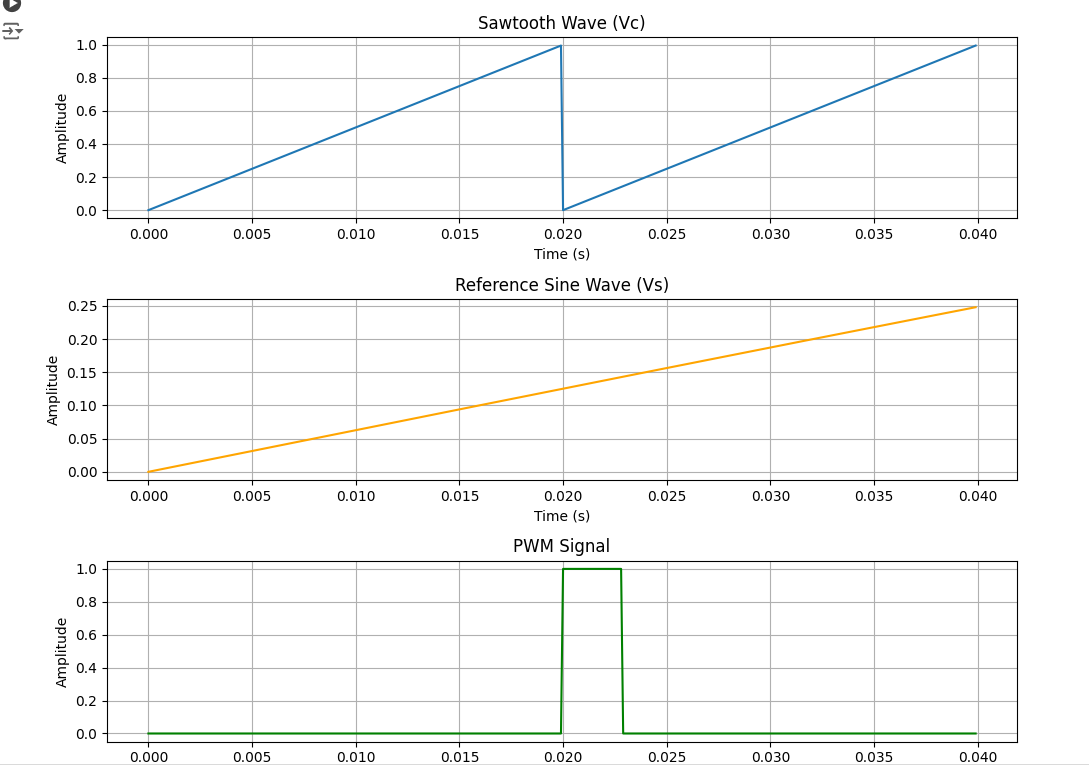
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# PWM parameters
frequency = 50 # Hz
period = 1 / frequency # seconds
sampling_rate = 10000 # samples per second
t = np.linspace(0, 2 * period, int(sampling_rate * 2 * period), endpoint=False) # Time array
# Create a sawtooth wave (carrier signal)
Vc = np.mod(t, period) / period
# Define the reference sine wave (Vs)
Vs_frequency = 1 # Hz
Vs_amplitude = 1
Vs = Vs_amplitude * np.sin(2 * np.pi * Vs_frequency * t)
# Generate the PWM signal
PWM_signal = np.where(Vs > Vc, 1, 0)
# Plotting
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
# Plot the carrier signal (sawtooth wave)
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, Vc, label='Sawtooth Wave (Vc)')
plt.title('Sawtooth Wave (Vc)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the reference signal (sine wave)
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(t, Vs, label='Reference Sine Wave (Vs)', color='orange')
plt.title('Reference Sine Wave (Vs)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the PWM signal
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.plot(t, PWM_signal, label='PWM Signal', color='green')
plt.title('PWM Signal')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# PWM parameters
frequency = 5000 # Hz for the triangular wave
period = 1 / frequency # seconds
sampling_rate = 10000000 # samples per second
t = np.linspace(0, 2 * period, int(sampling_rate * 2 * period), endpoint=False) # Time array
# Create a triangular wave (input B)
B = 2 * np.abs(2 * (t / period - np.floor(t / period + 0.5))) - 1
# Define the reference sine wave (input A)
A_frequency = 1 # Hz
A_amplitude = 1
A = A_amplitude * np.sin(2 * np.pi * A_frequency * t)
# Generate the comparator output (input C)
C = np.where(A > B, 1, 0)
# Define RL circuit parameters
R = 1 # ohms
L = 0.01 # henries
V_dc = 5 # DC voltage in volts
# Initialize current array for the RL circuit
I = np.zeros_like(t)
dt = t[1] - t[0] # Time step
# Simulate the RL circuit
for i in range(1, len(t)):
dI_dt = (V_dc * C[i-1] - R * I[i-1]) / L
I[i] = I[i-1] + dI_dt * dt
# Plotting
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
# Plot the sine wave (input A)
plt.subplot(4, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, A, label='Sine Wave (Input A)')
plt.title('Sine Wave (Input A)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the triangular wave (input B)
plt.subplot(4, 1, 2)
plt.plot(t, B, label='Triangular Wave (Input B)', color='orange')
plt.title('Triangular Wave (Input B)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the comparator output (input C)
plt.subplot(4, 1, 3)
plt.plot(t, C, label='Comparator Output (Input C)', color='green')
plt.title('Comparator Output (Input C)')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
# Plot the RL circuit current
plt.subplot(4, 1, 4)
plt.plot(t, I, label='Current through RL Circuit', color='red')
plt.title('Current through RL Circuit')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Current (A)')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 搬送波(三角波)の生成
