Problem
この問題では、Stoneの重さのリストが与えられます。各ターンで最も重い2つの石を選び、それらを互いに衝突させます。2つの石の重さがxとy(x <= y)であるとすると、衝突後の結果は次のようになります:
- xとyが等しい場合、両方の石が破壊されます。
- xとyが等しくない場合、重さxの石が破壊され、重さyの石は新たに重さy - xとなります。
ゲームの終わりには、最大1つの石が残ります。この最後に残った石の重さを返すように求められています。もし石が残らない場合は0を返します。
InputとOutputの例は次になります。
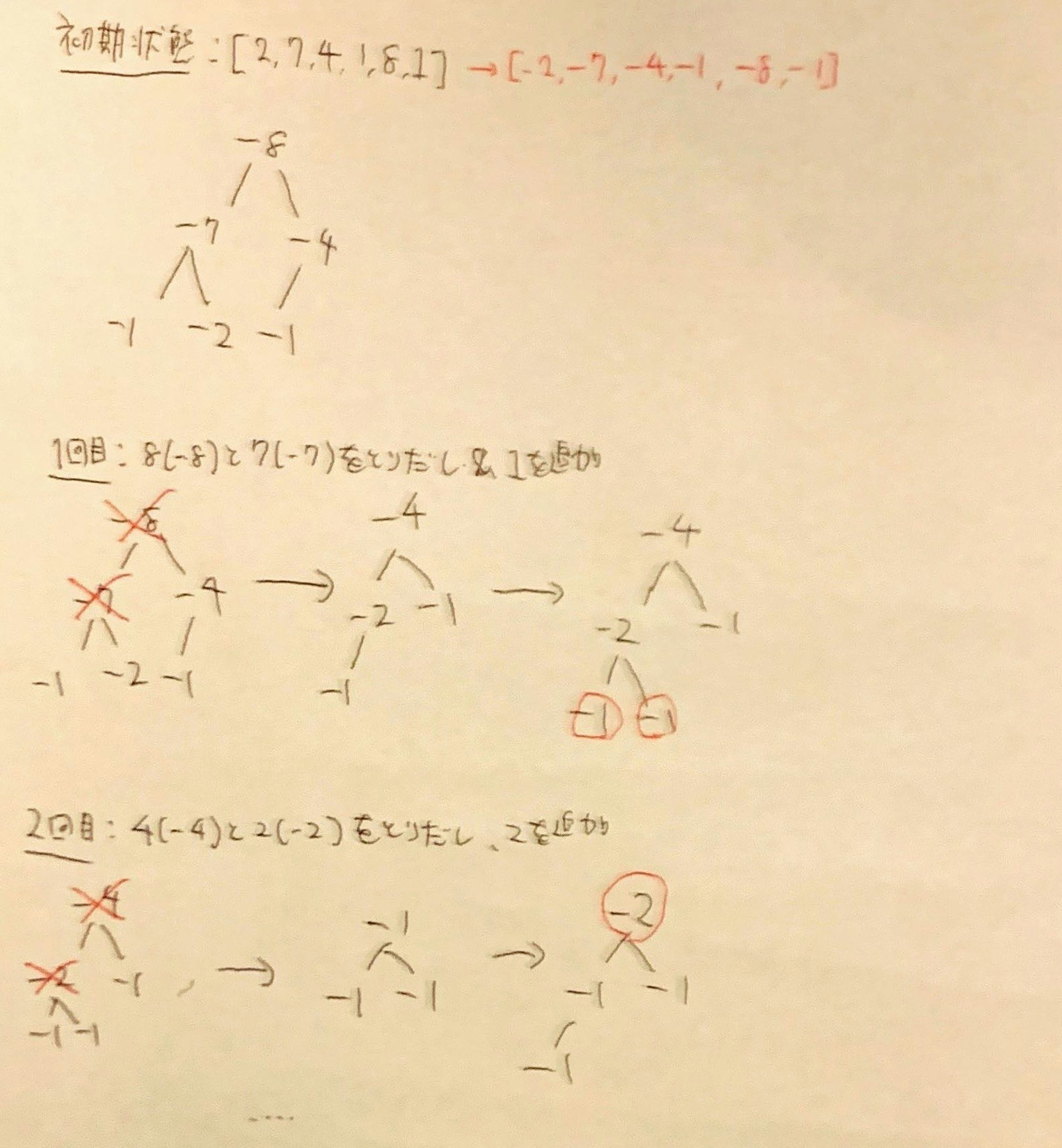
Input: stones = [2,7,4,1,8,1]
Output: 1
Explanation:
We combine 7 and 8 to get 1 so the array converts to [2,4,1,1,1] then,
we combine 2 and 4 to get 2 so the array converts to [2,1,1,1] then,
we combine 2 and 1 to get 1 so the array converts to [1,1,1] then,
we combine 1 and 1 to get 0 so the array converts to [1] then that's the value of the last stone.
Key Idea
直感的に考えると、問題の指示どおりに、毎回最も重い2つの石を探し、それらを削除もしくはその差となる数字を追加する作業を繰り返すことで問題を解くこと自体は可能です。しかし、この方法は効率が非常に悪いという欠点があります。(Time complexity : O(N^2))
最大ヒープ(最大値が常にトップにあるヒープ)を使うと、最も重い2つの石を効率的に取り出すことができます。ヒープから最大値を取り出す操作(heap pop)はO(log n)のTime complexityで、新たな石をヒープに追加する操作(heap push)もO(log n)のTime complexityですみます。
Implementation
最大ヒープを用いた実装は、下記のようになります。Pythonのheapqモジュールは、デフォルトでは最小ヒープしか提供していません。したがって、最大ヒープを作成するには、値をネガティブにして扱う必要があります。
アルゴリズムは次の通りです:
- すべての石を最大ヒープに追加します。
- ヒープに2つ以上の石がある限り、最も重い2つの石を取り出し、その差をヒープに戻します(差が0でない場合)。
- 最後に残った石の重さを返します。石がなければ0を返します。
import heapq
def lastStoneWeight(stones):
# Pythonのheapqは最小ヒープなので、全ての要素を負にして最大ヒープを作成
stones = [-stone for stone in stones]
heapq.heapify(stones)
while len(stones) > 1:
# 最も重い2つの石を取り出す
stone1 = heapq.heappop(stones)
stone2 = heapq.heappop(stones)
# 2つの石が同じ重さでなければ、その差をヒープに追加
if stone1 != stone2:
heapq.heappush(stones, stone1 - stone2)
# ヒープが空でなければ、最後に残った石の重さを返す(値は負になっているので符号を反転)
# ヒープが空なら0を返す
return -stones[0] if stones else 0
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity: O(N log N)
- 最初にヒープを構築するには O(N)
- 最悪の場合 N - 1回の石を衝突を繰り返す可能性があります。また、それぞれの衝突で、2回 Pop (O(log N)) と1回のPush (O (log N))が必要です。
- つまり、O(N) + (N-1) x 3 x(O (log N) で、すなわち O(N log N) となります。
- Space complexity: O(N)。
- ヒープに格納されるすべての石は元の配列から来ており、その数はn個なので、Space complexityはO(n)となります。
- Pythonでは、リストからヒープへの変換はインプレースで行われるため、O(1)しか必要としません。
Reference