前回の記事『ARKit+Vision+iOS14 で らくがき のジオメトリ化』でらくがきをコピーしたので、今回は物体をコピーするために必要な処理を調べてみた。
概要としては、物体の切り出しに Vision+CoreML(DeeplabV3)、立体感を出すのにARKit の depthMap(iOS14〜) を利用。
立体感は深度情報をコピーボタンタップのワンショットでしか取得しないため、立て看板に立体感を与えた感じまで。
↓は車をコピーした結果を SCNView で表示したときのもの。

この記事では主に depthMap を使うにあたり苦労した点を説明します。
本題に入る前にARKitから取得できる深度情報とその信頼度について。
depthMap
iPhone12Pro等、LiDAR搭載の端末では、背面カメラからリアルタイムに深度情報を取得できる。

この例は画面中段部分の深度情報をグレースケールで可視化しているが、実際には 深度情報は カメラからの距離で単位はメートル(iPhone12Proで確認すると型はFloat32。この例は0〜5mを0〜255階調で表示)。このgif動画だと深度が少し遅れているように見えるが、これはiOSの画面収録を利用しているせいで、収録しなければ遅延はほとんど分からないレベル。
深度情報の取得・加工方法については後述。
confidenceMap
ARKitからは深度情報とあわせて、その情報の信頼度を深度情報と同じ解像度で取得することができる。
精度は ARConfidenceLevel で定義されていて low, medium, high の3段階。high が一番信頼できることを表す。
精度情報をlow = 黒、medium = グレー、high = 白 として画像化したのがこれ。

物体の輪郭部分の精度が比較的よくないこと、カメラの向きの方向に指のような細かな物体が並んでいると精度が悪いことがわかる(物体のカメラをむている面は信頼度が高く、側面向かうにしたがって信頼度が落ちていく、という傾向に見える。LiDARのセンサーは一箇所なので、センサーから見えにくい側面の精度は落ちる、というのは納得)。
【本題】 物体のコピーのしかた
この記事では次の手順で実現。
①キャプチャした画像の中心部分を 513 x 513ピクセルで切り取る
②深度情報を①の位置・アスペクト比で切り取る
③深度の信頼度情報を②と同様に切り取る
④Vision+CoreMLを使って①をセグメンテーション
⑤④で認識した物体、且、③の信頼度の高い部分の座標を取得
⑥⑤の深度情報(2D)を3D座標に変換
⑦⑥を3Dモデル化して、シーンに追加
苦労したのが②。
①で切り出した位置・サイズに合わせて深度情報を取得する必要がありこの変換が面倒だった。
③で信頼度を取得しそれを⑤の判定で利用しているが、これは、物体と背景、物体と物体の境界部分の深度値が疑わしい場合が多く(極端に距離が遠く)、3Dモデルがおかしくなることを抑止するためにやっている。
以下、手順を解説します。
①キャプチャした画像の中心部分を 513 x 513ピクセルで切り取る
物体を切り出すためにVision+CoreMLを利用しており、Core MLモデルは Apple が公開しているDeeplabV3モデル を利用。このCoreMLモデルで扱える画像サイズが 513 x 513 であるため、キャプチャした画像の中心部分をこのサイズで切り取る。
ここでARKitから渡されるキャプチャ画像は、端末の向き・画面サイズが考慮されていない。表示されている部分を切り出す方法は以前書いたARKit+Vision+iOS14 で らくがき のジオメトリ化①【輪郭検出】で解説しているので参照ください。
②深度情報を①の位置・アスペクト比で切り取る
深度情報は Float32の配列 で提供される。したがって、深度情報を切り出したり加工したりするのに CIImage/CGImage は使えない。この記事のサンプルを作り始めた時は画像として取り扱えばいいか、と考えたが単位がメートルなので別物。。。Float32を8bit単位に分割してRGBAに割り当てて、、、も頭によぎったが、加工中にもとのFloat32に戻らなくなるかもしれない(カラースペースとかエッジの処理とかで)のでちゃんとやることにした。
深度情報 depthMap は ARFrame の sceneDepth 経由で取得できる。
このサンプルでは ARFrame の extension から取得しているので次のようになる。
guard let pixelBuffer = self.sceneDepth?.depthMap else { return ([], 0) }
iPhone12Pro+iOS14.2 で確認すると depthMap で取得できる深度情報のサイズは
256 x 192
となっている。
一方、ARFrame の capturedImage から取得できる画像の解像度は
1920 x 1440
である。
両方とも 1.333 : 1 なので、①と同様にARFrame の displayTransform を使えば切り取れそうである。
var displayTransform = self.displayTransform(for: .portrait, viewportSize: viewPortSize)
