この記事はGraphQL Advent Calendar 2020の15日目の記事です。
不動産スタートアップ 株式会社estieでエンジニアをやっています、savacanです。
 はじめに
はじめに
たまには業務に関係ないものをいじって遊ぼう!
ということで、今回はapollo federationなるものをいじってみようと思います。
ある程度仕組みがわかった気になれたらゴールにしようと思ってます。
 対象読者
対象読者
- graphql興味ある方
- apollo federation聞いたことあるけど触ったことないよーという方
- 新しい物が好きな方
今回は全てJSで書いているのでフロントエンドエンジニアフレンドリーになっています。
 きっかけ
きっかけ
近頃(?)Webpack5がリリースされましたね!
自分は以前よりマイクロフロントエンドの発想に注目していて、module federationのpluginの動向などをボーッと追いかけてみたり、reactにvueをマウントしてキャッキャしたり、custom elementをいじってみたり……etcと色々やっていました。このあたりはまたの機会に。
その中で、~federationと名の付くなにやら面白そうなものを発見しました。
そう、それがapollo federationです。マイクロフロントエンドの文脈からは随分外れますが……
触ってみようと思いながらも、まだ触れていなかったのでこれを期に戯れてみたいと思います。
まだ使ったことのない技術を触ってみる時ってなんだかワクワクしますよね。
 そもそもapolloって何……??
そもそもapolloって何……??
- graphqlバリバリ運用してるよ!
- apollo使いこなしてるよ!
というツヨツヨな方はとりあえずここはスキップしてください。
いじってみたコードとかも載せますのでそこまでお待ちを!
 graphqlってなんぞ?
graphqlってなんぞ?
公式ページでは
GraphQLは、APIのクエリ言語であり、既存のデータでこれらのクエリを実行するためのランタイムです。GraphQLは、API内のデータの完全で理解しやすい説明を提供し、クライアントが必要なものだけを正確に要求できるようにし、時間の経過とともにAPIを進化させやすくし、強力な開発者ツールを有効にします。
と説明されていますね。
詳しい説明は他の紹介記事の方がずっとわかりやすいので割愛します。
要するに、フロントエンド目線で言うと、欲しいデータを欲しい分だけ取得できる仕組み・規格です。
しかも、schemaできっちりと定義するため、型の自動生成なども行えます。
 apollo……?
apollo……?
これまた公式ページから
Apolloは業界標準のGraphQL実装であり、最新のアプリをクラウドに接続するデータグラフレイヤーを提供します。
とのことです。
つまるところ、graphqlの実装を提供しています。
また、それだけに止まらず、パフォーマンス等の分析に用いるapollo studioや、clientも提供しています。そして、その中の一つにapollo federationが存在するというわけです。
 apollo federation
apollo federation
ようやくここにたどり着きました。
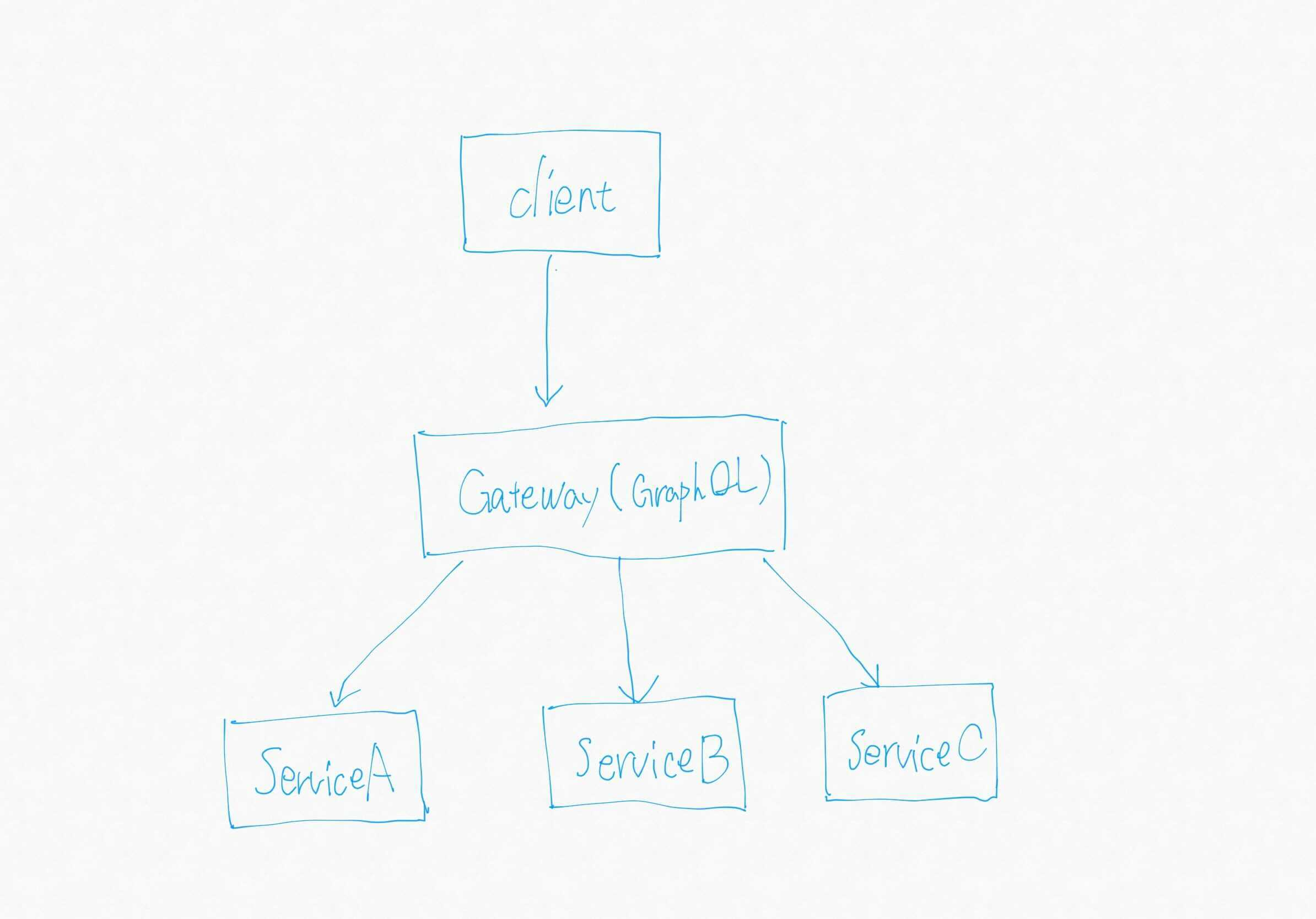
graphqlはその仕組み上、単一のデータグラフを公開する必要があり、規模がデカくなればなるほど単一のgraphqlサーバで大規模なデータグラフを表現するのが難しくなってくる場合があります。
つまり、以下の図のような形で管理できたらベストなわけです。(唐突な手書きすみません)
各serviceを独立したgraphqlサーバとして開発でき、schemaを分散して管理することができる状態です。
そこでapollo federationの前に利用されていた仕組みがschema stitchingです。
今回は詳しく説明しませんが、schema stitchingはその名の通り、複数のgraphql APIのschemaを継ぎ接ぎし単一のschemaとして表現するやり方です。この仕組みの場合gatewayとなるgraphqlサーバにおいて、schemaの結合を行うためのコードを書く必要があり、gatewayが複雑になるという問題があったようです。
では、このschema stitchingの次に出てきたapollo federationをみていきましょう。
公式サイトより
他の分散GraphQLアーキテクチャ(スキーマスティッチングなど)とは異なり、Apollo Federationは宣言型プログラミングモデルを使用して、各実装サービスが担当するグラフの部分のみを実装できるようにします。
つまりどういうこと……?
