==>関連記事を書きました(2021/12/01)。FastAPI と SQLModel - Qiita
今回は、FastAPIでDBを使う方法を紹介します。ここではsqlite3を使用しますが、PostgreSQLやMySQLなども同様に使えるはずです。
FastAPIからDBを使う方法はいくつかありますが、ここではTortoise ORMというマッパーを使用します。DjangoのORMにインスパイヤーされたとありますが、Djangoよりは使いやすい気がします。しかしFastAPIはその根幹のところでPydantic クラスを採用していて、Tortoise ORMのクラスと重複してしまいますので両者のコンバートなどが必要になり少し面倒です。
FastAPIやPydantic、Tortoise ORMなどの基本的なところは以下の過去記事を参照してください。
【過去記事】
FastAPIで作るWebアプリ - 基本
FastAPIで作るWebアプリ - Body validation
Pydantic Data Model入門
Tortoise ORM入門
まずモデルの定義を行います。
from tortoise import fields
from tortoise.models import Model
from tortoise.contrib.pydantic import pydantic_model_creator
class Users(Model):
id = fields.IntField(pk=True)
name = fields.CharField(max_length=100)
age = fields.IntField()
User_Pydantic = pydantic_model_creator(Users, name="User")
UserIn_Pydantic = pydantic_model_creator(Users, name="UserIn", exclude_readonly=True)
ここで注意すべきことは、pydantic_model_creatorで、Tortoise ORMモデルからpydanticモデルを作成していることです。
User_Pydantic はUsersと同じフィールドを持ちますが、UserIn_Pydantic はidフィールドは持ちません。このことは後でSwgger UIで確認します。
以下がメインです。create_userの一つしかエンドポイントを持たない簡単なものです。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from model import User_Pydantic, UserIn_Pydantic, Users
from tortoise.contrib.fastapi import register_tortoise
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/users", response_model=User_Pydantic)
async def create_user(user: UserIn_Pydantic):
user_obj = await Users.create(**user.dict(exclude_unset=True))
return await User_Pydantic.from_tortoise_orm(user_obj)
register_tortoise(
app,
db_url="sqlite://db.sqlite3",
modules={"models": ["model"]},
generate_schemas=True,
add_exception_handlers=True,
)
create_user()の引数がUser_PydanticでなくUserIn_Pydanticの型であることに注意してください。Requestパラメータにはidは含まれないからです。
(1) Response Model
Response Model - FastAPI
@app.get()や@app.post()などのデコレーターのパスオペレーションの中にresponse_modelを宣言することができます。指定できるモデルはPydantic modelです。Pydantic modelのリスト[User_Pydantic]などもOKです。
response_modelを使う理由はデータをValidateしたり、ResponseのためのJSON Schemaを追加したり、output データを指定したmodelに制限するためです。
(2) model.dict(...)
model.dict(...) - Pydantic
Pydanticモデルをdictにコンバートするための方法です。
exclude_unset引数は、モデルを作成するときに明示的に値を指定されていないフィールドは排除される、というものです。デフォルト値とかですかね。
User_Pydantic.from_tortoise_ormはTortoiseモデルのオブジェクトをPydanticのオブジェクトに変換します。User_Pydantic.from_tortoise_orm(user_obj)をそのままreturnしているのは、Response Modelの宣言に即しています。
(3) register_tortoise
- FastAPIのためのTortoiseの設定を行います。
- modules={"models": ["model"]}でmodel.pyにモデルクラスが定義されていることを教えます。
- generate_schemas=Trueで自動的にスキーマを生成します。
- add_exception_handlers=Trueでカスタム例外ハンドラーをFastAPIに追加します。
Swgger UIでの検証
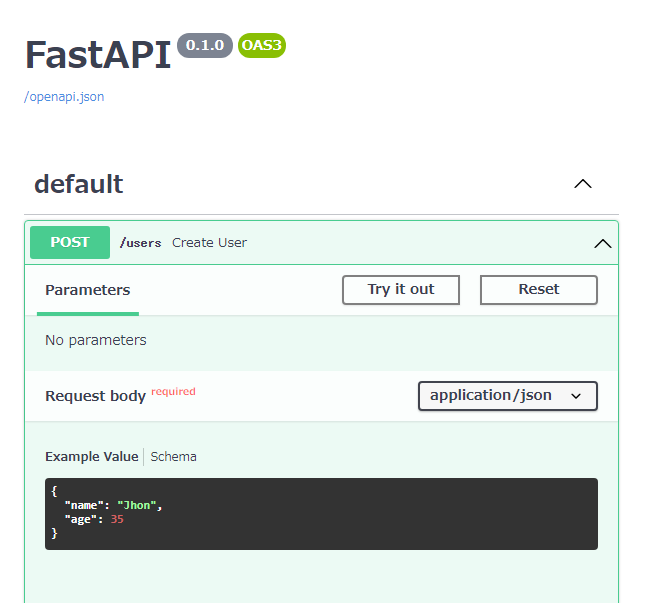
以下Swgger UIで簡単なテストを行いました。
RequestはUserIn_Pydantic型なのでidは含まれていません。
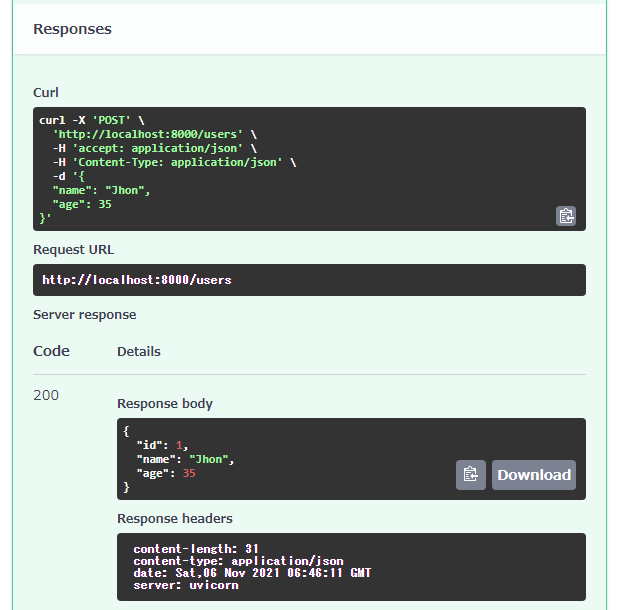
Response bodyを見ると、Response Modelが正しく動作しているのが確認できます。
試しにcreate_user()の引数をUser_Pydanticにしてみると、idが現れます。Requestにidを指定するのは、もちろん現実的な意味を持ちませんが。
今回の記事でFastAPIの基本的なところを押さえることができたのかな、と思います。が多分まだまだいろいろありますね。認証とか。
とりあえず今回は以上です。