この記事作成の動機
Fortranの標準ライブラリstdlibの紹介や、fpm (Fortran Package Manager)の使い方等の記事を参考に、実際にこれらを利用したプログラムを作成しました。その際、折角なので、遊び半分で「FortranからRを操作してみよう」と思い立ち、データまたはコマンドをRへ流す方法を考えました。本記事ではM_processライブラリを用いることにします。
準備
fpmを利用すれば、依存関係にあるライブラリを芋蔓式に取得可能です。
fpmのダウンロードとインストール
wget https://github.com/fortran-lang/fpm/releases/download/v0.5.0/fpm-0.5.0-linux-x86_64
パスの通っている場所(例えば/usr/local/bin/) にバイナリを移動し、実行権限を付けます。
chmod +x fpm-0.5.0-linux-x86_64
# ln -s fpm-0.5.0-linux-x86_64 fpm #好みに応じてシンボリックリンクを作る
fpm new R_fortran
+ mkdir -p koma_fortran
+ cd koma_fortran
+ mkdir -p R_fortran/src
+ mkdir -p R_fortran/app
+ mkdir -p R_fortran/test
+ git init R_fortran
Initialized empty Git repository in /...ファイルパス..../R_fortran/.git/
fpm: Leaving directory '/home'
cd R_fortran
Fortranでパイプラインを利用するためのライブラリ取得
githubから、stdlibとM_processをダウンロードして使ってみます。
fpm.tomlに下記2行を付け加えるだけで、ライブラリの取得やビルドについて、fpmがよしなに対処してくれます。
[dependencies]
M_process = { git = "https://github.com/urbanjost/M_process.git" }
stdlib = { git="https://github.com/fortran-lang/stdlib", branch="stdlib-fpm" }
srcディレクトリの中身
fpmによって生成されるsrcディレクトリの中に、Rを扱うモジュールを作成しました。
ここでは練習がてら、実装とインターフェイスをsubmoduleを使って分離しています。
R_fortran.f90
module R_fortran
use M_process
implicit none
private
character(len=10),protected :: rcmd="R"
public set_r_cmd
type,public :: t_robj
type(streampointer) :: fp
integer :: ierr
contains
procedure :: open => open_r_process
procedure :: close => close_r_process
procedure :: write => write_r_process
procedure :: fflush => fflush_r_process
end type
interface
module subroutine set_r_cmd(txt)
character(len=*),intent(in) :: txt
end subroutine
module subroutine open_r_process(self,option)
class(t_robj),intent(inout) :: self
character(len=*),intent(in),optional :: option
end subroutine
module subroutine close_r_process(self)
class(t_robj),intent(inout) :: self
end subroutine
module subroutine write_r_process(self,line)
class(t_robj),intent(inout) :: self
character(len=*),intent(in) :: line
end subroutine
module subroutine fflush_r_process(self,line)
class(t_robj),intent(inout) :: self
character(len=*),intent(in) :: line
end subroutine
end interface
end module R_fortran
R_fortran_sub.f90
submodule (R_fortran) R_fortran_sub
contains
module procedure set_r_cmd
rcmd=txt(1:len_trim(txt))
end procedure
module procedure open_r_process
use stdlib_optval
character(len=:),allocatable :: txt
txt=Rcmd//" "//optval(option,"--no-save -q")
call process_open_write(txt, self%fp, self%ierr)
end procedure
module procedure close_r_process
call process_close(self%fp, self%ierr)
end procedure
module procedure write_r_process
call process_writeline(line(1:len_trim(line)),self%fp, self%ierr)
end procedure
module procedure fflush_r_process
!self%ierr=fflush(self%fp%handle)
end procedure
end submodule
app ディレクトリの中身
- sub1ルーチンは、Rの
lm.glmに関するデモを実行しています。 - sub2ルーチンでは、fortranで生成した配列を、テキストファイル経由で
Rへ渡してデータのプロットを実行しています。
main.f90
program main
use iso_fortran_env
use R_fortran
implicit none
type(t_robj) :: robj !Rとの通信オブジェクト
call compilerinfo()
call set_r_cmd("R") !Rの実行コマンドが違う場合はset_r_cmdで変更
call sub1(robj)
call sub2(robj)
contains
subroutine compilerinfo()
use iso_fortran_env
print *, "!==================================="
print *, "! compiler information"
print *, "!---"
print *, compiler_version()
print *, "!---"
print *, compiler_options()
print *, "!==================================="
end subroutine
subroutine sub1(ro)
class(t_robj) :: ro
real(kind=real64) :: ts,te
call cpu_time(ts)
print *, "sub1"
call ro%open()
call ro%write("demo(lm.glm)")
call ro%write("data.frame(x=seq(1,3),y=rep(2,3))")
call ro%write("q(save='no')")
call ro%close()
call cpu_time(te)
print *, "CPUTIME(s)@fortran_sub1 : ",te-ts
end subroutine
subroutine sub2(ro)
use stdlib_math
class(t_robj) :: ro
integer,parameter :: n=1000
real(kind=real64) :: t(n),x(n),y(n)
integer :: i,uni
print *, "sub2"
open(newunit=uni,file="scratch.txt")
!------------------
t=linspace(0d0,10d0,n)
call random_number(x)
y=sin(t)+x/5d0
do i=1,n
write(uni,*) t(i),x(i),y(i)
end do
!------------------
call ro%open()
call ro%write("df<-read.table('scratch.txt')")
call ro%write("png(file='sample.dataframe.png')")
call ro%write("plot(df)")
call ro%write("dev.off()")
call ro%write("q(save='no')")
call ro%close()
!------------------
close(uni)
end subroutine
end program main
このプログラム例ではテキストファイルによるデータの受け渡しとしましたが、HDF5形式などで受け渡すことで、R側でデータの読み込みが非常に早くなると思います。
h5fortranにも、fpmによるビルド設定ファイルが付属しているので、ひと昔前に比べれば、HDF5によるデータ書き出しプログラムの作成が格段と簡略化されたように感じます。
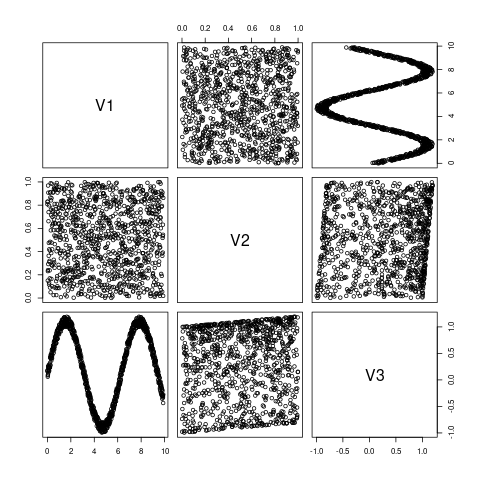
なお、call sub2()のplot(df)で書き出されたグラフは次のようになります。
fpmを使ってみた感想
初めてFortranのパッケージマネージャ(fpm)を利用してみました。fpmに対応しているライブラリであれば、GitHubから芋蔓式に必要なコードを類を取得できる点がとても良いと思います。
また、今回はRを呼び出しましたが、gnuplotの呼び出しも可能であることを確認しました。M_processライブラリは、コマンドラインで呼び出し可能なプログラムであれば、ほぼ何でも利用できると思います1。
-
何でもできますが、何でもFortranから呼び出せばよいかというとそうでは無いので程々に。(自戒の念を込めて) ↩