という感じですね。こういう時は手を動かすに限ります。
 tutorialしてみた。
tutorialしてみた。
こちらがコードですどうぞ -> savacan
今回は以下3つのサービスを作成し、apollo federationの仕組みを利用して一つのgraphqlサーバとして振舞えるか確かめてみようと思います。
イメージはゲームのレビューサイトで、userはgameに対してreviewを行うことができ、userは自分の書いたreviewを確認できるものとします。
また、これらのサービスは全て別のチームが開発しているという想定です。
- user service : ユーザ情報を取り扱うservice
- game service : ゲーム情報を取り扱うservice
- review service : レビューを取り扱うservice
上記3つにgatewayを加えて計4つのgraphqlサーバが立ち上がることになります。
 serviceを実装する
serviceを実装する
とりあえず雑にapollo serverをドンと立てます。
今回は簡単に立てたかったので全てapollo serverで実装しましたが、apollo federationの仕様を満たしていればserviceの実装はなんでも良いっぽいです(こちらサポートリスト)
簡単に立て方を載せておきます。知っている方はfederationまでスキップ。
基本的に普通のapollo serverと同じです。
まずnode環境を用意します。自分はnodenvを使っているのでこんな感じ。
$ mkdir user
$ cd user
$ nodenv local 14.15.0
$ echo node_modules > .gitignore
次にapollo serverを入れて、index.jsを生やします。
$ npm init --yes
$ npm i apollo-server graphql
$ touch index.js
次にscehmaを定義します。今回はindexに全部詰め込んでいきます。
簡単にuserのschemaを定義しています。
const { gql } = require('apollo-server');
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
me: User
}
type User {
id: ID!
username: String
}
`;
次にresolver
// ~~~省略
const resolvers = {
Query: {
me() {
return { id: "1", username: "@savacan" }
}
}
}
次にapollo serverの実行
雑に3001番に起動するようにしておきます。
const { gql, ApolloServer } = require('apollo-server');
// ~~~省略
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});
server.listen(3001).then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`user serverが ${url} に立ち上がったよ!!!`);
})
最後に起動コマンドをpackage.jsonのscriptsに追加します。
"start": "node ./index.js"
このコマンドで起動し、以下の画面にアクセスできれば無事apollo serverが立ち上がっています。
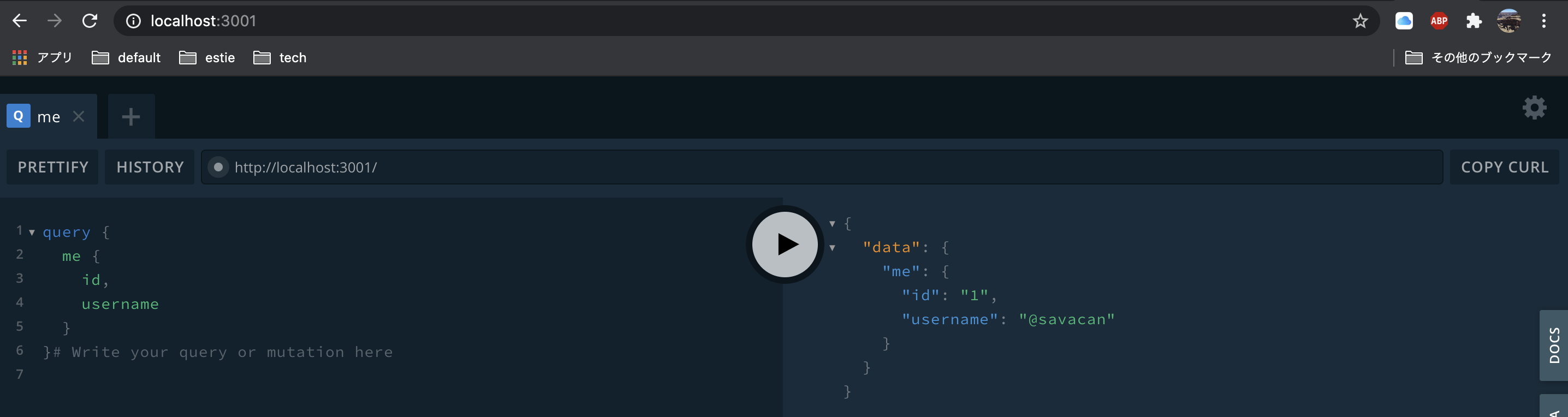
この画面では立ち上がっているgraphql serverに対して実際にqueryを投げることができるので試しに投げてみましょう。
無事返ってきていますね。
では早速federationの実装サービスを作っていきます。
user serviceの実装
まず、federation用のモジュールをインストールします。
$ npm i @apollo/federation
apollo federationではEntityという概念が登場します。
federation architectureでは他の実装サービスがこのサービスが公開しているTypeを拡張できるように実装する必要があり、そうすることでgatewayがqueryをプランニングできるようになっています。
上記で作成したschemaとresolverをfederationに対応した形に変更します。
今回バックエンドサーバは用意していないので雑にユーザを定義しています。
const {
ApolloServer,
gql,
ApolloError
} = require("apollo-server")
const users = [
{ id: "0", username: "@test" },
{ id: "1", username: "@savacan" },
{ id: "2", username: "@alice" },
{ id: "3", username: "@bob" }
]
const fetchUserById = (id) => {
const user = users.find(e => e.id === id);
if (!user) throw new ApolloError("user not found", 404);
return user
}
const typeDefs = gql`
extend type Query {
me: User
}
type User @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID!
