1. はじめに
1.モチベーション
「Javaの基礎(というか、オブジェクト指向)がわかれば対戦ゲームが作れる!」と気づいたので作成しました。
「何を作ればいいかわからないから、学習のモチベーションがわかない」と考えている方に是非見ていただきたいです!!
※「スッキリわかるJava入門 第2版」を参考にして作成しました。
2.アウトプット
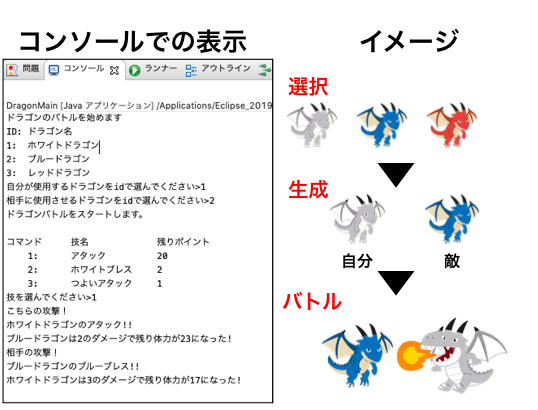
1.ゲームルール
ドラゴン同士が戦うゲーム。
最初に、自分と敵のドラゴンを選択して生成。<選択・生成フェーズ>
互いに技を出し、HPが0になると終了。<バトルフェーズ>
※詳細は下記のゲームルールで記載。
2.オブジェクト指向との関係
1.選択したドラゴンを設計図(=クラス)を用いて自分と敵とで生成する=オブジェクト指向のインスタンス化
2.技を使用した結果(HPの減少)はオブジェクト内の値を参照・更新する=getterとsetterの使用
2. 内容
1.はじめに
1.ゲームルール
・選択・生成フェーズとバトルフェーズで、それぞれドラゴンと使う技をユーザ選択により決定する。
・ドラゴンを自分と敵とで1体づつ選択する<選択・生成フェーズ>
・ドラゴンは名前・HP・技が違う3体を用意
・技は1体のドラゴンにつき3つ持つ。
・ドラゴンに技を命令しバトルする<バトルフェーズ>
・技は自分→相手の順番で出す。
・自分のドラゴンは選択した技を、相手のドラゴンはドラゴンの持つ技をランダムで1つ繰り出す。
・技を出し相手のHPを減らした段階で相手のHPが0かどうかの判定を行い、0なら攻撃した側の勝ちとなる。
2.フォルダ構成
├── DragonMain.java
├── bean
│ ├── ButtleDragon.java
│ ├── Action.java
│ └── SimpleDragon.java
└── util
├── buttle
│ ├── ButtleContents.java
│ ├── ButtleMain.java
│ └── RandomEnemyChoice.java
└── choice
└── ChoiceDragon.java
beanフォルダ内のクラスを使用してドラゴンをインスタンス化(生成)する。
選択・生成フェーズでの
「選択」段階では、SimpleDragon.javaを
「生成」段階では、ButtleDragon.javaとAction.javaを使用。
2.全体処理
↓mainメソッド
package dragon;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import dragon.bean.ButtleDragon;
import dragon.util.buttle.ButtleMain;
import dragon.util.choice.ChoiceDragon;
public class DragonMain{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
System.out.println("ドラゴンのバトルを始めます");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try{
//ドラゴン一覧を取得する
ChoiceDragon.searchDrageon();
//どのドラゴンを作成するかを選択する
String choiceMyDragon = null;
String choiceOpponentDragon = null;
System.out.print("自分が使用するドラゴンをidで選んでください>");
choiceMyDragon = br.readLine();
System.out.print("相手に使用させるドラゴンをidで選んでください>");
choiceOpponentDragon = br.readLine();
//ドラゴン生成
ButtleDragon myDragon = ChoiceDragon.makeDragon(Integer.parseInt(choiceMyDragon));
ButtleDragon oppoDragon = ChoiceDragon.makeDragon(Integer.parseInt(choiceOpponentDragon));
//Buttle
ButtleMain.doButtle(myDragon,oppoDragon);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("深刻なエラーが出ました");
}
}
}
ChoiceDragon.searchDrageon();:ドラゴン一覧を取得
ChoiceDragon.makeDragon());:自分と敵のドラゴンを生成しそれぞれ「myDragon」「oppoDragon」に格納
ButtleMain.doButtle();:「myDragon」と「oppoDragon」を引数にしてバトルスタート
3.選択・生成フェーズ
ドラゴン一覧を取得し、選択されたドラゴンを生成・ドラゴンに技を紐付ける
・クラス(Bean)
↓シンプルドラゴンを生成するために使用。
技を持たない、選択時にIDとドラゴン名の一覧を表示するときに使用
package dragon.bean;
public class SimpleDragon {
int dragonId;
String dragonName;
int hitPoint;
//シンプルドラゴンのコンストラクタ
public SimpleDragon(int dragonId,String dragonName, int hitPoint){
this.dragonId = dragonId;
this.dragonName = dragonName;
this.hitPoint = hitPoint;
}
public int getDragonId() {
return dragonId;
}
public void setDragonId(int dragonId) {
this.dragonId = dragonId;
}
