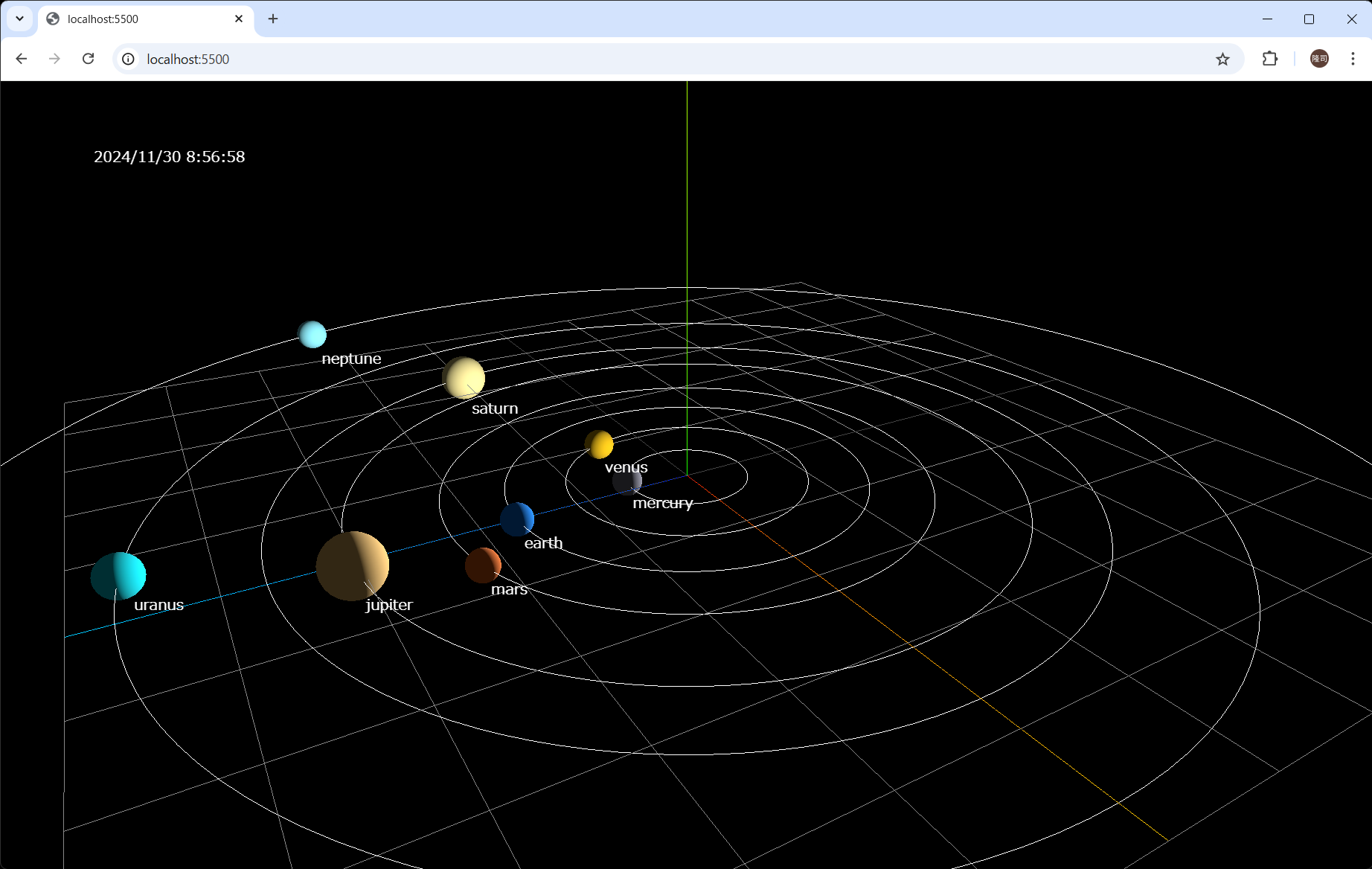
最近小学生の娘が天体に興味を持ち始めたので、太陽系の惑星を可視化し現在日時の各惑星の位置を計算して表示するシミュレーションを作ってみました。
完成イメージ
作成したプログラムでは以下のことが可能です:
- 太陽を中心に各惑星の軌道と現在位置を描画
- 惑星サイズや距離をデフォルメして見やすく表示(コードを弄ればリアル表示も可能)
- カメラの操作でシーンを自由に閲覧可能
- コードを弄ることで公転アニメーションも可能
使用した技術
- Three.js: WebGLを簡単に扱うためのJavaScriptライブラリ
データの準備
各惑星のデータを用意します。
子供達に自分で調べさせて入力させるのも楽しいかもしれません。
| 名前 | 半径 | 公転半径 | 公転周期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 水星 (Mercury) | 2439 km | 57910000 km | 87.969日 |
| 金星 (Venus) | 6051 km | 108208930 km | 224.701日 |
| 地球 (Earth) | 6356 km | 149600000 km | 365.256日 |
| 火星 (Mars) | 3396 km | 227920000 km | 686.980日 |
| 木星 (Jupiter) | 69000 km | 778412010 km | 4332.59日 |
| 土星 (Saturn) | 58232 km | 953707032 km | 10759.22日 |
| 天王星 (Uranus) | 25559 km | 1919126393 km | 30688.5日 |
| 海王星 (Neptune) | 24622 km | 4514953000 km | 60182.0日 |
ただし画面表示時は各サイズをデフォルメして分かりやすくしています。リアルに近い表示をするコードもコメントアウトで残してあります。
惑星の各位置の計算
以下の手順で惑星の位置(角度のみ)を計算します。
より精密な計算が必要な場合は、楕円軌道や軌道傾斜などの要素を考慮する必要がありますが、今回は簡易的に真円で計算しています。
1. 日付をユリウス日(JD)に変換する
JD = \frac{date}{86400000} + 2440587.5
- date: 現在の日時(1970年1月1日 00:00:00 UTCからのミリ秒)
- 86400000: ミリ秒を日単位に変換(1日は86,400,000ミリ秒)
- 2440587.5: 1970年1月1日 00:00:00 UTCに対応するユリウス日
2. 惑星の平均運動を計算
惑星の平均運動(1日あたりの公転角度の進み方)を計算する。
n = \frac{360}{P \times 365.25}
- n: 平均運動(度/日)
- P: 惑星の公転周期(地球年単位)
- 365.25: 地球年の日数
3. J2000 基準日時からの経過日数を計算
基準日時(J2000:2000年1月1日12:00 UT)からの経過日数を計算
Δ𝑇 = JD − J2000
- JD: 計算対象の日付のユリウス日
- J2000: J2000 に対応するユリウス日 2451545.0
4. 経度の計算
惑星の現在の経度を計算:
L=L0+n \times ΔT
- L: 平均経度(度)
- L0: J2000 における惑星の平均経度
- n: 平均運動(度/日)
- ΔT: J2000 からの経過日数
基準日時の平均経度とは?
ユリウス暦2000年1月1日正午における各惑星の公転軌道上での位置を示す角度です。惑星が楕円軌道ではなく円軌道を描いていると仮定した場合の位置を示します。
J2000 における平均経度
| 惑星 | 平均経度 |
|---|---|
| 水星 (Mercury) | 252.25090552 |
| 金星 (Venus) | 181.97980085 |
| 地球 (Earth) | 100.46645683 |
| 火星 (Mars) | 355.43299958 |
| 木星 (Jupiter) | 34.35151874 |
| 土星 (Saturn) | 50.07744430 |
| 天王星 (Uranus) | 314.05500511 |
| 海王星 (Neptune) | 304.34866548 |
function calculatePlanetAngles(date) {
// 惑星の基本データ(J2000基準: 2000年1月1日12:00 UT)
const planets = {
Mercury: { period: 0.2408467, longitudeAtEpoch: 252.25090552 },
Venus: { period: 0.61519726, longitudeAtEpoch: 181.97980085 },
Earth: { period: 1.0000174, longitudeAtEpoch: 100.46645683 },
Mars: { period: 1.8808476, longitudeAtEpoch: 355.43299958 },
Jupiter: { period: 11.862615, longitudeAtEpoch: 34.35151874 },
Saturn: { period: 29.447498, longitudeAtEpoch: 50.07744430 },
Uranus: { period: 84.016846, longitudeAtEpoch: 314.05500511 },
