Jetson nanoでLEDテープを動かすことができたので共有します。
https://github.com/seitomatsubara/Jetson-nano-WS2812-LED-
準備
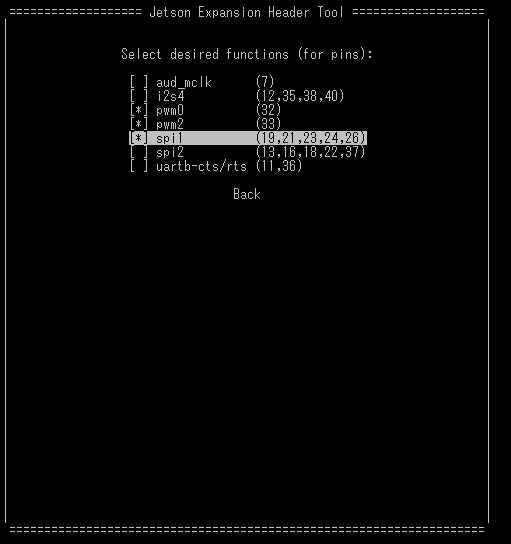
Jetson-IO tool でSPI設定
$ sudo /opt/nvidia/jetson-io/jetson-io.py
Configure 40-pin expansion headerを選択する。

接続
spi1なら19ピン、spi2なら13ピンにLEDテープのシグナルピンをつなぐ。
spi通信のプロトコルを用いる関係上、spi通信で使うピン(spi1なら21,23,24,26)は使用不能。
GNDも接続する必要あり。
電源は適宜供給する。
spidevをpipでインストールする
$ sudo pip install spidev
コード
import spidev
import sys
class SPItoWS():
def __init__(self, ledc):
self.led_count = ledc
self.X = '' # X is signal of WS281x
for i in range(self.led_count):
self.X = self.X + "100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100"
self.spi = spidev.SpiDev()
self.spi.open(0, 0)
self.spi.max_speed_hz = 2400000
def __del__(self):
self.spi.close()
def _Bytesto3Bytes(self, num, RGB): # num is number of signal, RGB is 8 bits (1 byte) str
for i in range(8):
if RGB[i] == '0':
self.X = self.X[:num * 3 * 8 + i * 3] + '100' + self.X[num * 3 * 8 + i * 3 + 3:]
elif RGB[i] == '1':
self.X = self.X[:num * 3 * 8 + i * 3] + '110' + self.X[num * 3 * 8 + i * 3 + 3:]
def _BytesToHex(self, Bytes):
return ''.join(["0x%02X " % x for x in Bytes]).strip()
def LED_show(self):
Y = []
for i in range(self.led_count * 9):
Y.append(int(self.X[i*8:(i+1)*8],2))
WS = self._BytesToHex(Y)
self.spi.xfer3(Y, 2400000,0,8)
def RGBto3Bytes(self, led_num, R, G, B):
if (R > 255 or G > 255 or B > 255):
print("Invalid Value: RGB is over 255\n")
sys.exit(1)
if (led_num > self.led_count - 1):
print("Invalid Value: The number is over the number of LED")
sys.exit(1)
RR = format(R, '08b')
GG = format(G, '08b')
BB = format(B, '08b')
self._Bytesto3Bytes(led_num * 3, GG)
self._Bytesto3Bytes(led_num * 3 + 1, RR)
self._Bytesto3Bytes(led_num * 3 + 2, BB)
def LED_OFF_ALL(self):
self.X = ''
for i in range(self.led_count):
self.X = self.X + "100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100100"
self.LED_show()
使い方
SPItoWS(<LEDの個数>)
LEDの指定
SPItoWS.RGBto3Bytes(i, R, G, B)
i: LEDの位置
R, G, B: LEDの強さ。0-255で指定
LEDを光らせる
SPItoWS.LED_show()
RGBto3Bytes関数を使って指定したLEDを光らせる。
すべてオフにする
SPItoWS.LED_OFF_ALL()
全てのLEDをオフにする。
使用例
if __name__ == "__main__":
import time
LED_COUNT = 3
sig = SPItoWS(LED_COUNT)
sig.RGBto3Bytes(0, 255, 0, 0)
sig.RGBto3Bytes(1, 0, 255, 0)
sig.RGBto3Bytes(2, 0, 0, 255)
sig.LED_show()
time.sleep(1)
sig.LED_OFF_ALL()
1秒間LEDが赤、緑、青に点灯した後、消えます。