1. この記事について
待望のReact Router v7のstatic版が登場したので
チュートリアルを一通りやってみます
2. React Router v7について
最近はSPAといえどルーティングしたいというのが一般的になっていて、SPA書くときにも素のReactで書くのではなくReact-RouterかRemix SPAモードかを選択するケースが増えているのではないかと思います。npx create-react-appが非推奨になったこともあってその傾向が助長されていて、2024年1月に公開された以下のスライドからもそんな雰囲気が伺えます
https://speakerdeck.com/nkzn/the-spas-chronicle-reaches-to-remix
2024年5月、React Routerがv7からRemixと統合されるというアナウンスが出て、Remix SPAモード勢が喜んだり?、React Router勢がまた書き方変わるのかと不平を並べたりしていました
https://remix.run/blog/merging-remix-and-react-router
そして、待望のReact Router v7 安定版初期リリースであるv7.0.1が2024年11月に公開されました。ちょうど新しいSPAを書く予定があったので、今回はこれで書こうとチュートリアル読みつつメモ書きしていくというのがこの記事です
https://remix.run/blog/react-router-v7
3. インストール
node.jsを入れた環境で以下を実行します
npx create-react-router@latest my-app
開発サーバーを起動します
cd my-app
npm i
npm run dev
開発サーバーを起動すると http://localhost:5173 に初期ページが待機します
ディレクトリ構造はこんな感じ
root.tsxから始まって、routes.tsに書いているルーティング設定通りにコンポーネントを開くようになっています
4. Routing
ということで、まずはroutes.tsを読めるようにならないと何も分かりません
routes.tsにどう書けば良いのかやり方を見ていきます
4-1. Routingの手動設定
app/routes.tsでrouting方式の設定ができます
npx create-react-routerで生成されるroutes.tsは以下のようになっていて、routes/home.tsxをインデックスとするシングルページ構成を指示しています
import {
type RouteConfig,
index
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
index("routes/home.tsx")
] satisfies RouteConfig;
公式ドキュメントに書かれているシンプル版が以下で、/some/pathに./some/file.tsxを表示するようにルーティングします。表示するページが固定されているならこれだけで問題ないですね
import {
type RouteConfig,
route,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
route("some/path", "./some/file.tsx"),
// pattern ^ ^ module file
] satisfies RouteConfig;
indexとrouteを組み合わせて色々足したのが以下
import {
type RouteConfig,
route,
index,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
// renders into the root.tsx Outlet at /
index("./home.tsx"),
route("dashboard", "./dashboard.tsx", [
// renders into the dashboard.tsx Outlet at /dashboard
index("./dashboard-home.tsx"),
route("settings", "./dashboard-settings.tsx"),
]),
] satisfies RouteConfig;
4-2. Nested Routes
共通のナビゲーションバーやサイドバーを表示するような場合に、共通部分を分けて書ける仕組みがNested Routesです。以下では./dashboard.tsxに共通部分を書いて、./home.tsx, ./settings.tsxがそれぞれのURLに表示する内容を書いていて、URLで見ると/dashboard/に./dashboard.tsx+./home.tsx、/dashboard/settings/に./dashboard.tsx+./settings.tsxが表示されるわけです
import {
type RouteConfig,
route,
index,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
// parent route
route("dashboard", "./dashboard.tsx", [
// child routes
index("./home.tsx"),
route("settings", "./settings.tsx"),
]),
] satisfies RouteConfig;
共通部分になる./dashboard.tsxには個別部分をOutlet要素として書くことで自動的に置き換えて表示してくれる仕組みです。これはRemixと同様のスタイルですね
import { Outlet } from "react-router";
export default function Dashboard() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Dashboard</h1>
{/* will either be home.tsx or settings.tsx */}
<Outlet />
</div>
);
}
4-3. Layout Routes
routeの代わりにlayoutを使うとNestしつつURLの移動はないというのが書けます
以下の場合は
/ に./dashboard.tsx+./home.tsx が表示
/settings/に./dashboard.tsx+./settings.tsxが表示
となります
import {
type RouteConfig,
layout,
route,
index,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
// parent route
layout("./dashboard.tsx", [
// child routes
index("./home.tsx"),
