TypeScriptとお友達になりたくて・・・
はじめに
Robots1 をTypeScript で実装してみた(でも、CUI)
Robots について
- robots - Wikipediaの説明を拝借すると下記の通り。
robots(ロボッツ)は、ターン制のコンピュータゲームである。プレイヤーキャラクターを追いかけて殺すようにプログラムされたロボットから逃げ、ロボット同士や障害物と衝突させて破壊するのが目的である。
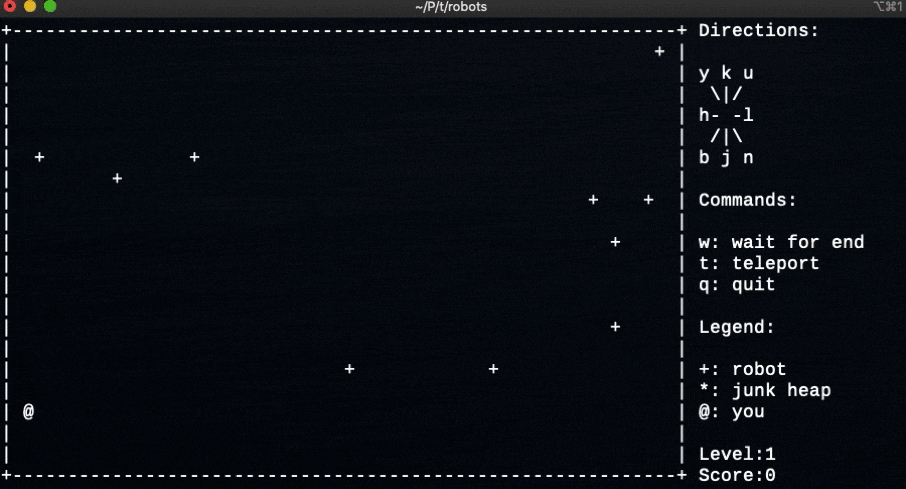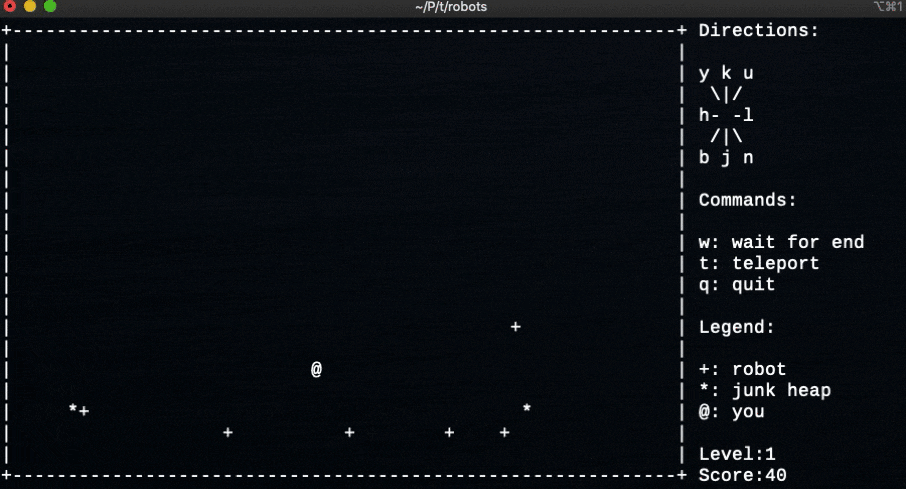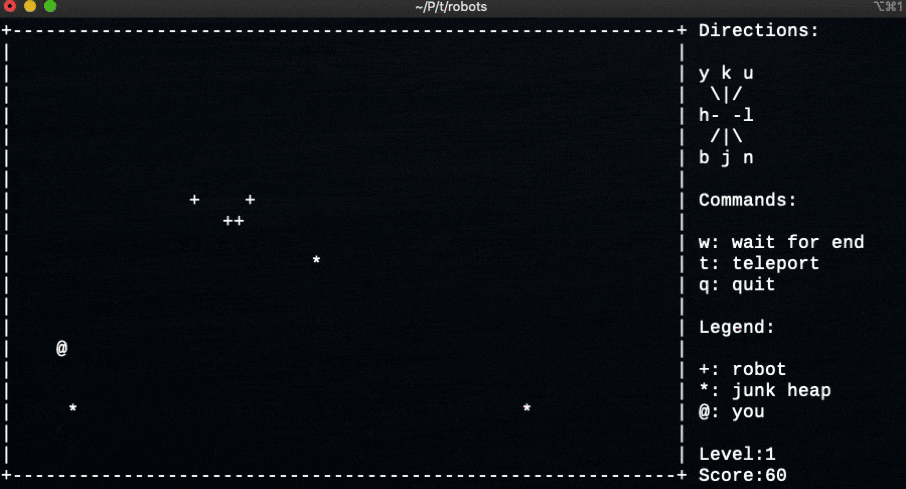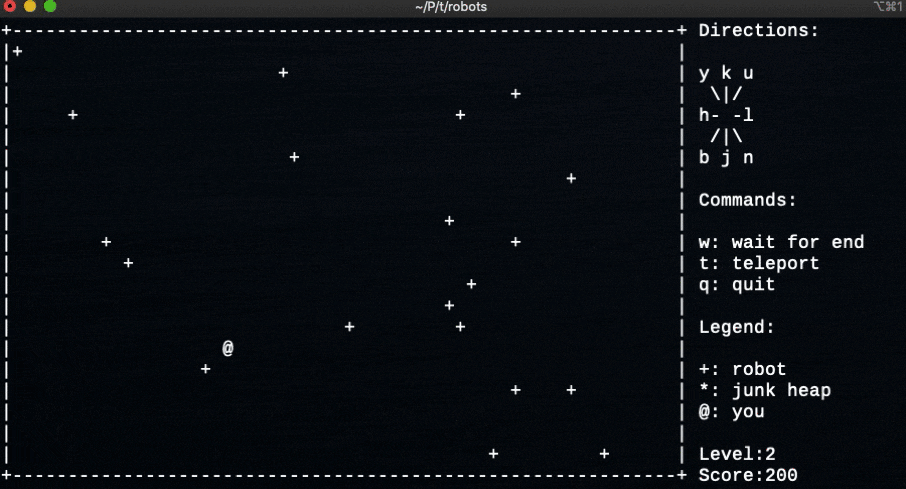
- 百聞は一見にしかずということで、ゲームをプレイしている様子
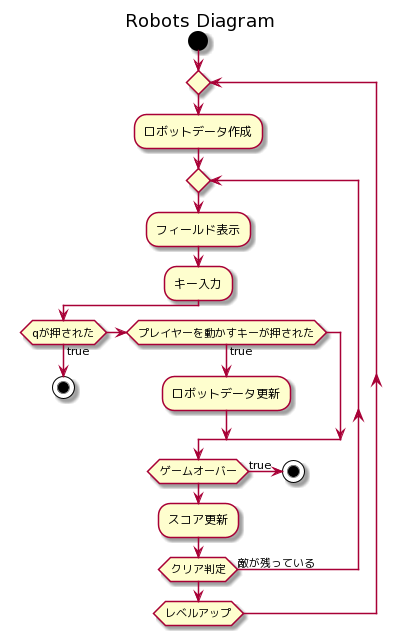
フローチャート
ざっくりこんな感じ (実際のコードとは微妙に違うかも)
処理
ロボットデータ作成
- フィールド上にはプレイヤー一体、敵(レベル×10体)、敵同士が衝突して発生するスクラップの3種類が存在し、フィールド上のロボットの状態を示す列挙体を定義
- フィールド上の全てのロボットをロボットの配列で表現し、InterfaceRobotで定義
- ロボットの座標は乱数で決め、初期配置ではすでにロボットが配置されている場所には配置しない
// ロボットの種類(プレイヤー、敵、スクラップ)
enum type {
Player,
Enemy,
Scrap
}
// ロボットのインタフェース
interface InterfaceRobot {
// x座標
x: number
// y座標
y: number
// ロボットの種類
type: type
}
// プレイヤーロボット、敵ロボットの初期配置
function make_robots(robots: InterfaceRobot[], width: number, height: number, level: number) {
let x = Math.floor((Math.random() * width) + 1)
let y = Math.floor((Math.random() * height) + 1)
robots.push({ x, y, type: type.Player })
const numOfEnemy = level * 10
let count = 0
while (count < numOfEnemy) {
x = Math.floor((Math.random() * width) + 1)
y = Math.floor((Math.random() * height) + 1)
if (!check_put_robots(robots, x, y)) {
// 同じ場所にロボットを置かない
continue
}
robots.push({ x, y, type: type.Enemy })
count++
}
}
フィールド表示
- 幅60[px], 高さ20[px]のフィールドを作成 (print_field)
- フィールド内にロボット配列の内容に応じて、プレイヤー、敵を配置 (put_robots)
- フィールドの右に操作方法、レベル、スコアを表示 (print_guide)
// フィールドの表示
function print_field(width: number, height: number) {
// tslint:disable-next-line: no-console
console.clear()
// top of field
process.stdout.write("+")
for (let i = 0; i < width; i++) {
process.stdout.write("-")
}
process.stdout.write("+\n")
// inside of field
for (let j = 0; j < height; j++) {
process.stdout.write("|")
for (let i = 0; i < width; i++) {
process.stdout.write(" ")
}
process.stdout.write("|\n")
}
// bottom of field
process.stdout.write("+")