username: String
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
me() {
return { id: "1", username: "@savacan" }
}
},
User: {
__resolveReference(user) {
return fetchUserById(user.id)
}
}
}
最後にserverに渡すschemaをfederatedSchemaにしてDoneです。
const { buildFederatedSchema } = require("@apollo/federation")
// ~~~省略
const server = new ApolloServer({
schema: buildFederatedSchema([{ typeDefs, resolvers }])
});
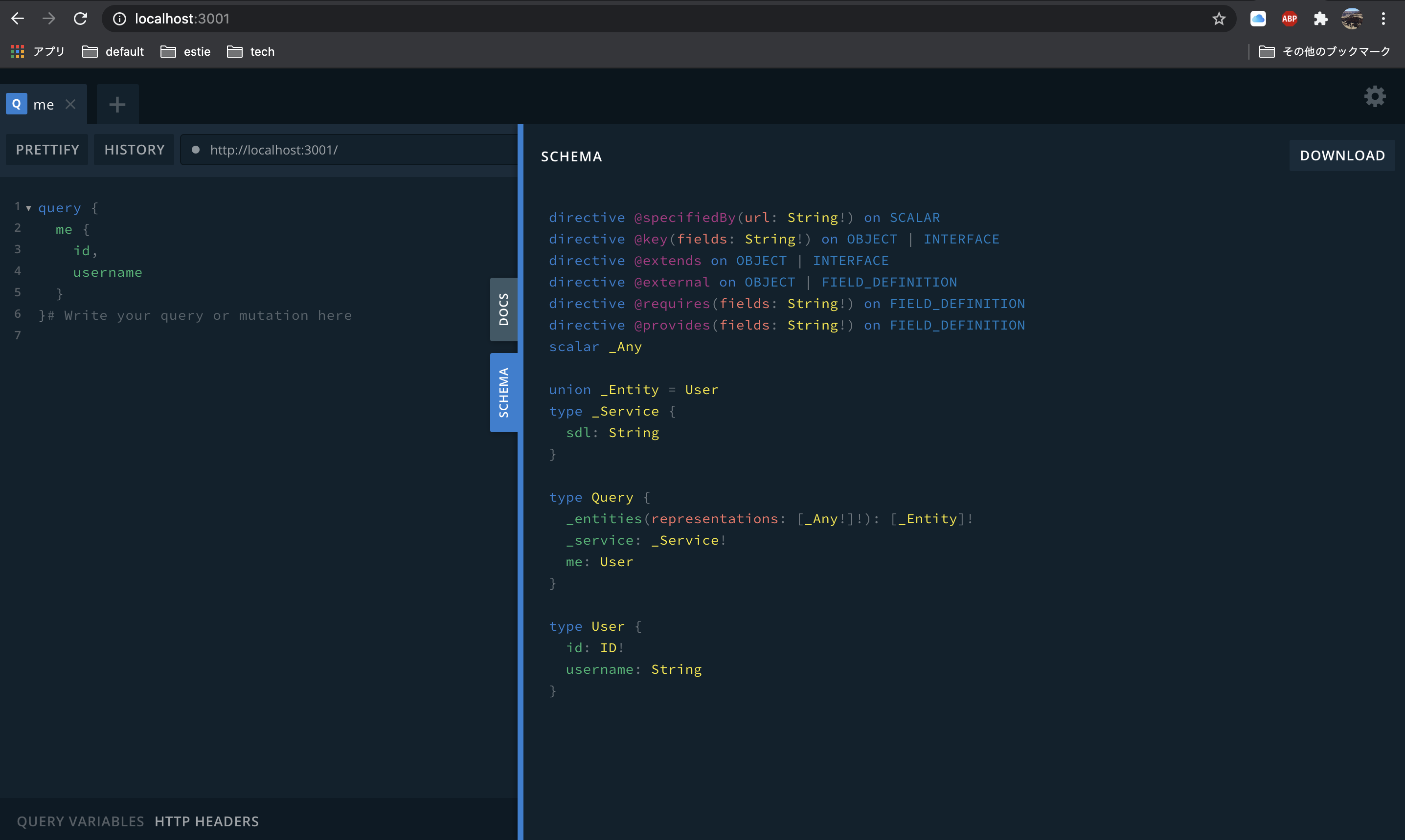
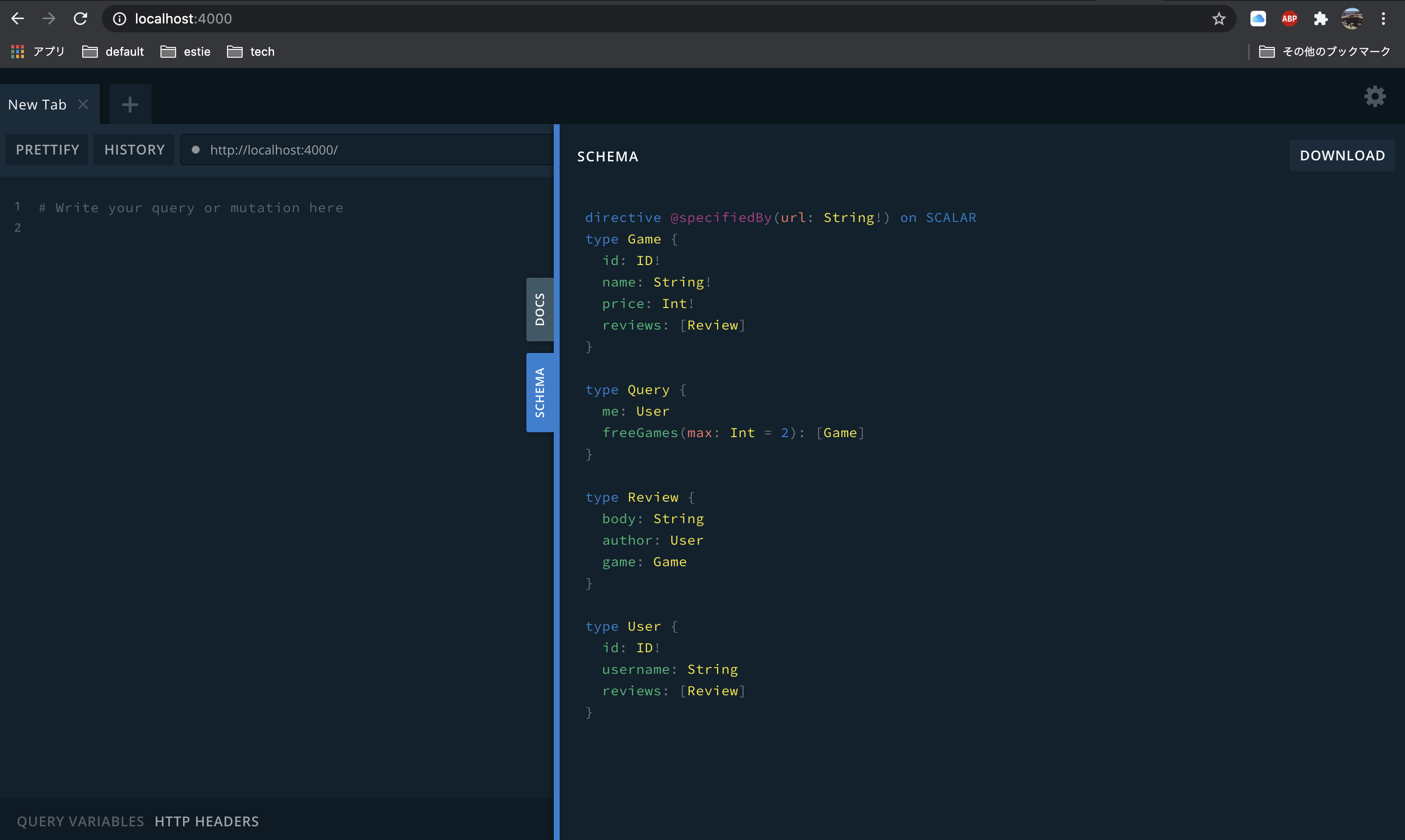
早速起動して、どういったschemaが公開されているのか確認してみましょう。
なにやらよくわからない物が生えてきていますね……
_serviceはsdlを, _entitiesは_Entityを返すようになっていそうです。
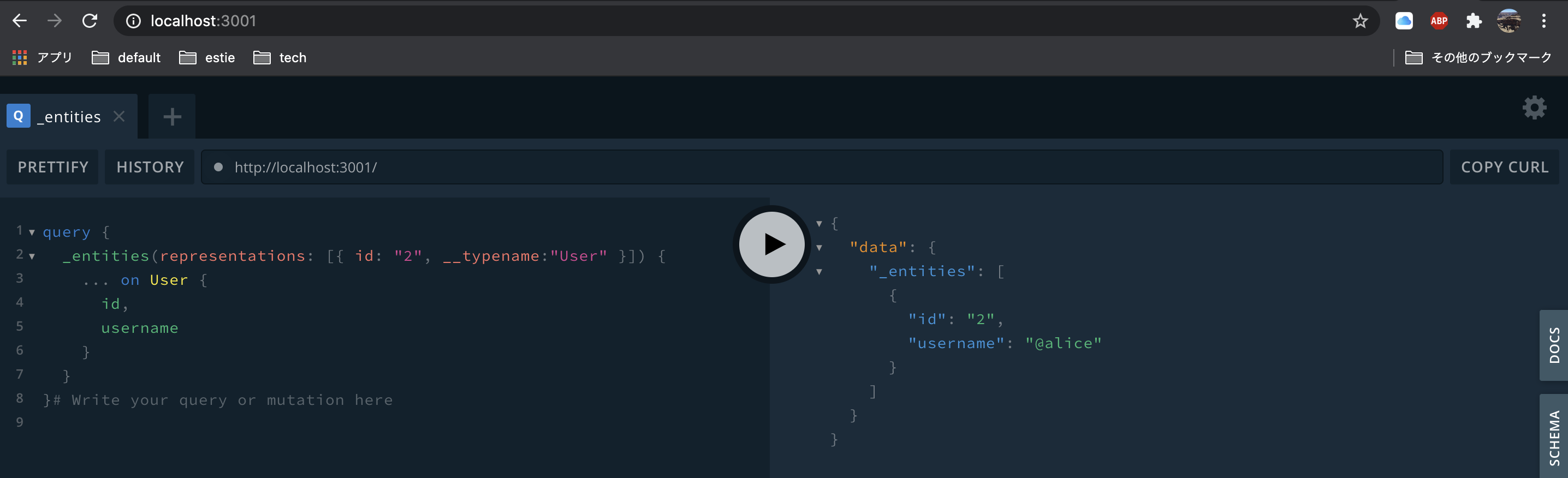