route("settings", "./settings.tsx"),
]),
] satisfies RouteConfig;
4-4. Route Prefixes
prefixを使うと親ファイルなしでNestできます
/projects/ に./projects/home.tsx
/projects/:pid に./projects/project.tsx
/projects/:pid/edit に./projects/edit-project.tsx
を表示します
import {
type RouteConfig,
route,
layout,
index,
prefix,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
export default [
layout("./marketing/layout.tsx", [
index("./marketing/home.tsx"),
route("contact", "./marketing/contact.tsx"),
]),
...prefix("projects", [
index("./projects/home.tsx"),
layout("./projects/project-layout.tsx", [
route(":pid", "./projects/project.tsx"),
route(":pid/edit", "./projects/edit-project.tsx"),
]),
]),
] satisfies RouteConfig;
4-5. Dynamic Segment
4-5-1. 単独
動的なルーティングをしたい場合は以下のように「:」を頭に付けます
例えば以下のように書くと /teams/123/ が team.tsxに引数teamId=123としてルーティングされます
route("teams/:teamId", "./team.tsx"),
ページコンポーネント側はデータ受け取りを担当するloaderさんにparamsとして受け取るように書いていて、params.teamIdとしてコンポーネント内で使えるように書きます
import type { Route } from "./+types/team";
export async function loader({ params }: Route.LoaderArgs) {
// ^? { teamId: string }
}
export default function Component({
params,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
params.teamId;
// ^ string
}
4-5-2. 複数
複数の動的なセグメントを入れることもできます
route("c/:categoryId/p/:productId", "./product.tsx"),
import type { Route } from "./+types/product";
async function loader({ params }: LoaderArgs) {
// ^? { categoryId: string; productId: string }
}
4-6. Optional Segments
セグメントがあってもなくても同じファイルにルーティングする場合「?」をつけてやります
例えば以下だと動的セグメントである /:lang/ があってもなくても ./categories.tsx にルーティングされます
route(":lang?/categories", "./categories.tsx"),
動的でないセグメントもOptionalにできます
route("users/:userId/edit?", "./user.tsx");
4-7. Splats
「*」で指定するとそこに何がきても同じファイルにルーティングできます
route("files/*", "./files.tsx"),
コンポーネント側はparams["*"]で受け取れます
export async function loader({ params }: Route.LoaderArgs) {
// params["*"] will contain the remaining URL after files/
}
params[""] と書くのがちょっとめんどい、という方は適当な名前に代入して扱えます。例えば以下のように書くと const splat = params[""] として扱うことができます
const { "*": splat } = params;
4-8. Component Routes
なんとTSXタグとしてルーティングが書けるようです
例えば下のように書くと
/ に <StepOne />
/step-2/ に <StepTwo />
/step-3/ に <StepThree />
が表示されます
import { Routes, Route } from "react-router";
function Wizard() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Some Wizard with Steps</h1>
<Routes>
<Route index element={<StepOne />} />
<Route path="step-2" element={<StepTwo />} />
<Route path="step-3" element={<StepThree />}>
</Routes>
</div>
);
}
混乱しそう
慣れるのだろうか?
なお、この書き方だとloader, actionなどのRoute Moduleの機能が使えないようです
5. Route Module
以下の./team.tsxのように routes.ts で割り当てているファイルをRoute Moduleというようです
route("teams/:teamId", "./team.tsx"),
// route module ^^^^^^^^
Route Moduleには以下のような機能があるようです
・automatic code-splitting
・data loading
・actions
・revalidation
・error boundaries
・and more
5-1. 基本の書き方
Route Moduleと言ってますが、Reactのコンポーネントと同じ書き方が基本型で、ここにReact Router独自の機能を追加したものをRoute Moduleと呼んでいるようです
export default function MyRoute() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Look ma!</h1>
<p>
I'm still using React Router after like 10 years.