displayTransform を取得するあたり viewPortSize に何を設定するかがまず悩む。APIドキュメントには「The size, in points, of the view intended for rendering the camera image.(カメラ画像のレンダリングを目的としたビューのサイズ(ポイント単位))」とあるので、描画サイズを指定したいところであるが、深度情報は画面サイズとは異なる。APIドキュメントには「The affine transform does not scale to the viewport's pixel size.(アフィン変換は、ビューポートのピクセルサイズに合わせて拡大縮小されません)」とも記載されており、画面サイズではなくてアスペクト比を与えればいいんじゃないか?と考えて実際に確認した結果が次の通り(iPhone12Pro+iOS14.2で確認)。
アスペクト比を与えてみる:CGSize(width: 1.0, height: 844 / 390)
▿ CGAffineTransform
- a : 0.0
- b : 1.0
- c : -1.623076923076923
- d : 0.0
- tx : 1.3115384615384615
- ty : -0.0
画面サイズ(pt)を与えてみる:CGSize(width: 390, height: 844)
▿ CGAffineTransform
- a : 0.0
- b : 1.0
- c : -1.623076923076923
- d : 0.0
- tx : 1.3115384615384615
- ty : -0.0
一致している。
画面のアスペクト比を設定することにする。
ここからはアフィン変換行列を使って depthMap データを画面に見えている、且つ、CoreMLで解析できる範囲で抽出する。
displayTransform は CGAffineTransform で中身は次の行列になっている。
\begin{bmatrix}
a & b & 0 \\
c & d & 0 \\
t_{x} & t_{y} & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
ポートレートの場合、キャプチャ画像(および深度情報)のX軸、Y軸がひっくり返っているので、それを加味する。
\begin{bmatrix}
-1 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & -1 & 0 \\
1 & 1 & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
a & b & 0 \\
c & d & 0 \\
t_{x} & t_{y} & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
-a & -b & 0 \\
-c & -d & 0 \\
a+c+t_{x} & b+d+t_{y} & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
x' & y' & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
x & y & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
×
\begin{bmatrix}
-a & -b & 0 \\
-c & -d & 0 \\
a+c+t_{x} & b+d+t_{y} & 1 \\
\end{bmatrix}
x' = -ax + -cy + a + c + t_{x} \\
= -a(x-1)-c(y-1)+ t_{x} \\
y' = -bx + -dy + b + d + t_{y} \\
= -b(x-1)-d(y-1)+ t_{y} \\
取得済みの値を当てはめてみる。
x' = 1.62(y-1)+ 1.31 \\
y' = -(x-1) \\
この結果からわかることは次の通り。
- x軸とy軸は入れ替わる。
- 変換後のxは -0.31 〜 1.31 の値をとる。つまり、変換前のyの中央の 1/1.62 部分しか表示されない(確認した限りでは表示されるのは0〜1の範囲)。
- 変換後の y は 1.0 〜 0.0 の値をとる。つまり、変換前のx方向の全てが表示される。
変換後のx軸の両サイドを切り落とす必要があるので、そのサイズを求める。切り取るのは中央部分であることがわかっているので c と深度情報の height で求める。
let sideCutoff = Int((1.0 - (1.0 / displayTransform.c)) / 2.0 * CGFloat(pixelBuffer.height))
これを計算すると 36 となる。取得した深度情報のサイズは 256 x 192 なので両側 36 を切り落とすと変換後は 120 x 256 (縦横は入れ替わる)ということになる。
あとは、CoreMLに渡すデータが正方形なので、それに合わせて正方形部分を切り出す。結果は120x120のサイズになる。
func cropPortraitCenterData<T>(sideCutoff: Int) -> ([T], Int) {
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(self, CVPixelBufferLockFlags(rawValue: CVOptionFlags(0)))
