はじめに
以前に第一報
で報告しましたが、「Python で学ぶ音声合成」(教科書)の Tacotron2 でメルスペクトログラムを合成するプログラムを、LSTM から Transformer に改修したので、その後を、報告させていただきます。報告する内容は、学習の概略。合成した音声。合成したメルスペクトログラム。Stop Token では合成音声の終端が検出できず工夫したこと。プログラムです。
学習の概略。
学習は、Python で学ぶ音声合成の Tacotron2 の学習に準拠して行った。学習データは、JSUT ver 1.1 の 5000 発話のうち、4700 がtrain、200が development、100 が test です。Epoch は 2900 で、batch_size = 32 です。steps_per_epoch は train が 147で、development が 7 です。train についての loss と steps のグラフを掲載します。
また、development についての loss と steps のグラムも掲載します。
合成した音声
次の2種類について、予測合成した音声を掲載します。
BASIC5000_4999.wav (元の音声)
BASIC5000_5000.wav (元の音声)
合成した音声、4999
合成した音声、5000
ある程度の品質で合成できていると考えます。ボコーダーには、「Python で学ぶ音声合成」の wavenet のボコーダーを使いました。
合成したメルスペクトログラム
4999 番について合成したメルスペクトログラムの図
図の一番上が、元の音声をメルスペクトログラムに変換したものです。図の二番目が、韻律記号付き音素と 1だけ後ろにずらしたスペクトログラムを入力して teacher forcing で予測したメルスペクトログラムです。図の三番目が、韻律記号付き音素を入力して合成したメルスペクトログラムです。一番目と二番目の図は、2.5秒くらいまでですが、三番目の図は、3.5 秒までとなっています。これは、余分な音声まで予測してしまうことを示しています。
5000 番について合成したメルスペクトログラムの図
一番目の図と二番目の図は、2.5秒程度までですが、三番目の図は 3.2 秒程度まであります。これも、余分な音声を予測しています。
5000番の stop token
5000番の stop token の sigmoid を見てみると、Time[frame] が 250 frame まで、0 付近です。ここで、 1frame = 0.0125 秒なので、250 frame は、3.125 秒です。
余分な音声の手前で終了
余分な音声の手前で終了するために、メルスペクトログラム out_feats_fine の dim = 1 について sum
out_feats_fine5 = torch.sum( out_feats_fine, dim = 1 )
をグラフ化します。
4999番のグラフ
time frame = 180 くらい。2.25秒程度で -50 以下が 10 frame 以上続いています。
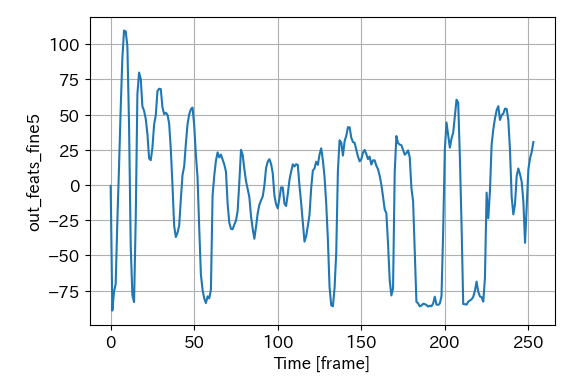
5000番のグラフ
time frame = 180 くらい。2.25秒程度で -50 以下が 10 frame 以上続いています。
これらより、out_feats_fine5 が -50 以下が10frame 以上続いたら終了としました。
使用したプログラム
プログラムは、「python で学ぶ音声合成」の拡張として動かすように作りました。この教科書でインストールする ttslearn-master フォルダの中で考えます。recipes/tacotron フォルダを実行して、recipes/transtron フォルダとしてコピーします。 notebooks フォルダに 以下に示すプログラムを ch96_learning_transtron.ipynb として置き、実行します。
ch96_learning_transtron.ipynb の中身。
ライブラリーの読み込みなど
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.cuda.FloatTensor')
表示の設定など
import japanize_matplotlib
# warning表示off
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
# デフォルトフォントサイズ変更
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 14
# デフォルトグラフサイズ変更
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (6,6)
# デフォルトで方眼表示ON
plt.rcParams['axes.grid'] = True
# numpyの表示桁数設定
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True, precision=5)
current ディレクトリの変更
import os
from ttslearn.env import is_colab
from os.path import exists
# recipeのディレクトリに移動
cwd = os.getcwd()
if cwd.endswith("notebooks"):
os.chdir("../recipes/transtron/")
elif is_colab():
os.chdir("recipes/transtron/")
LayerNorm と Linear クラス
class LayerNorm(nn.LayerNorm):
def forward(self, x):
return super().forward(x.float()).type(x.dtype)
class Linear(nn.Linear):
def forward(self, x):
return F.linear(
x,
self.weight.to(x.dtype),
None if self.bias is None else self.bias.to(x.dtype),
)
MultiHeadAttention クラス
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_state: int, n_head: int):
super().__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.query = Linear(n_state, n_state)
self.key = Linear(n_state, n_state, bias=False)
self.value = Linear(n_state, n_state)
self.out = Linear(n_state, n_state)
def forward(
self,
x,
xa = None,
mask = None
):
#print( " size of x:{}".format( x.size() ))
q = self.query(x)
if xa is None:
