ちょっと自分用のメモです。
こんな感じのコード。2つ並行で動かして片方がエラーの時にもう片方も止まる。
class Action() : CoroutineScope {
val job = Job()
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext get() = Dispatchers.Default + job
fun zipLoadError() {
launch(coroutineContext) {
println("before")
val result1Deferred = async {
println("async1 before")
val s = fetchString()
println("async1 after")
s
}
val result2Deferred = async {
println("async2 before")
fetchStringWithException()
println("async2 after")
}
println("after1 ${result1Deferred.await()}")
println("after2 ${result2Deferred.await()}")
}
}
private suspend fun fetchString(): String = suspendCancellableCoroutine {
thread {
Thread.sleep(10000)
it.resume("result1")
}
}
private suspend fun fetchStringWithException(): String = suspendCancellableCoroutine {
thread {
it.resumeWithException(RuntimeException())
}
}
出力結果はこうなる。片方が死ぬのでもう片方も止まる。
***two async error
before
async1 before
async2 before
Exception in thread "DefaultDispatcher-worker-2 @coroutine#2" java.lang.RuntimeException
at exception.Action$fetchStringWithException$2$1.invoke(Exception.kt:156)
at exception.Action$fetchStringWithException$2$1.invoke(Exception.kt:23)
at kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1.run(Thread.kt:30)
内部的になぜこうなるのかを知りたかったです。
コードを読んでいると、Coroutineの状態( JobSupport#_state)としてエラーなどを伝える先を保持しており、エラーが起きた時にその先に知らせることで、伝搬していることがわかりました。
内部のCoroutineの状態の変化をデバッグで出力してみます。
■で始まる行が変更されるCoroutineで、->の前が変更前の状態、->の後が変更後の状態になる。
Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:60380', transport: 'socket'
■ JobImpl{Active}@5700d6b1
Empty{Active}
->
ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Active}@1e397ed7]
before
■ "coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Active}@1e397ed7:
Empty{Active}
->
ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac]
async1 before
■"coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Active}@1e397ed7:
ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac]
->
List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac]]
■"coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac:
Empty{Active}
->
ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result1Deferred$1@4f56af49]){Active}@6f8a0358]
async2 before
■"coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@3c294eef:
Empty{Active}
->
ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result2Deferred$1@4c75664f]){Active}@4364feea]
■ "coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac:
ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result1Deferred$1@4f56af49]){Active}@6f8a0358]
->
List{Active}[ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result1Deferred$1@4f56af49]){Active}@6f8a0358]]
