初めに
「「IronPython 3」が登場 ~Python 3をターゲットにした初めてのIronPython」というニュースを見た。
(IronRubyとか、他のスクリプト言語は復活しないのかなぁ~!?)
そういえば、私のツールには、IronPythonでのスクリプティング機能があり(「これ」と「これ」)。
IronPython3系は動かないにしても、最新の2.7.12では動くのでは!?
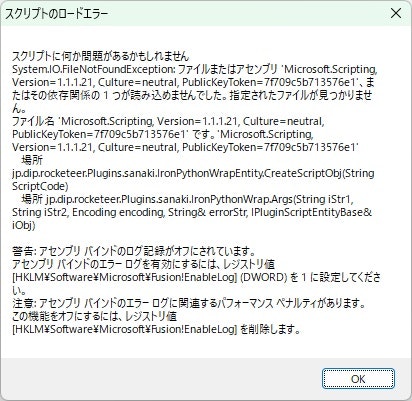
と試してみたら、こんなエラー
あれれ!?
ソースコードを見つつ、確かIronPythonは(IronRubyと違って)GACを汚すから、バージョンにこだわらず、DLLは.NETアプリなら参照されるはず・・・と思いつつ・・・あれ、ダメだ。静的バインディングだと、コンパイルした ver2.7.6.3じゃないとダメなんだー...。
GAC内部のIronPythonを参照設定しても、バージョン固定になるので、違うバージョンがインストールされていると、動かなくなる。
DLL地獄には落ちないけど、IronPythonのバージョンごとにコンパイルして、バイナリを用意するのは面倒だなぁ~、といろいろと検索すると、遅延バインディングという仕組みがあることを発見。
IntelliSenseが効かないとか不便はあるようだけど、静的バインディングから遅延バインディングへの切り替えだから、特に不便はないかもしれない。
(静的バインディングでコードを整理整頓してから、遅延バインディングにすればいいのかな....と)
と思い、挑戦してみた。
遅延バインディングには、Assemby.LoadFile() というメソッドを使った。
一番てこずったのは、Assemby.Load("IronPython") としても、アセンブリのファイルを見つけてくれない事。
GACの中にあるから、適当にロードしてくれてもいいのに、してくれない。
ver2.7.7の場合は、こんな感じ
c:\>dir /s /b IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\Platforms\Net35\IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\Platforms\Net40\IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\Platforms\Net45\IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\Platforms\Sl5\IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\Silverlight\bin\IronPython.dll
c:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\IronPython\v4.0_2.7.7.0__7f709c5b713576e1\IronPython.dll
c:\>
GACの中にあるのに・・・
GACをスキャンすることにした
Assemby.Load("IronPython") だと埒が明かないので、直接的なメソッド名である Assembly.LoadFile() メソッドでやってみることにした。
すると、直接、「c:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\IronPython\v4.0_2.7.7.0__7f709c5b713576e1\IronPython.dll」を与えればうまく行くことを検証で確認できたので、
- あるディレクトリ(%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL)をスキャン
- その中に「IronPython」というディレクトリを見つける
- 2で見つけたディレクトリ内部を再帰的にファイルをスキャンして、「IronPython.dll」のフルパスを探す
という処理をしてから、Assemby.LoadFile()を呼び出す事にした
少し戻って、IronPythonの状況
IronPython.dllのインストール場所は、ver2.7.7もver2.7.6.3も、ver2.7.9もver2.7.11もver2.7.12も似たような感じだったので、上記のGACをスキャンするという方法を採用した。
GACをスキャンすることにした(ソースコード)
スキャンするクラスはこんな感じ
/* using とnamespaceは省略*/
public class FilePath{
public static String GACPath(String name) {
String ansStr = null;
String tempStr = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("systemroot");
ansStr = GACPath(name, tempStr + "\\Microsoft.NET\\assembly\\GAC_MSIL");
if (ansStr == null) {
ansStr = GACPath(name, tempStr + "\\assembly\\GAC_MSIL");
}
return ansStr;
}
public static String GACPath(String name, String directoryPath) {
String ansStr = null;
DirectoryInfo di = new DirectoryInfo(directoryPath);
DirectoryInfo[] dHako = di.GetDirectories();
if ((dHako != null) && (0 < dHako.Length)){
for (int i = 0; i < dHako.Length; i++){
if (dHako[i].Name.ToLower() == name.ToLower()){
ansStr = GetDLLPath(name, dHako[i]);
break;
}
}
}
return ansStr;
}
public static String GetDLLPath(String name, DirectoryInfo di) {
String ansStr = null;
FileInfo[] fHako = di.GetFiles();
if ((fHako != null) && (0 < fHako.Length)) {
for (int i = 0; i < fHako.Length; i++) {
if (fHako[i].Name.ToLower() == (name + ".dll").ToLower()) {
return fHako[i].FullName;
}
}
}