# hooks, if installed (i.e. kv_cache is not None), will prepend the cached kv tensors;
# otherwise, perform key/value projections for self- or cross-attention as usual.
k = self.key(x if xa is None else xa)
v = self.value(x if xa is None else xa)
else:
k = self.key( xa )
v = self.value( xa )
wv, qk, w = self.qkv_attention(q, k, v, mask)
return self.out(wv), qk, w
def qkv_attention(
self, q, k, v, mask = None
):
n_batch, n_ctx, n_state = q.shape
scale = (n_state // self.n_head) ** -0.25
q = q.view(*q.shape[:2], self.n_head, -1).permute(0, 2, 1, 3) * scale
k = k.view(*k.shape[:2], self.n_head, -1).permute(0, 2, 3, 1) * scale
v = v.view(*v.shape[:2], self.n_head, -1).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
qk = q @ k
if mask is not None:
qk = qk + mask[:n_ctx, :n_ctx]
qk = qk.float()
w = F.softmax(qk, dim=-1).to(q.dtype)
return (w @ v).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).flatten(start_dim=2), qk.detach(), w
ResidualAttentionBlock クラス
class ResidualAttentionBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_state: int, n_head: int, ffn_dim: int, cross_attention: bool = False):
super().__init__()
self.attn = MultiHeadAttention(n_state, n_head)
self.attn_ln = LayerNorm(n_state)
self.cross_attn = MultiHeadAttention(n_state, n_head ) if cross_attention else None
self.cross_attn_ln = LayerNorm(n_state) if cross_attention else None
#n_mlp = n_state * 4
n_mlp = ffn_dim
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_state, n_mlp), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(n_mlp, n_state))
self.mlp_ln = LayerNorm(n_state)
def forward(
self,
x,
xa,
mask = None
):
#x = x + self.attn(self.attn_ln(x), self.attn_ln(x), self.attn_ln(x), attn_mask=mask)[0]
#x = x + self.attn(self.attn_ln(x), mask=mask)[0]
xx, _, attn1 = self.attn(self.attn_ln(x), mask=mask)
x = x + xx
if self.cross_attn:
#x = x + self.cross_attn(self.cross_attn_ln(x), xa, mask = None)[0]
xx, _, attn2 = self.cross_attn(self.cross_attn_ln(x), xa, mask = None)
x = x + xx
else:
attn2 = []
x = x + self.mlp(self.mlp_ln(x))
return x, attn1, attn2
Encoder クラス
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
num_vocab=51,
embed_dim=512,
conv_layers=3,
conv_channels=512,
conv_kernel_size=5,
enc_hidden_dim = 512,
num_enc_layers = 8,
num_heads = 4,
enc_dropout_rate = 0.1,
conv_dropout_rate = 0.1,
input_maxlen = 300,
ffn_dim = 2048
):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# 文字の埋め込み表現
self.embed = nn.Embedding(num_vocab, embed_dim, padding_idx=0)
self.pos_emb = nn.Embedding(input_maxlen, embed_dim)
# 1 次元畳み込みの重ね合わせ:局所的な時間依存関係のモデル化
convs = nn.ModuleList()
for layer in range(conv_layers):
in_channels = embed_dim if layer == 0 else conv_channels
out_channels = enc_hidden_dim if layer == conv_layers - 1 else conv_channels
#print( " in_channels:{}".format( in_channels ))
#print( " out_channels:{}".format( out_channels ))
convs += [
nn.Conv1d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
conv_kernel_size,
padding=(conv_kernel_size - 1) // 2,
bias=False, # この bias は不要です
),
nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(conv_dropout_rate),
]
self.convs = nn.Sequential(*convs)
self.blocks: Iterable[ResidualAttentionBlock] = nn.ModuleList(
[ResidualAttentionBlock(embed_dim, num_heads, ffn_dim, cross_attention = False) for _ in range(num_enc_layers)]
)
self.input_maxlen = input_maxlen
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=enc_dropout_rate)
self.num_enc_layers = num_enc_layers
def forward(self, x, in_lens ):
emb = self.embed(x)
# 1 次元畳み込みと embedding では、入力のサイズ が異なるので注意
#print( "size of emb:{}".format( emb.size() ))
out = self.convs(emb.transpose(1, 2)).transpose(1, 2)
#print( "encoder out:{}".format( out ))
maxlen = out.size()[1]
#print( "size of out:{}".format( out.size()))
positions = torch.range(start=0, end=self.input_maxlen - 1, step=1).to(torch.long)
positions = self.pos_emb(positions)[:maxlen,:]
#print( "size of positions:{}".format( positions.size()))
x = out + positions
#print( "0 encoder x:{}".format( x ))
x = self.dropout( x )
#print( "1 encoder x:{}".format( x ))
#for i in range(self.num_enc_layers):
# x = self.enc_layers[i](x )
#print( "2 x:{}".format( x ))
for block in self.blocks:
x, attn1, attn2 = block(x, x, mask = None)
return x # (batch_size, input_seq_len, d_model)
Prenet クラス
class Prenet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, dec_hidden_dim, layers=8, hidden_dim=512, dropout=0.5):
super().__init__()
self.dropout = dropout
prenet = nn.ModuleList()
for layer in range(layers):
in_dims = in_dim if layer == 0 else hidden_dim
out_dims = dec_hidden_dim if layer == layers - 1 else hidden_dim
prenet += [
nn.Linear(in_dims, out_dims ),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout) # added by Toshio Uchiyama
]
self.prenet = nn.Sequential(*prenet)
def forward(self, x):
for layer in self.prenet:
# 学習時、推論時の両方で Dropout を適用します
#x = F.dropout(layer(x), self.dropout, training=True)
x = layer(x) # original is above
return x
Decoder クラス
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
decoder_hidden_dim=512,
out_dim=80,
layers=8,
prenet_layers=2,
prenet_hidden_dim=512,
prenet_dropout=0.5,
ffn_dim=2048,
dropout_rate = 0.1,
dec_input_maxlen=3000,
num_heads = 4
):
super().__init__()
self.out_dim = out_dim
self.num_heads = num_heads
# Prenet
self.prenet = Prenet(out_dim, decoder_hidden_dim, prenet_layers, prenet_hidden_dim, prenet_dropout)
#self.prenet = nn.Linear( out_dim, prenet_hidden_dim )
#self.prenet.eval()
# DecoderLayer
#self.dec_layers = [DecoderLayer(decoder_hidden_dim, num_heads, ffn_dim, dropout_rate)
# for _ in range(layers)]
self.blocks: Iterable[ResidualAttentionBlock] = nn.ModuleList(
[ResidualAttentionBlock(decoder_hidden_dim, num_heads, ffn_dim, cross_attention=True) for _ in range(layers)]
)
#self.blocks.eval()
#self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.pos_emb = nn.Embedding(dec_input_maxlen, decoder_hidden_dim)
#self.pos_emb.eval()
# 出力への projection 層
proj_in_dim = decoder_hidden_dim
#print( "proj_in_dim:{}".format( proj_in_dim ))
#print( "out_dim:{}".format( out_dim ))