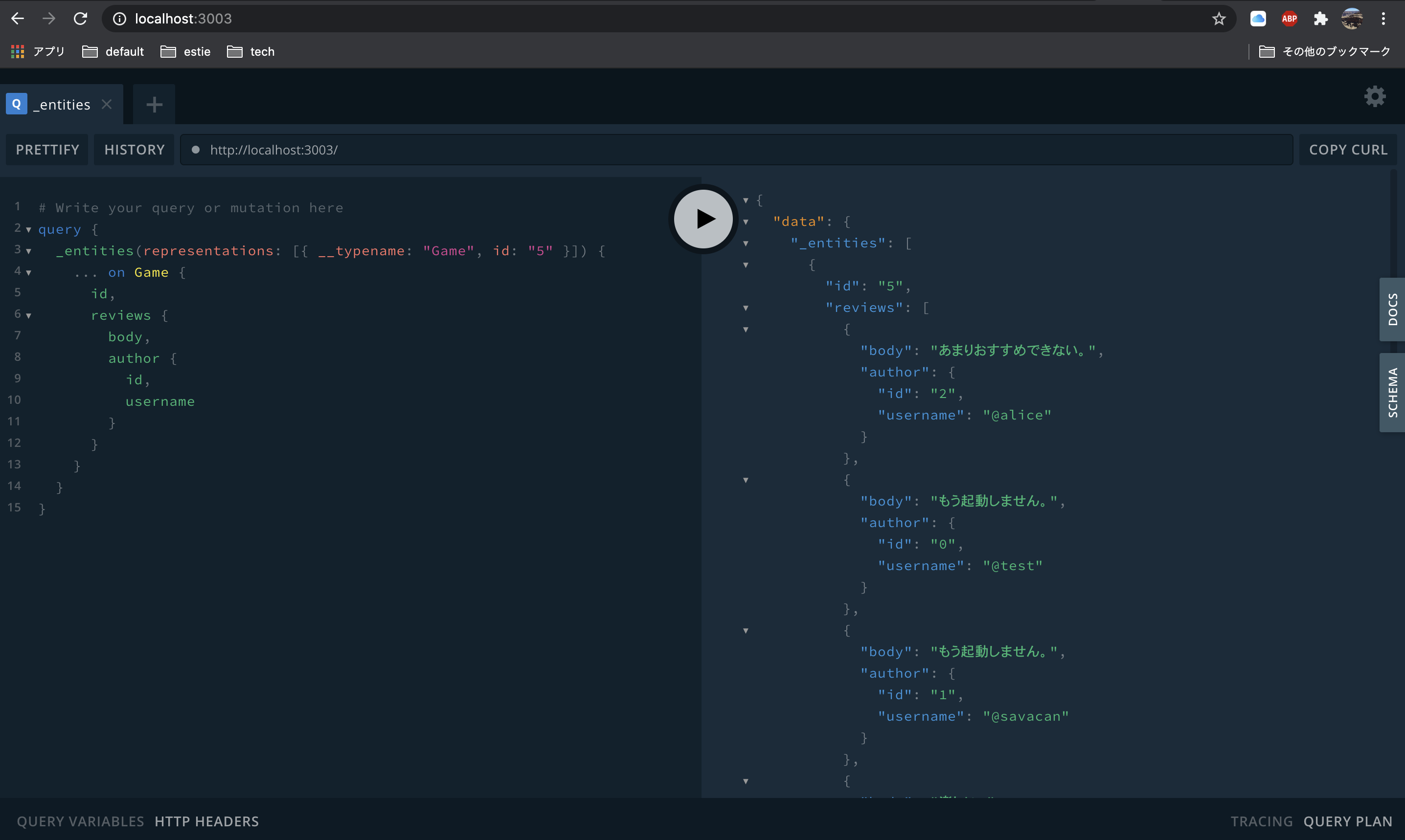
とりあえず試しに_entitiesを叩いてみましょう。
どうやらこのqueryを使ってentityを解決するようですね。
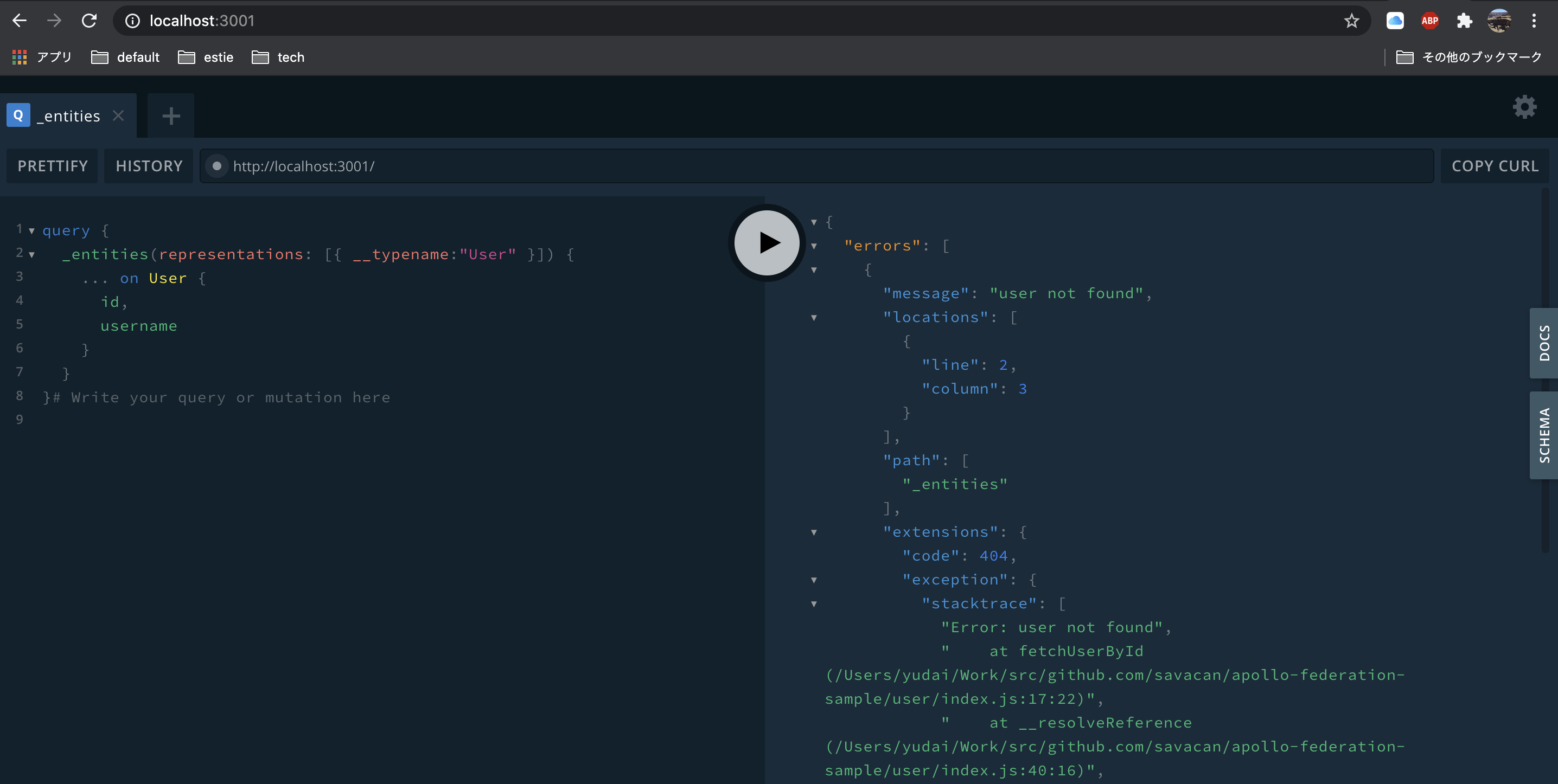
idを指定せずに叩いてみると。
ちゃんとErrorが返ってきていますね。
game serviceの実装
userと同様にapollo serverを作っていきます(割愛
そして以下のようなindex.jsを作成。
const {
ApolloServer,
gql,
ApolloError
} = require("apollo-server")
const { buildFederatedSchema } = require("@apollo/federation")
const games = [
{ id: "0", name: "ABA", price: 0 },
{ id: "1", name: "Call and Dirty: CW", price: 8000 },
{ id: "2", name: "Call and Dirty: MW", price: 8000 },
{ id: "3", name: "Battle ground V", price: 10000 },
{ id: "4", name: "Battle ground 1", price: 9000 },
{ id: "5", name: "APEX Kings", price: 0 },
{ id: "6", name: "User Unknown Battle Fields", price: 0 },
{ id: "7", name: "DUUM", price: 6000 },
{ id: "8", name: "Counter Straight", price: 0 },
{ id: "9", name: "Counter Straight: GO", price: 0 },
]
const fetchGameById = (id) => {
const game = games.find(e => e.id === id);
if (!game) throw new ApolloError("game not found", 404);
return game
}
const fetchFreeGames = ({ max }) => {
const freeGames = games.filter(e => e.price === 0);
return freeGames.slice(0, max);
}
const typeDefs = gql`
extend type Query {
freeGames(max: Int = 2): [Game]
}
type Game @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID!
name: String!
price: Int!
