この記事は何か
adversarial validationとは何かを説明した後に、試しに実装してみたコードを記載する。
備忘録、知識の整理も兼ねてここに記していく。
本記事を投稿するにあたって参考にしたコードはこちら
adversarial validationとは
trainデータの分布がtestデータと異なる場合、validationデータの分布もtrainデータの分布に寄ってしまい、上手くtestデータを予測できないことがある。その時に用いられる手法の一つがadversarial validationである。
adversarial validationとは、trainデータとtestデータを分類するモデルを構築し、それを用いてtestデータになるべく近い分布のvalidationデータを作成することである。
実装
目的変数の作成
trainデータ、testデータに新たな列を作成し、trainデータには0を、testデータには1を入れる。
import pandas as pd
train['target'] = 0
test['target'] = 1
train_test = pd.concat([train, test], axis=0).reset_index(drop=True)
train_test.head()
学習と分類
今回、モデルの構築にはlightgbmを使用した。交差検証を行い、全てのtrainデータに対して、testデータである可能性(probability)を測っている。
import numpy as np
import lightgbm as lgb
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
params = {'objective': 'binary',
'max_depth': 5,
'boosting': 'gbdt',
'metric': 'auc'}
features = [col for col in train_test.columns if col not in ('target',)]
oof_pred = np.zeros((len(train_test), ))
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
for fold, (train_idx, val_idx) in enumerate(cv.split(train_test, train_test['target'])):
x_train, x_predict = train_test[features].iloc[train_idx], train_test[features].iloc[val_idx]
y_train = train_test['target'][train_idx]
train_set = lgb.Dataset(x_train, label=y_train)
model = lgb.train(params, train_set)
oof_pred[val_idx] = model.predict(x_predict).reshape(oof_pred[val_idx].shape)
validationデータの作成
probabilityの値を降順にソートし、(testである可能性が)高い順に任意のデータ数取得し、validationデータを作成する
train_test['probability'] = oof_pred
train = train_test[train_test.target==0].drop('target', axis=1).sort_values('probability', ascending=False)
valid_idx = int(len(train)) / 5 # 今回は決め打ちで上位20%としている
validation_data = train.iloc[:valid_idx]
train_data = train.iloc[valid_idx:]
クラスにしてまとめてみた
class Adversarial_validator:
def __init__(self, train, test, features, categoricals):
self.train = train
self.test = test
self.features = features
self.categoricals = categoricals
self.union_df = self.train_test_union(self.train, self.test)
self.cv = self.get_cv()
self.models = []
self.oof_pred = self.fit()
self.report_plot()
def fit(self):
oof_pred = np.zeros((len(self.union_df), ))
for fold, (train_idx, val_idx) in enumerate(self.cv):
x_train, x_predict = self.union_df[self.features].iloc[
train_idx], self.union_df[self.features].iloc[val_idx]
y_train = self.union_df['target'][train_idx]
train_set = self.convert_dataset(x_train, y_train)
model = self.train_model(train_set)
self.models.append(model)
oof_pred[val_idx] = model.predict(
x_predict).reshape(oof_pred[val_idx].shape)
self.union_df['prediction'] = oof_pred
return oof_pred
def train_test_union(self, train, test):
train['target'] = 0
test['target'] = 1
return pd.concat([train, test], axis=0).reset_index(drop=True)
def get_cv(self):
cv = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5,
shuffle=True, random_state=42)
return cv.split(self.union_df, self.union_df['target'])
def convert_dataset(self, X, y):
return lgb.Dataset(X, label=y, categorical_feature=self.categoricals)
def train_model(self, train_set):
return lgb.train(self.get_params(), train_set)
def get_params(self):
param = {'num_leaves': 50,
'num_round': 100,
'min_data_in_leaf': 30,
'objective': 'binary',
'max_depth': 5,
'learning_rate': 0.2,
'min_child_samples': 20,
'boosting': 'gbdt',
'feature_fraction': 0.9,
'bagging_freq': 1,
'bagging_fraction': 0.9,
'bagging_seed': 44,
'verbose_eval': 50,
'metric': 'auc',
'verbosity': -1}
return param
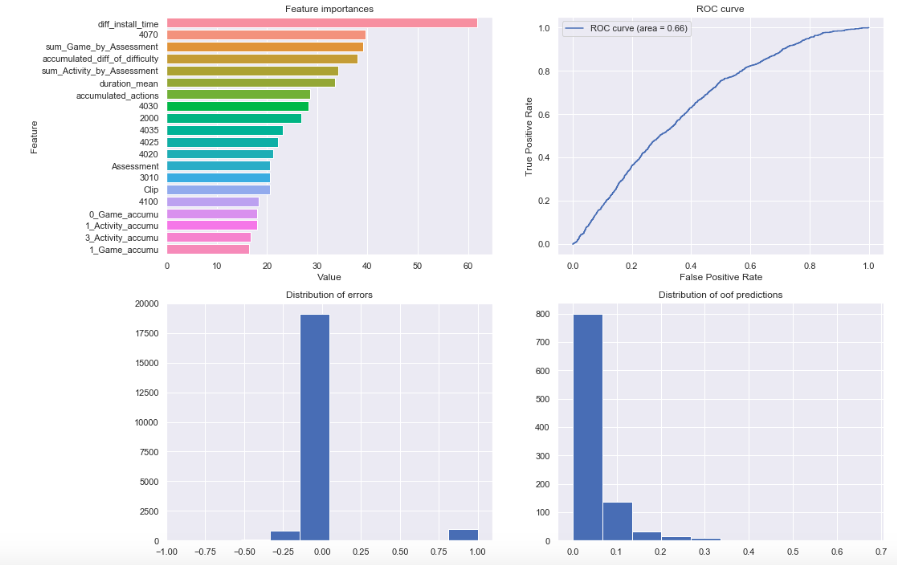
def report_plot(self):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 12))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
self.plot_feature_importance()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
self.plot_roc_curve()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.hist(self.union_df['target'] - self.oof_pred)
plt.title('Distribution of errors')
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.hist(np.random.choice(self.oof_pred, 1000, False))
plt.title('Distribution of oof predictions')
def get_feature_importance(self):
n = len(self.models)
feature_imp_df = pd.DataFrame()
for i in range(n):
tmp = pd.DataFrame(zip(self.models[i].feature_importance(
), self.features), columns=['Value', 'Feature'])
tmp['n_models'] = i
feature_imp_df = pd.concat([feature_imp_df, tmp])
del tmp
self.feature_importance = feature_imp_df
return feature_imp_df
def plot_feature_importance(self, n=20):
imp_df = self.get_feature_importance().groupby(
['Feature'])[['Value']].mean().reset_index(False)
imp_top_df = imp_df.sort_values('Value', ascending=False).head(n)
sns.barplot(data=imp_top_df, x='Value', y='Feature', orient='h')
plt.title('Feature importances')
def plot_roc_curve(self):
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(
self.union_df['target'], self.oof_pred)
auc = metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label='ROC curve (area = %.2f)' % auc)
plt.legend()
plt.title('ROC curve')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
adv = Adversarial_validator(train, test, features, categoricals)
データはkaggleコンペの2019 Data Science Bowlのデータを使用している。
validationデータ作成以外の活用法
- importanceの高い特徴量を削除してtrainデータの分布をtestデータに近づける
- 学習時のデータの重みづけの参考(weight_column)
まとめ
簡単にだがadversarial validationについて紹介してみた。この記事を読んだ方の一助になれば幸いである。