pythonの代表的なグラフ描画ツールであるmatplotlibを勉強するついでに、Rの代表的なグラフ描画ツールであるggplotとmatplotlibのコードを比較していこうと思います。備忘録的要素が強いですが、ggplotに慣れている方や、逆にmatplotlibに慣れている方がもう片方を勉強する際の助けになれば幸いです。
データセットの読み込み
今回は、定番であるirisデータセットを使っていきます。
# python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
df=sns.load_dataset("iris")
df.head()
# python
sepal_length sepal_width petal_length petal_width species
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
# R
library(tidyverse)
df <- iris
df %>% head()
# R
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
5 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
6 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 setosa
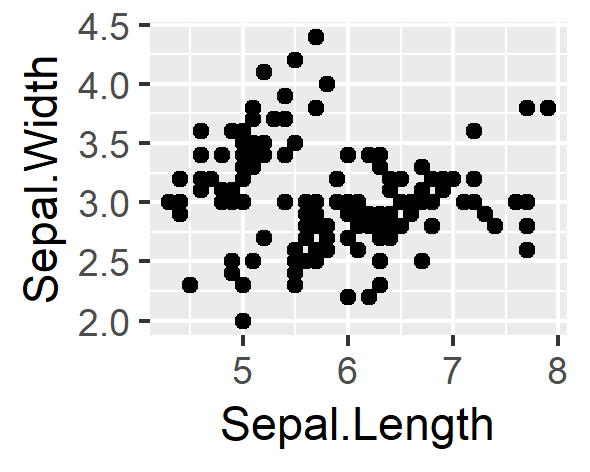
散布図
geom_point()関数 / Axes.scatter()メソッド
# ggplot
ggplot(data = df,aes(x=Sepal.Length,y=Sepal.Width))+
geom_point()
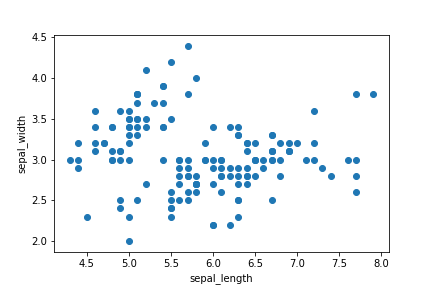
# matplotlib
fig=plt.figure()#pyplot.figureクラスをインスタンス化
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#1行1列のサブプロットを作成し、1番目にaxを配置
ax.scatter(df["sepal_length"],df["sepal_width"])#axに散布図を描画
ax.set_xlabel("sepal_length")#x軸ラベルを指定
ax.set_ylabel("sepal_width")#y軸ラベルを指定
plt.show()
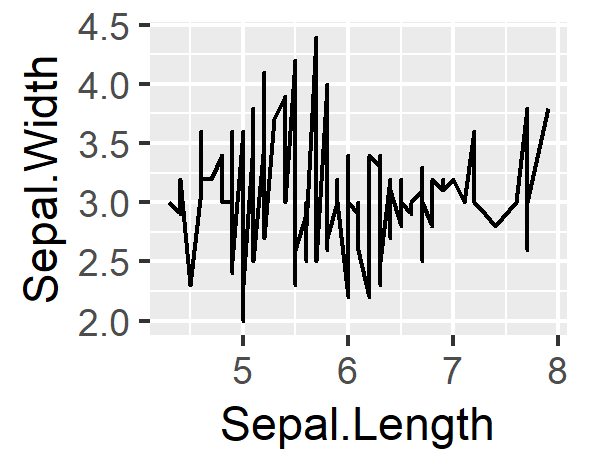
折れ線グラフ
geom_line()関数 / Axes.plot()メソッド
# ggplot
ggplot(data = df,aes(x=Sepal.Length,y=Sepal.Width))+
geom_line()
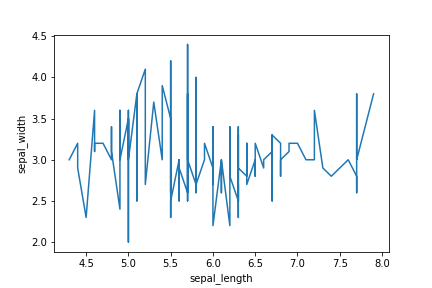
# matplotlib
fig=plt.figure()#pyplot.figureクラスをインスタンス化
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#1行1列のサブプロットを作成し、axを配置
ax.plot(df["sepal_length"],df["sepal_width"])#axに折れ線グラフを描画
ax.set_xlabel("sepal_length")#x軸ラベルを指定
ax.set_ylabel("sepal_width")#y軸ラベルを指定
plt.show()
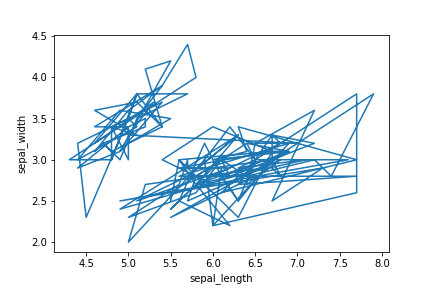
上記のコードでは、データの上の行の点から順番に結んでしまうらしい。そこで、x軸の列であるsepal_lengthをsortしたデータフレームを用意する。