Neptune: { period: 164.79132, longitudeAtEpoch: 304.34866548 }
};
// 日付をユリウス日(JD)に変換
const julianDate = date.getTime() / 86400000 + 2440587.5;
const J2000 = 2451545.0; // ユリウス日2000.0
const angles = {};
for (const [planet, { period, longitudeAtEpoch }] of Object.entries(planets)) {
// 平均運動 (度/日)
const meanMotion = 360 / (period * 365.25);
// J2000を基準とした経度計算
const meanLongitude = (longitudeAtEpoch + meanMotion * (julianDate - J2000)) % 360;
// 経度を0~360の範囲に調整
angles[planet] = (meanLongitude + 360) % 360;
}
return angles;
}
// 使用例
const date = new Date(); // 現在の日付
const angles = calculatePlanetAngles(date);
console.log("太陽を中心とした惑星の角度:", angles);
Three.jsを使って3Dで表示する
見栄えを良くしたかったのでThree.jsを使用しましたが、大きくは依存していないので他の言語やプラットフォームでも実装は容易だと思います。
Three.jsの解説をいれると長くなるので手順だけ簡潔にまとめます。
- WebGLレンダラーを初期化
- ラベル表示用レンダラーを初期化
- シーン、カメラ、カメラコントローラーを作成
- 各惑星のメッシュを作成してシーンに追加
- 環境光源と点光源(太陽)をシーンに追加
- 更新処理にて毎フレーム毎の各惑星の位置をセットし、レンダリングを行う
Three.jsには線で円を描画する機能が無かったので、惑星の軌跡を描画する部分は少し工夫しています。
コード全体
以下が今回のプロジェクト全体のコードです。
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"three": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/three@0.167.0/build/three.module.js",
"three/addons/": "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/three@0.167.0/examples/jsm/"
}
}
</script>
<style>
.label {
color: #FFF;
font-family: sans-serif;
padding: 2px;
background: rgba( 0, 0, 0, .6 );
}
</style>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
import { OrbitControls } from "three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js";
import { CSS2DRenderer, CSS2DObject } from 'three/addons/renderers/CSS2DRenderer.js';
const planets = [
{ index: 1, name: "Mercury", jname: "水星", size: 2439, radius: 57910000, period: 87.969, color: 0x9090a0 },
{ index: 2, name: "Venus", jname: "金星", size: 6051, radius: 108208930, period: 224.701, color: 0xf0c000 },
{ index: 3, name: "Earth", jname: "地球", size: 6356, radius: 149600000, period: 365.256, color: 0x1090FF },
{ index: 4, name: "Mars", jname: "火星", size: 3396, radius: 227920000, period: 686.980, color: 0xff8030 },
{ index: 5, name: "Jupiter", jname: "木星", size: 69000, radius: 778412010, period: 4332.59, color: 0xffd080 },
{ index: 6, name: "Saturn", jname: "土星", size: 58232, radius: 953707032, period: 10759.22, color: 0xfff0a0 },
{ index: 7, name: "Uranus", jname: "天王星", size: 25559, radius: 1919126393, period: 30688.5, color: 0x00f0ff },
{ index: 8, name: "Neptune", jname: "海王星", size: 24622, radius: 4514953000, period: 60182.0, color: 0x90f0ff },
];
// サイズを指定