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
freeGames(_, { max }) {
return fetchFreeGames({ max });
}
},
Game: {
__resolveReference(game) {
return fetchGameById(game.id)
}
}
}
const server = new ApolloServer({
schema: buildFederatedSchema([{ typeDefs, resolvers }])
});
server.listen(3002).then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`game serverが ${url} に立ち上がったよ!!!`);
});
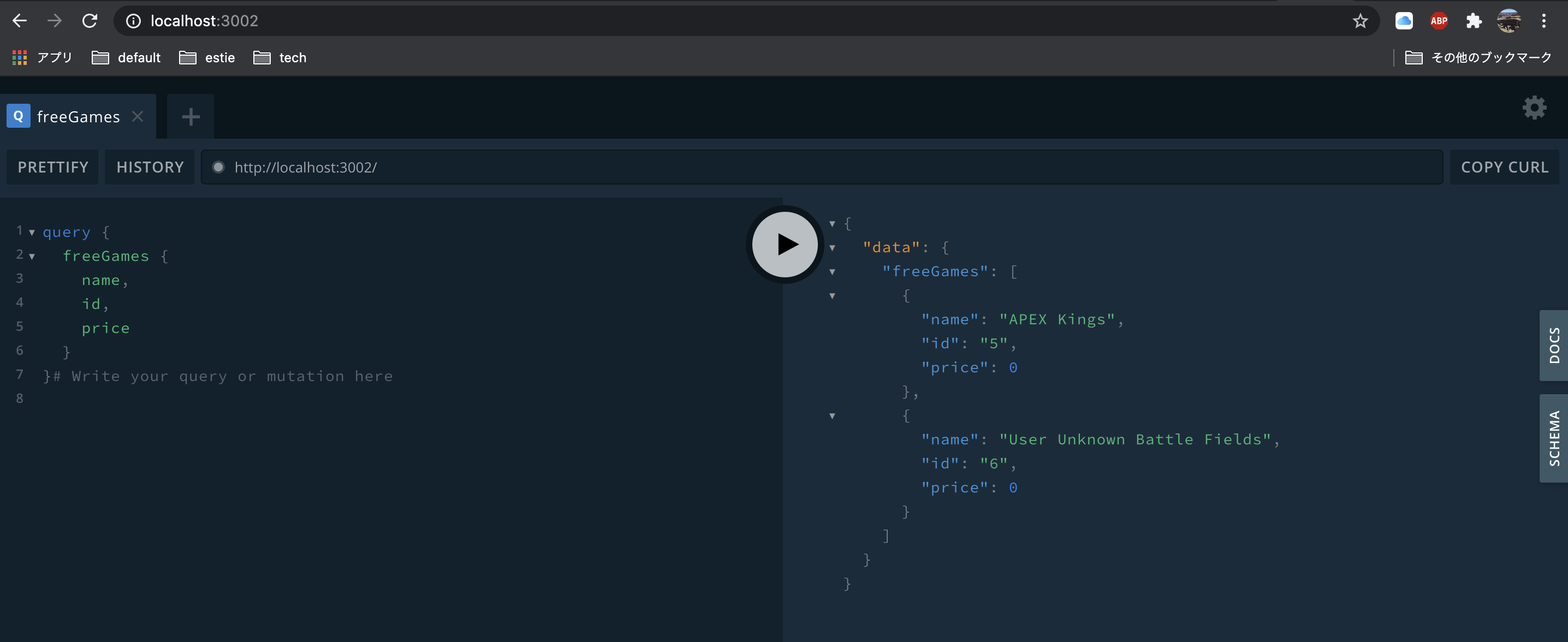
無料ゲーム取得のqueryがあるゲーム情報のサービスですね。
こちらも単独で立ち上げて確認してみましょう。
無事無料ゲームの一覧が取得できていますね。良い感じです。
review serviceの実装
userと同様にapollo serverを作っていきます(割愛
そして以下のようなindex.jsを作成。
このサービスはuserとgameを拡張するものになっており、少し複雑になっています。
(reviewを雑に生成してます許してください……)
const { ApolloServer, gql, ApolloError } = require("apollo-server");
const { buildFederatedSchema } = require("@apollo/federation");
const arr = (n) => [...Array(n)].map((_, i) => i);
const setupReviews = () => {
const users = [
{ userId: "0", username: "@test" },
{ userId: "1", username: "@savacan" },
{ userId: "2", username: "@alice" },
{ userId: "3", username: "@bob" },
];
const reviewBody = [
"神ゲーすぎる",
"今後のアプデに期待",
"楽しい。",
"あまりおすすめできない。",
"もう起動しません。"
]
// randomにreviewを100件生成
const randomIdx = max => Math.floor(Math.random() * Math.floor(max));
const createRandomReview = id => ({ id, body: reviewBody[randomIdx(5)], ...users[randomIdx(4)], gameId: "" + randomIdx(10) });
const result = arr(100).map(createRandomReview);
return result;
};
const reviewsData = setupReviews();
const fetchReviewsByUserId = (userId) => {
const reviews = reviewsData.filter(e => e.userId === userId);
return reviews;
};
const fetchReviewsByGameId = (gameId) => {
const games = reviewsData.filter((e) => e.gameId === gameId);
return games;
};
const typeDefs = gql`
type Review {
body: String
author: User @provides(fields: "username")
game: Game
}
extend type User @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID! @external
username: String @external
reviews: [Review]
}
extend type Game @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID! @external
reviews: [Review]