</p>
</div>
);
}
5-2. ErrorBoundary
ルーティング処理でエラーが出た時にエラーハンドリングすることができます。データフェッチなどでエラーが出た場合に専用の表示を出すような使い方が想定されているようです
import {
isRouteErrorResponse,
useRouteError,
} from "react-router";
export function ErrorBoundary() {
const error = useRouteError();
if (isRouteErrorResponse(error)) {
return (
<div>
<h1>
{error.status} {error.statusText}
</h1>
<p>{error.data}</p>
</div>
);
} else if (error instanceof Error) {
return (
<div>
<h1>Error</h1>
<p>{error.message}</p>
<p>The stack trace is:</p>
<pre>{error.stack}</pre>
</div>
);
} else {
return <h1>Unknown Error</h1>;
}
}
5-3. HydrateFallback
データフェッチなどの処理が入るページで、処理が完了するまでの間にローディングページなどを表示することができます
export async function clientLoader() {
const data = await fakeLoadLocalGameData();
return data;
}
export function HydrateFallback() {
return <p>Loading Game...</p>;
}
export default function Component({ loaderData }) {
return <Game data={loaderData} />;
}
5-4. HTTP headers
HTTPヘッダを以下のように書くことができます
export function headers() {
return {
"X-Stretchy-Pants": "its for fun",
"Cache-Control": "max-age=300, s-maxage=3600",
};
}
5-5. handle
パンくずリストのようなルート経路を使った表示をつくりたい場合、以下のように各コンポーネントでexport constしておいて、useMatchesで受け取ることができます
export const handle = {
breadcrumb: "Home",
};
export default function Index() {
return <h1>Home Page</h1>;
}
export const handle = {
breadcrumb: "About",
};
export default function About() {
return <h1>About Page</h1>;
}
export const handle = {
breadcrumb: "Contact",
};
export default function Contact() {
return <h1>Contact Page</h1>;
}
import { useMatches, Link } from "@remix-run/react";
export default function Breadcrumbs() {
const matches = useMatches();
// ルートのhandleでパンくずリスト情報が定義されているもののみ取得
const breadcrumbs = matches
.map((match) => {
if (match.handle && match.handle.breadcrumb) {
return {
breadcrumb: match.handle.breadcrumb,
pathname: match.pathname, // ルートのパス
};
}
return null;
})
.filter(Boolean); // nullを取り除く
return (
<nav aria-label="Breadcrumb">
<ul style={{ listStyle: "none", display: "flex", gap: "8px", padding: 0 }}>
{breadcrumbs.map((crumb, index) => (
<li key={crumb.pathname}>
<Link to={crumb.pathname}>
{crumb.breadcrumb}