guard let baseAddress = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(self) else { return ([], 0) }
let pointer = UnsafeMutableBufferPointer<T>(start: baseAddress.assumingMemoryBound(to: T.self),
count: width * height)
var dataArray: [T] = []
// 画面上の横幅のサイズを計算。画面の横サイズいっぱいから左右は切り落とした値。
// ※紛らわしいがポートレート時にARKitから取得されるデータは横向きなので height で計算。
let size = height - sideCutoff * 2
// 画面の縦方向の中央部分のデータを取得。取得順番は上下逆転。
for x in (Int((width / 2) - (size / 2)) ..< Int((width / 2) + (size / 2))).reversed() {
// 画面の横方向の中央部分のデータを取得。取得順番は左右逆転。
for y in (sideCutoff ..< (height - sideCutoff)).reversed() {
let index = y * width + x
dataArray.append(pointer[index])
}
}
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(self, CVPixelBufferLockFlags(rawValue: CVOptionFlags(0)))
return (dataArray, size)
}
切り出す処理は CVPixelBuffer の extension で書いた。
後述する深度の信頼度情報の場合、CVPixelBuffer に格納されているデータがUInt8の配列のため、型はジェネリクスで扱っている。
配列の中身を一発でアフィン変換してくれるようなものが見つからなかったので、x軸とy軸の入れ替え&データの上下左右逆にする処理も自力で実装するしかなかった(ポートレートのみだけど)。
ここまで変換できれば後は、この記事の冒頭部分のdepthMap,confidenceMapのgif動画のようにカメラキャプチャ画像と合成することも容易になる(ちなみにMetalでMTLTextureに変換して収録)。
③深度の信頼度情報を②と同様に切り取る
処理内容は②と同様。
confidenceMap は ARFrame の sceneDepth 経由で取得できる。
guard let pixelBuffer = self.sceneDepth?.confidenceMap else { return ([], 0) }
深度情報は Float32 であるのに対し信頼度情報は UInt8 である点に注意。
④Vision+CoreMLを使って①をセグメンテーション
Vison+CoreML(DeepLabV3) を使って物体のセグメンテーション を行う。
やり方はこの参考記事『Simple Semantic Image Segmentation in an iOS Application — DeepLabV3 Implementation』 と同様。
DeepLabV3 でセグメンテーションできる物体の種類は、XcodeからMetadataを参照すると次の通り。
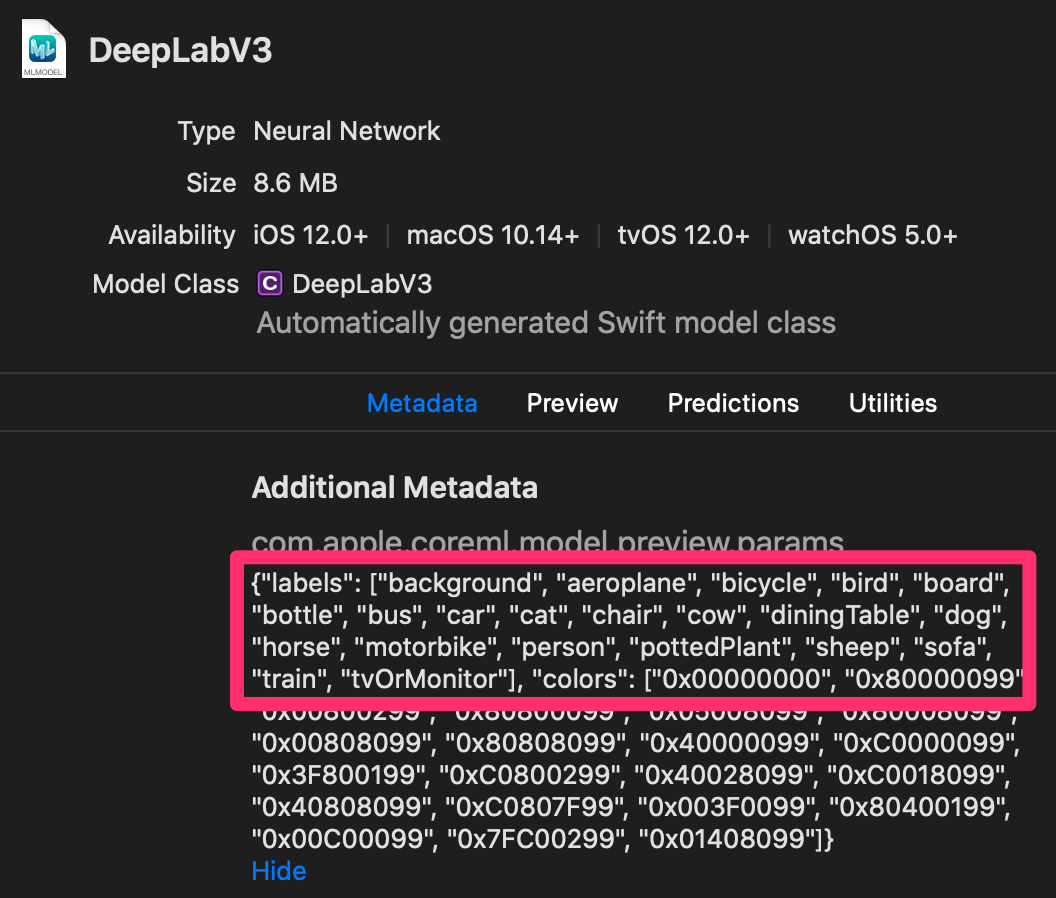
実際に手を認識させるとラベル値=15("labels"のpersonの位置)が得られる。

これは手を撮影してセグメンテーション結果をキャプチャ画像に重ねて表示した例。
手の認識が若干遅れていているのがわかる。今回は人体だけでなく車とか植木鉢を認識させたかったので DeepLabV3 を利用してみたが、人体を認識させたいだけならARKitのピープルオクルージョンの方が高速。
参考:ARKit+Metal で みんな超サイヤ人
ポイントになるのはセグメンテーション結果が格納される MLMultiArray へのアクセス方法。
MLMultiArray には dataPointer というプロパティがあり、assumingMemoryBound(to:) を通して配列としてアクセスができる。
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNCoreMLFeatureValueObservation],
let segmentationmap = observations.first?.featureValue.multiArrayValue else { return }
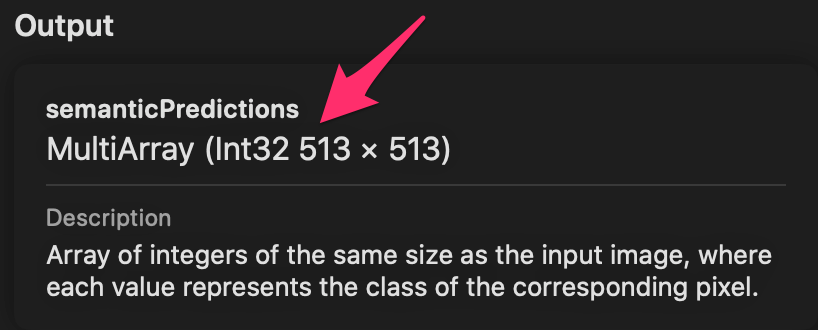
// セグメンテーション結果はInt32の配列
let labels = segmentationmap.dataPointer.assumingMemoryBound(to: Int32.self)
let centerLabel = labels[centerIndex]
Int32の配列としてアクセスしている。これはXcodeから DeepLabV3.mlmodel を確認すると、そのように定義されているから。実際にInt32で値は正しく取れる。