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Review: {
author(review) {
return { __typename: "User", id: review.userId, username: review.username }
},
game(review) {
return { __typename: "Game", id: review.gameId }
}
},
User: {
reviews(user) {
return fetchReviewsByUserId(user.id);
},
},
Game: {
reviews(game) {
return fetchReviewsByGameId(game.id);
}
}
};
const server = new ApolloServer({
schema: buildFederatedSchema([{ typeDefs, resolvers }]),
});
server.listen(3003).then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`review serverが ${url} に立ち上がったよ!!!`);
});
かなり複雑に見えますがやっていることは単純です。
まず、reviewは当然gameに紐付きますのでGameEntityを拡張しています。
また同様に、userは自分の書いたreviewを確認できるのでUserEntityを拡張しています。
そして、reviewにはGameとUserが紐づいています。
reviewは単独でqueryを投げられることは想定していません。
さて実際に生成されるschemaを確認してみましょう。
queryを定義していないので、実行できるのはapolloが勝手に生やしたqueryのみです。
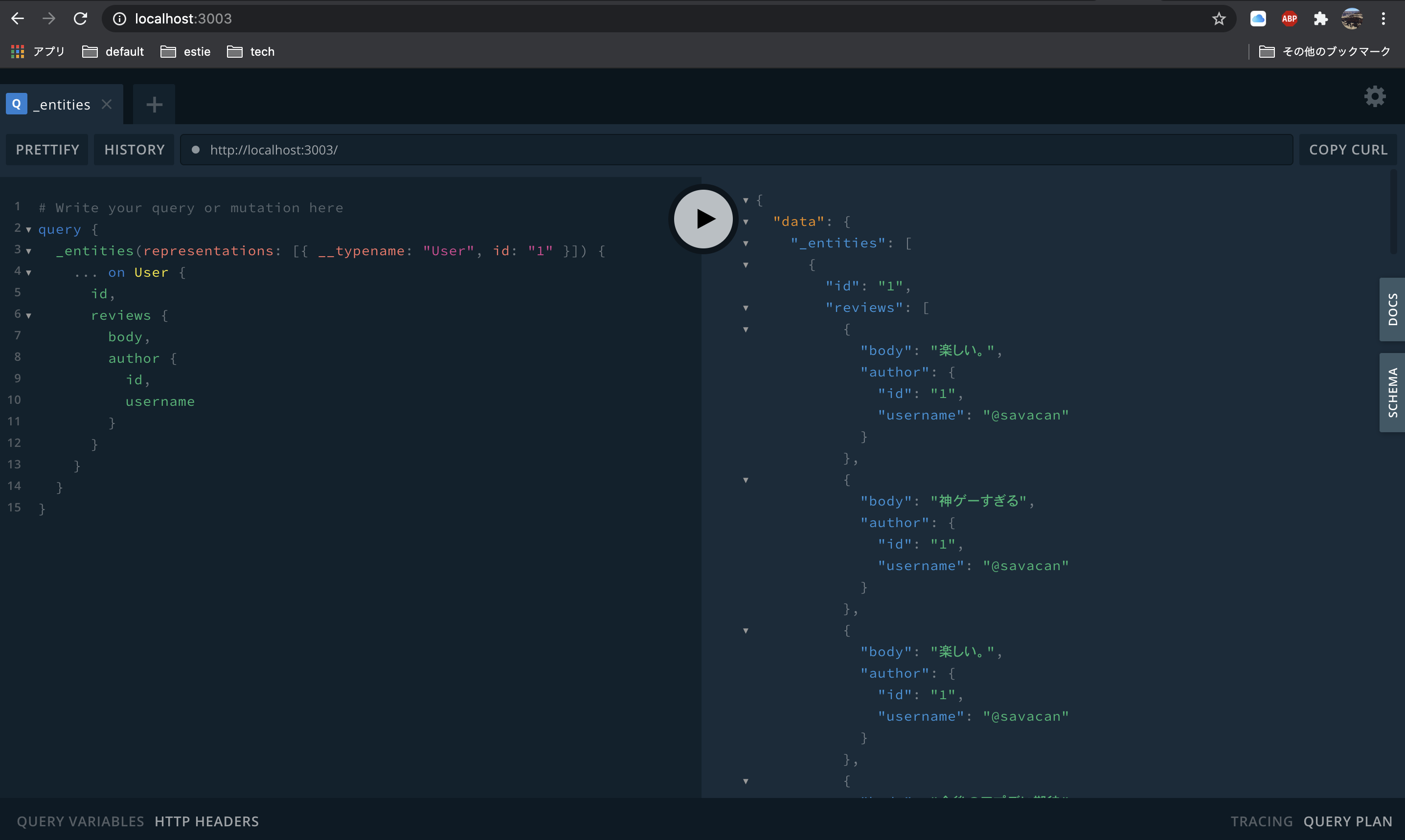
では実際に特定のUserに紐づくreviewが取得できるのか、queryを実行してみましょう。
当然ですが、他のサービスとまだ結合はされていないので、このreviewサービスで定義されている値しか取得することはできません。
@savacanさんは比較的好意的レビューが多いようですね。
次に特定のゲームに紐づくqueryを実行してみましょう。
どうやらこのゲームの評判はいまいちのようですね……
それではserviceの準備はできたのでこれらのschemaを結合していきましょう。
 gatewayを実装する
gatewayを実装する
これまで作成してきたserviceをgatewayで結合していきましょう。
まず、node環境を用意した後に以下のパッケージをインストールします。
$ npm i @apollo/gateway apollo-server graphql
次にindex.jsを作成します。
const { ApolloServer } = require('apollo-server');
const { ApolloGateway } = require('@apollo/gateway');
const gateway = new ApolloGateway({
serviceList: [
{ name: 'user', url: 'http://localhost:3001' },
{ name: 'game', url: 'http://localhost:3002' },
{ name: 'review', url: 'http://localhost:3003' },
],
});
const server = new ApolloServer({
gateway,
subscriptions: false,
});
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`);
});
gatewayの初期化時、serviceListに各serviceの場所と名前を指定しています。
この実装をみてわかる通りgatewayはserviceの詳細については何も知りません。知っているのは名前と場所だけです。
gatewayの実装はたったこれだけです。本当にschemaはうまく結合されるのでしょうか?
最後にpackage.jsonに起動コマンドを追加して実行してみましょう。
"start": "node ./index.js"
注意) この際、対象となるserviceが全て起動していないとうまく起動できませんので気をつけてください。
無事立ち上がったのでschemaを確認してみましょう。
非常にシンプルに各schemaが結合されていますね!