public String getDragonName() {
return dragonName;
}
public void setDragonName(String dragonName) {
this.dragonName = dragonName;
}
public int getHitPoint() {
return hitPoint;
}
public void setHitPoint(int hitPoint) {
this.hitPoint = hitPoint;
}
}
↓バトルドラゴンを作成するために使用。
シンプルドラゴンクラスを継承し、バトル中に参照するHPと技を持たせる。
package dragon.bean;
package dragon.bean;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
* バトル中に使用するドラゴンクラス
* HPの増減に使用する
*/
public class ButtleDragon extends SimpleDragon {
int buttleHp;
int action1;
int action2;
int action3;
Map<Integer, Action> actions;
/**
* バトル用ドラゴンのコンストラクタ。バトル用HPの初期値はHPとする
* @param dragonId
* @param dragonName
* @param hitPoint
*/
public ButtleDragon(int dragonId, String dragonName, int hitPoint) {
super(dragonId,dragonName,hitPoint);
this.buttleHp = hitPoint;
}
public int getButtleHp() {
return buttleHp;
}
public void setButtleHp(int buttleHp) {
this.buttleHp = buttleHp;
}
public int getAction1() {
return action1;
}
public void setAction1(int action1) {
this.action1 = action1;
}
public int getAction2() {
return action2;
}
public void setAction2(int action2) {
this.action2 = action2;
}
public int getAction3() {
return action3;
}
public void setAction3(int action3) {
this.action3 = action3;
}
public Map<Integer, Action> getActions() {
return actions;
}
public void setActions(Map<Integer, Action> actions) {
this.actions = actions;
}
}
↓技を作成するために使用。
package dragon.bean;
/*
* バトル中に使用する技クラス
*/
public class Action {
int actionId;
String actionName;
int power;
int actionPoint;
int buttleActionPoint;
/**
* 技のコンストラクタ。
* 戦闘中のMPは[buttleActionPoint]を使用して増減させる
*
* @param actionName
* @param power
* @param actionPoint
*/
public Action(int actionId,String actionName, int power, int actionPoint) {
this.actionId = actionId;
this.actionName = actionName;
this.power = power;
this.actionPoint = actionPoint;
this.buttleActionPoint = actionPoint;
}
public int getActionId() {
return actionId;
}
public void setActionId(int actionId) {
this.actionId = actionId;
}
public String getActionName() {
return actionName;
}
public void setActionName(String actionName) {
this.actionName = actionName;
}
public int getPower() {
return power;
}
public void setPower(int power) {
this.power = power;
}
public int getActionPoint() {
return actionPoint;
}
public void setActionPoint(int actionPoint) {
this.actionPoint = actionPoint;
}
public int getButtleActionPoint() {
return buttleActionPoint;
}
public void setButtleActionPoint(int buttleActionPoint) {
this.buttleActionPoint = buttleActionPoint;
}
}
・ChoiceDragon
↓ドラゴンを選択するためのリストの取得や、選択されたドラゴンの生成を行う。生成した後のドラゴンに技を持たせるのもここで行う。
package dragon.util.choice;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import dragon.bean.Action;
