本記事ではMATLAB/Symbolic Math Toolboxを使って車輪型倒立振子の運動方程式を導出していきます。
この記事を通して、MATLABを利用して複雑な微分方程式が解けることを実感していただければと思います。
前置き
トランジスタ技術7月号に車輪型倒立振子の数学モデルの詳しい導出が書かれているため、本記事では途中式の解説はしません。7月号には数学や力学に関する丁寧な解説がたくさん詰まってるので、1冊持っておいて損はないと思います。買いましょう。笑
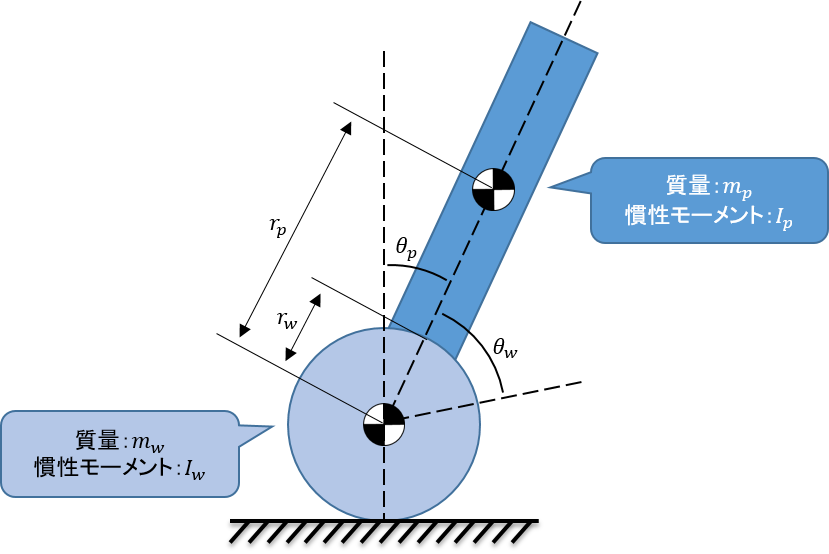
車輪型倒立振子の各パラメータ
MATLABに導出してもらう運動方程式に含まれる「位置エネルギー」と「運動エネルギー」について、「振子」と「車輪」の2つの観点から導出していきます。
車輪型倒立振子の物理量
〇車輪(wheel)の物理量
車輪の重心座標を$(x_w, y_w)$とする。
重心座標
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
x_w = r_w(\theta_p + \theta_w) \\
y_w = 0
\end{array}
\right.
重心速度
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
\dot{x}_w = r_w(\dot{\theta}_p + \dot{\theta}_w) \\
\dot{y}_w = 0
\end{array}
\right.
並進運動エネルギー
K_{w1} = \frac{1}{2}m_w\dot{x}_w^2 +\frac{1}{2}m_w\dot{y}_w^2 \\
= \frac{1}{2}m_wr_w^2(\dot{\theta}_p + \dot{\theta}_w)^2
回転運動エネルギー
K_{w2} = \frac{1}{2}I_w(\dot{\theta}_p + \dot{\theta}_w)^2
位置エネルギー
U_w = m_wgy_w = 0
〇振子(pendulum)の物理量
振子の重心座標を$(x_p, y_p)$とする。
重心座標
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
x_p = x_w + r_psin(\theta_p) = r_w(\theta_p + \theta_w) + r_psin(\theta_p) \\
y_p = r_pcos(\theta_p)
\end{array}
\right.
重心速度
\left\{
\begin{array}{ll}
\dot{x}_p = r_w(\dot{\theta}_p + \dot{\theta}_w) + r_p\dot{\theta}_pcos(\theta_p) \\
\dot{y}_p = -r_p\dot{\theta}_psin(\theta_p)
\end{array}
\right.