self.feat_out = nn.Linear(proj_in_dim, out_dim, bias=False)
#self.feat_out.eval()
self.prob_out = nn.Linear(proj_in_dim, 1)
#self.prob_out.eval()
self.dec_input_maxlen = dec_input_maxlen
self.layers = layers
hidden_dim = decoder_hidden_dim
def forward(self, encoder_outs, in_lens, decoder_targets=None):
# Pre-Net
#prenet_out = self.prenet(prev_out)
#print( " size of decoder_targets:{}".format( decoder_targets.size()))
#print( "encoder_outs:{}".format(encoder_outs) )
#print( "decoder_targets:{}".format( decoder_targets))
prenet_out = self.prenet(decoder_targets)
#print( "prenet_out:{}".format( prenet_out))
maxlen = prenet_out.size()[1]
#print( "size of prenet_out:{}".format( prenet_out.size()))
positions = torch.range(start=0, end=self.dec_input_maxlen - 1, step=1).to(torch.long)
positions = self.pos_emb(positions)[:maxlen,:]
#print( "positions:{}".format( positions))
#print( "size of positions:{}".format( positions.size()))
x = prenet_out + positions
#print( "0 x:{}".format( x ))
attention_weights = {}
for i, block in enumerate( self.blocks ):
T = x.size()[1]
#T = 1
look_ahead_mask = torch.empty(T, T).fill_(-np.inf).triu_(1)
x, attn1, attn2 = block(x, encoder_outs, mask=look_ahead_mask)
attention_weights['{}'.format(2*i)] = attn1
attention_weights['{}'.format(2*i + 1)] = attn2
#print( "size of x:{}".format( x.size()))
outs = self.feat_out(x)
#print( "outs:{}".format(outs))
outs = torch.permute(outs, (0, 2, 1))
logits = torch.squeeze( self.prob_out(x), axis=2 )
return outs, logits, attention_weights
Postnet クラス
class Postnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_dim=80,
layers=5,
channels=512,
kernel_size=5,
dropout=0.5,
):
super().__init__()
postnet = nn.ModuleList()
for layer in range(layers):
in_channels = in_dim if layer == 0 else channels
out_channels = in_dim if layer == layers - 1 else channels
postnet += [
nn.Conv1d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride=1,
padding=(kernel_size - 1) // 2,
bias=False,
),
nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channels),
]
if layer != layers - 1:
postnet += [nn.Tanh()]
postnet += [nn.Dropout(dropout)]
self.postnet = nn.Sequential(*postnet)
def forward(self, xs):
return self.postnet(xs)
Transtron クラス
class Transtron(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
num_vocab=52,
embed_dim=512,
conv_layers=3,
conv_channels=512,
conv_kernel_size=5,
enc_hidden_dim = 512,
num_enc_layers = 8,
enc_num_heads = 4,
enc_dropout_rate = 0.1,
conv_dropout_rate = 0.1,
enc_input_maxlen = 300,
enc_ffn_dim = 2048,
decoder_hidden_dim=512,
out_dim=80,
num_dec_layers=8,
prenet_layers=2,
prenet_hidden_dim=512,
prenet_dropout=0.5,
dec_ffn_dim=2048,
dec_dropout_rate = 0.1,
dec_input_maxlen=3000,
dec_num_heads = 4,
postnet_in_dim=80,
postnet_layers=5,
postnet_channels=512,
postnet_kernel_size=5,
postnet_dropout=0.5
):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(
num_vocab,
embed_dim,
conv_layers,
conv_channels,
conv_kernel_size,
enc_hidden_dim,
num_enc_layers,
enc_num_heads,
enc_dropout_rate,
conv_dropout_rate,
enc_input_maxlen,
enc_ffn_dim
)
self.decoder = Decoder(
decoder_hidden_dim,
out_dim,
num_dec_layers,
prenet_layers,
prenet_hidden_dim,
prenet_dropout,
dec_ffn_dim,
dec_dropout_rate,
dec_input_maxlen,
dec_num_heads
)
self.postnet = Postnet(
postnet_in_dim,
postnet_layers,
postnet_channels,
postnet_kernel_size,
postnet_dropout
)
def forward(self, seq, in_lens, decoder_targets):
# エンコーダによるテキストに潜在する表現の獲得
encoder_outs = self.encoder(seq, in_lens)
# デコーダによるメルスペクトログラム、stop token の予測
outs, logits, att_ws = self.decoder(encoder_outs, in_lens, decoder_targets)
# Post-Net によるメルスペクトログラムの残差の予測
outs_fine = outs + self.postnet(outs)
# (B, C, T) -> (B, T, C)
outs = outs.transpose(2, 1)
outs_fine = outs_fine.transpose(2, 1)
return outs, outs_fine, logits, att_ws
'''
def inference(self, seq):
seq = seq.unsqueeze(0) if len(seq.shape) == 1 else seq
in_lens = torch.tensor([seq.shape[-1]], dtype=torch.long, device=seq.device)
return self.forward(seq, in_lens, None)
def inference(self, in_feats ):
"""Performs inference over one batch of inputs using greedy decoding."""
in_feats = torch.unsqueeze( in_feats, axis = 0 )
bs = in_feats.size()[0]
in_lens = []
for feats in ( in_feats):
in_lens.append( len( feats ))
# エンコーダによるテキストに潜在する表現の獲得
encoder_outs = model.encoder(in_feats, in_lens)
decoder_targets_maxlen = in_lens[0] * 10
#dec_input = tf.ones((bs, 1), dtype=tf.int32) * target_start_token_idx
decoder_targets = encoder_outs.new_zeros((encoder_outs.size()[0], 1, 80))
#decoder_targets = None
#dec_logits = []
for i in range(decoder_targets_maxlen ):
print( "i:{}".format( i ))
# デコーダによるメルスペクトログラム、stop token の予測
outs, logits, att_ws = model.decoder(encoder_outs, in_lens, decoder_targets)
print( "torch.sigmoid(logits[0, -1]):{}".format(torch.sigmoid(logits[0, -1])))
if i > 40 and torch.sigmoid(logits[0, -1]) >= 0.5:
break
#print( "0 size of outs:{}".format( outs.size() ))
outs = torch.permute(outs, (0, 2, 1))
outs2 = torch.unsqueeze( outs[:,-1,:], axis = 1 )
#print( "size of outs2:{}".format( outs2.size()))
#print( "1 size of outs:{}".format( outs.size() ))
#print( "1 size of decoder_targets:{}".format( decoder_targets.size()))
decoder_targets = torch.cat( (decoder_targets, outs2), axis = 1 )
#print( "2 size of decoder_targets:{}".format( decoder_targets.size()))
#logits = self.classifier(dec_out)
#logits = tf.argmax(logits, axis=-1, output_type=tf.int32)
#last_logit = tf.expand_dims(logits[:, -1], axis=-1)
#decoder_targets = torch.concat([decoder_targets, outs], axis=-1)
# Post-Net によるメルスペクトログラムの残差の予測
outs = torch.permute(outs, (0, 2, 1))
outs_fine = outs + model.postnet(outs)
# (B, C, T) -> (B, T, C)
outs = outs.transpose(2, 1)
outs_fine = outs_fine.transpose(2, 1)
#print( "size of outs_fine:{}".format( outs_fine.size() ))
return outs[0], outs_fine[0], logits[0], att_ws
'''
model 定義
model = Transtron(
num_vocab=52,
embed_dim=512,
conv_layers=3,
conv_channels=512,
conv_kernel_size=5,
enc_hidden_dim = 512,
num_enc_layers = 8,
enc_num_heads = 4,
enc_dropout_rate = 0.1,
conv_dropout_rate = 0.1,
enc_input_maxlen = 300,
enc_ffn_dim = 2048,
decoder_hidden_dim=512,
