Abstract
pickleで保存したバイナリファイルやPytorchのパラメータの情報を保存したバイナリファイルは、通常はVSCodeから中身を確認できません。
vscode-pydata-viewer はそんなお悩みを解決する拡張機能です。
 図: 拡張機能を導入したことで保存したpickleファイルを確認している様子
図: 拡張機能を導入したことで保存したpickleファイルを確認している様子
とりあえずインストールするだけで十分に役に立つでしょう。
本記事では、この vscode-pydata-viewer を紹介して、表示をカスタマイズする方法まで紹介します。
環境
- Python 3.10.4
- Windows 10
機能紹介
Display Python data files in VSCode.
Numpy Files: .npz .npy
Pickle Files: .pkl .pck .pickle
Torch Files: .pth .pt .ckpt
つまり: Pythonで主に扱うバイナリファイルを閲覧することができる拡張機能
例えば、次のようなコードでpickleファイルを保存してみます。(冒頭の図のコードです。)
import pickle
import numpy as np
obj = {
'str': 'Hello, World',
'int': 12,
'float': 0.125,
'list': [
1, 2, 3, 4, 5
],
'tuple': (0, 1, 2, 3),
'ndarray': np.arange(10)
}
with open('./data/test.pickle', mode = 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(obj, f)
その後、生成された test.pickle は拡張機能を入れていないと閲覧できませんが、拡張機能を導入すると...
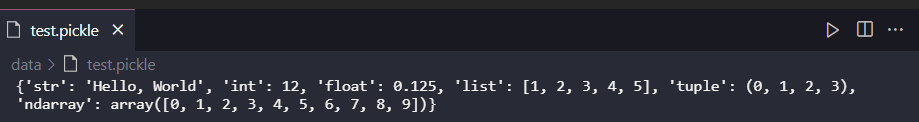
図: test.pickle を閲覧している様子
なるほどなるほど~~~!!
python.exeのパスを通しておく必要があります。
特定のPythonインタープレターを指定したい場合は、設定からvscode-pydata-viewer.pythonPathで指定をしてください。
{
// 絶対パスで指定しなさいって公式には書かれている。
"vscode-pydata-viewer.pythonPath": "C:/path/to/python.exe"
}
How to work?
裏側でPythonファイルを動かしています。ファイルを実行して得られた標準出力を表示しているようです。
なのでnumpyを含むpickleファイルはnumpyがインストールされていないと動かないし、当然PyTorchのファイルもそうでしょう。
動かしているPythonファイルの本体は C:\Users\TakeMe\.vscode\extensions\percy.vscode-pydata-viewer-x.x.x\pyscripts\read_files.py (Windowsの場合のパス)です。
拡張機能側から、読み込むファイルの種類とパスを引数で渡しているようです。
改造
デフォルトだとネストされたオブジェクトの表示が正直微妙です。
やっぱりpythonistaならpprintは使いたいですよね。
動かしているpythonファイルのC:\Users\TakeMe\.vscode\extensions\percy.vscode-pydata-viewer-x.x.x\pyscripts\read_files.pyを直接変更しても良いですが、拡張機能が更新されるたびに上書きされるので、外部ファイルを指定できる設定 vscode-pydata-viewer.scriptPath を利用します。
適当な場所に read_files.py をコピーしてください。そしてその絶対パスを次のように設定します。
{
"vscode-pydata-viewer.scriptPath": "path/to/read_file.py"
}
pprintを利用する
今回はpickleファイルの表示を変更してみます。
先ほどコピーしてきたファイルを開いて下さい。
69行目 (v0.0.10現在) からがpickleファイルの読み込みをしている部分です。
というわけで、from pprint import pprintを加えてprintを置換しましょう。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
sys.argv[1]: `.npy` or `.npz` file path
"""
import sys
file_type = int(sys.argv[1])
file_path = sys.argv[2]
from enum import Enum
class FileType(Enum):
NUMPY = 0
PICKLE = 1
PYTORCH = 2
+ from pprint import pprint
# ... (省略)
elif file_type == FileType.PICKLE.value:
# Solve pickle files .pkl
try:
import pickle
with open(file_path, "rb") as f:
content = pickle.load(f)
- print(content)
+ pprint(content)
except UnicodeDecodeError:
with open(file_path, "rb") as f:
content = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin1")
print(content)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
これでpickleファイルの表示がpprintに従った形になります。
pprintのフォーマットを設定してから利用する
これは拡張機能というより、pprint自体のお話になりますが、pprintはクッソ長いリストとかを省略してくれないんですね。
そこで下記のstackoverflowを参考にして、いい感じに省略してくれるようにします。
その他、pprintの設定は公式ドキュメントを参照してください。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
sys.argv[1]: `.npy` or `.npz` file path
"""
import sys
# the file type corresopmnding to the `FileType` below.
file_type = int(sys.argv[1])
# the file path to load
file_path = sys.argv[2]
from enum import Enum
class FileType(Enum):
NUMPY = 0
PICKLE = 1
PYTORCH = 2
- from pprint import pprint
+ from pprint import PrettyPrinter
# 下記のクラスを追加
class CroppingPrettyPrinter(PrettyPrinter):
"""pprint with limiting the length of lists.
ref: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38533282/python-pretty-print-dictionary-of-lists-abbreviate-long-lists
"""
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.maxlist = kwargs.pop('maxlist', 6)
PrettyPrinter.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs)
# override the internal format method
def _format(self, obj, stream, indent, allowance, context, level):
if isinstance(obj, list):
if len(obj) > self.maxlist:
cropped_obj = obj[:self.maxlist - 1]
cropped_obj.extend(['...', obj[-1]])
return PrettyPrinter._format(self, cropped_obj, stream, indent, allowance, context, level)
return PrettyPrinter._format(self, obj, stream, indent, allowance, context, level)
# you can change `width` freely. defaults to `80`, but it's too short for my monitor.
+ printer_options = {"maxlist": 3, "width": 100}
# if `sort_dicts = True`, the dictionary object will be sorted. Added since 3.8.
+ if sys.version_info > (3, 8): printer_options["sort_dicts"] = False
+ printer = CroppingPrettyPrinter(**printer_options)
+ def pprint(obj):
+ printer.pprint(obj)
# ... (省略)
設定の値は個人で調整したり変更してりしてみてください。
上記の設定だと、冒頭のデータは次の図のようになります。
なお、自作のクラスなど(ビルトインではないclass)は__repr__を実装していないと、まともに表示されません。
まとめ
本記事では、Pythonで扱うバイナリファイルをVSCode上で確認できる拡張機能、vscode-pydata-viewerを紹介しました。
加えて、表示をカスタマイズすることが可能なので、pprintを利用するサンプルを紹介しました。
皆様も是非ともインストールしてみてください。
それではよきPython生活を~~~