const width = window.innerWidth;
const height = window.innerHeight;
// WebGLレンダラー
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
canvas: document.querySelector("#myCanvas"),
});
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
renderer.setSize(width, height);
// ラベルレンダラー
const labelRenderer = new CSS2DRenderer();
labelRenderer.setSize(window.innerWidth - 10, window.innerHeight - 10);
labelRenderer.domElement.style.position = 'absolute';
labelRenderer.domElement.style.top = '0px';
document.body.appendChild(labelRenderer.domElement);
// シーンを作成
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// カメラを作成
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, width / height);
camera.position.set(100, 150, 500);
camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
// カメラコントローラー
const orbitControls = new OrbitControls(camera, labelRenderer.domElement);
orbitControls.enableDamping = true;
// グリッド
const grid = new THREE.GridHelper(600);
scene.add(grid);
// 軸
const axis = new THREE.AxesHelper(300);
scene.add(axis);
const date = new Date();
for (var planet of planets) {
// planet.r = planet.radius * 0.0000004;
planet.r = planet.index * 32 + planet.radius * 0.00000003; // デフォルメ半径
// planet.size = planet.size * 0.0002;
planet.size = 8 + planet.size * 0.00012; // デフォルメサイズ
const geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(planet.size, 32, 16);
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({color: planet.color});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
planet.mesh = mesh;
scene.add(mesh);
// ラベル
const div = document.createElement( 'div' );
div.className = 'label';
div.textContent = planet.jname;
div.style.backgroundColor = 'transparent';
const label = new CSS2DObject( div );
label.position.set(0, -planet.size * 1.1, 0);
label.center.set(0, 0);
mesh.add( label );
// 軌跡
orbit(planet.r);
}
// 環境光源
const alight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xFFFFFF, 0.1);
scene.add(alight);
// 点光源
const light = new THREE.PointLight(0xFFFFFF, 4, 0, 0);
light.position.set(0, 0, 0);
scene.add(light);
update();
// 更新処理
function update() {
// date.setHours(date.getHours() + 1); // 時間を進める
const tf = document.getElementById("date");
tf.innerHTML = date.toLocaleString();
for (var planet of planets) {
// 惑星の位置を計算
const angle = calculatePlanetAngles(date, planet.name);
const w = (2.0 * Math.PI) / planet.period;
planet.mesh.position.x = planet.r * Math.sin(angle);
planet.mesh.position.y = 0;
planet.mesh.position.z = planet.r * Math.cos(angle);