import dragon.bean.ButtleDragon;
import dragon.bean.SimpleDragon;
public class ChoiceDragon {
/**
* ドラゴンを選択する
* ※この部分をDBから取得すると良いかもしれません
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void searchDrageon(){
//ここで選択できるドラゴンを作成する
SimpleDragon dragon1 = new SimpleDragon(1,"ホワイトドラゴン", 20);
SimpleDragon dragon2 = new SimpleDragon(2,"ブルードラゴン", 25);
SimpleDragon dragon3 = new SimpleDragon(3,"レッドドラゴン", 15);
//作成したドラゴンをリストにつめる
List<SimpleDragon> choiceDragonList = new ArrayList<SimpleDragon>();
choiceDragonList.add(dragon1);
choiceDragonList.add(dragon2);
choiceDragonList.add(dragon3);
//リストを表示する
System.out.println("ID:\tドラゴン名");
for(SimpleDragon list : choiceDragonList){
System.out.println(list.getDragonId()+":\t"+list.getDragonName());
}
}
/**
* 選択された値を元にして、リストからドラゴンを生み出す
* その後、技を持たせる
*/
public static ButtleDragon makeDragon(int DragonId){
//ドラゴンを生み出す
ButtleDragon buttleDragon = makeButtleDragon(DragonId);
//技リストを取得する
Map<Integer, Action> buttleActionMap = makeButtleAction() ;
//技をドラゴンに持たせる
Map<Integer, Action> buttleDragonActionMap = new HashMap<>();
//ドラゴンが持つ技のidを取得する
int actionId_1 = buttleDragon.getAction1();
int actionId_2 = buttleDragon.getAction2();
int actionId_3 = buttleDragon.getAction3();
//ドラゴンが持つ技を技リストから取得する
Action action1 = buttleActionMap.get(actionId_1);
Action action2 = buttleActionMap.get(actionId_2);
Action action3 = buttleActionMap.get(actionId_3);
//ドラゴンと技を結びつける
buttleDragonActionMap.put(1, action1);
buttleDragonActionMap.put(2, action2);
buttleDragonActionMap.put(3, action3);
buttleDragon.setActions(buttleDragonActionMap);
return buttleDragon;
}
/**
* ドラゴンを生成し、技リストのidをそれぞれに付与する。
* ※ここでDBを使用すると良いと思います。
* @param dragonId
* @return
*/
private static ButtleDragon makeButtleDragon(int dragonId) {
ButtleDragon makeDragon = null;
//引数によって異なるドラゴンを生み出す
switch(dragonId) {
case 1:
//バトルドラゴンのコンストラクタへの引数はID・ドラゴンの名前・HP
ButtleDragon dragon1 = new ButtleDragon(1,"ホワイトドラゴン", 20);
//バトルドラゴンに技をセットする
dragon1.setAction1(1);
dragon1.setAction2(2);
dragon1.setAction3(5);
makeDragon = dragon1;
break;
case 2:
ButtleDragon dragon2 = new ButtleDragon(2,"ブルードラゴン", 25);
dragon2.setAction1(1);
dragon2.setAction2(3);
dragon2.setAction3(5);
makeDragon = dragon2;
break;
case 3:
ButtleDragon dragon3 = new ButtleDragon(3,"レッドドラゴン", 15);
dragon3.setAction1(1);
dragon3.setAction2(4);
dragon3.setAction3(5);
makeDragon = dragon3;
break;
}
return makeDragon;
}
/**
* 技リストを取得する。
* ※ここでDBを使用すると良いと思います。
* @return
*/
private static Map<Integer, Action> makeButtleAction() {
//技リスト一覧を宣言する
Action action1 = new Action(1,"アタック\t", 2, 20);
Action action2 = new Action(2,"ホワイトブレス", 4, 2);
Action action3 = new Action(3,"ブルーブレス", 3, 2);
Action action4 = new Action(4,"レッドブレス", 5, 2);