⑤④で認識した物体、且、③の信頼度の高い部分の座標を取得
次のルールで描画するか否かを決める。
- セグメンテーション結果のうち、画面の中央と同じ物体のみ表示
- 深度情報の信頼度が高い部分のみ表示
セグメンテーション結果は下記 isInSegment 部分で判定。
let depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor = Float(self.detectSize) / Float(self.depthSize) // 検出解像度/デプス解像度比
let isInSegment: (Int, Int) -> Bool = { (x, y) in
guard x < self.depthSize && y < self.depthSize else { return false }
let segmentX = Int(Float(x) * depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor + depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor / 2)
let segmentY = Int(Float(y) * depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor + depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor / 2)
let segmentIndex = (segmentedImageSize - segmentY - 1) * segmentedImageSize + segmentX
// 中央のラベルと一致する場合、モデル化
return labels[segmentIndex] == centerLabel
}
引数は深度情報の座標。今回のサンプルをiPhone12Pro+iOS14.2 で動作させると深度情報は 120x120 となるので、この座標に対応するセグメンテーション結果(513x513) で判定。
信頼度の判定は下記 isConfidentDepth 部分で判定。
// 信頼度が高い深度情報のみ3Dモデル化
let isConfidentDepth: (Int, Int) -> Bool = { (x, y) in
guard x < self.depthSize && y < self.depthSize else { return false }
return self.depthArray[y * self.depthSize + x] >= 0.0
}
この判定処理の前にdepthArrayの中で信頼度の低い深度情報を -1 にしているので 0.0 以上が有効と判定している。
ちなみに、-1 を設定している場所はこの部分。
guard depthArray.count == depthConfidenceArray.count else { return }
self.depthArray = depthConfidenceArray.enumerated().map {
// 信頼度が high 未満は深度を -1 に書き換え
return $0.element >= UInt8(ARConfidenceLevel.high.rawValue) ? depthArray[$0.offset] : -1
}
深度の信頼度情報をチェックして、対応する深度情報の値を書き換えている。
⑥⑤の深度情報(2D)を3D座標に変換
self.cameraIntrinsicsInversed = frame.camera.intrinsics.inverse
// (略)
let depth = self.depthArray[y * self.depthSize + x]
let x_px = Float(x) * depthScreenScaleFactor
let y_px = Float(y) * depthScreenScaleFactor
// 2Dの深度情報を3Dに変換
let localPoint = cameraIntrinsicsInversed * simd_float3(x_px, y_px, 1) * depth
ARCamera の intrinsics には、3Dのスケールを2Dに変換する行列が入っている。なので、この逆行列を使うことで、2Dとなっている深度情報を3Dのスケールに広げることができる。
この部分のコードはAppleのLiDARのサンプル Visualizing a Point Cloud Using Scene Depth を流用。
intrinsicsの中身についてはこちらの記事 『ARKitで本物のオセロ盤に評価値を重畳表示してみた』 でイメージがつきました。
ここまでで3Dとして表示すべき情報(任意の画像セグメント、且つ、信頼度の高い深度情報を持つの部分の3D座標)を手に入れたのでこれをモデル化する。
⑦⑥を3Dモデル化して、シーンに追加
深度情報の配列の並びを基に3Dにする。
深度情報の、とある位置おいて、真下と右隣の深度情報で三角形、左隣下と真下の深度情報で三角形、というルールでポリゴンを作っていく。
// 三角形(下向き)