out_dim=80,
num_dec_layers=8,
prenet_layers=2,
prenet_hidden_dim=512,
prenet_dropout=0.5,
dec_ffn_dim=2048,
dec_dropout_rate = 0.1,
dec_input_maxlen=3000,
dec_num_heads = 4,
postnet_in_dim=80,
postnet_layers=5,
postnet_channels=512,
postnet_kernel_size=5,
postnet_dropout=0.5
)
学習に必要な関数
#学習で必要な関数
def ensure_divisible_by(feats, N):
if N == 1:
return feats
mod = len(feats) % N
if mod != 0:
feats = feats[: len(feats) - mod]
return feats
#学習で必要な関数
from ttslearn.util import pad_1d, pad_2d
def collate_fn_transtron(batch):
xs = [x[0] for x in batch]
ys = [ensure_divisible_by(x[1], 1) for x in batch]
in_lens = [len(x) for x in xs]
out_lens = [len(y) for y in ys]
in_max_len = max(in_lens)
out_max_len = max(out_lens)
x_batch = torch.stack([torch.from_numpy(pad_1d(x, in_max_len)) for x in xs])
y_batch = torch.stack([torch.from_numpy(pad_2d(y, out_max_len)) for y in ys])
in_lens = torch.tensor(in_lens, dtype=torch.long)
out_lens = torch.tensor(out_lens, dtype=torch.long)
stop_flags = torch.zeros(y_batch.shape[0], y_batch.shape[1])
for idx, out_len in enumerate(out_lens):
stop_flags[idx, out_len - 1 :] = 1.0
return x_batch, in_lens, y_batch, out_lens, stop_flags
#学習で必要なミニバッチデータ
from pathlib import Path
from ttslearn.train_util import Dataset
from functools import partial
in_paths_dev = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/dev/in_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
in_paths = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/train/in_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
#in_paths = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/dev/in_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
#print( "in_paths:{}".format( in_paths ))
out_paths_dev = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/dev/out_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
out_paths = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/train/out_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
#out_paths = sorted(Path("./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/dev/out_tacotron/").glob("*.npy"))
dataset = Dataset(in_paths, out_paths)
dataset_dev = Dataset(in_paths_dev, out_paths_dev)
#print( " len of dataset:{}".format( len( dataset )))
collate_fn = partial(collate_fn_transtron)
#data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn, num_workers=0)
#data_loader_dev = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_dev, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn, num_workers=0)
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, collate_fn=collate_fn, num_workers=0)
data_loader_dev = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset_dev, batch_size=32, collate_fn=collate_fn, num_workers=0)
in_feats, in_lens, out_feats, out_lens, stop_flags = next(iter(data_loader))
print("入力特徴量のサイズ:", tuple(in_feats.shape))
print("出力特徴量のサイズ:", tuple(out_feats.shape))
print("stop flags のサイズ:", tuple(stop_flags.shape))
#学習前にミニバチデータの可視化(教師データ,out_feats)
import librosa.display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from ttslearn.notebook import get_cmap, init_plot_style, savefig
cmap = get_cmap()
init_plot_style()
sr = 16000
fig, ax = plt.subplots(len(out_feats), 1, figsize=(8,40), sharex=True, sharey=True)
for n in range(len(in_feats)):
x = out_feats[n].data.numpy()
hop_length = int(sr * 0.0125)
mesh = librosa.display.specshow(x.T, sr=sr, x_axis="time", y_axis="frames", hop_length=hop_length, cmap=cmap, ax=ax[n])
fig.colorbar(mesh, ax=ax[n])
mesh.set_clim(-4, 4)
# あとで付け直すので、ここではラベルを削除します
ax[n].set_xlabel("")
ax[-1].set_xlabel("Time [sec]")
for a in ax:
a.set_ylabel("Mel channel")
plt.tight_layout()
savefig("fig/e2etts_impl_minibatch")
#device = torch.device('cuda:0') if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device('cpu')
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = model.to( device )
#学習の前準備
from torch import optim
# lr は学習率を表します
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
#optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001, eps=1e-9, amsgrad=True)
#optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001, eps=1e-9, amsgrad=True)
#optimizer = optim.RMSprop(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False)
# gamma は学習率の減衰係数を表します
#lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, gamma=0.5, step_size=500000)
```python
import gc
gc.collect()
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
学習
#学習
from ttslearn.util import make_non_pad_mask
from ttslearn.tacotron import Tacotron2TTS
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
from IPython.display import Audio
import pandas as pd
history = np.zeros((0, 7))
history_dev = np.zeros((0, 6))
num_epochs = 10000
#num_epochs = 30
it_train = 0
it_dev = 0
for epoch in range( num_epochs ):
model.train()
total_decoder_out_loss = 0
total_postnet_out_loss = 0
total_stop_token_loss = 0
total_loss = 0
count = 0
# DataLoader を用いたミニバッチの作成: ミニバッチ毎に処理する
phar = tqdm( range( len(data_loader) ), desc='train' )
Iter_train = iter(data_loader)
for i in phar:
#for in_feats, in_lens, out_feats, out_lens, stop_flags in tqdm(data_loader):
in_feats, in_lens, out_feats, out_lens, stop_flags = next(Iter_train)
in_feats = in_feats.to(device)
in_lens = in_lens.to(device)
out_feats = out_feats.to(device)
out_lens = out_lens.to(device)
stop_flags = stop_flags.to(device)
in_lens, indices = torch.sort(in_lens, dim=0, descending=True)
in_feats, out_feats, out_lens = in_feats[indices], out_feats[indices], out_lens[indices]
out_feats0 = torch.zeros_like( out_feats )
out_feats0[:,1:,:] = out_feats[:,:-1,:]
#count += len( in_feats )
count += 1
# 順伝搬の計算
#print( "size of in_feats:{}".format( in_feats.size()))
#print( "size of in_lens:{}".format( in_lens.size()))
#print( "in_lens:{}".format( in_lens ))
#print( "size of out_feats:{}".format( out_feats.size ))
#out_feats2 = out_feats[:,:-1,:]
#outs, outs_fine, logits, _ = model(in_feats, in_lens, out_feats)
outs, outs_fine, logits, _ = model(in_feats, in_lens, out_feats0)
#print( "size of out_feats:{}".format( out_feats.size()))
#out_feats2 = torch.zeros_like( out_feats )