■ "coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@3c294eef:
ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result2Deferred$1@4c75664f]){CompletedExceptionally}@4364feea]
->
Empty{Active}
■ "coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@3c294eef:
Empty{Active}
->
Finishing[cancelling=false, completing=true, rootCause=null, exceptions=null, list=List{Active}[]]
■ "coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Active}@1e397ed7:
List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac], ChildHandle["coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Cancelling}@3c294eef], ChildContinuation[AwaitContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.DeferredCoroutine$await$1@4685392e]){Active}@243e0d69]]
->
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=false, rootCause=java.lang.RuntimeException, exceptions=null, list=List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac], ChildHandle["coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Cancelling}@3c294eef], ChildContinuation[AwaitContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.DeferredCoroutine$await$1@4685392e]){Active}@243e0d69]]]
■ "coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Active}@343253ac:
List{Active}[ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result1Deferred$1@4f56af49]){Active}@6f8a0358], ResumeAwaitOnCompletion[AwaitContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.DeferredCoroutine$await$1@4685392e]){Active}@243e0d69]]
->
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=false, rootCause=kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.JobCancellationException: Parent job is Cancelling; job="coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7, exceptions=null, list=List{Active}[ChildContinuation[CancellableContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, exception.Action$zipLoadError$1$result1Deferred$1@4f56af49]){Active}@6f8a0358], ResumeAwaitOnCompletion[AwaitContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.DeferredCoroutine$await$1@4685392e]){Active}@243e0d69]]]
■ JobImpl{Active}@5700d6b1:
ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]
->
List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]]
■ JobImpl{Active}@5700d6b1:
List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]]
->
Finishing[cancelling=false, completing=true, rootCause=null, exceptions=null, list=List{Active}[ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]]]
■ "coroutine#3":DeferredCoroutine{Cancelling}@3c294eef:
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=true, rootCause=java.lang.RuntimeException, exceptions=SEALED, list=List{Active}[]]
->