if isInSegment(x, y), isInSegment(x, y + 1), isInSegment(x + 1, y),
isConfidentDepth(x, y), isConfidentDepth(x, y + 1), isConfidentDepth(x + 1, y) {
// セグメント内、且、深度情報の信頼度が高いならポリゴンのインデックスを追加
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x + 1))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x))
if localPoint.y > yMax { yMax = localPoint.y }
if localPoint.y < yMin { yMin = localPoint.y }
}
// 三角形(上向き)
if isInSegment(x, y), isInSegment(x - 1, y + 1), isInSegment(x, y + 1),
isConfidentDepth(x, y), isConfidentDepth(x - 1, y + 1), isConfidentDepth(x, y + 1){
// セグメント内、且、深度情報の信頼度が高いならポリゴンのインデックスを追加
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x - 1))
if localPoint.y > yMax { yMax = localPoint.y }
if localPoint.y < yMin { yMin = localPoint.y }
}
このルールだけだと境界部分の精度が悪いとギザギザが目立つ。改良の余地あり。

ジオメトリ&ノードの作り方の詳細はこちらの記事 『SceneKitでカスタムジオメトリの作り方+おまけ』 が詳しいです。
ジオメトリ ができたら床との衝突判定ができるようにする。
let bodyGeometry = SCNBox(width: 5.0,
height: CGFloat(yMax - yMin),
length: 5.0,
chamferRadius: 0.0)
let bodyShape = SCNPhysicsShape(geometry: bodyGeometry, options: nil)
node.physicsBody = SCNPhysicsBody(type: .dynamic, shape: bodyShape)
// 3m上から落とす
node.simdWorldPosition = SIMD3<Float>(0.0, 3.0, 0.0)
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.scnView.scene.rootNode.addChildNode(node)
}
作ったジオメトリの形状は深度情報を基にしているので、カメラから対象物体の距離までのサイズとなる。このとき、ジオメトリの原点はカメラの位置になる。衝突判定に用いるSCNPhysicsShapeもジオメトリ のサイズに合わせるべきだが、今回は床に衝突できれば良いので、高さだけジオメトリ の高さを設定し、横幅・奥行きは確実に衝突すると考えられるサイズ(5m)にしている。
最後に
今回作ったサンプルは、カメラを原点としてカメラが向いている方向を基準にジオメトリを作っている(カメラの向きが基準となっている)。なので、水平面は考慮していないし向きも考慮していない。

上の例では、車を斜めから見下ろして撮影したので、その向きでジオメトリが作られている。
水平をきちんと考慮すれば、外側の白い線(BoundingBox)に水平なジオメトリを作れるはず。
この辺りは、AppleのLiDARのサンプル Visualizing a Point Cloud Using Scene Depth が描画時にきちんとワールド座標に変換してやってそうだったのでまた別の機会で対応。
説明は以上です。
手探りで作ったので間違っているところや、こうやれば良い、という部分があると思います。
指摘もらえると助かります。
全体ソースコード
import ARKit
import Vision
import UIKit
import SceneKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, ARSessionDelegate, ARSCNViewDelegate {
@IBOutlet weak var scnView: ARSCNView!
// セグメンテーション範囲。DeepLabV3.mlmodelの画像サイズに合わせる
private let detectSize: CGFloat = 513.0
// Vision Model
private var visonRequest: VNCoreMLRequest?
// デプス加工結果
private var depthArray: [Float32] = []
private var depthSize = 0
private var cameraIntrinsicsInversed: simd_float3x3?
// 3Dのテクスチャ画像。コピーボタン押下時のキャプチャ画像が設定される。
private var texutreImage: CGImage?