#out_feats2[:,:-1,:] = out_feats[:,1:,:]
#print( "size of out_feats2:{}".format( out_feats2.size()))
#stop_flags2 = torch.ones_like( stop_flags )
#stop_flags2[:,:-1] = stop_flags[:,1:]
# ゼロパディグした部分を損失関数のの計算から除外するためにマスクを適用します
# Mask (B x T x 1)
mask = make_non_pad_mask(out_lens).unsqueeze(-1)
#print( out_feats2.size())
out_feats = out_feats.masked_select(mask)
#out_feats2 = out_feats2.masked_select(mask)
outs = outs.masked_select(mask)
outs_fine = outs_fine.masked_select(mask)
#print( "size of stop_flags:{}".format( stop_flags.size()))
#print( "stop_flags[0][-1]:{}".format( stop_flags[0][-1]))
stop_flags = stop_flags.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
#stop_flags2 = stop_flags2.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
logits = logits.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
#print( out_feats.size())
# 損失の計算
#decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')(outs, out_feats2)
#decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs, out_feats2)
#postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')(outs_fine, out_feats2)
#postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs_fine, out_feats2)
decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs, out_feats)
postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs_fine, out_feats)
#print( "logits", logits )
#print( "stop_flags", stop_flags)
stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(logits, stop_flags)
#stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction='mean')(logits, stop_flags2)
#stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(logits, stop_flags2)
# 損失の合計
loss = decoder_out_loss + postnet_out_loss + stop_token_loss
total_loss += loss.item()
#print( "loss:{}".format(total_loss))
total_decoder_out_loss += decoder_out_loss.item()
#print( "decoder_out_loss:{}".format(total_decoder_out_loss))
total_postnet_out_loss += postnet_out_loss.item()
#print( "postnet_out_loss:{}".format(total_postnet_out_loss))
total_stop_token_loss += stop_token_loss.item()
#print( "stop_token_loss:{}".format(total_stop_token_loss))
# 損失の値を出力
it_train += 1
# optimizer に蓄積された勾配をリセット
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 誤差の逆伝播
loss.backward()
# gradient clipping
#a = nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0, norm_type=2)
#a = nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=2.0, norm_type=2)
#print( "a:{}".format(a))
#nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=5.0, norm_type=2)
#nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=0.5, norm_type=2)
#nn.utils.clip_grad_value_(model.parameters(), clip_value=0.5)
# パラメータの更新
optimizer.step()
# 学習率スケジューラの更新
current_lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"]
#lr_scheduler.step()
avg_loss = total_loss / count
#プログラスバーに cer 表示
phar.set_postfix( loss = avg_loss )
avg_loss = total_loss / count
avg_decoder_out_loss = total_decoder_out_loss / count
avg_postnet_out_loss = total_postnet_out_loss / count
avg_stop_token_loss = total_stop_token_loss / count
print(f"epoch: {epoch+1:3d}, train it: {it_train:6d}, decoder_out: {avg_decoder_out_loss :.5f}, postnet_out: {avg_postnet_out_loss :.5f}, stop_token: {avg_stop_token_loss :.5f}, loss: {avg_loss :.5f}")
item = np.array([epoch+1, it_train, avg_decoder_out_loss , avg_postnet_out_loss , avg_stop_token_loss , avg_loss , current_lr ])
history = np.vstack((history, item))
model.eval()
total_dev_decoder_out_loss = 0
total_dev_postnet_out_loss = 0
total_dev_stop_token_loss = 0
total_dev_loss = 0
count = 0
# DataLoader を用いたミニバッチの作成: ミニバッチ毎に処理する
phar = tqdm( range( len(data_loader_dev) ), desc='dev' )
Iter_dev = iter(data_loader_dev)
for i in phar:
#for in_feats, in_lens, out_feats, out_lens, stop_flags in tqdm(data_loader_dev):
in_feats, in_lens, out_feats, out_lens, stop_flags = next(Iter_dev)
in_feats = in_feats.to(device)
in_lens = in_lens.to(device)
out_feats = out_feats.to(device)
out_lens = out_lens.to(device)
stop_flags = stop_flags.to(device)
in_lens, indices = torch.sort(in_lens, dim=0, descending=True)
in_feats, out_feats, out_lens = in_feats[indices], out_feats[indices], out_lens[indices]
out_feats0 = torch.zeros_like( out_feats )
out_feats0[:,1:,:] = out_feats[:,:-1,:]
#count += len( in_feats )
count += 1
#outs, outs_fine, logits, _ = model(in_feats, in_lens, out_feats)
outs, outs_fine, logits, _ = model(in_feats, in_lens, out_feats0)
#out_feats2 = torch.zeros_like( out_feats )
#out_feats2[:,:-1,:] = out_feats[:,1:,:]
#stop_flags2 = torch.ones_like( stop_flags )
#stop_flags2[:,:-1] = stop_flags[:,1:]
# ゼロパディグした部分を損失関数のの計算から除外するためにマスクを適用します
# Mask (B x T x 1)
mask = make_non_pad_mask(out_lens).unsqueeze(-1)
#out_feats2 = out_feats2.masked_select(mask)
out_feats = out_feats.masked_select(mask)
outs = outs.masked_select(mask)
outs_fine = outs_fine.masked_select(mask)
stop_flags = stop_flags.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
#stop_flags2 = stop_flags2.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
logits = logits.masked_select(mask.squeeze(-1))
# 損失の計算
#print( " size of outs:{}".format( outs.size()))
#print( " size of out_feats2:{}".format( out_feats2.size()))
#dev_decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')(outs, out_feats2)
#dev_decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs, out_feats2)
#dev_postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')(outs_fine, out_feats2)
#dev_postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs_fine, out_feats2)
dev_decoder_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs, out_feats)
dev_postnet_out_loss = nn.MSELoss()(outs_fine, out_feats)
dev_stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(logits, stop_flags)
#dev_stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(reduction='mean')(logits, stop_flags2)
#dev_stop_token_loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(logits, stop_flags2)
# 損失の合計
dev_loss = dev_decoder_out_loss + dev_postnet_out_loss + dev_stop_token_loss
total_dev_loss += dev_loss.item()
total_dev_decoder_out_loss += dev_decoder_out_loss.item()
total_dev_postnet_out_loss += dev_postnet_out_loss.item()
