こんにちは、たなたつです ![]()
汎用性高めのExtension集です。Protocolやstructなども一部含まれています。
使うと手放せなくなるSwift Extension集 (Swift 4版)のSwift 5版です。 (2年ぶりの更新)
Swift 5.1の新機能や記法の最適化によって段々と良くなっています。
今回紹介したExtensionは全て下記のリポジトリに入っています。他にも便利な機能がたくさん入っているので、利用したい方はコピペやSwift PM/Carthageで導入してみてください。
https://github.com/tattn/SwiftExtensions
※ Swift 5.1, Xcode 11.2.1 で動作確認をしています。
※ コード片ごとに紹介していますが、別のコード片のExtensionに依存している場合がありますので、ご注意ください。
※ これらの中には用途に合わせて型を作った方がメンテナビリティが高い実装もありますので、参考程度に読んでください
Foundation
クラス名の取得
public protocol ClassNameProtocol {
static var className: String { get }
var className: String { get }
}
public extension ClassNameProtocol {
public static var className: String {
String(describing: self)
}
public var className: String {
Self.className
}
}
extension NSObject: ClassNameProtocol {}
UIView.className //=> "UIView"
UILabel().className //=> "UILabel"
配列でオブジェクトのインスタンスを検索して削除
public extension Array where Element: Equatable {
@discardableResult
mutating func removeFirst(_ element: Element) -> Index? {
guard let index = firstIndex(of: element) else { return nil }
remove(at: index)
return index
}
}
let array = ["foo", "bar"]
array.removeFirst("foo")
array //=> ["bar"]
Out of Rangeを防いで、要素を取得
public extension Collection {
subscript(safe index: Index) -> Element? {
startIndex <= index && index < endIndex ? self[index] : nil
}
}
let array = [0, 1, 2]
if let item = array[safe: 5] {
print("unreachable")
}
NSLocalizedStringを使いやすくする
public extension String {
var localized: String {
NSLocalizedString(self, comment: self)
}
func localized(withTableName tableName: String? = nil, bundle: Bundle = Bundle.main, value: String = "") -> String {
NSLocalizedString(self, tableName: tableName, bundle: bundle, value: value, comment: self)
}
}
let message = "Hello".localized
様々なRangeで部分文字列を取得
public extension String {
subscript(bounds: CountableClosedRange<Int>) -> String {
let start = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.lowerBound)
let end = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.upperBound)
return String(self[start...end])
}
subscript(bounds: CountableRange<Int>) -> String {
let start = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.lowerBound)
let end = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.upperBound)
return String(self[start..<end])
}
subscript(bounds: PartialRangeUpTo<Int>) -> String {
let end = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.upperBound)
return String(self[startIndex..<end])
}
subscript(bounds: PartialRangeThrough<Int>) -> String {
let end = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.upperBound)
return String(self[startIndex...end])
}
subscript(bounds: CountablePartialRangeFrom<Int>) -> String {
let start = index(startIndex, offsetBy: bounds.lowerBound)
return String(self[start..<endIndex])
}
}
let string = "0123456789"
string[0...5] //=> "012345"
string[1...3] //=> "123"
string[3..<7] //=> "3456"
string[...4] //=> "01234
string[..<4] //=> "0123"
string[4...] //=> "456789"
文字列からURLを作成/文字列リテラルからURLを生成
public extension String {
var url: URL? {
URL(string: self)
}
}
extension URL: ExpressibleByStringLiteral {
public init(stringLiteral value: String) {
guard let url = URL(string: value) else {
fatalError("\(value) is an invalid url")
}
self = url
}
public init(extendedGraphemeClusterLiteral value: String) {
self.init(stringLiteral: value)
}
public init(unicodeScalarLiteral value: String) {
self.init(stringLiteral: value)
}
}
if let url = "https://example.com".url {
}
let url: URL = "https://example.com"
Kotlinっぽいスコープ関数を使う
public protocol Applicable {}
public extension Applicable {