</Link>
{index < breadcrumbs.length - 1 && <span> / </span>}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</nav>
);
}
5-6. links
linkタグに書く内容をまとめて定義しておいて、各ページに共通して追加することができます
export function links() {
return [
{
rel: "icon",
href: "/favicon.png",
type: "image/png",
},
{
rel: "stylesheet",
href: "https://example.com/some/styles.css",
},
{
rel: "preload",
href: "/images/banner.jpg",
as: "image",
},
];
}
以下のように書くとLinks要素のところに
import { Links } from "react-router";
export default function Root() {
return (
<html>
<head>
<Links />
</head>
<body />
</html>
);
}
5-7. meta
metaタグの内容もまとめて書いておけます
export function meta() {
return [
{ title: "Very cool app" },
{
property: "og:title",
content: "Very cool app",
},
{
name: "description",
content: "This app is the best",
},
];
}
import { Meta } from "react-router";
export default function Root() {
return (
<html>
<head>
<Meta />
</head>
<body />
</html>
);
}
5-8. shouldRevalidate
routes.tsにshouldRevalidate関数を書いておくとrevalidateするかどうか指示することが出来ます。ユーザーがフォーム送信するなどしてデータが更新されたときに、値を再評価してレンダリングしなおすrevalidateがデフォルトではすべてのページで有効になっていますが、その必要がないページはrevalidate無効としておくことでパフォーマンスを改善できます
import type { Route } from "./+types/my-route";
export function shouldRevalidate(
arg: Route.ShouldRevalidateArg
) {
return true;
}
shouldRevalidateの引数には以下のような値を受け取れるので、これを使ってrevalidateするかどうか条件分岐することができます
| key | 内容 |
|---|---|
| currentUrl | 現在のURL |
| nextUrl | ナビゲーション後のURL |
| defaultShouldRevalidate | React Routerがデフォルトで適用するshouldRevalidateロジックの結果 |
| formMethod | 現在のフォーム送信のHTTPメソッド("POST", "PUT"など) |
| formData | フォーム送信に関連するデータ(FormDataオブジェクト) |
| currentParams | 現在のルートパラメータ |
| nextParams | ナビゲーション後のルートパラメータ |
import {
type RouteConfig,
layout,
route,
index,
} from "@react-router/dev/routes";
// shouldRevalidateの定義例
function myShouldRevalidate({ currentUrl, nextUrl }: { currentUrl: URL; nextUrl: URL }) {
return currentUrl.pathname !== nextUrl.pathname; // パスが変更された場合のみ再取得
}
export default [
// parent route
layout("./dashboard.tsx", [
// child routes
index("./home.tsx", { shouldRevalidate: myShouldRevalidate }), // ホームルートに追加