total_dev_stop_token_loss += dev_stop_token_loss.item()
avg_dev_loss = total_dev_loss / count
#プログラスバーに cer 表示
phar.set_postfix( dev_loss = avg_dev_loss )
# 損失の値を出力
it_dev += 1
avg_dev_loss = total_dev_loss / count
avg_dev_decoder_out_loss = total_dev_decoder_out_loss / count
avg_dev_postnet_out_loss = total_dev_postnet_out_loss / count
avg_dev_stop_token_loss = total_dev_stop_token_loss / count
print(f"epoch: {epoch+1:3d}, dev it: {it_dev:6d}, decoder_out: {avg_dev_decoder_out_loss:.5f}, postnet_out: {avg_dev_postnet_out_loss:.5f}, stop_token: {avg_dev_stop_token_loss:.5f}, loss: {avg_dev_loss:.5f}")
item = np.array([epoch+1, it_dev, avg_dev_decoder_out_loss , avg_dev_postnet_out_loss , avg_dev_stop_token_loss , avg_dev_loss ])
history_dev = np.vstack((history_dev, item))
if ( epoch + 1 ) == num_epochs:
epoch_str = "last_" + format(epoch+1,"04d")
hist_df = pd.DataFrame(history)
filename_his = "./ch96/history_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".csv"
hist_df.to_csv(filename_his, header=False, index=False)
hist_dev_df = pd.DataFrame(history_dev)
filename_his_dev = "./ch96/history_dev_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".csv"
hist_dev_df.to_csv(filename_his_dev, header=False, index=False)
save_path = "./ch96/transtron_weight_training_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".pt"
torch.save({'epoch': epoch,
'model_state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer.state_dict(),
'loss': avg_loss,
'dev_loss': avg_dev_loss,},
save_path)
elif (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
epoch_str = format(epoch+1,"04d")
hist_df = pd.DataFrame(history)
filename_his = "./ch96/history_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".csv"
hist_df.to_csv(filename_his, header=False, index=False)
hist_dev_df = pd.DataFrame(history_dev)
filename_his_dev = "./ch96/history_dev_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".csv"
hist_dev_df.to_csv(filename_his_dev, header=False, index=False)
save_path = "./ch96/transtron_weight_training_ch96_" + epoch_str + ".pt"
torch.save({'epoch': epoch,
'model_state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer.state_dict(),
'loss': avg_loss,
'dev_loss': avg_dev_loss,},
save_path)
学習を評価するためのプログラム
モデルのロード
#モデルのロード
import torch
import pandas as pd
model = Transtron(
num_vocab=52,
embed_dim=512,
conv_layers=3,
conv_channels=512,
conv_kernel_size=5,
enc_hidden_dim = 512,
num_enc_layers = 8,
enc_num_heads = 4,
enc_dropout_rate = 0.1,
conv_dropout_rate = 0.1,
enc_input_maxlen = 300,
enc_ffn_dim = 2048,
decoder_hidden_dim=512,
out_dim=80,
num_dec_layers=8,
prenet_layers=2,
prenet_hidden_dim=512,
prenet_dropout=0.5,
dec_ffn_dim=2048,
dec_dropout_rate = 0.1,
dec_input_maxlen=3000,
dec_num_heads = 4,
postnet_in_dim=80,
postnet_layers=5,
postnet_channels=512,
postnet_kernel_size=5,
postnet_dropout=0.5
)
#device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
device = torch.device("cpu")
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
model = model.to(device)
model.eval()
save_path2 = "./ch96/transtron_weight_training_ch96_0100.pt"
checkpoint = torch.load(save_path2, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
#optimizer.load_state_dict(checkpoint['optimizer_state_dict'])
#for state in optimizer.state.values():
# for k, v in state.items():
# if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor):
# state[k] = v.to('cuda')
ヒストリーのロード
#ヒストリーのロード
import numpy as np
history = np.loadtxt("./ch96/history_ch96_0100.csv", delimiter=",", dtype = "unicode")
history = [[ float(s) for s in s1 ] for s1 in history]
history = np.array( history )
print( history )
history_dev = np.loadtxt("./ch96/history_dev_ch96_0100.csv", delimiter=",", dtype = "unicode")
history_dev = [[ float(s) for s in s1 ] for s1 in history_dev]
history_dev = np.array( history_dev )
print( history_dev )
ヒストリーの可視化
#ヒストリーの可視化
import pandas as pd
# デフォルトフォントサイズ変更
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 10
# 学習ログ解析
def evaluate_history(history, history_val):
#損失と精度の確認
print(f'decoder_out_loss: {history[0,2]:.5f}, postnet_out_loss: {history[0,3]:.5f}, stop_token_loss: {history[0,4]:.5f}, loss: {history[0,5]:.5f}, lr: {history[0,6]:.5f}')
print(f'decoder_out_loss: {history[-1,2]:.5f}, postnet_out_loss: {history[-1,3]:.5f}, stop_token_loss: {history[-1,4]:.5f}, loss: {history[-1,5]:.5f}, lr: {history[-1,6]:.5f}' )
it_train = history[-1,1]
print( it_train )
if it_train < 10:
unit = 1
else:
unit = it_train // 10
# 学習曲線の表示 (損失) train
plt.figure(figsize=(9,8))
plt.plot(history[:,1], history[:,2], 'y', label='decoder_out_loss')
plt.plot(history[:,1], history[:,3], 'k', label='postnet_out_loss')
plt.plot(history[:,1], history[:,4], 'r', label='stop_token_loss')
plt.plot(history[:,1], history[:,5], 'b', label='loss')
plt.xticks(np.arange(0,it_train+1, unit))
plt.xlabel('繰り返し回数')
plt.ylabel('損失')
plt.title('学習曲線(損失)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
it_dev = history_dev[-1,1]
if it_dev < 10:
unit = 1
else:
unit = it_dev // 10
# 学習曲線の表示 (損失) dev
plt.figure(figsize=(9,8))
plt.plot(history_dev[:,1], history_val[:,2], 'y', label='decoder_out_loss')
plt.plot(history_dev[:,1], history_val[:,3], 'k', label='postnet_out_loss')
plt.plot(history_dev[:,1], history_val[:,4], 'r', label='stop_token_loss')
plt.plot(history_dev[:,1], history_val[:,5], 'b', label='loss')
plt.xticks(np.arange(0,it_dev+1, unit))
plt.xlabel('繰り返し回数')
plt.ylabel('損失')
plt.title('学習曲線(損失)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# lr
it_train = history[-1,1]
print( it_train )
if it_train < 10:
unit = 1
else:
unit = it_train // 10
plt.figure(figsize=(9,8))
plt.plot(history[:,1], history[:,6], 'b', label='lr')
plt.xticks(np.arange(0,it_train+1,unit))
plt.xlabel('繰り返し回数')
plt.ylabel('lr')
plt.title('lr')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
evaluate_history( history, history_dev)
inference 関数
#最終的には、model.inference にしたいのだが、inference 関数を修正しながらメルスペクトルを見るので、ここの関数を使っている。
model.eval()
def inference( in_feats ):
"""Performs inference over one batch of inputs using greedy decoding."""