for (let i = 0; i < width; i++) {
process.stdout.write("-")
}
process.stdout.write("+")
}
// ロボットのタイプに応じて表示方法を変える
function put_robots(robots: InterfaceRobot[]) {
for (const item of robots) {
process.stdout.cursorTo(item.x, item.y)
if (item.type === type.Player) {
// put player robot
process.stdout.write('@')
} else if (item.type === type.Enemy) {
// put enemy robots
process.stdout.write('+')
} else if (item.type === type.Scrap) {
// put scrap
process.stdout.write('*')
} else {
;
}
}
}
// 右端のゲームのガイドを表示
function print_guide(width: number, level: number, score: number) {
// tslint:disable-next-line: variable-name
const cursor_x = width + 3
// tslint:disable-next-line: variable-name
let cursor_y = 0
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y)
process.stdout.write("\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
cursor_y++
process.stdout.write("Directions:\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("y k u\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write(" \\|/\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("h- -l\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write(" /|\\ \n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("b j n\n\n")
cursor_y++
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("Commands:\n\n")
cursor_y++
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("w: wait for end\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("t: teleport\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("q: quit\n\n")
cursor_y++
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("Legend:\n\n")
cursor_y++
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("+: robot\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("*: junk heap\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("@: you\n\n")
cursor_y++
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("Level:" + level + "\n\n")
process.stdout.cursorTo(cursor_x, cursor_y++)
process.stdout.write("Score:" + score + "\n\n")