route("settings", "./settings.tsx", { shouldRevalidate: myShouldRevalidate }), // 設定ルートに追加
]),
] satisfies RouteConfig;
6. loader, action
6-1. コンセプトとか経緯とか
2020年11月にRemixがloader, actionを提案してフロントエンドを書くときにいちいちデータ更新を考える必要をなくそう、バックエンドのデータを更新したらフロントエンドも更新されるように勝手になる仕組みを作ろう、というコンセプトを提唱しました
https://remix.run/docs/en/main/discussion/data-flow
https://remix.run/blog/remix-data-flow
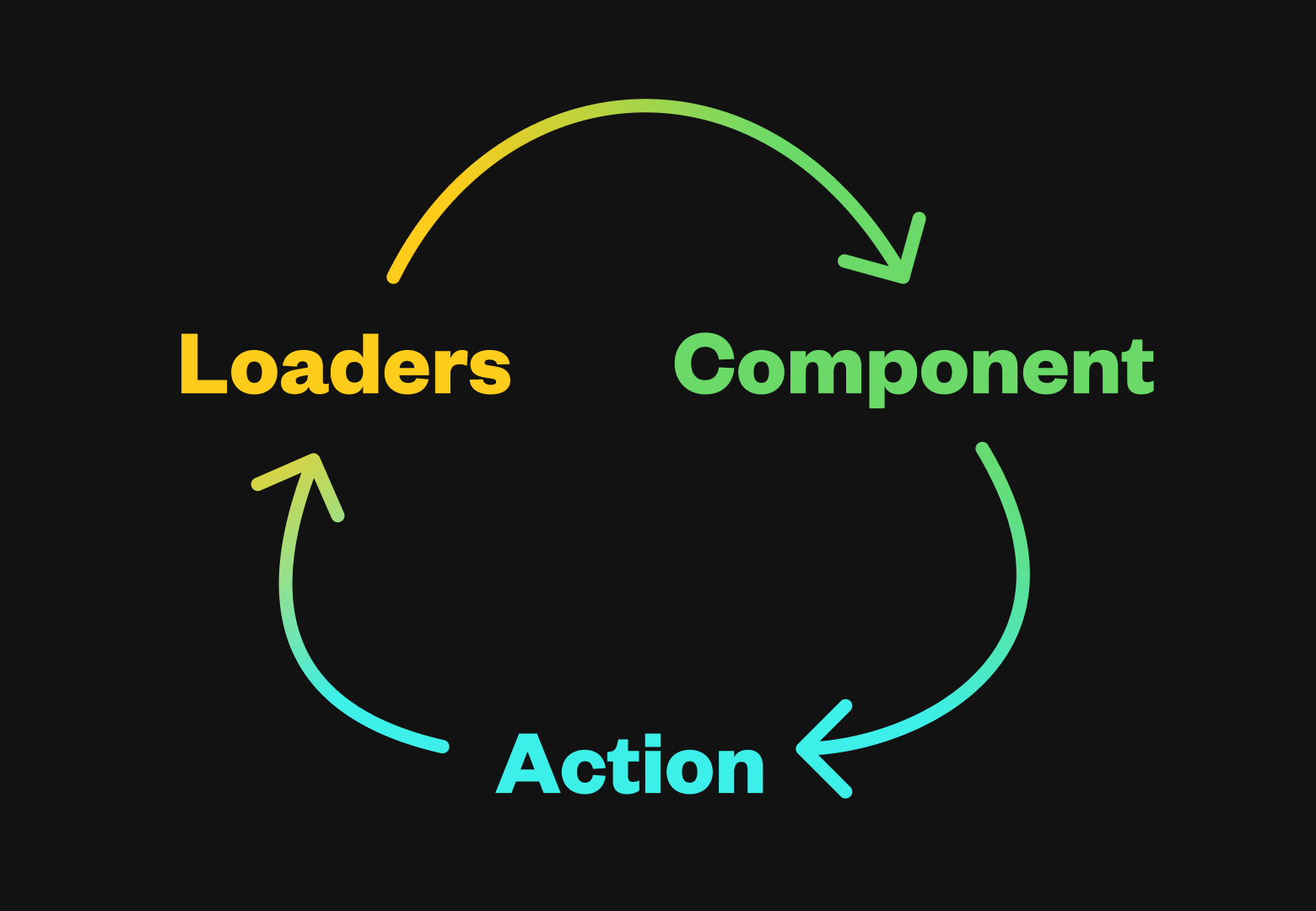
SSRとCSRが混在している現在のフロントエンドでこのコンセプトがすごく良いというのは僕にも分かりますし、実際界隈にも受け入れられたようで2022年9月のReact Routerもv6.4からloader, actionを導入、2024年春にRemixとのマージをブログで発表、2024年11月v7がリリースされています
https://remix.run/blog/merging-remix-and-react-router
React Router v6.4について書かれたブログを見ると少なからず驚きをもって迎えられている雰囲気が伝わってきます
https://zenn.dev/monicle/articles/react-router-v6-4?utm_source=chatgpt.com
そうして導入されてきたloader, actionはReact Router v7ではどうなっているでしょうか
6-2. Rendering Strategies
SSRを有効にするか、どのページをprerenderするかまとめて設定しておくことができます
6-2-1. Server Side Rendering
デフォルトだとSSRが有効になっています
import type { Config } from "@react-router/dev/config";
export default {
ssr: true,
} satisfies Config;
6-2-2. Client Side Rendering
SPAにしたいときは無効にします
ssr: false,
6-2-3. Static Pre-rendering
prerenderに指定しておくことでビルド時に静的ファイルを生成してくれるようです
import type { Config } from "@react-router/dev/config";
export default {
// return a list of URLs to prerender at build time
async prerender() {
return ["/", "/about", "/contact"];
},
} satisfies Config;
公式ドキュメントにpre-renderingのページがあり、ここを読むと他の書き方も紹介されています
https://reactrouter.com/how-to/pre-rendering#pre-rendering
以下のように3つの書き方がまとめて紹介されていますが、通常はどれか1つを選択するのではないかと思います
prerender: trueは静的なrouteを全部pre-renderするけど動的なrouteは対象外
prerender: ["/", "/blog"]は指定のpathのrouteをpre-render
async prerender()はCMSなどのフェッチデータなどから動的にrouteを指定できるようです
import type { Config } from "@react-router/dev/config";
export default {
// all static route paths
// (no dynamic segments like "/post/:slug")
prerender: true,
// any url
prerender: ["/", "/blog", "/blog/popular-post"],
// async function for dependencies like a CMS
async prerender({ getStaticPaths }) {
let posts = await fakeGetPostsFromCMS();
return ["/", "/blog"].concat(
posts.map((post) => post.href)
);
},
} satisfies Config;
動的に指定できるってことはSSGも出来るのかな?