// コピーボタンが押下状態
private var isButtonPressed = false
// 床の厚さ(m)
private let floorThickness: CGFloat = 0.5
// 床のローカル座標。床の厚さ分、Y座標を下げる
private lazy var floorLocalPosition = SCNVector3(0.0, -floorThickness/2, 0.0)
// 最初に認識したアンカー
private var firstAnchorUUID: UUID?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// CoreMLの設定
setupVison()
// AR Session 開始
self.scnView.delegate = self
self.scnView.session.delegate = self
let configuration = ARWorldTrackingConfiguration()
if ARWorldTrackingConfiguration.supportsFrameSemantics(.sceneDepth) {
configuration.planeDetection = [.horizontal]
configuration.frameSemantics = [.sceneDepth]
self.scnView.session.run(configuration, options: [.removeExistingAnchors, .resetTracking])
} else {
print("この端末では動作しません")
}
}
// アンカーが追加された
func renderer(_: SCNSceneRenderer, didAdd node: SCNNode, for anchor: ARAnchor) {
guard anchor is ARPlaneAnchor, self.firstAnchorUUID == nil else { return }
self.firstAnchorUUID = anchor.identifier
// 床ノードを追加
let floorNode = SCNScene.makeFloorNode(width: 10.0, height: self.floorThickness, length: 10.0)
floorNode.position = floorLocalPosition
DispatchQueue.main.async {
node.addChildNode(floorNode)
}
}
// アンカーが更新された
func renderer(_: SCNSceneRenderer, didUpdate node: SCNNode, for anchor: ARAnchor) {
guard anchor is ARPlaneAnchor else { return }
if let childNode = node.childNodes.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
// 床ノードの位置を再設定
childNode.position = self.floorLocalPosition
}
}
}
// ARフレームが更新された
func session(_ session: ARSession, didUpdate frame: ARFrame) {
guard self.isButtonPressed else { return }
self.isButtonPressed = false
let aspectRatio = self.scnView.bounds.height / self.scnView.bounds.width
// キャプチャ画像の中央をDeeplabV3のサイズ(513x513)で切り抜く
let image = frame.cropCenterSquareImage(fullWidthScale: self.detectSize,
aspectRatio: aspectRatio,
orientation: self.scnView.window!.windowScene!.interfaceOrientation)
let context = CIContext(options: nil)
self.texutreImage = context.createCGImage(image, from: image.extent)
// 深度情報を取得
let (depthArray, depthSize) = frame.cropPortraitCenterSquareDepth(aspectRatio: aspectRatio)
// 深度の信頼度情報を取得
let (depthConfidenceArray, _) = frame.cropPortraitCenterSquareDepthConfidence(aspectRatio: aspectRatio)
// 信頼度が高い深度情報のみ抽出
guard depthArray.count == depthConfidenceArray.count else { return }
self.depthArray = depthConfidenceArray.enumerated().map {
// 信頼度が high 未満は深度を -1 に書き換え
return $0.element >= UInt8(ARConfidenceLevel.high.rawValue) ? depthArray[$0.offset] : -1
}
self.depthSize = depthSize
// 「カメラの焦点距離と中心点オフセット情報」の逆行列。2Dの深度情報を3Dに広げるために準備。参考:https://qiita.com/tanaka-a/items/042fdbd3da6d6332e7e2
self.cameraIntrinsicsInversed = frame.camera.intrinsics.inverse
// セグメンテーション 実行
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(ciImage: image, options: [:])
try? handler.perform([self.visonRequest!])
}
// コピーボタンが押された
@IBAction func pressButton(_ sender: Any) {
isButtonPressed = true
}
}
// MARK: -
extension ViewController {
private func setupVison() {
guard let visionModel = try? VNCoreMLModel(for: DeepLabV3(configuration: MLModelConfiguration()).model) else { return }
let request = VNCoreMLRequest(model: visionModel) { request, error in
// セグメンテーション結果受け取り
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNCoreMLFeatureValueObservation],
let segmentationmap = observations.first?.featureValue.multiArrayValue else { return }
// マスク部分の3Dモデル生成
self.draw3DModel(segmentationmap: segmentationmap)
}
request.imageCropAndScaleOption = .centerCrop
self.visonRequest = request
}
private func draw3DModel(segmentationmap: MLMultiArray) {
guard !self.depthArray.isEmpty, let cameraIntrinsicsInversed = self.cameraIntrinsicsInversed else { return }
// セグメンテーション結果はInt32の配列
let labels = segmentationmap.dataPointer.assumingMemoryBound(to: Int32.self)
// 画面中央のラベルを取得
let segmentedImageSize = Int(self.detectSize)
let centerIndex = (segmentedImageSize / 2) * segmentedImageSize + (segmentedImageSize / 2)
let centerLabel = labels[centerIndex]