@discardableResult
func apply(closure: (Self) -> Void) -> Self {
closure(self)
return self
}
}
public protocol Runnable {}
public extension Runnable {
@discardableResult
func run<T>(closure: (Self) -> T) -> T {
closure(self)
}
}
extension NSObject: Applicable {}
extension NSObject: Runnable {}
let view = UIView().apply {
$0.backgroundColor = .red
$0.frame = .init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 200, height: 200)
}
Optionalがnilの時にErrorとしてThrowできるようにする
public extension Optional {
func orThrow(_ error: @autoclosure () -> Error) throws -> Wrapped {
guard let value = self else { throw error() }
return value
}
}
let value: String? = nil
struct OptionalError: Error {}
do {
let v = try value.orThrow(OptionalError())
print(v) // unreachable
} catch {
print(error) //=> OptionalError
}
Dictionaryの値取得時にkeyがなければErrorをThrowする
public struct DictionaryTryValueError: Error {
public init() {}
}
public extension Dictionary {
func tryValue(forKey key: Key, error: Error = DictionaryTryValueError()) throws -> Value {
guard let value = self[key] else { throw error }
return value
}
}
var dictionary: [String: Int] = [:]
do {
let value = try dictionary.tryValue(forKey: "foo")
print(value) // unreachable
} catch {
print(error) //=> DictionaryTryValueError
}
.exでアクセスできるプロパティやメソッドを作る
public struct TargetedExtension<Base> {
let base: Base
init (_ base: Base) {
self.base = base
}
}
public protocol TargetedExtensionCompatible {
associatedtype Compatible
static var ex: TargetedExtension<Compatible>.Type { get }
var ex: TargetedExtension<Compatible> { get }
}
public extension TargetedExtensionCompatible {
public static var ex: TargetedExtension<Self>.Type {
TargetedExtension<Self>.self
}
public var ex: TargetedExtension<Self> {
TargetedExtension(self)
}
}
// UIViewに.exを増やす場合
extension UIView: TargetedExtensionCompatible {}
private extension TargetedExtension where Base: UIView {
func foo() {}
}
UIView().ex.foo()
Codableで値がdecodeできないことを許容する
@propertyWrapper
public struct Safe<Wrapped: Codable>: Codable {
public let wrappedValue: Wrapped?
public init(wrappedValue: Wrapped?) {
self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue
}
public init(from decoder: Decoder) throws {
do {
let container = try decoder.singleValueContainer()
self.wrappedValue = try container.decode(Wrapped.self)
} catch {
self.wrappedValue = nil
}
}
public func encode(to encoder: Encoder) throws {
var container = encoder.singleValueContainer()
try container.encode(wrappedValue)
}
}
let json = """
{"url": "https://foo.com", "url2": "invalid url string"}
""".data(using: .utf8)!
struct Model: Codable {
@Safe var url: URL?
@Safe var url2: URL?
}
let model = try! JSONDecoder().decode(Model.self,
from: json)
model.url?.absoluteString //=> "https://foo.com"
model.url2 //=> nil
// ===
let json2 = """
[
{"name": "Taro"},
{"name": 123}
]
""".data(using: .utf8)!
struct User: Codable {
let name: String
}
let users = try! JSONDecoder().decode([Safe<User>].self,
from: json2)
users[0].wrappedValue?.name //=> "Taro"
users[1].wrappedValue //=> nil
CodableでStringを任意の型に変換して受け取る
@propertyWrapper
public struct FromString<T: LosslessStringConvertible>: Codable {
public let wrappedValue: T
public init(wrappedValue: T) {
self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue
}
public init(from decoder: Decoder) throws {
let container = try decoder.singleValueContainer()
let stringValue = try container.decode(String.self)
guard let value = T(stringValue) else {
throw DecodingError.dataCorrupted(
.init(codingPath: decoder.codingPath,
debugDescription: "The string cannot cast to \(T.self).")