CompletedExceptionally[java.lang.RuntimeException]
■ "coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Cancelling}@343253ac:
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=true, rootCause=kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.JobCancellationException: Parent job is Cancelling; job="coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7, exceptions=SEALED, list=List{Active}[ResumeAwaitOnCompletion[AwaitContinuation(DispatchedContinuation[DefaultDispatcher, kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.DeferredCoroutine$await$1@4685392e]){Cancelled}@243e0d69], ChildCompletion[ChildHandle["coroutine#2":DeferredCoroutine{Cancelling}@343253ac], CompletedExceptionally[kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.JobCancellationException: Parent job is Cancelling; job="coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]]]]
->
CompletedExceptionally[kotlinx.coroutines.experimental.JobCancellationException: Parent job is Cancelling; job="coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7]
Exception in thread "DefaultDispatcher-worker-2 @coroutine#2" java.lang.RuntimeException
at exception.Action$fetchStringWithException$2$1.invoke(Exception.kt:156)
at exception.Action$fetchStringWithException$2$1.invoke(Exception.kt:23)
at kotlin.concurrent.ThreadsKt$thread$thread$1.run(Thread.kt:30)
■ "coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7:
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=true, rootCause=java.lang.RuntimeException, exceptions=SEALED, list=List{Active}[ChildCompletion[ChildHandle["coroutine#1":StandaloneCoroutine{Cancelling}@1e397ed7], CompletedExceptionally[java.lang.RuntimeException]]]]
->
CompletedExceptionally[java.lang.RuntimeException]
■ JobImpl{Cancelling}@5700d6b1:
Finishing[cancelling=true, completing=true, rootCause=java.lang.RuntimeException, exceptions=SEALED, list=List{Active}[]]
->
CompletedExceptionally[java.lang.RuntimeException]
長い ![]()
これを読み解いていきます。
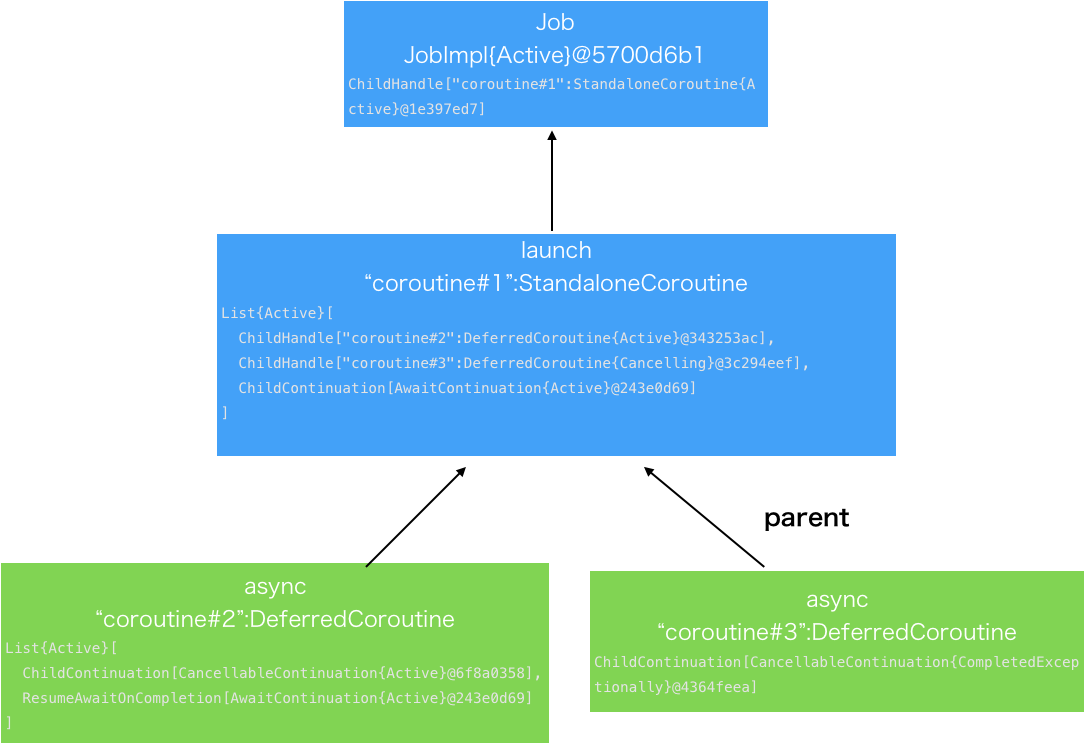
最初の状態
まず最初は全てEmpty{Active}になっている。
これを図にするとこうなる。

このように木が作られる。
コードで言うと以下のようになる。
class Action() : CoroutineScope {
val job = Job() // ← ****ここがJob****
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext get() = Dispatchers.Default + job
fun zipLoadError() {
launch(coroutineContext) { // ← ****ここがcoroutine#1****
println("before")
val result1Deferred = async { // ← ****ここがcoroutine#2****
println("async1 before")
val s = fetchString()
println("async1 after")
s
}
val result2Deferred = async { // ← ****ここがcoroutine#3****
println("async2 before")
fetchStringWithException()
println("async2 after")
}
println("after1 ${result1Deferred.await()}")
println("after2 ${result2Deferred.await()}")