}
キー入力
- TypeScriptでキー入力のやり方がよく分からず、実はここが一番時間がかかってしまった(Node.js/JavaScriptなど周辺の事情が全くわからないまま、見様見真似で実装・・・)
通常移動
下記のキーが入力されたとき、プレイヤーを一コマ動かす
- y:左上
- k:上
- u:右上
- h:左
- l:右
- b:左下
- j:下
- n:右下
- w:待機 (wキーが押されたときは待機し、敵ロボットだけが動く)
テレポート
- tキーが押されたときはランダムでフィールドのどこかにプレイヤーを移動(テレポート)させる
- 運が悪いと敵の隣にテレポートして即死します
// keypressライブラリを読み込む
const keypress = require('keypress')
// keypressを標準入力に設定
// make `process.stdin` begin emitting "keypress" events
keypress(process.stdin)
// keypressイベントの購読を開始
// listen for the "keypress" event
process.stdin.on('keypress', (ch: any, key: any) => {
let inputCheck = true
let x = robots[0].x
let y = robots[0].y
// 入力情報を取得
switch (ch) {
case 'y':
// 左上に1マス移動, スクラップの上には移動できない
if (x - 1 <= 0 || y - 1 <= 0 || !check_scrap(robots, x - 1, y - 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break;
}
robots[0].x--
case 'k':
// 上に1マス移動
if (y - 1 <= 0 || !check_scrap(robots, robots[0].x, y - 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break;
}
robots[0].y--
break
case 'u':
// 右上に1マス移動
if (x + 1 >= width + 1 || y - 1 <= 0 || !check_scrap(robots, x + 1, y - 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].y--
case 'l':
// 右に1マス移動
if (x + 1 >= width + 1 || !check_scrap(robots, x + 1, robots[0].y)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].x++
break
case 'n':
// 右下に1マス移動
if (x + 1 >= width + 1 || y + 1 >= height + 1 || !check_scrap(robots, x + 1, y + 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].x++
case 'j':
// 下に1マス移動
if (y + 1 >= height + 1 || !check_scrap(robots, robots[0].x, y + 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].y++
break
case 'b':
// 左下に1マス移動
if (x - 1 <= 0 || y + 1 >= height + 1 || !check_scrap(robots, x - 1, y + 1)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].y++
case 'h':
// 左に1マス移動
if (x - 1 <= 0 || !check_scrap(robots, x - 1, robots[0].y)) {
inputCheck = false
break
}
robots[0].x--
break
case 't':
// スクラップ以外にテレポート. 運が悪いと敵の隣にテレポートで即死.