)
}
self.wrappedValue = value
}
public func encode(to encoder: Encoder) throws {
var container = encoder.singleValueContainer()
try container.encode(wrappedValue.description)
}
}
let json = """
{
"number": "100",
}
""".data(using: .utf8)!
struct Model: Codable {
@FromString var number: Int
}
let model = try! JSONDecoder().decode(Model.self, from: data)
model.number //=> 100 (Int型)
値型を参照で保持する
@propertyWrapper @dynamicMemberLookup
public class Ref<Wrapped> {
public var wrappedValue: Wrapped
public init(wrappedValue: Wrapped) {
self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue
}
public init(_ wrappedValue: Wrapped) {
self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue
}
public subscript<T>(dynamicMember keyPath: KeyPath<Wrapped, T>) -> T {
wrappedValue[keyPath: keyPath]
}
}
struct Holder {
@Ref var refValue: Int = 0
var value: Int = 0
}
var holder = Holder()
holder.refValue = 1
holder.value = 1
var copyHolder = holder
copyHolder.refValue = 2
copyHolder.value = 2
XCTAssertEqual(holder.refValue, 2) // passed!
XCTAssertEqual(holder.value, 1) // passed!
オブジェクトをweak参照で保持する
@dynamicMemberLookup
public class Weak<Wrapped: AnyObject> {
public weak var wrappedValue: Wrapped?
public init(_ wrappedValue: Wrapped?) {
self.wrappedValue = wrappedValue
}
public subscript<T>(dynamicMember keyPath: ReferenceWritableKeyPath<Wrapped, T>) -> T? {
get { wrappedValue?[keyPath: keyPath] }
set {
if let newValue = newValue {
wrappedValue?[keyPath: keyPath] = newValue
}
}
}
public subscript<T>(dynamicMember keyPath: ReferenceWritableKeyPath<Wrapped, T?>) -> T? {
get { wrappedValue?[keyPath: keyPath] }
set { wrappedValue?[keyPath: keyPath] = newValue }
}
}
class Object {
var value = 1
}
struct WeakHolder {
let array: [Weak<Object>]
}
var array = [Object(), Object()]
let holder = WeakHolder(array: array.map { Weak($0) })
XCTAssertEqual(holder.array[0].value, 1) // passed!
array = []
XCTAssertNil(holder.array[0].value) // passed!
UIKit
XIBの登録・取り出し
UITableView
public extension UITableView {
public func register(cellType: UITableViewCell.Type, bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
let className = cellType.className
let nib = UINib(nibName: className, bundle: bundle)
register(nib, forCellReuseIdentifier: className)
}
public func register(cellTypes: [UITableViewCell.Type], bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
cellTypes.forEach { register(cellType: $0, bundle: bundle) }
}
public func dequeueReusableCell<T: UITableViewCell>(with type: T.Type, for indexPath: IndexPath) -> T {
dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: type.className, for: indexPath) as! T
}
}
tableView.register(cellType: MyCell.self)
tableView.register(cellTypes: [MyCell1.self, MyCell2.self])
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(with: MyCell.self, for: indexPath)