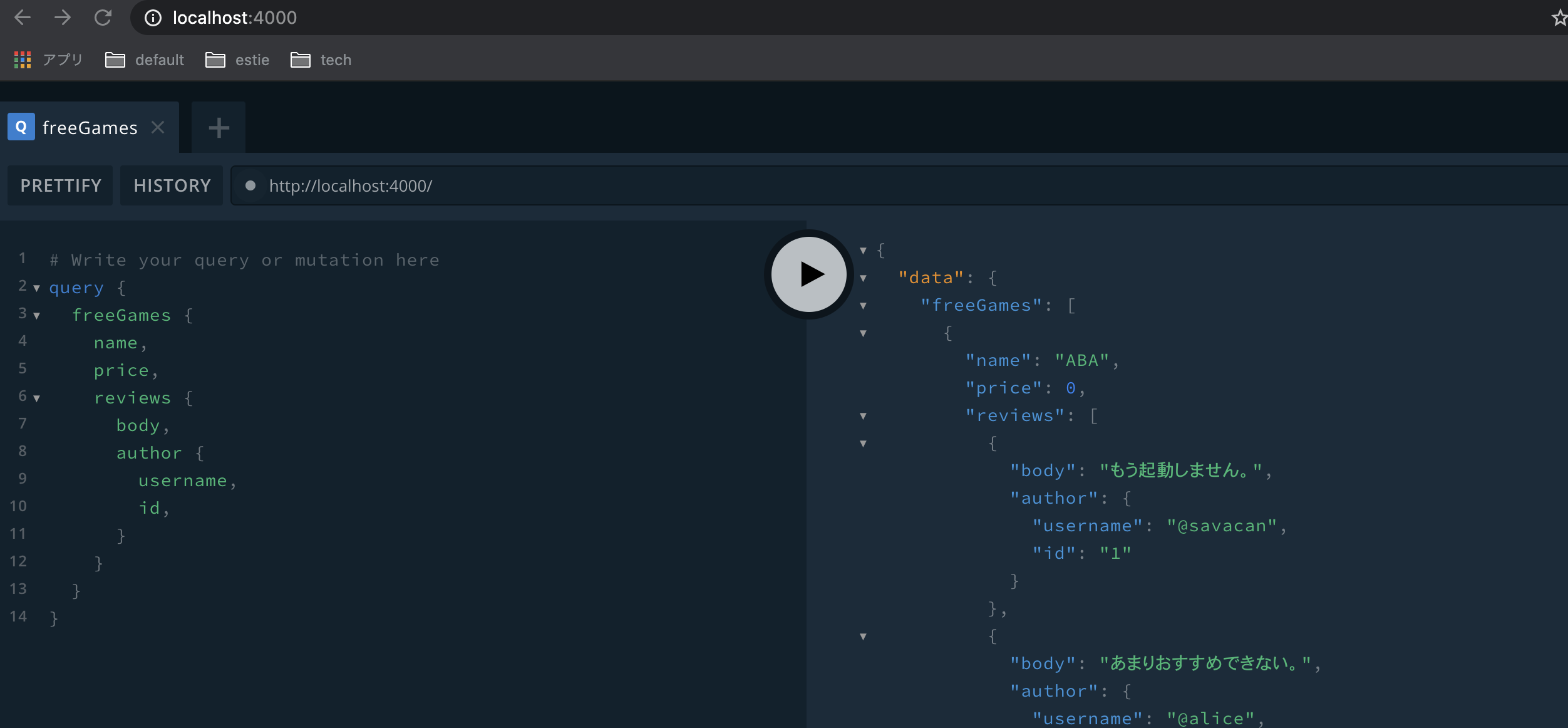
早速無料ゲームの評判を覗いてみましょう。
きっちりと複数サービスに跨ったデータが取得できていることがわかるかと思います。
どうやらこのゲームは評価が分かれている模様……
 色々ためしてみる
色々ためしてみる
動く環境が出来上がったので、色々と試していこうと思います。
serviceのschemaが結合できない場合
せっかくserviceのサーバが分かれているのだから、おそらく各サービスは別のチームが作成しているものかと思います。そんな中で、結合できないschemaを定義してしまったチームが現れた場合gatewayはどうなるのでしょうか?やってみましょう。
reviewサービスはGameEntityを拡張していますが、reviewチームもgameチームの一部のデータソースにアクセスできるというシチュエーションを考えます。パフォーマンスの効率化のためGameEntityの内、nameもreviewチームが解決しようとした場合、以下のようなschemaに変更することが考えられます。
const typeDefs = gql`
type Review {
body: String
author: User @provides(fields: "username")
game: Game @provides(fields: "name")
}
extend type User @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID! @external
username: String @external
reviews: [Review]
}
extend type Game @key(fields: "id") {
id: ID! @external
name: String @external
reviews: [Review]
}
`;
しかし、GameEntityのnameは必須fieldとして定義されています。
この状態でgatewayを起動しようとすると以下のようにErrorで教えてくれます。
gatewayが発行しているqueryをみてみる
gatewayの初期化時にdebugモードを指定できるので、そこで確認してみましょう。
const gateway = new ApolloGateway({
serviceList: [
{ name: 'user', url: 'http://localhost:3001' },
{ name: 'game', url: 'http://localhost:3002' },
{ name: 'review', url: 'http://localhost:3003' },
],
debug: true,
});
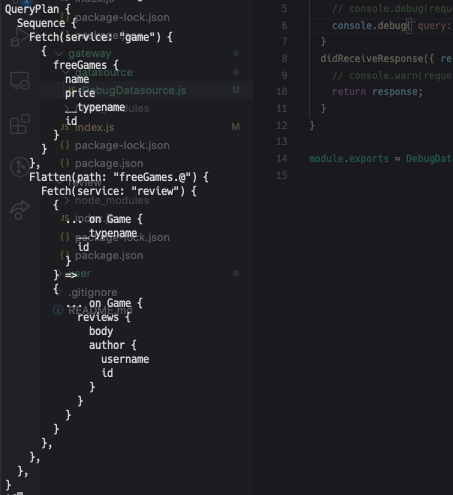
次のようなqueryを発行した場合
以下のようにplanningされているようですね。
Gameサービスのqueryを実行し、 次にReviewサービスでentityを解決しているようです。
概ね予想通りの挙動ですね!だんだん仕組みが理解できてきたような気がします。
 まだまだ試したいことはありますが
まだまだ試したいことはありますが
無限に時間を吸われそうなのでこの辺りで。
今回はunmanagedと呼ばれるモードでの検証をやってきましたが、次はmanagedモードにチャレンジしたいですね。一応念のために次にやりたいことをメモしておきます。
- managed modeの挙動を追う
- custom directiveを試す
- test書いてみる
- apollo以外でservice実装してみる
- 実装を読む
 おわりに
おわりに
想定していたよりずっと簡単にローカルで動くものを試すことができました!
schema stitchingではgatewayとなるサーバに色々と書く必要がありましたが、apollo federationではgatewayを本当に薄くつくることができそうですね。まだ挙動を確かめているような段階で、実際のユースケースに当てはめてどう、といったレベルでの把握はできていませんが、新しい技術に触れられて満足しています。実際にapollo federationを運用していらっしゃる方がいれば是非話を聞いてみたいなぁと思いました。
まだ触っていない方は是非触ってみてください!
 さいごに
さいごに
僕が所属する 株式会社estieでは、Python/JS/Rubyエンジニアを積極採用中です!
不動産領域でのプロダクト開発に興味のある方は是非、blogや採用ページをご覧ください!