Durable Functionsとは?
Azure Durable Functionsは、Azure Functionsの拡張機能であり、状態を持った関数のオーケストレーションを可能にするフレームワークです。長時間実行する処理や複雑なワークフローの管理に便利です。今回はタイムアウトしてしまっていたプロセスをDurable Functionsにして構築しなおして解決しましたので、その後ちょっと調べてまとめています。
本記事では、Durable FunctionsのIsolated Worker Process(.NET 6以降)を基本として解説します。
公式ドキュメントはこちら:
Durable Functions Overview
Durable Functionsを使うケース
Durable Functionsを利用すると、複雑な処理を簡潔に管理できます。代表的なユースケースを以下に紹介します。
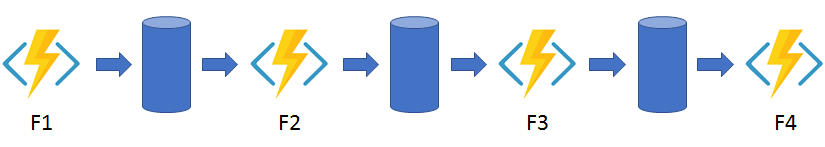
Function Chaining
複数の関数を直列に実行するケース。前の関数の出力を次の関数の入力に利用します。
Example Code (Isolated Mode)
[Function("FunctionChaining")]
public static async Task<List<string>> RunOrchestrator(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
var results = new List<string>();
results.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("Hello", "Step 1"));
results.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("Hello", "Step 2"));
results.Add(await context.CallActivityAsync<string>("Hello", "Step 3"));
return results;
}
[Function("Hello")]
public static string SayHello([ActivityTrigger] string name)
{
return $"Hello, {name}!";
}
Fan Out / Fan In
並列処理が必要な場合に使用します。複数の関数を並列実行し、その結果を統合します。
Example Code
[Function("FanOutFanIn")]
public static async Task<int> RunOrchestrator(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
var tasks = new List<Task<int>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
tasks.Add(context.CallActivityAsync<int>("ProcessData", i));
}
int[] results = await Task.WhenAll(tasks);
return results.Sum();
}
[Function("ProcessData")]
public static int ProcessData([ActivityTrigger] int input)
{
return input * 2;
}
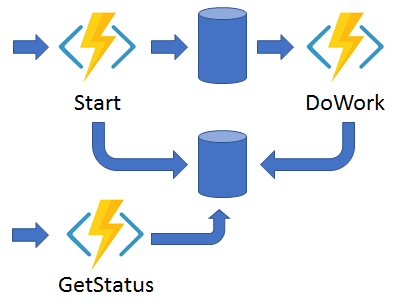
Async HTTP APIs
非同期でHTTP APIを呼び出し、処理完了後に結果を取得するパターン。
Example Code
[Function("HttpStart")]
public static async Task<HttpResponseData> HttpStart(
[HttpTrigger(AuthorizationLevel.Function, "post")] HttpRequestData req,
[DurableClient] DurableTaskClient client)
{
string instanceId = await client.StartNewAsync("AsyncOrchestration", null);
return client.CreateCheckStatusResponse(req, instanceId);
}
Monitor
定期的に特定の状態をチェックする必要があるケース。ポーリングを実装する場合に便利です。
Example Code
[Function("Monitor")]
public static async Task RunOrchestrator(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
while (true)
{
bool isConditionMet = await context.CallActivityAsync<bool>("CheckStatus", null);
if (isConditionMet) break;
await context.CreateTimer(context.CurrentUtcDateTime.AddSeconds(30), CancellationToken.None);
}
}
Human Interaction
ユーザーの入力を待つ必要があるワークフローを作成できます。
Example Code
[Function("WaitForUser")]
public static async Task<string> RunOrchestrator(
[OrchestrationTrigger] TaskOrchestrationContext context)
{
return await context.WaitForExternalEvent<string>("UserResponse");
}
Orchestrator Codeの制限
Orchestrator Functionは決定論的である必要があります。そのため、以下のような制約があります。
-
現在時刻の取得禁止:
DateTime.NowやGuid.NewGuid()は使用不可。 -
HTTPリクエストの実行禁止: 外部API呼び出しは
Activity Functionで行う必要がある。 -
スレッド操作の禁止:
Task.DelayやThread.Sleepの使用は避ける。