}
orbitControls.update();
// レンダリング
renderer.render(scene, camera);
labelRenderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(update);
}
// 軌跡
function orbit(r) {
const shape = new THREE.Shape()
.moveTo( 0, 0 )
.absarc( 0, 0, r, 0, Math.PI * 2, false );
const points = shape.getPoints(64);
const geometryPoints = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints( points );
let line = new THREE.Line( geometryPoints, new THREE.LineBasicMaterial( { color: 0xffffff } ) );
line.position.set( 0, 0, 0 );
line.rotation.set( Math.PI/2, 0, 0 );
line.scale.set( 1, 1, 1 );
scene.add( line );
}
// 惑星の角度を計算
function calculatePlanetAngles(date, name) {
// 惑星の基本データ(J2000基準: 2000年1月1日12:00 UT)
const planets = {
Mercury: { period: 0.2408467, longitudeAtEpoch: 252.25090552 },
Venus: { period: 0.61519726, longitudeAtEpoch: 181.97980085 },
Earth: { period: 1.0000174, longitudeAtEpoch: 100.46645683 },
Mars: { period: 1.8808476, longitudeAtEpoch: 355.43299958 },
Jupiter: { period: 11.862615, longitudeAtEpoch: 34.35151874 },
Saturn: { period: 29.447498, longitudeAtEpoch: 50.07744430 },
Uranus: { period: 84.016846, longitudeAtEpoch: 314.05500511 },
Neptune: { period: 164.79132, longitudeAtEpoch: 304.34866548 }
};
const planet = planets[name];
// 日付をユリウス日(JD)に変換
const julianDate = date.getTime() / 86400000 + 2440587.5;
const J2000 = 2451545.0; // ユリウス日2000.0
// 平均運動 (度/日)
const meanMotion = 360 / (planet.period * 365.25);
// J2000を基準とした経度計算
const meanLongitude = (planet.longitudeAtEpoch + meanMotion * (julianDate - J2000)) % 360;
// 経度をラジアンに変換して範囲を調整
const angle = ((meanLongitude + 360) % 360) * (Math.PI / 180);
return angle;
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<!-- Three.js用のcanvasタグ -->
<canvas id="myCanvas" style="position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0"></canvas>
<!-- 日時表示-->
<div id="date" style="position: absolute; top: 70px; left: 100px; color: white;"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
実行
ブラウザでそのまま実行できます。
- マウス左ドラッグ: カメラ回転
- マウス右ドラッグ: カメラ移動
- マウスホィール: 拡大縮小
画面イメージはこの記事のトップに貼っている通りです。
惑星の位置がなんか偏っていたので計算ミスかなと思ったのですが、天体アプリで確認したら2024年11月30日の惑星の位置はこれで合っているようです。
改造
コメントアウトしている以下の行を解除すると時間が進んで各惑星が太陽の周りを回り始めます。
// date.setHours(date.getHours() + 1); // 時間を進める
この時、カメラの向き(camera.lookAt)を地球に合わせるとNHK風のカッコいい天体アニメーションも再現できるので試してみてください。
最後に
今回、子供にもわかるようにシンプルに実装しましたが、軌道の精度向上やインタラクティブ性の追加等まだまだ改良の余地があります。楕円軌道や軌道傾斜が実装できたら冥王星も仲間に入れることができるかもしれません。
現在は衛星を追加して月の月齢をシミュレーションする機能を追加しているところです。
次回予告「自作天体シミュレーション衛星編、藤原道長が見た月は満月だったのか検証」