#print( in_feats )
in_feats = torch.unsqueeze( in_feats, axis = 0 )
bs = in_feats.size()[0]
in_lens = []
for feats in ( in_feats):
in_lens.append( len( feats ))
# エンコーダによるテキストに潜在する表現の獲得
encoder_outs = model.encoder(in_feats, in_lens)
decoder_targets_maxlen = in_lens[0] * 10
decoder_targets = encoder_outs.new_zeros((encoder_outs.size()[0], 1, 80))
for i in range(decoder_targets_maxlen ):
print( "i:{}".format( i ))
# デコーダによるメルスペクトログラム、stop token の予測
outs, logits, att_ws = model.decoder(encoder_outs, in_lens, decoder_targets)
if i > 40 and torch.sigmoid(logits[0, -1]) >= 0.5:
break
outs = torch.permute(outs, (0, 2, 1))
outs2 = torch.unsqueeze( outs[:,-1,:], axis = 1 )
decoder_targets = torch.cat( (decoder_targets, outs2), axis = 1 )
# Post-Net によるメルスペクトログラムの残差の予測
outs = torch.permute(decoder_targets, (0, 2, 1))
outs_fine = outs + model.postnet(outs)
# (B, C, T) -> (B, T, C)
outs = outs.transpose(2, 1)
outs_fine = outs_fine.transpose(2, 1)
return outs[0], outs_fine[0], logits[0], att_ws
ineference の計算
#自然音声のメルスペクトルと transtron で合成したメルスペクトルを比較するため inference の計算。
from ttslearn.util import find_lab, find_feats
from ttslearn.tacotron.frontend.openjtalk import text_to_sequence, pp_symbols
from ttslearn.util import find_lab, find_feats
from ttslearn.tacotron.frontend.openjtalk import text_to_sequence, pp_symbols
# 数値演算
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
# 音声波形の読み込み
from scipy.io import wavfile
# フルコンテキストラベル、質問ファイルの読み込み
from nnmnkwii.io import hts
# 音声分析
import pyworld
# 音声分析、可視化
import librosa
import librosa.display
import pandas as pd
# Pythonで学ぶ音声合成
import ttslearn
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
train_utt = "BASIC5000_0001"
test_utt = "BASIC5000_5000"
#test_utt = "BASIC5000_4999"
labels = hts.load(find_lab("downloads/jsut-label/", test_utt))
in_feats = text_to_sequence(pp_symbols(labels.contexts))
in_feats = torch.tensor(in_feats, dtype=torch.long)
with torch.no_grad():
out_feats, out_feats_fine, stop_flags, alignment0 = inference( in_feats )
# 比較用に、自然音声から抽出された音響特徴量を読み込みむ
feats = np.load(find_feats("dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/", test_utt, typ="out_tacotron"))
teacher forcing のメルスペクトログラムの計算
#teacher forcing のメルスペクトログラムを得る。
from pathlib import Path
from ttslearn.train_util import Dataset
from functools import partial
from nnmnkwii.io import hts
# teacher forcing での予測のスペクトルを作る。
labels = hts.load(find_lab("downloads/jsut-label/", test_utt))
in_feats = text_to_sequence(pp_symbols(labels.contexts))
in_feats = torch.tensor(in_feats, dtype=torch.long, requires_grad=False)
in_feats2 = torch.unsqueeze( in_feats, axis = 0 )
print("size of in_feats2:{}".format( in_feats2.size()))
in_lens = []
for lens in in_feats2:
in_lens.append( len(lens ))
in_lens = torch.tensor( in_lens, requires_grad=False )
in_lens = torch.unsqueeze( in_lens, axis = 0)
print( "size of in_lens:{}".format(in_lens.size()) )
out_path = Path( "./dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/eval/out_tacotron/" + test_utt + "-feats.npy" )
out_feats = np.load( out_path )
out_feats = torch.tensor( out_feats, requires_grad=False )
out_feats = torch.unsqueeze( out_feats, axis = 0 )
print("size of out_feats:{}".format( out_feats.size() ))
# エンコーダによるテキストに潜在する表現の獲得
encoder_outs = model.encoder(in_feats2, in_lens)
decoder_targets = out_feats
# デコーダによるメルスペクトログラム、stop token の予測
outs, logits, alignment = model.decoder(encoder_outs, in_lens, decoder_targets)
# Post-Net によるメルスペクトログラムの残差の予測
outs_fine = outs + model.postnet(outs)
# (B, C, T) -> (B, T, C)
outs = outs.transpose(2, 1)
outs_fine = outs_fine.transpose(2, 1)
三つのメルスペクトログラムの可視化
#自然音声のメルスペクトルの transtron で合成したメルスペクトルの可視化(自然音声、teacher forcing, inference )
from pathlib import Path
from ttslearn.notebook import get_cmap, init_plot_style, savefig
cmap = get_cmap()
sr = 16000
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(8,6))
ax[0].set_title("Mel-spectrogram of natural speech")
ax[1].set_title("Mel-spectrogram of Transtron output teacher forcing")
ax[2].set_title("Mel-spectrogram of Transtron output inference")
mindb = min(feats.min(), out_feats_fine.min())
maxdb = max(feats.max(), out_feats_fine.max())
hop_length = int(sr * 0.0125)
# 比較用に、自然音声から抽出された音響特徴量を読み込みむ
feats = np.load(find_feats("dump/jsut_sr16000/norm/", test_utt, typ="out_tacotron"))
mesh = librosa.display.specshow(
feats.T, sr=sr, x_axis="time", y_axis="frames", hop_length=hop_length, cmap=cmap, ax=ax[0])
mesh.set_clim(mindb, maxdb)
fig.colorbar(mesh, ax=ax[0])
outs_fine3 = outs_fine[0,:,:]
mesh = librosa.display.specshow(
outs_fine3.data.numpy().T, sr=sr, x_axis="time", y_axis="frames", hop_length=hop_length, cmap=cmap, ax=ax[1])
mesh.set_clim(mindb, maxdb)
fig.colorbar(mesh, ax=ax[1])
print( "size of out_fine3:{}".format( outs_fine3.size() ))
print( "size of out_feats_fine:{}".format( out_feats_fine.size()))
mesh = librosa.display.specshow(
out_feats_fine.data.numpy().T, sr=sr, x_axis="time", y_axis="frames", hop_length=hop_length, cmap=cmap, ax=ax[2])
mesh.set_clim(mindb, maxdb)
fig.colorbar(mesh, ax=ax[2])
for a in ax:
a.set_xlabel("Time [sec]")
a.set_ylabel("Mel filter channel")
fig.tight_layout()
# 図10-8
savefig("./fig/e2etts_impl_logmel_comp")
stop token の可視化
#Stop token の可視化
print( stop_flags.size())
#stop_flags = torch.squeeze( stop_flags )
#print( stop_flags.size())
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4))
ax.plot(torch.sigmoid(stop_flags).cpu().numpy())
ax.set_xlabel("Time [frame]")
ax.set_ylabel("Stop probability");
合成音声の終端計算
# 合成音声の終端を計算する。
#out_feats_fine5 の可視化
print( "size of out_feats_fine:{}".format( out_feats_fine.size()))
out_feats_fine5 = torch.sum( out_feats_fine, axis = 1)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4))
ax.plot(out_feats_fine5.cpu().numpy())
ax.set_xlabel("Time [frame]")
ax.set_ylabel("out_feats_fine5");
for i, x in enumerate( out_feats_fine5 ):
flag = 1
for j in range(10):
if i + j >= out_feats_fine5.size(0):
break
if out_feats_fine5[ i+j ] < -50:
flag *= 1
else:
flag *= 0
if flag == 1:
break
else:
flag = 1
print( "i:{}".format( i ))
onsei_end = i
アテンション重みの可視化
#アテンション重みの可視化
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig3, ax3 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig4, ax4 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig5, ax5 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig6, ax6 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig7, ax7 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig8, ax8 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig9, ax9 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig10, ax10 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig11, ax11 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig12, ax12 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig13, ax13 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig14, ax14 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig15, ax15 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