DirectoryInfo[] dHako = di.GetDirectories();
if ((dHako != null) && (0 < dHako.Length)) {
for (int i = 0; i < dHako.Length; i++) {
ansStr = GetDLLPath(name, dHako[i]);
if (ansStr != null) {
return ansStr;
}
}
}
return ansStr;
}
}
FilePath.GACPath("IronPython") で、%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\assembly\と%SystemRoot%\assembly\ 以下にインストールされたIronPyhton.dllのフルパスを返してくれる。
まとめると(遅延バインディングのコード)
全体的にまとめると、こんな感じになった。
/*using とnamespaceは省略*/
/* 静的パインディングなら、
IronPython.dll
IronPythonModules.dll
Microsoft.Scripting.dll
Microsoft.Scripting.meta.dll
を参照の設定をして、以下をusingする
using IronPython;
using IronPython.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Scripting.Hosting;
*/
using System.Reflection; // Assembyクラスに必要
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){
Class1 obj = new Class1();
String dllPath = FilePath.GACPath("IronPython");
Assembly lib = Assembly.LoadFile(dllPath);
Type type = lib.GetType("Hosting.Python");
if (type == null) {
Type[] typeHako = lib.GetTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < typeHako.Length; i++) {
if (typeHako[i].FullName == "IronPython.Hosting.Python") {
type = typeHako[i];
break;
}
}
}
MethodInfo createEngine = type.GetMethod("CreateEngine", new Type[] { }, null);
dynamic pythonScriptEngine = createEngine.Invoke(null, null);
// スコープをロード
dynamic scope = pythonScriptEngine.CreateScope();
// 変数をセットする
scope.SetVariable("myObj", obj);
// ソースコードを読み込み
dynamic source = pythonScriptEngine.CreateScriptSourceFromString(textBox1.Text);
dynamic csource = source.Compile();
// 実行する
csource.Execute(scope);
// 関数を実行する
Action action = pythonScriptEngine.Operations.GetMember<Action>(scope, "testFunc");
action();
//
textBox2.Text = obj.myStr;
}
ボタンを押したら、textBox1.TextにPythonコードを読み出して、testFunc関数を実行する。
オブジェクトとしてセットした Class1クラスのmyStrプロパティに実行結果が保持されているので、それをtextBox2.Textに表示して動作確認する。
という内容のコードです。
とりあえず、ver2.7.6.3, ver2.7.7, ver2.7.9, ver2.7.11, ver2.7.12 のどれがインストールされていても、一つのバイナリで動作するようになった。
IronPyhton3.4.0 の場合
IronPython3.4.0の場合、GACは汚さないらしい。
c:\>dir /s /b IronPython.dll
c:\Program Files\IronPython 3.4\IronPython.dll
c:\>
それならそれで、IronRubyのように、環境変数などでインストール先ディレクトが分かるようなインストーラーであればいいけど、私の環境ではどこにインストールされたか分からない。
IronRubyの場合
c:\>set i
IRONRUBY_11=C:\Program Files (x86)\IronRuby 1.1\bin
c:\>
な感じで、環境変数でインストール先ディレクトリが分かるのに・・・
「インストーラーで環境変数にどこにインストールしたか分かるようにしてほしい」って、プルリクを送った方がいいのかな!?
IronPyhton3.4.0 の場合(2023/08/09追記)
ルー語のような日本語のような英語で質問したら、返事が来た。
(つたない英語を読み解いてくれて、感謝感謝)
結論から言うと、「レジストリにあるからそれを読めばいいんじゃね!?」
レジストリ
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\IronPython\3.4\InstallPath
を読みだせばいいということ。...これって、Windows環境だけで、マルチプラットフォームを掲げている.NET Core!?の思想から外れるような気がするが、、、まぁ、気にしないことにする。
ルー語のような英語の質問をした流れはこちら
(恥ずかしいけど、歴史的事実としてリンクしておく)
IronPyhton3.4.0 で遅延バインディング
続編です。
IronPythonを遅延バインディングで呼び出してみた(ver3.4.0の場合)
蛇足(AutoGenerateBindingRedirects)
拡張子、.csprojというファイルに**「<AutoGenerateBindingRedirects>true</AutoGenerateBindingRedirects>」**と書くという方法もあるようだけど、私のVisualStudio2019ではうまく動作しなかった。
.NET Framework4.0以上にしているからなのかな!?...よく分からんけど、動作しなかった。
まとめ
遅延バインディングすごい。
これで、バージョンごとにコンパイルしたバイナリを事前用意しなくてよくなった。