# matplotlib
df1=df.sort_values(by=["sepal_length"])#sepal_lengthによって、dfをsortする
fig=plt.figure()#pyplot.figureクラスをインスタンス化
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#1行1列のサブプロットを作成し、1番目にaxを配置
ax.plot(df1["sepal_length"],df1["sepal_width"])#axに折れ線グラフを描画
ax.set_xlabel("sepal_length")#x軸ラベルを指定
ax.set_ylabel("sepal_width")#y軸ラベルを指定
棒グラフ
geom_bar()関数 / Axes.bar()メソッド
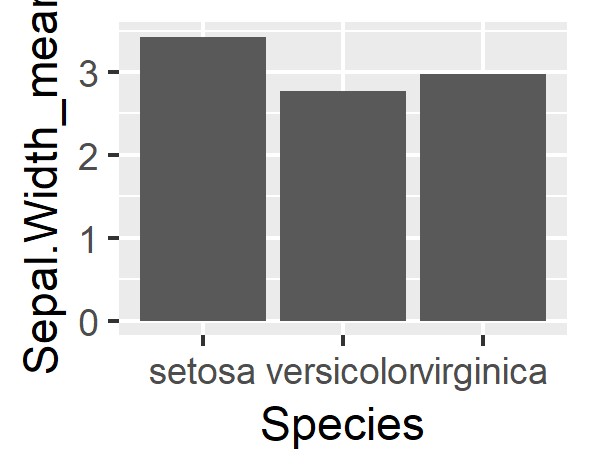
棒グラフを作成するためのデータとして、SpeciesごとのSepal.Widthの平均値をgroup_byにより作成する。
# R
df1 <-
df %>%
group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(Sepal.Width_mean=mean(Sepal.Width))
df1
# R
Species Sepal.Width_mean
<fct> <dbl>
1 setosa 3.43
2 versicolor 2.77
3 virginica 2.97
# python
df2=\ #"\"を書くことで、コードの途中でも改行できる。
df.groupby("species").aggregate({"sepal_width":"mean"})
df2
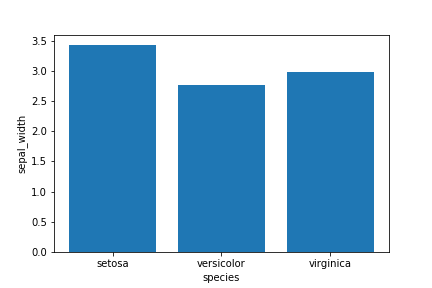
# python
sepal_width
species
setosa 3.428
versicolor 2.770
virginica 2.974
# ggplot
ggplot(data = df1,aes(x=Species,y=Sepal.Width_mean))+
geom_bar(stat = "identity")
# matplotlib
fig=plt.figure()#pyplot.figureクラスをインスタンス化
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#1行1列のサブプロットを作成し、1番目にaxを配置
x=[1,2,3]#x座標を与える
y=[df2.query("species=='setosa'").sepal_width,\
df2.query("species=='versicolor'").sepal_width,\
df2.query("species=='virginica'").sepal_width]#y軸の値を与える
labels=["setosa","versicolor","virginica"]
ax.bar(x,y,tick_label=labels)##axに棒グラフを描画し、x座標をlabelsに置き換える
ax.set_xlabel("species")#x軸ラベルを指定
ax.set_ylabel("sepal_width")#y軸ラベルを指定
plt.show()
随時更新していきます。2018/10/24
[参考文献]
Pythonによるデータ分析入門 第2版 ―NumPy、pandasを使ったデータ処理
Pythonデータサイエンスハンドブック ―Jupyter、NumPy、pandas、Matplotlib、scikit-learnを使ったデータ分析、機械学習
PythonユーザのためのJupyter[実践]入門
Rグラフィックスクックブック ―ggplot2によるグラフ作成のレシピ集
Rではじめるデータサイエンス
Tidyverse