アルゴリズム
- k近傍法
- k-means
k近傍法
k近傍法は機械学習アルゴリズムの一つであり、分類問題を解くための教師あり学習である。
訓練データ生成
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
def gen_data():
x0 = np.random.normal(size=50).reshape(-1, 2) - 1
x1 = np.random.normal(size=50).reshape(-1, 2) + 1.
x_train = np.concatenate([x0, x1])
y_train = np.concatenate([np.zeros(25), np.ones(25)]).astype(np.int)
return x_train, y_train
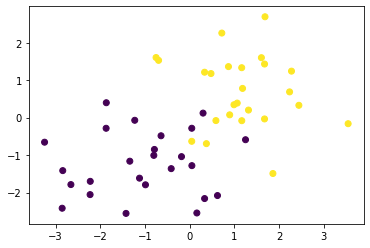
X_train, ys_train = gen_data()
plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=ys_train)
予測
予測するデータ店との距離が最も近いk個の訓練データのラベルの最頻値を割り当てる。
ここでkを変化させると結果も変わる。
def distance(x1, x2):
return np.sum((x1 - x2)**2, axis=1)
def knc_predict(n_neighbors, x_train, y_train, X_test):
y_pred = np.empty(len(X_test), dtype=y_train.dtype)
for i, x in enumerate(X_test):
distances = distance(x, X_train)
nearest_index = distances.argsort()[:n_neighbors]
mode, _ = stats.mode(y_train[nearest_index])
y_pred[i] = mode
return y_pred
def plt_resut(x_train, y_train, y_pred):
xx0, xx1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 100), np.linspace(-5, 5, 100))
xx = np.array([xx0, xx1]).reshape(2, -1).T
plt.scatter(x_train[:, 0], x_train[:, 1], c=y_train)
plt.contourf(xx0, xx1, y_pred.reshape(100, 100).astype(dtype=np.float), alpha=0.2, levels=np.linspace(0, 1, 3))
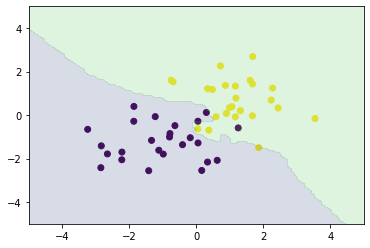
n_neighbors = 3
xx0, xx1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 100), np.linspace(-5, 5, 100))
X_test = np.array([xx0, xx1]).reshape(2, -1).T
y_pred = knc_predict(n_neighbors, X_train, ys_train, X_test)
plt_resut(X_train, ys_train, y_pred)
numpyで実装する場合
xx0, xx1 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 100), np.linspace(-5, 5, 100))
xx = np.array([xx0, xx1]).reshape(2, -1).T
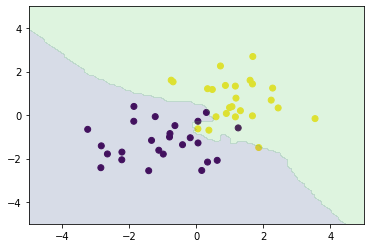
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knc = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=n_neighbors).fit(X_train, ys_train)
plt_resut(X_train, ys_train, knc.predict(xx))
k-means
k-meansは、クラスタリングアルゴリズムの一つであり、与えられたデータをk個のクラスタに分類するための教師なし学習である。
クラスタリングとは、特徴の似ているもの同士をグループ化することである。
手順
①各クラスタ中心の初期値を設定する
②各データ点に対して、各クラスタ中心との距離を計算し、最も距離が近いクラスタを割り当てる
③各クラスタの平均ベクトルを計算する
④収束するまで②、③の処理を繰り返す