Action action5 = new Action(5,"つよいアタック", 6, 1);
//技リストをマップにつめる
Map<Integer, Action> actionList = new HashMap<>();
actionList.put(1, action1);
actionList.put(2, action2);
actionList.put(3, action3);
actionList.put(4, action4);
actionList.put(5, action5);
return actionList;
}
}
1.ドラゴン一覧の取得
ChoiceDragon.searchDrageonメソッド内で行う。
SimpleDragon dragon1 = new SimpleDragon()でそれぞれドラゴンを生成。
SimpleDragon型のドラゴンをコンストラクタを利用して生成し、id・名前・HPをそれぞれ格納
choiceDragonListで生成したドラゴンをリストに格納して全て表示する
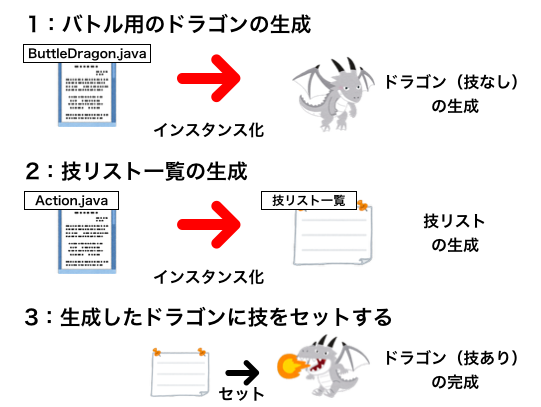
2.バトル用のドラゴンの生成
ChoiceDragon.makeDragonメソッド内で行う。
1:バトル用のドラゴンの生成
ButtleDragon(SimpleDragonに、使用する技のidとバトル用のHP(攻撃を受けると減少する)を追加したクラス)から生成される
2:技リスト一覧の生成
Actionとしてid・技名・威力・MPを生成し、idとActionを紐付けた「技リスト一覧」マップを生成
3:生成したドラゴンと技を結びつける
ドラゴンには使用する技のidが降られているので、それに合致する技を技リスト一覧から取得して格納
敵のドラゴンでも同じ内容を実施することで、「技を持つドラゴン」が2体生成される
4.バトルフェーズ
↓バトルのメインメソッド。自分のターンと相手のターンを、どちらかのHPがなくなるまで続ける。
package dragon.util.buttle;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import dragon.bean.ButtleDragon;
public class ButtleMain {
/**
* Buttleの基本的な流れ
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void doButtle(ButtleDragon myDragon, ButtleDragon oppoDragon) throws IOException{
boolean enemyDownFlg = false; //敵が倒れたかどうかの判定
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("ドラゴンバトルをスタートします。");
do{
ButtleContents.outputActionList(myDragon);
String str = null;
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println("こちらの攻撃!");
ButtleContents.useAction(myDragon.getActions().get(Integer.parseInt(str)), myDragon, oppoDragon);
if(oppoDragon.getButtleHp() == 0){
enemyDownFlg = true;
break;
}
System.out.println("相手の攻撃!");
RandomEnemyChoice.randomChoice(oppoDragon,myDragon);
}while(myDragon.getButtleHp() != 0);
ButtleContents.outputResult(enemyDownFlg);
System.out.println("バトルが終了しました");
}
}
↓技を出したときの流れ。
テキストを表示し、敵のHPを減らし、自分の技のMPを減らす。
package dragon.util.buttle;
import dragon.bean.Action;
import dragon.bean.ButtleDragon;
public class ButtleContents {
/**
* 基本的な技の流れ
* @param offenceAction:攻撃側の技
* @param offenceDragon:攻撃側のドラゴン
* @param defenceDragon:防御側のドラゴン
*/
public static void useAction(Action offenceAction,ButtleDragon offenceDragon, ButtleDragon defenceDragon){
int nokoriMP = offenceAction.getActionPoint(); //現在のMP
//攻撃技の表示
String actionName = offenceAction.getActionName().replaceAll("\t", "");//技名に含まれているタブ区切りを解除する
System.out.println(offenceDragon.getDragonName()+"の"+actionName+"!!");
//攻撃技
Attack(offenceAction,offenceDragon,defenceDragon);
//MPの減少
nokoriMP--;
offenceAction.setButtleActionPoint(nokoriMP);
}
/**
* 攻撃技の流れ
* @param offenceAction
* @param offenceDragon
* @param defenceDragon
*/
public static void Attack(Action offenceAction,ButtleDragon offenceDragon, ButtleDragon defenceDragon){