6-3. loader
React Router v7ではrouting, loader, actionが一体となって動作します
データの受け取りをすべてloader内でやると適切なタイミングでrevalidateしてくれます
loaderとclientLoaderの2種類が用意されていて、SSRやstatic pre-renderingのときはloader、CSRのときはclientLoaderを使います
6-3-1. Client Data Loading
clientLoader関数内でデータフェッチしてreturnしてやると、Route Module側でloaderDataとして受け取れます
// route("products/:pid", "./product.tsx");
import type { Route } from "./+types/product";
export async function clientLoader({
params,
}: Route.ClientLoaderArgs) {
const res = await fetch(`/api/products/${params.pid}`);
const product = await res.json();
return product;
}
export default function Product({
loaderData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
const { name, description } = loaderData;
return (
<div>
<h1>{name}</h1>
<p>{description}</p>
</div>
);
}
clientLoaderはreact-router.config.tsxでssr: falseにしていても使う事ができますので、SPAをビルドして使うときもclient側フェッチはこちらで書くことになります
https://reactrouter.com/how-to/spa
6-3-2. Server Data Loading
こちらも同様にデータフェッチしてreturnしてやるとloaderDataとして受け取れます
サーバーサイド側はDBから取得すると思いますので、prismaなどを使って取ってくる感じでしょうか
// route("products/:pid", "./product.tsx");
import type { Route } from "./+types/product";
import { fakeDb } from "../db";
export async function loader({ params }: Route.LoaderArgs) {
const product = await fakeDb.getProduct(params.pid);
return product;
}
export default function Product({
loaderData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
const { name, description } = loaderData;
return (
<div>
<h1>{name}</h1>
<p>{description}</p>
</div>
);
}
6-3-3. Static Data Loading
プリレンダリングするときは普通にloaderで書いておいて、react-router.config.tsxでprerenderするだけです
// route("products/:pid", "./product.tsx");
import type { Route } from "./+types/product";
export async function loader({ params }: Route.LoaderArgs) {
let product = await getProductFromCSVFile(params.pid);
return product;
}
export default function Product({
loaderData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
const { name, description } = loaderData;
return (
<div>
<h1>{name}</h1>
<p>{description}</p>
</div>
);
}
import type { Config } from "@react-router/dev/config";
export default {
async prerender() {
let products = await readProductsFromCSVFile();
return products.map(
(product) => `/products/${product.id}`
);
},
} satisfies Config;
6-3-4. 両方使う
なんと、loaderとclientLoaderの両方を同時に使う事ができます
受け取り側はloaderDataでまとめて受け取り
// route("products/:pid", "./product.tsx");
import type { Route } from "./+types/product";
import { fakeDb } from "../db";
export async function loader({ params }: Route.LoaderArgs) {
return fakeDb.getProduct(params.pid);
}
export async function clientLoader({
params,
}: Route.ClientLoader) {
const res = await fetch(`/api/products/${params.pid}`);
return res.json();
}
export default function Product({
loaderData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
const { name, description } = loaderData;
return (
<div>
<h1>{name}</h1>
<p>{description}</p>
</div>
);
}
素晴らしい
早くこれで書きたい
6-4. action
バックエンドへの書き込みを担当するのがactionです
データの更新処理をactionに書いておいて、actionをトリガーするイベントが発生するとrevalidateしてくれます
6-4-1. clientAction
client側で実行されるべきアクションはclientActionに書きます
以下の場合は、Form内のsubmitボタンがactionをトリガーしてくれます
// route('/projects/:projectId', './project.tsx')
import type { Route } from "./+types/project";
import { Form } from "react-router";
import { someApi } from "./api";
export async function clientAction({
request,
}: Route.ClientActionArgs) {
let formData = await request.formData();
let title = await formData.get("title");
let project = await someApi.updateProject({ title });
return project;
}
export default function Project({
actionData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
return (
<div>
<h1>Project</h1>
<Form method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</Form>
{actionData ? (
<p>{actionData.title} updated</p>
) : null}
</div>
);
}
6-4-2. action
actionも書き方は同じですがサーバーサイドでのactionを想定しているので、公式ドキュメントの例でもDBへの書き込み処理を記述しています
// route('/projects/:projectId', './project.tsx')
import type { Route } from "./+types/project";
import { Form } from "react-router";