do {
x = Math.floor((Math.random() * width) + 1)
y = Math.floor((Math.random() * height) + 1)
} while (!check_scrap(robots, x, y))
robots[0].x = x
robots[0].y = y
break
case 'w':
// 待機
break
case 'q':
// 終了
inputCheck = false
process.stdin.pause()
break
default:
inputCheck = false
}
// プレイヤーロボットを動かせたとき
// ・・・略
})
ロボットデータ更新/ゲームオーバー
- プレイヤーを動かした位置をもとに敵を動かす(プレイヤーの向かうように敵を動かす)
- 敵同士がぶつかればスクラップ化
- プレイヤーと敵同士が衝突したらゲームオーバー
// 敵ロボットの移動、スクラップ確認、プレイヤーロボットと敵ロボット座標が一致したときゲームオーバー
function move_robots(robots: InterfaceRobot[]): boolean {
for (const item of robots) {
if (item.type === type.Player || item.type === type.Scrap) {
continue
}
// プレイヤーの位置に向かうように敵を一マス動かす
if (robots[0].x === item.x && robots[0].y > item.y) {
item.y++
} else if (robots[0].x === item.x && robots[0].y < item.y) {
item.y--
} else if (robots[0].x > item.x && robots[0].y === item.y) {
item.x++
} else if (robots[0].x < item.x && robots[0].y === item.y) {
item.x--
} else if (robots[0].x < item.x && robots[0].y < item.y) {
item.x--
item.y--
} else if (robots[0].x < item.x && robots[0].y > item.y) {
item.x--
item.y++
} else if (robots[0].x > item.x && robots[0].y < item.y) {
item.x++
item.y--
} else if (robots[0].x > item.x && robots[0].y > item.y) {
item.x++
item.y++
}
}
// 敵同士が衝突したらスクラップにする
const length = robots.length
for (let i = 1; i < length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
if ((robots[i].x === robots[j].x) && (robots[i].y === robots[j].y)) {
robots[i].type = type.Scrap
robots[j].type = type.Scrap
}
}
}
// プレイヤーと敵が衝突したらゲームオーバー
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if ((robots[0].x === robots[i].x && robots[0].y === robots[i].y)) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
スコア更新
- 敵をスクラップにしたらスコア加算
- 敵一体につき+10pt
// スコアの計算 (スクラップ1体あたり10点)
function calc_score(robots: InterfaceRobot[]): number {
const length = robots.length
let count = 0
for (let i = 1; i < length; i++) {
if (robots[i].type === type.Scrap) {
count++
}
}
return count * 10
}
クリア判定
- 全てのロボットを動かしたあとで、Enemyが0になっていればクリア
// 敵ロボットがいない場合クリア
function check_clear(robots: InterfaceRobot[]): boolean {
for (let i = 1; i < robots.length; i++) {
if (robots[i].type === type.Enemy) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
レベルアップ
- レベルを一つ上げて、ボーナスポイントをスコアに加算
- フローチャートの最初のロボットデータ作成に移り、新しいレベルのロボットデータを作成する
・・・(略)
// プレイヤー、敵、スクラップ表示
print_field(width, height)
put_robots(robots)
score = calc_score(robots)
print_guide(width, level, sum_score + score)
if (check_clear(robots)) {
// クリア判定
// レベルx100のボーナスポイント
sum_score += (score + level * 100)
// レベルアップステージ作成及び表示
robots = []
make_robots(robots, width, height, ++level)
print_field(width, height)
put_robots(robots)
print_guide(width, level, sum_score)
}
・・・(略)
ソースコード
動作確認環境
- OS: macOS Catalina Version 10.15.7
- Node.js : v12.19.0
動作方法
- ソースコードをクローンもしくはダウンロード
- ts-robots-cui/フォルダへ移動し、
npm initで初期化 -
npm install --save-dev typescript tslint @types/nodeで TypeScript をコンパイルする環境構築 -
./node_modules/.bin/tscでコンパイル -
node ./dist/index.jsで実行
実行画面
おわりに
- TypeScriptでRobotsゲームのロジック部分ができたので、フロントエンドと組み合わせればブラウザ上でRobotsが動く・・・と思う
- 正直、TypeScriptの恩恵にあずかった書き方ではないような・・・そもそもアルゴリズムのセンスが微妙(もっとスマートに書けると思う)
- 少しはTypeScriptとお近づきになったと思いたい
参考資料
- keypress - npm
- O'Reilly Japan - プログラミングTypeScript
- Node.js + webpack+ TypeScript 超ざっくりブラウザゲーム制作入門 | 作っちゃうおじさん制作記録
-
余談ですが、高専在籍時に C++ で Robots を実装する課題があって、これがきっかけで Robots を知りました ↩