int damage = offenceAction.getPower(); //技の威力
int defenceDragonNokoriHp = 0; //buttleで更新する防御側ドラゴンのHP量
//相手の残りHPの計算
defenceDragonNokoriHp = defenceDragon.getButtleHp() - damage;
if(defenceDragonNokoriHp <= 0){
defenceDragon.setButtleHp(0);
}else{
defenceDragon.setButtleHp(defenceDragonNokoriHp);
}
System.out.println(defenceDragon.getDragonName()+"は"+damage+"のダメージで残り体力が"+defenceDragon.getButtleHp()+"になった!");
}
/**
* 技リストを表示する
* @param myDragon
*/
public static void outputActionList(ButtleDragon myDragon){
System.out.println("\nコマンド\t\t技名\t\t\t\t残りポイント");
System.out.println("\t1:\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(1).getActionName()+"\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(1).getButtleActionPoint() );
System.out.println("\t2:\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(2).getActionName()+"\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(2).getButtleActionPoint() );
System.out.println("\t3:\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(3).getActionName()+"\t\t"+myDragon.getActions().get(3).getButtleActionPoint() );
System.out.print("技を選んでください>");
}
/**
* 勝敗結果を表示する
* @param enemyDownFlg
*/
public static void outputResult(boolean enemyDownFlg){
if(enemyDownFlg){
System.out.println("\n勝ちました!");
}else{
System.out.println("\n負けました‥");
}
}
}
↓敵の繰り出す技をランダムに決めて、技を繰り出す処理
package dragon.util.buttle;
import dragon.bean.ButtleDragon;
/**
* 敵側のランダムな動きを指定するクラス
*
*/
public class RandomEnemyChoice {
/**
* ランダムに技を生成し、実行する
* @param oppoDragon
* @param myDragon
*/
public static void randomChoice(ButtleDragon oppoDragon, ButtleDragon myDragon){
//ランダムに繰り出す技を選択する
int randomChoice = 0;
randomChoice = (int)(Math.random()*3 + 1);
//技を繰り出す
ButtleContents.useAction(oppoDragon.getActions().get(randomChoice),oppoDragon, myDragon);
}
}
1.処理の流れ(ButtleMain.java)
敵が倒れる(oppoDragon.getButtleHp() == 0)か、自分が倒れる(myDragon.getButtleHp() == 0)までバトルを続ける。
自分の攻撃はButtleContents.useActionメソッドに入力値を渡して、敵の攻撃はRandomEnemyChoice.randomChoiceメソッド内のButtleContents.useActionメソッドにランダム値を渡して処理を行う。
インスタンス化されたドラゴンが保持している値を更新(getter)・参照(setter)しながら処理を進める。
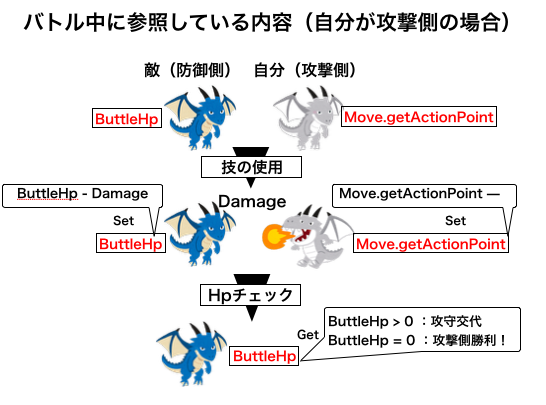
2.技を選択した時の処理(ButtleContents.useAction)
1.メソッドの説明
このメソッドは引数として「offenceAction・offenceDragon・defenceDragon」の3つを取る。今回のゲームでは、自分のドラゴンが技を使用して攻撃する時には、相手のドラゴンが防御側のドラゴンになる(攻撃側が敵の場合ももちろん、防御側は自分のドラゴンとなる)。
そのため、自分が攻撃する時と相手が攻撃する時には第2・第3引数に渡すドラゴンを交換するだけで、「攻撃側が防御側にダメージを与えた」という処理が攻撃側=自分でも、攻撃側=敵でも成立する。
また、このメソッドに入った時点で、攻撃側が選択した技が引数として渡っている(offenceAction)。
2.技選択時の処理の流れ
1:メッセージ表示
2:攻撃処理(ButtleContents.Attack)
技から技の威力を取得し、防御側の残りHPを計算する。その後計算した値を防御側のButtleHPにセットする。
3:MPの減少
攻撃側が使用した技のMPを減らす
3. 最後に
ここまで読んでいただいてありがとうございました!
内容を読んでいただく・実際に作成していただく等でドラゴンが生成される・動く(=インスタンス化される・使用される)をイメージしていただければ幸いです。