import { fakeDb } from "../db";
export async function action({
request,
}: Route.ActionArgs) {
let formData = await request.formData();
let title = await formData.get("title");
let project = await fakeDb.updateProject({ title });
return project;
}
export default function Project({
actionData,
}: Route.ComponentProps) {
return (
<div>
<h1>Project</h1>
<Form method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</Form>
{actionData ? (
<p>{actionData.title} updated</p>
) : null}
</div>
);
}
6-4-3. actionをトリガーするイベント
HTTPリクエスト
先ほどの例で書かれていたFormのボタン操作のように、HTTPリクエストをトリガーとする場合です。action側でPOSTリクエストを引数requestとして受け取って処理します
import { Form } from "react-router";
function SomeComponent() {
return (
<Form action="/projects/123" method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</Form>
);
}
useSubmit
useSubmitによりactionをトリガーできます
任意のイベントから実行できるので、これで書くことが多そうです
import { useCallback } from "react";
import { useSubmit } from "react-router";
import { useFakeTimer } from "fake-lib";
function useQuizTimer() {
let submit = useSubmit();
let cb = useCallback(() => {
submit(
{ quizTimedOut: true },
{ action: "/end-quiz", method: "post" }
);
}, []);
let tenMinutes = 10 * 60 * 1000;
useFakeTimer(tenMinutes, cb);
}
useFetcher
FormやuseSubmitを使うとブラウザのナビゲーション履歴が残りますが、useFetcherを使うと履歴が残らなくできます
import { useFetcher } from "react-router";
function Task() {
let fetcher = useFetcher();
let busy = fetcher.state !== "idle";
return (
<fetcher.Form method="post" action="/update-task/123">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">
{busy ? "Saving..." : "Save"}
</button>
</fetcher.Form>
);
}
fetcher.submit(
{ title: "New Title" },
{ action: "/update-task/123", method: "post" }
);
7. Navigation
React Router v7のルーティングに沿ってページ遷移する為の仕組みとして<Link>, <NavLink>, <Form>, redirect, and useNavigateが準備されています
7-1. NavLink
ルーティングのPathを指定してリンクすることができます
アクティブやペンディングなどの状態を反映して表示などを変えたい場合はNavLink
使わない場合はLinkを使います
import { NavLink } from "react-router";
export function MyAppNav() {
return (
<nav>
<NavLink to="/" end>
Home
</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/trending" end>
Trending Concerts
</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/concerts">All Concerts</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/account">Account</NavLink>
</nav>
);
}
NavLinkにCSSを適用する場合、以下のように書くだけで上手くやってくれます
a.active {
color: red;
}
a.pending {
animate: pulse 1s infinite;
}
a.transitioning {
/* css transition is running */
}
普通の要素と同様、stateを使ってclassNameなどを変更することができます
// className
<NavLink
to="/messages"
className={({ isActive, isPending, isTransitioning }) =>
[
isPending ? "pending" : "",
isActive ? "active" : "",
isTransitioning ? "transitioning" : "",
].join(" ")
}
>
Messages
</NavLink>
// style
<NavLink
to="/messages"
style={({ isActive, isPending, isTransitioning }) => {
return {
fontWeight: isActive ? "bold" : "",
color: isPending ? "red" : "black",
viewTransitionName: isTransitioning ? "slide" : "",
};
}}
>
Messages
</NavLink>
// children
<NavLink to="/tasks">
{({ isActive, isPending, isTransitioning }) => (
<span className={isActive ? "active" : ""}>Tasks</span>
)}
</NavLink>
7-2. Link
アクティブやペンディングなどの状態を使わない場合はLinkを使います
import { Link } from "react-router";
export function LoggedOutMessage() {
return (
<p>
You've been logged out.{" "}
<Link to="/login">Login again</Link>
</p>
);
}
7-3. Form
Formを使ってナビゲートすることもできます
<Form action="/search">
<input type="text" name="q" />
</Form>
上の場合に例えば journey と入力すると、以下のようなPathへのナビゲートを要求します
/search?q=journey
7-4. redirect
loaderやactionの中でリダイレクトすることができるようです
import { redirect } from "react-router";
export async function loader({ request }) {
let user = await getUser(request);
if (!user) {
return redirect("/login");
}
return { userName: user.name };
}
import { redirect } from "react-router";
export async function action({ request }) {
let formData = await request.formData();
let project = await createProject(formData);
return redirect(`/projects/${project.id}`);
}
7-5. useNavigate
適当なイベントからuseNavigateを使ってナビゲートできます