並進運動エネルギー
K_{p1} = \frac{1}{2}m_p\dot{x}_p^2 + \frac{1}{2}m_p\dot{y}_p^2 \\
= \frac{1}{2}m_p\bigl(r_w(\dot{\theta}_p + \dot{\theta}_w) + r_p\dot{\theta}_pcos(\theta_p)\bigr)^2 + \frac{1}{2}m_p\bigl(-r_p\dot{\theta}_psin(\theta_p)\bigr)^2
回転運動エネルギー
K_{p2} = \frac{1}{2}I_p\dot{\theta}_p^2
位置エネルギー
U_p = m_pgy_p = m_pgr_pcos(\theta_p)
ラグランジュ運動方程式の導出
モデルの運動エネルギーと位置エネルギーの導出ができたら、
MATLAB/Symbolic Math Toolboxを使って、車輪型倒立振子のラグランジュの運動方程式を導出していきます。
clear; format compact %initialize
syms m_w r_w theta_w dtheta_w ddtheta_w I_w real % wheel
syms m_p r_p theta_p dtheta_p ddtheta_p I_p real % pendulum
syms theta_w dtheta_w ddtheta_w phi_p dphi_p ddphi_p real % radian
syms f_w g real % torque, gravity
q = [theta_w theta_p]';
dq = [dtheta_w dtheta_p]';
ddq = [ddtheta_w ddtheta_p]';
f = [f_w 0]';
%--------------------------------------------------------
x_w = r_w*(q(1) + q(2));
y_w = 0;
dx_w = diff(x_w, q(1))*dq(1) + diff(x_w, q(2))*dq(2);
dy_w = diff(x_w, q(1))*dq(1) + diff(y_w, q(2))*dq(2);
x_p = x_w + r_p*sin(q(2));
y_p = r_p*cos(q(2));
dx_p = diff(x_p, q(1))*dq(1) + diff(x_p, q(2))*dq(2);
dy_p = diff(x_p, q(1))*dq(1) + diff(y_p, q(2))*dq(2);
%--------------------------------------------------------
K_w1 = 0.5*m_w*dx_w^2 + 0.5*m_w*dy_w^2;
K_w2 = 0.5*I_w*(dq(1) + dq(2))^2;
U_w = m_w*g*y_w;
K_p1 = 0.5*m_p*dx_p^2 + 0.5*m_p*dy_p^2;
K_p2 = 0.5*I_p*dq(2)^2;
U_p = m_p*g*y_p;
L = (K_w1 + K_w2 + K_p1 + K_p2) - (U_w + U_p);
%--------------------------------------------------------
N = length(q);
for i = 1:N
dLq(i) = diff(L, dq(i));
temp = 0;
for j = 1:N
temp = temp + diff(dLq(i),dq(j))*ddq(j) + diff(dLq(i),q(j))*dq(j);
end
ddLq(i) = temp;
eq(i) = ddLq(i) - diff(L,q(i)) - f(i);
end
eq = simplify(eq')
mファイルを実行することで、車輪と振子に関するラグランジュ運動方程式が導出できます。
>> lagrange
eq =
ddtheta_p*(I_w + m_w*r_w^2 + m_p*r_w*(r_w + r_p*cos(theta_p)) - m_p*r_p*r_w*sin(theta_p)) - dtheta_p*(dtheta_p*m_p*r_p*r_w*cos(theta_p) + dtheta_p*m_p*r_p*r_w*sin(theta_p)) - f_w + ddtheta_w*(I_w + 2*m_p*r_w^2 + 2*m_w*r_w^2)
I_p*ddtheta_p + I_w*ddtheta_p + I_w*ddtheta_w + ddtheta_p*m_p*r_p^2 + ddtheta_p*m_p*r_w^2 + ddtheta_w*m_p*r_w^2 + ddtheta_p*m_w*r_w^2 + ddtheta_w*m_w*r_w^2 - g*m_p*r_p*sin(theta_p) - dtheta_p^2*m_p*r_p*r_w*sin(theta_p) + 2*ddtheta_p*m_p*r_p*r_w*cos(theta_p) + ddtheta_w*m_p*r_p*r_w*cos(theta_p) - ddtheta_w*m_p*r_p*r_w*sin(theta_p)
MATLABの出力結果は数式としては見づらいため、markdownの数式モードを使って整形しました。
上の式が車輪、下の式が振子の運動方程式を表しています。
\ddot{\theta}_p(I_w + m_wr_w^2 + m_pr_w(r_w + r_pcos(\theta_p)) - m_pr_pr_wsin(\theta_p)) - \dot{\theta}_p(\dot{\theta}_pm_pr_pr_wcos(\theta_p) + \dot{\theta}_pm_pr_pr_wsin(\theta_p)) - f_w + \ddot{\theta}_w(I_w + 2m_pr_w^2 + 2m_wr_w^2) = 0
I_p\ddot{\theta}_p + I_w\ddot{\theta}_p + I_w\ddot{\theta}_w + \ddot{\theta}_pm_pr_p^2 + \ddot{\theta}_pm_pr_w^2 + \ddot{\theta}_wm_pr_w^2 + \ddot{\theta}_pm_wr_w^2 + \ddot{\theta}_wm_wr_w^2 - m_pgr_psin(\theta_p) - \dot{\theta}_p^2m_pr_pr_wsin(\theta_p) + 2\ddot{\theta}_pm_pr_pr_wcos(\theta_p) + \ddot{\theta}_wm_pr_pr_wcos(\theta_p) - \ddot{\theta}_wm_pr_pr_wsin(\theta_p) = 0