UICollectionView
public extension UICollectionView {
public func register(cellType: UICollectionViewCell.Type, bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
let className = cellType.className
let nib = UINib(nibName: className, bundle: bundle)
register(nib, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: className)
}
public func register(cellTypes: [UICollectionViewCell.Type], bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
cellTypes.forEach { register(cellType: $0, bundle: bundle) }
}
public func register(reusableViewType: UICollectionReusableView.Type,
ofKind kind: String = UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader,
bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
let className = reusableViewType.className
let nib = UINib(nibName: className, bundle: bundle)
register(nib, forSupplementaryViewOfKind: kind, withReuseIdentifier: className)
}
public func register(reusableViewTypes: [UICollectionReusableView.Type],
ofKind kind: String = UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader,
bundle: Bundle? = nil) {
reusableViewTypes.forEach { register(reusableViewType: $0, ofKind: kind, bundle: bundle) }
}
public func dequeueReusableCell<T: UICollectionViewCell>(with type: T.Type,
for indexPath: IndexPath) -> T {
dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: type.className, for: indexPath) as! T
}
public func dequeueReusableView<T: UICollectionReusableView>(with type: T.Type,
for indexPath: IndexPath,
ofKind kind: String = UICollectionElementKindSectionHeader) -> T {
dequeueReusableSupplementaryView(ofKind: kind, withReuseIdentifier: type.className, for: indexPath) as! T
}
}
collectionView.register(cellType: MyCell.self)
collectionView.register(cellTypes: [MyCell1.self, MyCell2.self])
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(with: MyCell.self, for: indexPath)
collectionView.register(reusableViewType: MyReusableView.self)
collectionView.register(reusableViewTypes: [MyReusableView1.self, MyReusableView2.self])
let view = collectionView.dequeueReusableView(with: MyReusableView.self, for: indexPath)
StoryboardからUIViewControllerを生成
public enum StoryboardInstantiateType {
case initial
case identifier(String)
}
public protocol StoryboardInstantiatable {
static var storyboardName: String { get }
static var storyboardBundle: Bundle { get }
static var instantiateType: StoryboardInstantiateType { get }
}
public extension StoryboardInstantiatable where Self: NSObject {
public static var storyboardName: String {
className
}
public static var storyboardBundle: Bundle {
Bundle(for: self)
}
private static var storyboard: UIStoryboard {
UIStoryboard(name: storyboardName, bundle: storyboardBundle)
}
public static var instantiateType: StoryboardInstantiateType {
.identifier(className)
}
}
public extension StoryboardInstantiatable where Self: UIViewController {