}
}
JobSupport.ktにある図でいうとここになっている。

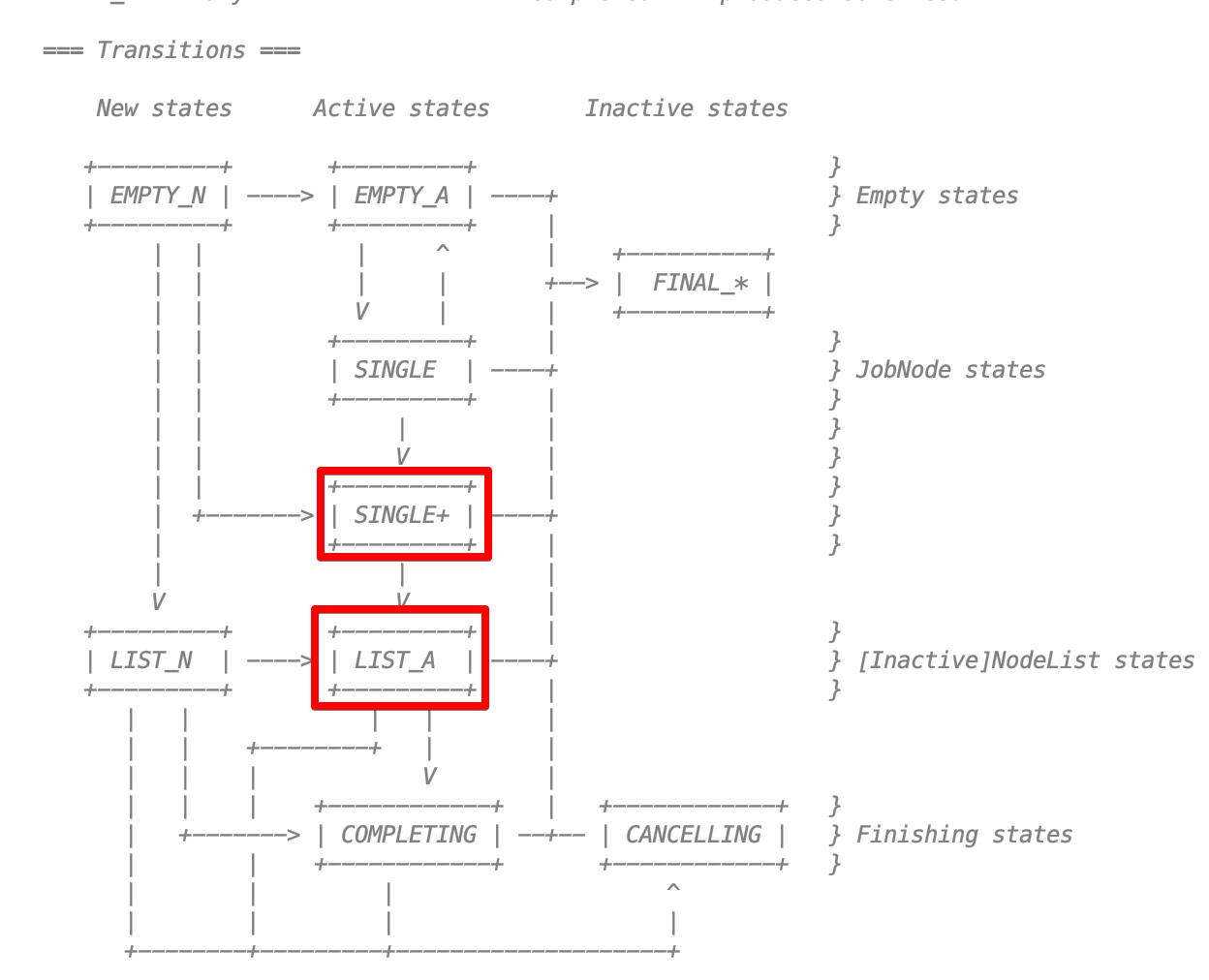
Exceptionが起きる直前
これがasync2 beforeの直前のExceptionが起きる直前はこうなる。
この状態のところに親や子に伝えるリスナーみたいなのが入っている。ChildContinuationが親にExceptionなどを知らせ、ChildHandleが子にExceptionなどを知らせるために使われる。
JobSupport.ktにある図でいうとここになっている。(たぶん)
Exceptionが起きた直後
終了する前にExceptionが起きた直後はまずFinishingになる。
まずcoroutine#3、つまりExceptionが起きるcoroutinesがまずFinishingになり、
その次にcoroutine#1、つまりlaunchがFinishingになる。その次にcoroutine#2がFinishingになる。
その3つが渡るとこうなります。
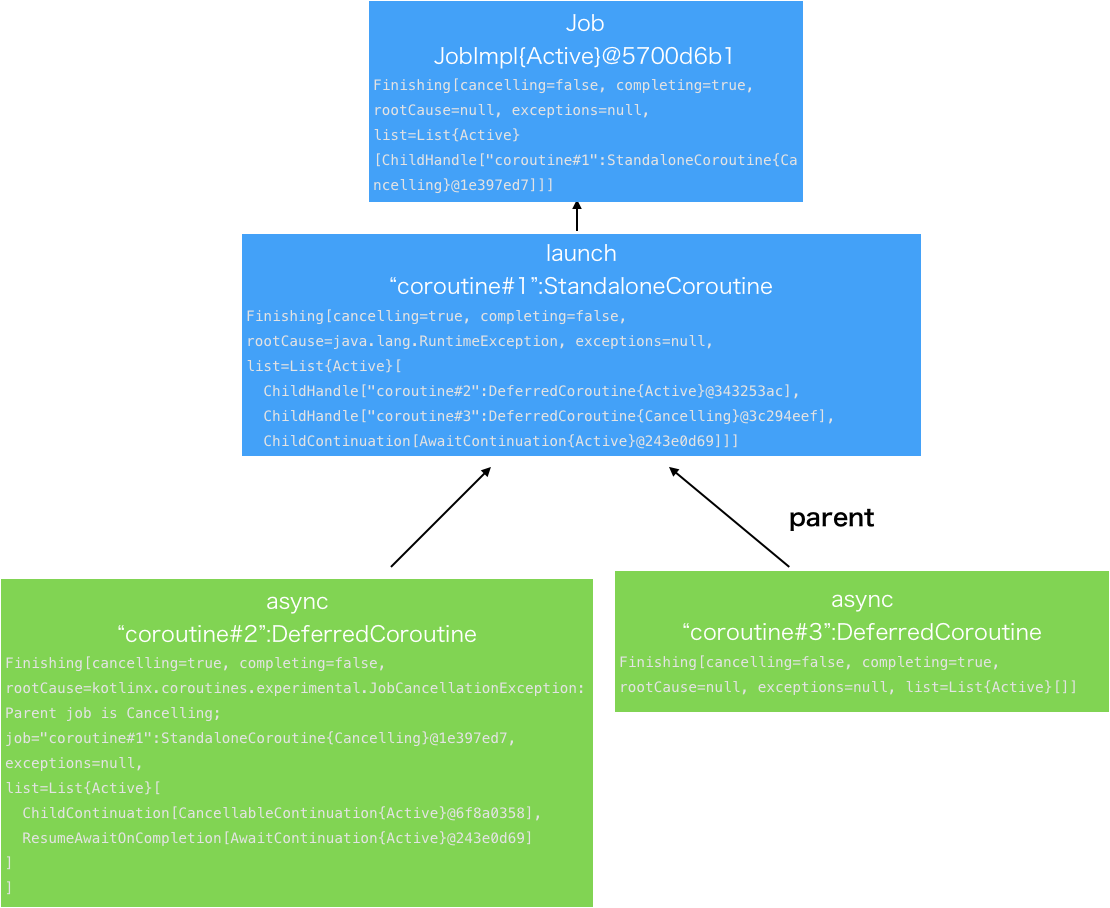
Exceptionが起きた後
Exceptionが起きた後は以下のようにCompletedExceptionally状態になります。
コードリーディング
完全には理解できていないが、DispatchedTaskのここが中断の再開などのタイミングで呼ばれる
public override fun run() {
try {
val delegate = delegate as DispatchedContinuation<T>
val continuation = delegate.continuation
val context = continuation.context
val job = if (resumeMode.isCancellableMode) context[Job] else null
val state = takeState() // NOTE: Must take state in any case, even if cancelled
withCoroutineContext(context) {
if (job != null && !job.isActive)
continuation.resumeWithException(job.getCancellationException())
else {
val exception = getExceptionalResult(state)
if (exception != null)
continuation.resumeWithException(exception)
else
continuation.resume(getSuccessfulResult(state))
}
ここから入っていく
if (exception != null)
continuation.resumeWithException(exception)
thisは渡しているasync()で渡しているFunction。exceptionにはRuntimeExceptionが入っている。
AbstractCoroutine.kt
override fun resumeWithException(exception: Throwable) {
processBareContinuationResume(completion!!) {
doResume(null, exception)
}
}
processBareContinuationResumeはこんなふうになっている。以下で出てくるblockはdoResume(null, exception)を呼んでいるブロック。
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
internal inline fun processBareContinuationResume(completion: Continuation<*>, block: () -> Any?) {
try {
val result = block()
if (result !== COROUTINE_SUSPENDED) {
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
(completion as Continuation<Any?>).resume(result)
}
} catch (t: Throwable) {
completion.resumeWithException(t)
}
}
仕組みはわからないが、おそらくこのdoResume(null, exception)を呼び出すと中断している場所でExceptionが起こる。そしてそれをまた自分でcatchして、async()で渡しているFunctionがもっているメンバ変数のcompletion(実態は"DeferredCoroutine")のresumeWithException()を呼び出す
(this = DeferredCoroutine)
public final override fun resumeWithException(exception: Throwable) {
makeCompletingOnce(CompletedExceptionally(exception), defaultResumeMode)
}
(this = DeferredCoroutine)
internal fun makeCompletingOnce(proposedUpdate: Any?, mode: Int): Boolean = loopOnState { state ->
when (tryMakeCompleting(state, proposedUpdate, mode)) {
COMPLETING_ALREADY_COMPLETING -> throw IllegalStateException("Job $this is already complete or completing, " +