fig16, ax16 = plt.subplots(figsize=(14,10))
alignment1 = torch.sum( alignment0["0"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment2 = torch.sum( alignment0["1"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment3 = torch.sum( alignment0["2"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment4 = torch.sum( alignment0["3"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment5 = torch.sum( alignment0["4"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment6 = torch.sum( alignment0["5"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment7 = torch.sum( alignment0["6"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment8 = torch.sum( alignment0["7"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment9 = torch.sum( alignment0["8"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment10 = torch.sum( alignment0["9"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment11 = torch.sum( alignment0["10"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment12 = torch.sum( alignment0["11"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment13 = torch.sum( alignment0["12"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment14 = torch.sum( alignment0["13"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment15 = torch.sum( alignment0["14"][0], axis = 0 )
alignment16 = torch.sum( alignment0["15"][0], axis = 0 )
im1 = ax1.imshow(alignment1.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig1.colorbar(im1, ax=ax1)
ax1.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax1.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im2 = ax2.imshow(alignment2.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig2.colorbar(im2, ax=ax2)
ax2.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax2.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im3 = ax3.imshow(alignment3.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig3.colorbar(im3, ax=ax3)
ax3.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax3.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im4 = ax4.imshow(alignment4.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig4.colorbar(im4, ax=ax4)
ax4.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax4.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im5 = ax5.imshow(alignment5.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig5.colorbar(im5, ax=ax5)
ax5.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax5.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im6 = ax6.imshow(alignment6.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig6.colorbar(im6, ax=ax6)
ax6.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax6.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im7 = ax7.imshow(alignment7.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig7.colorbar(im7, ax=ax7)
ax7.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax7.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im8 = ax8.imshow(alignment8.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig8.colorbar(im8, ax=ax8)
ax8.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax8.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im9 = ax9.imshow(alignment9.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig9.colorbar(im9, ax=ax9)
ax9.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax9.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im10 = ax10.imshow(alignment10.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig10.colorbar(im10, ax=ax10)
ax10.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax10.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im11 = ax11.imshow(alignment11.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig11.colorbar(im11, ax=ax11)
ax11.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax11.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im12 = ax12.imshow(alignment12.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig12.colorbar(im12, ax=ax12)
ax12.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax12.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im13 = ax13.imshow(alignment13.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig13.colorbar(im13, ax=ax13)
ax13.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax13.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im14 = ax14.imshow(alignment14.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig14.colorbar(im14, ax=ax14)
ax14.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax14.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im15 = ax15.imshow(alignment15.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig15.colorbar(im15, ax=ax15)
ax15.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [frame]")
ax15.set_ylabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
im16 = ax16.imshow(alignment16.cpu().data.numpy().T, aspect="auto", origin="lower", interpolation="nearest")
fig16.colorbar(im16, ax=ax16)
ax16.set_ylabel("Encoder time step [frame]")
ax16.set_xlabel("Decoder time step [phoneme]")
ボコーダーの読み込み
#wavenet ボコーダーの読み込み
import hydra
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
device = "cpu"
wavenet_config_name="wavenet_sr16k_mulaw256_30layers"
wavenet_config = OmegaConf.load(f"exp/jsut_sr16000/{wavenet_config_name}/model.yaml")
wavenet_model = hydra.utils.instantiate(wavenet_config.netG)
checkpoint = torch.load(f"exp/jsut_sr16000/{wavenet_config_name}/latest_ema.pth", map_location=device)
wavenet_model.load_state_dict(checkpoint["state_dict"])
# weight normalization は推論時には不要なため除く
wavenet_model.remove_weight_norm_()
wavenet_model.eval();
音声波形の生成関数
#音声波形の生成関数
from ttslearn.dsp import inv_mulaw_quantize
@torch.no_grad()
def gen_waveform(wavenet_model, out_feats):
# (B, T, C) -> (B, C, T)
c = out_feats.view(1, -1, out_feats.size(-1)).transpose(1, 2)
# 音声のサンプル数を計算
upsample_scale = np.prod(wavenet_model.upsample_scales)
T = (
c.shape[-1] - wavenet_model.aux_context_window * 2
) * upsample_scale
# WaveNet による音声波形の生成
# NOTE: 計算に時間がかかるため、tqdm によるプログレスバーを受け付けるようにしています
gen_wav = wavenet_model.inference(c, T, tqdm)
# One-hot ベクトルから1次元の信号に変換
gen_wav = gen_wav.max(1)[1].float().cpu().numpy().reshape(-1)
# Mu-law 量子化の逆変換
gen_wav = inv_mulaw_quantize(
gen_wav, wavenet_model.out_channels - 1
)
return gen_wav
wavenet で音声合成
# wavenet で音声合成
from ttslearn.util import find_lab, find_feats
from ttslearn.dsp import logmelspectrogram_to_audio
out_feats_fine2 = out_feats_fine[:onsei_end+10]
# WaveNet ボコーダによる音声波形の生成
gen_wav = gen_waveform(wavenet_model, out_feats_fine2)
音声確認
from IPython.display import Audio
import IPython
sr = 16000
IPython.display.display(Audio(gen_wav, rate=sr))
from scipy.io.wavfile import read, write
writefilename = "./test_inference.wav"
write(writefilename, rate=16000, data=gen_wav)