f_carrier = 1000 # 搬送波の周波数 [Hz]
t = np.linspace(0, 0.01, num=1000) # 時間配列 [s]
carrier_wave = 0.5 * (1 + np.sin(2 * np.pi * f_carrier * t))
# 基本波(正弦波)の生成
f_signal = 50 # 基本波の周波数 [Hz]
signal_wave = np.sin(2 * np.pi * f_signal * t)
# PWM制御による出力信号の生成
pwm_output = np.zeros_like(t)
for i in range(len(t)):
if signal_wave[i] > carrier_wave[i]:
pwm_output[i] = 1
else:
pwm_output[i] = 0
# プロット設定
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, carrier_wave, label='Carrier Wave (Triangle)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(t, signal_wave, label='Signal Wave (Sine)')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.step(t, pwm_output, where='mid', label='PWM Output')
plt.ylabel('Output')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylim([-0.1, 1.1])
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
他の変調
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 基本パラメータ
fs = 1000 # サンプリング周波数
t = np.arange(0, 1, 1/fs) # 時間ベクトル
f_carrier = 50 # 搬送波周波数
f_signal = 5 # 変調信号周波数
amplitude = 1 # 振幅
# 変調信号(正弦波)
modulating_signal = np.sin(2 * np.pi * f_signal * t)
# 振幅変調(AM)
am_signal = (1 + modulating_signal) * np.cos(2 * np.pi * f_carrier * t)
# 周波数変調(FM)
kf = 10 # 周波数感度
fm_signal = np.cos(2 * np.pi * f_carrier * t + kf * np.cumsum(modulating_signal) / fs)
# 位相変調(PM)
kp = np.pi / 2 # 位相感度
pm_signal = np.cos(2 * np.pi * f_carrier * t + kp * modulating_signal)
# プロット
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
# 振幅変調
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, am_signal)
plt.title('Amplitude Modulation (AM)')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
# 周波数変調
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(t, fm_signal)
plt.title('Frequency Modulation (FM)')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
# 位相変調
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.plot(t, pm_signal)
plt.title('Phase Modulation (PM)')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define time array
t = np.linspace(0, 0.01, 10000) # 10ms duration, high resolution
# Define the modulating wave (A) - a sinusoidal wave with frequency 50Hz
freq_modulating = 50 # in Hz
modulating_wave = np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq_modulating * t)
# Define the carrier wave (B) - a triangle wave with frequency 50kHz
freq_carrier = 5000 # in Hz
carrier_wave = np.abs(2 * (t * freq_carrier - np.floor(0.5 + t * freq_carrier)))
# Comparator output: 1 if modulating wave > carrier wave, else 0
comparator_output = np.where(modulating_wave > carrier_wave, 1, 0)
# Plot the modulating wave (A)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6))
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(t, modulating_wave, label='Modulating Wave (50Hz)')
plt.title('Modulating Wave ')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
# Plot the carrier wave (B)
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(t, carrier_wave, label='Carrier Wave (50kHz Triangle)', color='orange')