"but is being completed with $proposedUpdate", proposedUpdate.exceptionOrNull)
COMPLETING_COMPLETED -> return true
COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN -> return false
COMPLETING_RETRY -> return@loopOnState
else -> error("unexpected result")
}
}
completeしているかどうかのチェックなどがあり、最終的にtryFinalizeFinishingState()が呼ばれる。
(this = DeferredCoroutine)
private fun tryMakeCompleting(state: Any?, proposedUpdate: Any?, mode: Int): Int {
....
val child = firstChild(state)
if (child != null && tryWaitForChild(finishing, child, proposedUpdate))
return COMPLETING_WAITING_CHILDREN
// otherwise -- we have not children left (all were already cancelled?)
if (tryFinalizeFinishingState(finishing, proposedUpdate, mode)) ←ここにはいっていく
return COMPLETING_COMPLETED
// otherwise retry
return COMPLETING_RETRY
JobSupportのドキュメントに以下のように書いてある。メインの処理は3つあるみたい。
## COMPLETE: state !is Incomplete (CompletedExceptionally | Cancelled)
------ completion listeners are not admitted anymore, invokeOnCompletion returns NonDisposableHandle
+ parentHandle.dispose
+ notifyCompletion (invoke all completion listeners)
+ onCompletionInternal / onCompleted / onCompletedExceptionally
state.list?notifyCompletionを呼び出す。その処理内容はstateが持っているlistに全てinvokeを呼び出す。
(this = DeferredCoroutine)
private fun completeStateFinalization(state: Incomplete, update: Any?, mode: Int, suppressed: Boolean) {
...
state.list?.notifyCompletion(cause)
...
ここで面白いクラスが登場します。親によって使われる、子供のキャンセルを待つクラスです。このinvokeが呼び出されます。そしてこのparentはStandaloneCoroutineです。
// Used by parent that is waiting for child completion
private class ChildCompletion(
private val parent: JobSupport,
private val state: Finishing,
private val child: ChildHandleNode,
private val proposedUpdate: Any?
) : JobNode<Job>(child.childJob) {
override fun invoke(cause: Throwable?) {
parent.continueCompleting(state, child, proposedUpdate)
}
override fun toString(): String =
"ChildCompletion[$child, $proposedUpdate]"
}
StandaloneCoroutineのcontinueCompleting
this=StandaloneCoroutine
private fun continueCompleting(state: Finishing, lastChild: ChildHandleNode, proposedUpdate: Any?) {
require(this.state === state) // consistency check -- it cannot change while we are waiting for children
// figure out if we need to wait for next child
val waitChild = lastChild.nextChild()
// try wait for next child
if (waitChild != null && tryWaitForChild(state, waitChild, proposedUpdate)) return // waiting for next child
// no more children to wait -- try update state
if (tryFinalizeFinishingState(state, proposedUpdate, MODE_ATOMIC_DEFAULT)) return
}
ここでStandaloneCoroutineに対してtryFinalizeFinishingState()がまた呼び出され、最終的に終了状態になるみたいです。こんな感じで伝わっていきます。