はじめに
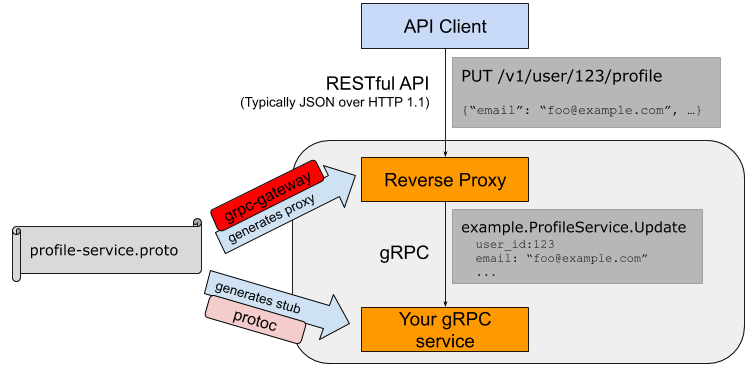
今回はgrpc-gatewayを用いて、gRPCサーバをREST APIに対応させてみます。
成果物はこちらのgithubにおいてありますので合わせてご確認ください。
grpc-gatewayとは
grpc-gatewayのリポジトリには
The grpc-gateway is a plugin of the Google protocol buffers compiler protoc. It reads protobuf service definitions and generates a reverse-proxy server which 'translates a RESTful HTTP API into gRPC. This server is generated according to the google.api.http annotations in your service definitions.
https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway
つまり、gRPCサーバで定義しているprotobufを読み取り、RESTful HTTP APIをgRPCに変換するリバースプロキシサーバの役割を担うことができる、というものです。
gRPCサーバの作成
なにはともあれ、grpc-gatewayを試すにはgRPCサーバが必要ですので、まずはそれをサクッと作成します。
まずはprotoファイルの定義から
syntax = "proto3";
package proto;
service SayHello {
rpc Echo(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse) {}
}
message HelloRequest {
string userName = 1;
}
message HelloResponse {
string message = 1;
}
protocを使って、.protoファイルをビルドして、.pb.goファイルを作成してください。
リクエストにuserNameを指定するとmessageを返すEchoメソッドを作成しました。
type helloService struct{}
func (hs *helloService) Echo(ctx context.Context, req *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloResponse, error) {
return &pb.HelloResponse{
Message: "hello, " + req.UserName,
}, nil
}
func Start(port string) {
listen, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":"+port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("server listen: " + listen.Addr().String())
server := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterSayHelloServer(server, &helloService{})
if err := server.Serve(listen); err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
return
}
このEchoメソッドはusenameに対して hello, username を返すように設定します。
Start関数でサーバ起動できます。
これでgRPCサーバは作成できました。
実際に疎通確認してみてもいいでしょう。それ用のクライアントサーバも作成します。
ここから先はgrpc-gatewayには必要ありません。
func Echo(conn *grpc.ClientConn, name string) {
client := pb.NewSayHelloClient(conn)
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)
defer cancel()
resp, err := client.Echo(ctx, &pb.HelloRequest{UserName: name})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Printf("message: %s\n", resp.Message)
}
func Call(port string) {
addr := fmt.Sprintf("localhost:" + port)
conn, err := grpc.Dial(addr, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
Echo(conn, "sakas")
defer conn.Close()
}
Call関数でEcho(conn, "sakas")をすることでusername=sakasでEchoメソッドにリクエストを投げます。
func main() {
serverPort := "19003"
go func() {
server.Start(serverPort)
}()
client.Call(serverPort)
return
}
試しに起動させると疎通できていることがわかると思います。
もちろん今はgrpc-gatewayを作成していませんので、REST APIでは疎通できません。
grpc-gatewayの作成
ここから本題です。
このgRPCサーバにgrpc-gatewayでREST API対応していきましょう。
protoファイルの修正
protoファイルを以下のように変更します。
syntax = "proto3";
package proto;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
service SayHello {
rpc Echo(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/echo"
};
}
}
message HelloRequest {
string userName = 1;
}
message HelloResponse {
string message = 1;
}
gRPC stubの生成
その上で、pb.goファイルを生成していきます。
grpc-gateway対応したので、import "google/api/annotations.proto";がパスを認識できるように、grpc-gatewayのパスを追加でincludeさせます。
公式のREADMEには
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--ruby_out=. \
path/to/your_service.proto
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=grpc_ruby_plugin \
--grpc-ruby_out=. \
path/to/your_service.proto
と書かれていましたが、自分はGO111MODULE=onでgrpc-gatewayをimportしたので、gomoduleでインストールされるパスを指定しました。
また、自分はbrewでprotobufを入れたため、protobufをimportしたいときに追加でIPATHを指定しています。
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/pkg/mod/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway@v1.12.2/third_party/googleapis \
-I/usr/local/opt/protobuf/include \
--go_out=plugins=grpc:. \
./proto/service.proto
grpc-gatewayの生成
リバースプロキシを生成します。
こちらも、公式READMEでは以下のようになっていましたが、
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:. \
path/to/your_service.proto
--pluginでprotoc-gen-grpc-gatewayの明記
protobufのIPATH追加
を変更しました。
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I/usr/local/opt/protobuf/include \
-I$GOPATH/pkg/mod/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway@v1.12.2/third_party/googleapis \
--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc-gateway=$GOPATH/bin/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway \
--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:. \
./proto/service.proto
これでpb.gw.goファイルが生成できます。
gatewayサーバの作成
func run(serverPort string, gwPort string) error {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()}
endpoint := fmt.Sprintf(":" + serverPort)
err := gw.RegisterSayHelloHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, endpoint, opts)
if err != nil {
return err
}
log.Printf("gateway port:" + gwPort)
log.Printf("server listen: " + serverPort)
return http.ListenAndServe(":"+gwPort, mux)
}
func Start(serverPort string, gwPort string) {
flag.Parse()
defer glog.Flush()
if err := run(serverPort, gwPort); err != nil {
glog.Fatal(err)
}
}
mux := runtime.NewServeMux() でhttpヘッダ←→gRPC contextの変換をしてくれます。
NewServeMux()の中身を追っていくと
func RegisterSayHelloHandlerClient(ctx context.Context, mux *runtime.ServeMux, client SayHelloClient) error {
mux.Handle("GET", pattern_SayHello_Echo_0, func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request, pathParams map[string]string) {
...
resp, md, err := request_SayHello_Echo_0(rctx, inboundMarshaler, client, req, pathParams)
...
forward_SayHello_Echo_0(ctx, mux, outboundMarshaler, w, req, resp, mux.GetForwardResponseOptions()...)
...
}
return nil
}
この記述があり、GETリクエストをhandler登録していて、内部ではresponseを取得してhttpで返却していることがわかります。
これだけの変更でgrpc-gatewayが完成します。
疎通確認
実際にREST APIを投げてみましょう
func main() {
serverPort := "19003"
gwPort := "50000"
go func() {
server.Start(serverPort)
}()
gateway.Start(serverPort, gwPort)
return
}
gRPCサーバのポートを19003番、gatewayのポートを50000番で起動させます。
❯ curl -XGET "localhost:50000/echo?userName=sakas1231"
{"message":"hello, sakas1231"}
無事、疎通確認ができました![]() 🎉
🎉![]() 🎉
🎉
まとめ
gRPCサーバさえあれば、導入しきい値は結構低いのではないかなと思っています。かなり簡単にgrpc-gatewayの疎通確認ができました。
再掲ですが、githubにコードを公開しています![]()
https://github.com/KatsuyaAkasaka/grpc-gateway-sample