print("画面中央のラベル値 [\(centerLabel)]")
// 深度情報のサイズ(このサンプルをiPhone12Pro+iOS14.2で実行した場合は120x120)を軸にして、セグメンテーション結果(513x513)を参照して3Dモデル対象か判定
let depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor = Float(self.detectSize) / Float(self.depthSize) // 検出解像度/デプス解像度比
let isInSegment: (Int, Int) -> Bool = { (x, y) in
guard x < self.depthSize && y < self.depthSize else { return false }
let segmentX = Int(Float(x) * depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor + depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor / 2)
let segmentY = Int(Float(y) * depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor + depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor / 2)
let segmentIndex = (segmentedImageSize - segmentY - 1) * segmentedImageSize + segmentX
// 中央のラベルと一致する場合、モデル化
return labels[segmentIndex] == centerLabel
}
// 信頼度が高い深度情報のみ3Dモデル化
let isConfidentDepth: (Int, Int) -> Bool = { (x, y) in
guard x < self.depthSize && y < self.depthSize else { return false }
return self.depthArray[y * self.depthSize + x] >= 0.0
}
// ポリゴン頂点座標、テクスチャ座標を生成
var vertices: [SCNVector3] = []
var texcoords: [CGPoint] = []
var indices: [Int32] = []
var yMax: Float = 0.0
var yMin: Float = 0.0
let depthScreenScaleFactor = Float(self.scnView.bounds.width * UIScreen.screens.first!.scale / CGFloat(self.depthSize))
for y in 0 ..< self.depthSize {
for x in 0 ..< self.depthSize {
// 頂点座標を作成(最終的に表示しないものも作る)
let depth = self.depthArray[y * self.depthSize + x]
let x_px = Float(x) * depthScreenScaleFactor
let y_px = Float(y) * depthScreenScaleFactor
// 2Dの深度情報を3Dに変換
let localPoint = cameraIntrinsicsInversed * simd_float3(x_px, y_px, 1) * depth
// 深度情報はプラス、SceneKitは奥がマイナスなのでZは符号反転
vertices.append(SCNVector3(localPoint.x, localPoint.y, -localPoint.z))
// キャプチャ画像上の座標をテクスチャ座標とする
let x_coord = CGFloat(x) * CGFloat(depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor) / self.detectSize
let y_coord = CGFloat(y) * CGFloat(depthDeeplabV3ScaleFactor) / self.detectSize
texcoords.append(CGPoint(x: x_coord, y: 1 - y_coord))
// 三角形(下向き)
if isInSegment(x, y), isInSegment(x, y + 1), isInSegment(x + 1, y),
isConfidentDepth(x, y), isConfidentDepth(x, y + 1), isConfidentDepth(x + 1, y) {
// セグメント内、且、深度情報の信頼度が高いならポリゴンのインデックスを追加
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x + 1))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x))
if localPoint.y > yMax { yMax = localPoint.y }
if localPoint.y < yMin { yMin = localPoint.y }
}
// 三角形(上向き)
if isInSegment(x, y), isInSegment(x - 1, y + 1), isInSegment(x, y + 1),
isConfidentDepth(x, y), isConfidentDepth(x - 1, y + 1), isConfidentDepth(x, y + 1){
// セグメント内、且、深度情報の信頼度が高いならポリゴンのインデックスを追加
indices.append(Int32(y * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x))
indices.append(Int32((y + 1) * self.depthSize + x - 1))
if localPoint.y > yMax { yMax = localPoint.y }
if localPoint.y < yMin { yMin = localPoint.y }
}
}
}
// ジオメトリ作成
let vertexSource = SCNGeometrySource(vertices: vertices)
let texcoordSource = SCNGeometrySource(textureCoordinates: texcoords)
let geometryElement = SCNGeometryElement(indices: indices, primitiveType: .triangles)
let geometry = SCNGeometry(sources: [vertexSource, texcoordSource], elements: [geometryElement])
// マテリアル作成
let material = SCNMaterial()
material.lightingModel = .constant
material.diffuse.contents = self.texutreImage
geometry.materials = [material]
// ノード作成
let node = SCNNode(geometry: geometry)
// 衝突判定のサイズは床にぶつかるようにするだけでサイズは適当。
let bodyGeometry = SCNBox(width: 5.0,
height: CGFloat(yMax - yMin),
length: 5.0,
chamferRadius: 0.0)
let bodyShape = SCNPhysicsShape(geometry: bodyGeometry, options: nil)
node.physicsBody = SCNPhysicsBody(type: .dynamic, shape: bodyShape)
// 3m上から落とす
node.simdWorldPosition = SIMD3<Float>(0.0, 3.0, 0.0)
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.scnView.scene.rootNode.addChildNode(node)
}
}
}
import UIKit
import ARKit
extension CVPixelBuffer {
var width: Int { CVPixelBufferGetWidth(self) }
var height: Int { CVPixelBufferGetHeight(self) }