plt.title('Carrier Wave ')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
# Plot the comparator output
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.plot(t, comparator_output, label='Comparator Output', color='green')
plt.title('Comparator Output')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Output')
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def generate_pwm(frequency, duty_cycle, duration, sampling_rate):
"""
Generate a PWM signal.
:param frequency: Frequency of the PWM signal in Hz
:param duty_cycle: Duty cycle of the PWM signal (0 to 1)
:param duration: Duration of the signal in seconds
:param sampling_rate: Sampling rate in Hz
:return: Time array and PWM signal array
"""
t = np.arange(0, duration, 1/sampling_rate)
pwm_signal = ((t * frequency) % 1) < duty_cycle
return t, pwm_signal.astype(float)
# Parameters
frequency = 10 # PWM frequency in Hz
duty_cycle = 0.9 # Duty cycle (0 to 1)
duration = 1 # Signal duration in seconds
sampling_rate = 1000 # Sampling rate in Hz
# Generate PWM signal
time, pwm_signal = generate_pwm(frequency, duty_cycle, duration, sampling_rate)
# Plot the PWM signal
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
plt.plot(time, pwm_signal)
plt.title(f'PWM Signal - Frequency: {frequency} Hz, Duty Cycle: {duty_cycle * 100}%')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import butter, lfilter
def generate_pwm(frequency, duty_cycle, duration, sampling_rate):
t = np.arange(0, duration, 1/sampling_rate)
pwm_signal = ((t * frequency) % 1) < duty_cycle
return t, pwm_signal.astype(float)
def butter_lowpass_filter(data, cutoff, fs, order=5):
nyquist = 0.5 * fs
normal_cutoff = cutoff / nyquist
b, a = butter(order, normal_cutoff, btype='low', analog=False)
y = lfilter(b, a, data)
return y
# Parameters
frequency = 10 # PWM frequency in Hz
duty_cycle = 0.6 # Duty cycle (0 to 1)
duration = 2 # Signal duration in seconds
sampling_rate = 1000 # Sampling rate in Hz
cutoff_frequency = 5 # Low-pass filter cutoff frequency in Hz
# Generate PWM signal
time, pwm_signal = generate_pwm(frequency, duty_cycle, duration, sampling_rate)
# Apply low-pass filter to simulate transient response
filtered_signal = butter_lowpass_filter(pwm_signal, cutoff_frequency, sampling_rate)
# Plot the PWM signal and the filtered signal
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(time, pwm_signal)
plt.title('PWM Signal')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
plt.plot(time, pwm_signal, label='Original Transient Response', color='orange')
plt.title('PWM Signal (Zoomed)')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.xlim(0, 0.1) # Zoom in to see the transient behavior
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.grid()
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
plt.plot(time, filtered_signal, label='Filtered Signal', color='green')
plt.title('Filtered Signal (Low-pass Filter)')
plt.xlabel('Time [s]')
plt.ylabel('Amplitude')
plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()