public static func instantiate() -> Self {
switch instantiateType {
case .initial:
return storyboard.instantiateInitialViewController() as! Self
case .identifier(let identifier):
return storyboard.instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: identifier) as! Self
}
}
}
// クラス名とStoryboard名、Storyboard IDが同じ
final class ViewController: UIViewController, StoryboardInstantiatable {
}
ViewController.instantiate()
// Is Initial View Controllerにチェックを入れている & クラス名とStoryboard名が同じ
final class InitialViewController: UIViewController, StoryboardInstantiatable {
static var instantiateType: StoryboardInstantiateType {
.initial
}
}
InitialViewController.instantiate()
XIBのViewの生成
public protocol NibInstantiatable {
static var nibName: String { get }
static var nibBundle: Bundle { get }
static var nibOwner: Any? { get }
static var nibOptions: [AnyHashable: Any]? { get }
static var instantiateIndex: Int { get }
}
public extension NibInstantiatable where Self: NSObject {
public static var nibName: String { className }
public static var nibBundle: Bundle { Bundle(for: self) }
public static var nibOwner: Any? { self }
public static var nibOptions: [AnyHashable: Any]? { nil }
public static var instantiateIndex: Int { 0 }
}
public extension NibInstantiatable where Self: UIView {
public static func instantiate() -> Self {
let nib = UINib(nibName: nibName, bundle: nibBundle)
return nib.instantiate(withOwner: nibOwner, options: nibOptions)[instantiateIndex] as! Self
}
}
// XIB名とクラス名が同じ & 0番目のView
final class View: UIView, NibInstantiatable {
}
View.instantiate()
// XIB名とクラス名が異なる & 2番目のView
final class View2: UIView, NibInstantiatable {
static var nibName: String { "Foo" } // Foo.xib
static var instantiateIndex: Int { 2 }
}
View2.instantiate()
Interface BuilderにXibで作ったカスタムViewを置く
public protocol EmbeddedNibInstantiatable {
associatedtype Embedded: NibInstantiatable
}
public extension EmbeddedNibInstantiatable where Self: UIView, Embedded: UIView {
public var embedded: Embedded { subviews[0] as! Embedded }
public func configureEmbededView() {
let view = Embedded.instantiate()
insertSubview(view, at: 0)
view.fillSuperview() // 後述
}
}
final class EmbeddedView: UIView, NibInstantiatable {
}
@IBDesignable
final class IBEmbeddedView: UIView, EmbeddedNibInstantiatable {
typealias Embedded = EmbeddedView
#if TARGET_INTERFACE_BUILDER
override func prepareForInterfaceBuilder() {
super.prepareForInterfaceBuilder()
configureEmbededView()
}
#endif
override func awakeFromNib() {
super.awakeFromNib()
configureEmbededView()
}
}
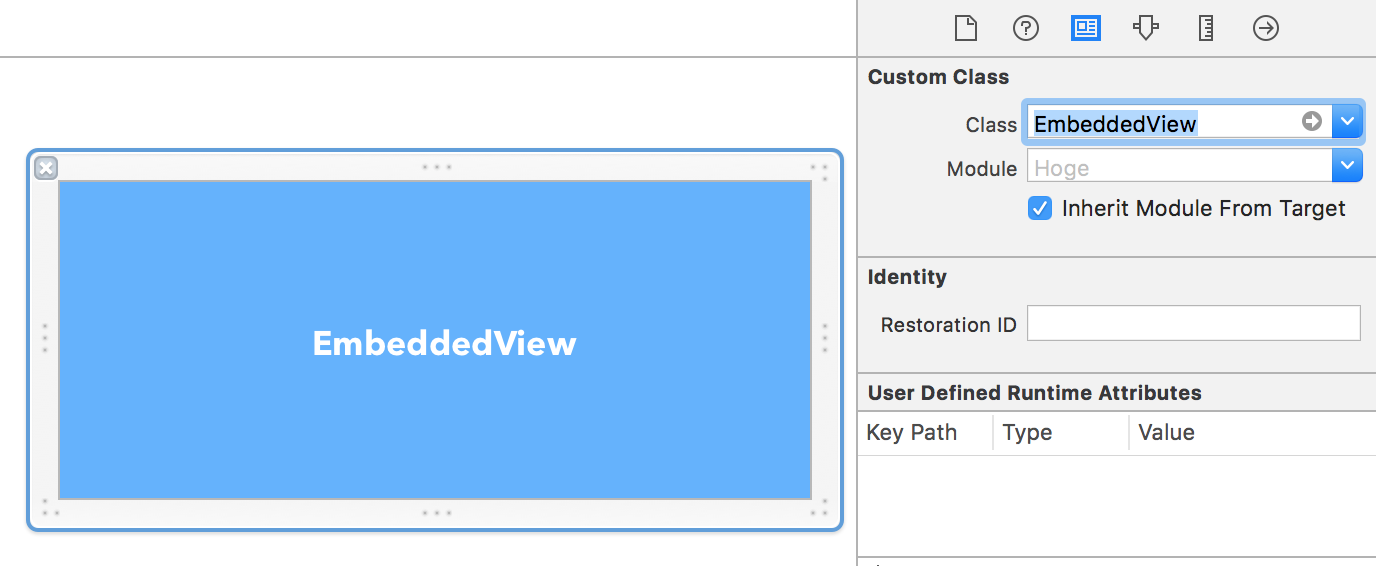
(例) EmbeddedView.xibに置いたUIViewのCustom Classを設定 (File's Ownerの方ではない)
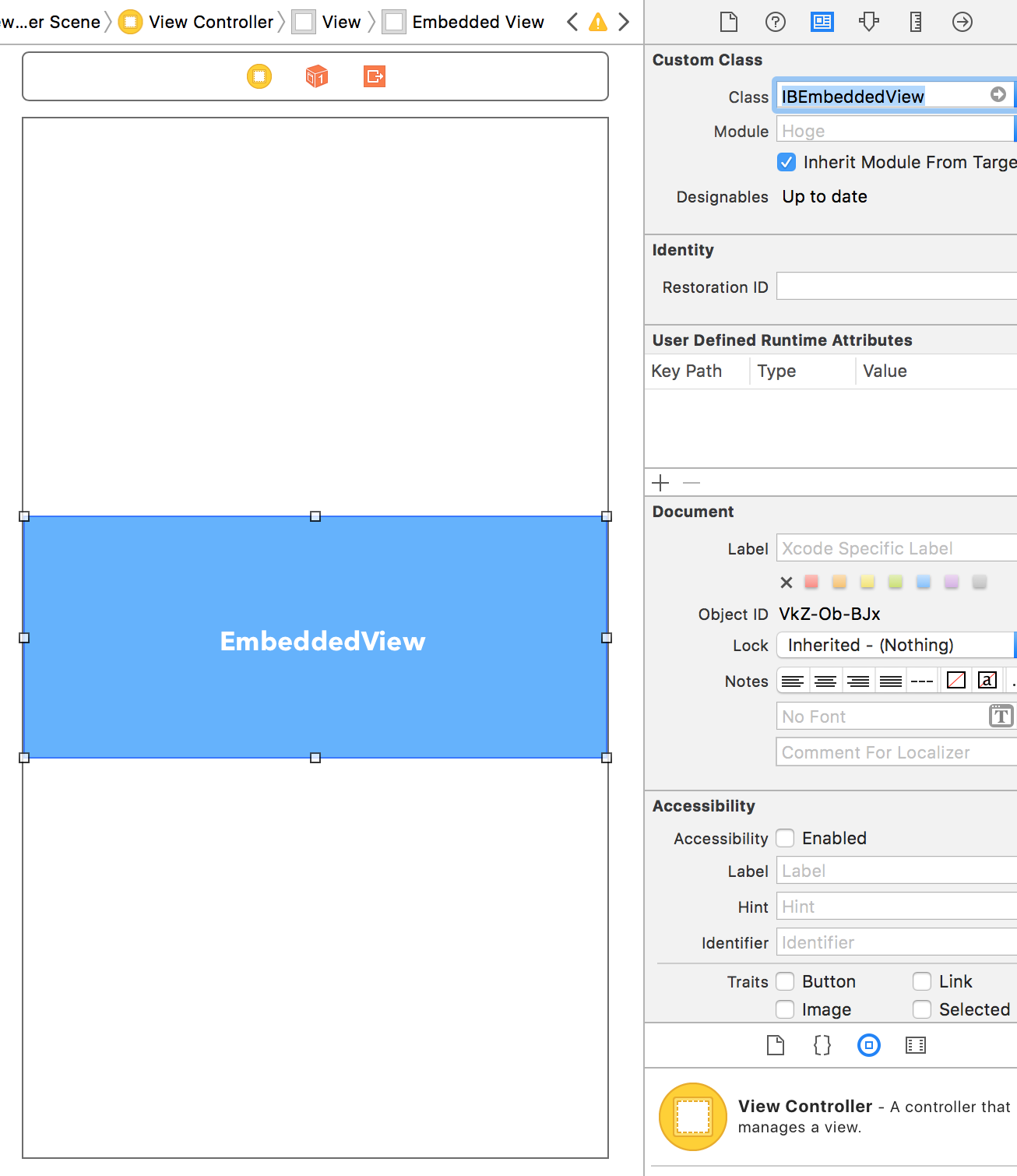
(例) Storyboard上のViewControllerにUIViewを載せて、カスタムクラスを設定
UIViewをSuperviewと同じ大きさにする
public extension UIView {