func cropPortraitCenterData<T>(sideCutoff: Int) -> ([T], Int) {
CVPixelBufferLockBaseAddress(self, CVPixelBufferLockFlags(rawValue: CVOptionFlags(0)))
guard let baseAddress = CVPixelBufferGetBaseAddress(self) else { return ([], 0) }
let pointer = UnsafeMutableBufferPointer<T>(start: baseAddress.assumingMemoryBound(to: T.self),
count: width * height)
var dataArray: [T] = []
// 画面上の横幅のサイズを計算。画面の横サイズいっぱいから左右は切り落とした値。
// ※紛らわしいがポートレート時にARKitから取得されるデータは横向きなので height で計算。
let size = height - sideCutoff * 2
// 画面の縦方向の中央部分のデータを取得。取得順番は上下逆転。
for x in (Int((width / 2) - (size / 2)) ..< Int((width / 2) + (size / 2))).reversed() {
// 画面の横方向の中央部分のデータを取得。取得順番は左右逆転。
for y in (sideCutoff ..< (height - sideCutoff)).reversed() {
let index = y * width + x
dataArray.append(pointer[index])
}
}
CVPixelBufferUnlockBaseAddress(self, CVPixelBufferLockFlags(rawValue: CVOptionFlags(0)))
return (dataArray, size)
}
}
extension ARFrame {
func cropCenterSquareImage(fullWidthScale: CGFloat, aspectRatio: CGFloat, orientation: UIInterfaceOrientation) -> CIImage {
let pixelBuffer = self.capturedImage
// 入力画像をスクリーンサイズに変換
let imageSize = CGSize(width: pixelBuffer.width, height: pixelBuffer.height)
let image = CIImage(cvImageBuffer: pixelBuffer)
// 1) 入力画像を 0.0〜1.0 の座標に変換
let normalizeTransform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: 1.0/imageSize.width, y: 1.0/imageSize.height)
// 2) ポートレートの場合、X軸Y軸を反転
var flipTransform = CGAffineTransform.identity
if orientation.isPortrait {
// X軸Y軸共に反転
flipTransform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: -1, y: -1)
// X軸Y軸共にマイナス側に移動してしまうのでプラス側に移動
flipTransform = flipTransform.concatenating(CGAffineTransform(translationX: 1, y: 1))
}
// 3) 入力画像上でのスクリーンの向き・位置に移動
let viewPortSize = CGSize(width: fullWidthScale, height: fullWidthScale * aspectRatio)
let displayTransform = self.displayTransform(for: orientation, viewportSize: viewPortSize)
// 4) 0.0〜1.0 の座標系からスクリーンの座標系に変換
let toViewPortTransform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: viewPortSize.width, y: viewPortSize.height)
// 5) 1〜4までの変換を行い、変換後の画像を指定サイズでクリップ
let transformedImage = image
.transformed(by: normalizeTransform
.concatenating(flipTransform)
.concatenating(displayTransform)
.concatenating(toViewPortTransform))
.cropped(to: CGRect(x: 0,
y: CGFloat(Int(viewPortSize.height / 2.0 - fullWidthScale / 2.0)),
width: fullWidthScale,
height: fullWidthScale))
return transformedImage
}
func cropPortraitCenterSquareDepth(aspectRatio: CGFloat) -> ([Float32], Int) {
guard let pixelBuffer = self.sceneDepth?.depthMap else { return ([], 0) }
return cropPortraitCenterSquareMap(pixelBuffer, aspectRatio)
}
func cropPortraitCenterSquareDepthConfidence(aspectRatio: CGFloat) -> ([UInt8], Int) {
guard let pixelBuffer = self.sceneDepth?.confidenceMap else { return ([], 0) }
return cropPortraitCenterSquareMap(pixelBuffer, aspectRatio)
}
private func cropPortraitCenterSquareMap<T>(_ pixelBuffer: CVPixelBuffer, _ aspectRatio: CGFloat) -> ([T], Int) {
let viewPortSize = CGSize(width: 1.0, height: aspectRatio)
var displayTransform = self.displayTransform(for: .portrait, viewportSize: viewPortSize)
// ポートレートの場合、X軸Y軸共に反転
var flipTransform = CGAffineTransform(scaleX: -1, y: -1)
// X軸Y軸共にマイナス側に移動してしまうのでプラス側に移動
flipTransform = flipTransform.concatenating(CGAffineTransform(translationX: 1, y: 1))
displayTransform = displayTransform.concatenating(flipTransform)
let sideCutoff = Int((1.0 - (1.0 / displayTransform.c)) / 2.0 * CGFloat(pixelBuffer.height))
return pixelBuffer.cropPortraitCenterData(sideCutoff: sideCutoff)
}
}
extension SCNScene {
static func makeFloorNode(width: CGFloat, height: CGFloat, length: CGFloat) -> SCNNode {
let geometry = SCNBox(width: width, height: height, length: length, chamferRadius: 0.0)
let material = SCNMaterial()
material.lightingModel = .shadowOnly
geometry.materials = [material]
let node = SCNNode(geometry: geometry)
node.castsShadow = false
node.physicsBody = SCNPhysicsBody.static()
return node
}
}