import { useNavigate } from "react-router";
export function useLogoutAfterInactivity() {
let navigate = useNavigate();
useFakeInactivityHook(() => {
navigate("/logout");
});
}
8. Pending UI
新しいrouteに移動するとき、actionをトリガーするユーザー入力があったときには画面はすぐ反応させたいので、待機ページを表示するか何かしら最適化した表示を出したいですが、手動でやるのはわりと面倒だったり難しかったりしたと思います。React Router v7ではRouting, loader, actionが統合的に組み込まれたことでこれを解決し、待機ページ表示を指定するだけで上手に表示してくれるようになったようです
8-1. Global Pending Navigation
Nesting Routeの親側コンポーネントで以下のように書いておくと、子コンポーネントに共通して読み込み中の表示を適用できます。以下のGlobalSpinner要素はデフォルトで存在するコンポーネントではないので、自分で何かスピナー的な要素を書いて配置する想定のサンプルコードだと思われます
import { useNavigation } from "react-router";
export default function Root() {
const navigation = useNavigation();
const isNavigating = Boolean(navigation.location);
return (
<html>
<body>
{isNavigating && <GlobalSpinner />}
<Outlet />
</body>
</html>
);
}
7-2. Local Pending Navigation
NavLink要素以下ではisPendingとして遷移中かどうかを取得できます。isPending === trueであるときに、遷移中表示が出るように書いておけば、遷移し終わったらページ自体が入れ替わりますので自然な待機表示が実現します
import { NavLink } from "react-router";
function Navbar() {
return (
<nav>
<NavLink to="/home">
{({ isPending }) => (
<span>Home {isPending && <Spinner />}</span>
)}
</NavLink>
<NavLink
to="/about"
style={({ isPending }) => ({
color: isPending ? "gray" : "black",
})}
>
About
</NavLink>
</nav>
);
}
7-3. Pending Form Submission
Formやfetcher.Formも待機表示が書けます
import { useFetcher } from "react-router";
function NewProjectForm() {
const fetcher = useFetcher();
return (
<fetcher.Form method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">
{fetcher.state !== "idle"
? "Submitting..."
: "Submit"}
</button>
</fetcher.Form>
);
}
import { useNavigation, Form } from "react-router";
function NewProjectForm() {
const navigation = useNavigation();
return (
<Form method="post" action="/projects/new">
<input type="text" name="title" />
<button type="submit">
{navigation.formAction === "/projects/new"
? "Submitting..."
: "Submit"}
</button>
</Form>
);
}
7-4. Optimistic UI
待機中表示と同様にOptimistic UIも書くことができます
以下では開始して完了するまでの表示と完了後の表示を指定しています
function Task({ task }) {
const fetcher = useFetcher();
let isComplete = task.status === "complete";
if (fetcher.formData) {
isComplete = fetcher.formData.get("status");
}
return (
<div>
<div>{task.title}</div>
<fetcher.Form method="post">
<button
name="status"
value={isComplete ? "incomplete" : "complete"}
>
{isComplete ? "Mark Incomplete" : "Mark Complete"}
</button>
</fetcher.Form>
</div>
);
}
8. Testing
actionでエラーが発生した場合にキャッチしてコンポーネントに表示できます
以下ではFormをsubmitしたときにaction内でエラーが出た場合にactionからreturnされたエラー表示を画面に出して、何がまずかったかユーザーに表示しようとしています
import { useActionData } from "react-router";
export function LoginForm() {
const errors = useActionData();
return (
<Form method="post">
<label>
<input type="text" name="username" />
{errors?.username && <div>{errors.username}</div>}
</label>
<label>
<input type="password" name="password" />
{errors?.password && <div>{errors.password}</div>}
</label>
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</Form>
);
}
この動作をテストする為にRoute Moduleのスタブを作ってテストするためのcreateRoutesStub関数が用意されています。これを使うと、単体のRoute Moduleのスタブを作って値を与えて挙動テストを実行することができます
import { createRoutesStub } from "react-router";
import * as Test from "@testing-library/react";
import { LoginForm } from "./LoginForm";
test("LoginForm renders error messages", async () => {
const USER_MESSAGE = "Username is required";
const PASSWORD_MESSAGE = "Password is required";
const Stub = createRoutesStub([
{
path: "/login",
Component: LoginForm,
action() {
return {
errors: {
username: USER_MESSAGE,
password: PASSWORD_MESSAGE,
},
};
},
},
]);
// render the app stub at "/login"
Test.render(<Stub initialEntries={["/login"]} />);
// simulate interactions
Test.user.click(screen.getByText("Login"));
await Test.waitFor(() => screen.findByText(USER_MESSAGE));
await Test.waitFor(() =>
screen.findByText(PASSWORD_MESSAGE)
);
});
まとめ
まだほとんど書けていませんが、RemixとReact Router v6に良いところ取りをしたような書き方になっているような印象です。SPAでもloader, actionが使えるようになったり、エラーハンドリングが洗練されたりと全体にパワーアップしているようですので早く書いてみたいところです
レッツトライ