func fillSuperview() {
guard let superview = self.superview else { return }
translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = superview.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints
if translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints {
autoresizingMask = [.flexibleWidth, .flexibleHeight]
frame = superview.bounds
} else {
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: superview.topAnchor),
bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: superview.bottomAnchor),
leftAnchor.constraint(equalTo: superview.leftAnchor),
rightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: superview.rightAnchor)
])
}
}
}
superView.addSubview(view)
view.fillSuperview()
最前面のUIViewController/UINavigationControllerの取得
public extension UIApplication {
var topViewController: UIViewController? {
let keyWindow = UIApplication.shared.windows.first { $0.isKeyWindow }
guard var topViewController = keyWindow?.rootViewController else { return nil }
while let presentedViewController = topViewController.presentedViewController {
topViewController = presentedViewController
}
return topViewController
}
var topNavigationController: UINavigationController? {
topViewController as? UINavigationController
}
}
UIApplication.shared.topViewController
そのUIViewを持つViewControllerを取得
public extension UIView {
var viewController: UIViewController? {
var parent: UIResponder? = self
while parent != nil {
parent = parent?.next
if let viewController = parent as? UIViewController {
return viewController
}
}
return nil
}
}
view.viewController
16進数でUIColorの作成
public extension UIColor {
convenience init(hex: Int, alpha: Double = 1.0) {
let r = CGFloat((hex & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0
let g = CGFloat((hex & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0
let b = CGFloat(hex & 0x0000FF) / 255.0
self.init(red: r, green: g, blue: b, alpha: CGFloat(alpha))
}
}
let color = UIColor(hex: 0xAABBCC)
特定の色で塗りつぶされたUIImageを生成
public extension UIImage {
convenience init(color: UIColor, size: CGSize) {
let image = UIGraphicsImageRenderer(size: size).image { context in
context.cgContext.setFillColor(color.cgColor)
context.fill(CGRect(origin: .zero, size: size))
}
if let cgImage = image.cgImage {
self.init(cgImage: cgImage)
} else {
self.init()
}
}
}
UIImage(color: .red, size: .init(width: 100, height: 100))
画像を別の色で塗りつぶす (透明色は塗りつぶさない)
public extension UIImage {
func image(withTint color: UIColor) -> UIImage {
guard let cgImage = cgImage else { return self }
let rect = CGRect(origin: .zero, size: size)
return UIGraphicsImageRenderer(size: size).image { context in
context.cgContext.scaleBy(x: 1, y: -1)
context.cgContext.translateBy(x: 0, y: -self.size.height)
context.cgContext.clip(to: rect, mask: cgImage)
context.cgContext.setFillColor(color.cgColor)
context.fill(rect)
}
}
