Overview
Here descibes ROS2 tracepoint related information, this is public info but not so organized well because this is mostly my own note to keep this in the mind. nobody blames on it. ROS2 tracepoint is actually depends on LTTng so knowing LTTng is to help to understand ROS2 tracepoint.
LTTng
Installation
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:lttng/ppa
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install lttng-tools lttng-modules-dkms babeltrace liblttng-ust-dev liblttng-ctl-dev
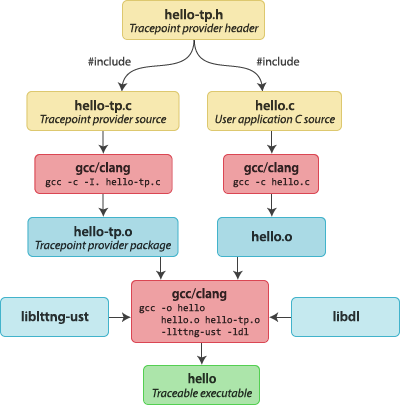
LTTng Modules
LTTng are the kernel modules, so that you can see a bunch of ko via lsmod command. Notable features are CTF(Common Trace Format) support, tracepoint, function tracer, monitoring and kprobes. LTTng is context aware so that able to attach context information to event in the trace.
Required Kconfig
- CONFIG_MODULES
- CONFIG_KALLSYMS
- CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS
- CONFIG_TRACEPOINTS
Tutorial
Trace Session Mode
- Local mode
LTTng writes the traces to the file system of the machine it traces (target system). - Network streaming mode
LTTng sends the traces over the network to a relay daemon running on a remote system. - Snapshot mode
LTTng does not write the traces by default. Instead, you can request LTTng to take a snapshot, that is, a copy of the tracing session’s current sub-buffers, and to write it to the target’s file system or to send it over the network to a relay daemon running on a remote system. - Live mode
This mode is similar to the network streaming mode, but a live trace viewer can connect to the distant relay daemon to view event records as LTTng generates them.
and there are so far five tracing domains are supported,
- Linux Kernel
- User space
- java.util.logging
- log4j
- Python
License
| Package | License |
|---|---|
| LTTng-tools | LGPLv2.1 and GPLv2 |
| LTTng-UST | LGPLv2.1, the MIT license and GPLv2 |
| LTTng-modules | LGPLv2.1, GPLv2 and the MIT license |