}
fooImage.image(withTint: .red)
ダイナミックカラーを作成する
public extension UIColor {
convenience init(light: UIColor, dark: UIColor) {
if #available(iOS 13, *) {
self.init { $0.userInterfaceStyle == .dark ? dark : light }
} else {
self.init(cgColor: light.cgColor)
}
}
}
// ライトモードの時は赤、ダークモードの時は青
UIColor(light: .red, dark: .blue)
ダークモードかどうかを判定する
public extension UITraitCollection {
static var isDarkMode: Bool {
if #available(iOS 13, *) {
return current.isDarkMode
}
return false
}
var isDarkMode: Bool {
if #available(iOS 13, *) {
return userInterfaceStyle == .dark
}
return false
}
}
if UITraitCollection.isDarkMode {
// ダークモードの時の処理
} else {
// ライトモードの時の処理
}
SwiftUI
型消去を簡単に
public extension View {
@inlinable var erased: AnyView { AnyView(self) }
}
func conditionView() -> AnyView {
switch type {
case .type1: return Type1View().erased
case .type2: return Type2View().erased
}
}
条件によってViewを非表示に
public extension View {
@inlinable func hidden(isHidden: Bool) -> some View {
Group {
if isHidden {
hidden()
} else {
self
}
}
}
}
InformationView()
.hidden(isHidden: self.isInformationViewHidden)
Stateの変化を監視する
@propertyWrapper
public struct ObservedState<Value>: DynamicProperty {
@State private var _wrappedValue: Value
public typealias ObservedChange = (oldValue: Value, newValue: Value)
private let _willChange = PassthroughSubject<ObservedChange, Never>()
private let _didChange = PassthroughSubject<ObservedChange, Never>()
public var wrappedValue: Value {
get { _wrappedValue }
nonmutating set {
let value = (_wrappedValue, newValue)
_willChange.send(value)
_wrappedValue = newValue
_didChange.send(value)
}
}
public var willChange: AnyPublisher<ObservedChange, Never> {
_willChange.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
public var didChange: AnyPublisher<ObservedChange, Never> {
_didChange.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
public init(wrappedValue: Value) {
__wrappedValue = .init(initialValue: wrappedValue)
}
public mutating func update() {
__wrappedValue.update()
}
public var projectedValue: Binding<Value> {
.init(get: { self.wrappedValue }, set: { self.wrappedValue = $0 })
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedState private var number: Int = 0
var body: some View {
Button("Increment") {
self.number += 1
}
.onReceive(_number.didChange) { value in
print(value.oldValue, value.newValue)
}
}
}
Bindingを別の型のBindingに変換する
public extension Binding {
func map<T>(get: @escaping (Value) -> T, set: @escaping (T) -> Value) -> Binding<T> {
.init(get: { get(self.wrappedValue) },
set: { self.wrappedValue = set($0) })
}
}
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var number: Int = 0
var body: some View {
VStack {
Button("Increment") {
self.number += 1
}
TextField("Number", text: $number.map(get: { "\($0)" }, set: { Int($0) ?? 0 }))
}
}
}
汎用的で便利なものができ次第追記していきます ![]()