0. 初めに
2020年末ぐらいにkaggleで開催された胸部レントゲン画像コンペに参加しました。胸のレントゲン画像にある病変部位を見つけるという、物体検知タスクのコンペでした。
このコンペで銅メダルをいただきましたが、しかしこれはGMの方のノートブックをベースにすこしいじってsubmitしただけであって、私自身の力ではありません。
せっかくなので物体検知について勉強し、記事を残したいと思います。
MNISTから以下のような物体検知用の画像を作り、detectron2でモデルを開発して評価を行います。
コードはgithubにあるのでよかったら見てみてください。
https://github.com/persimmon-persimmon/mnist-detection
Googleドライブ直下にmnist_detectionというフォルダを作ってファイルを入れてColabで起動すれば動くと思います。
1. データ準備
kerasのmnistからデータを作ります。アノテーションはCOCOフォーマットで作成します。
以下を実行すれば、imagesフォルダに画像が2万枚でき、train,val,testごとにCOCOフォーマットのjsonファイルができあがります。
COCOフォーマットについては「参考」の記事を参照。
| データまとめ | |
|---|---|
| 画像サイズ | 224x224 |
| 枚数 | 全部で2万枚(train:val:test=7,2,1) |
| クラス比率 | 8,9が出現しやすく、数字が小さくなるほど出現しにくくなる。 |
from keras.datasets import mnist
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import json
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import cv2
import random
from PIL import Image
(_x_train_val, _y_train_val), (_x_test, _y_test)=mnist.load_data()
_x_train, _x_val, _y_train, _y_val = train_test_split(_x_train_val, _y_train_val, test_size=0.2)
train={i:[x for x, t in zip(_x_train, _y_train) if t == i] for i in range(10)}
val={i:[x for x, t in zip(_x_val, _y_val) if t == i] for i in range(10)}
test={i:[x for x, t in zip(_x_test, _y_test) if t == i] for i in range(10)}
image_set={"train":train,"val":val,"test":test}
n_image={"train":14000,"val":4000,"test":2000}
random.seed(0)
height = 224
width = 224
ls=[i for i in range(-1,10)]
weight=[40,10,10,15,15,20,20,25,25,30,30] # 各クラスの登場頻度
os.makedirs("images", exist_ok=True)
# COCOフォーマット出力用変数
coco={}
coco["categories"]=[]
coco["categories"].append({"id":"0","name":"zero"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"1","name":"one"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"2","name":"two"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"3","name":"three"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"4","name":"four"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"5","name":"five"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"6","name":"six"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"7","name":"seven"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"8","name":"eight"})
coco["categories"].append({"id":"9","name":"nine"})
annotation_template={}
annotation_template["segmentation"]=0
annotation_template["area"]=28*28
annotation_template["iscrowd"]=False
annotation_template["isbbox"]=True
annotation_template["image_id"]=0
annotation_template["bbox"]=0
annotation_template["category_id"]=0
annotation_template["id"]=0
image_template={}
image_template["dataet_id"]=1
image_template["deleted"]=False
image_template["file_name"]=0
image_template["id"]=0
image_template["num_annotations"]=0
image_template["path"]=0
image_template["width"]=width
image_template["height"]=height
for data_type in ["train","val","test"]:
images=[]
annotations=[]
for t in range(1,n_image[data_type]+1):
blank = np.random.random((height, width, 3))*127
blank = np.int64(blank)
image_template["file_name"]=f"images/{data_type}_{str(t).zfill(6)}.jpg"
image_template["id"]+=1
image_template["path"]=f"images/{data_type}_{str(t).zfill(6)}.jpg"
for i,label in enumerate(random.choices(ls,k=4,weights=weight)):
if label==-1:continue
im=random.choice(image_set[data_type][label])
if i//2==0:
x_ = int(random.uniform(0,height//2 - 28))
else:
x_ = int(random.uniform(height//2,height - 28))
if i%2==0:
y_ = int(random.uniform(0,width//2 - 28))
else:
y_ = int(random.uniform(width//2, width - 28))
blank[x_:x_ + 28,y_:y_ + 28,0]+=np.int64(im/3)
blank[x_:x_ + 28,y_:y_ + 28,1]+=np.int64(im/3)
blank[x_:x_ + 28,y_:y_ + 28,2]+=np.int64(im/3)
x=y_
y=x_
annotation_template["image_id"]=image_template["id"]
annotation_template["bbox"]=[x,y,28,28]
annotation_template["category_id"]=str(label)
annotation_template["id"]+=1
annotation_template["segmentation"]=[[x,y,x+28,y,x+28,y+28,x,y+28]]
annotations.append(annotation_template.copy())
cv2.imwrite(image_template["path"],blank)
images.append(image_template.copy())
coco["images"]=images
coco["annotations"]=annotations
with open(f"coco_{data_type}.json","w") as f:
f.write(json.dumps(coco))
coco.pop("images")
coco.pop("annotations")
作成したデータを確認します。
!pip install pyyaml==5.1
import torch
TORCH_VERSION = ".".join(torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
CUDA_VERSION = torch.__version__.split("+")[-1]
print("torch: ", TORCH_VERSION, "; cuda: ", CUDA_VERSION)
!pip install detectron2 -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/$CUDA_VERSION/torch$TORCH_VERSION/index.html
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer, ColorMode
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog, DatasetCatalog
from detectron2.data.datasets import register_coco_instances
reg_name="mnist_detection_train"
register_coco_instances(reg_name, {}, "coco_train.json", "")
mnist_detection_metadata = MetadataCatalog.get(reg_name)
dataset_dicts = DatasetCatalog.get(reg_name)
for d in random.sample(dataset_dicts, 3):
print(d["file_name"])
img = cv2.imread(d["file_name"])
visualizer = Visualizer(img[:, :, ::-1], metadata=mnist_detection_metadata, scale=1.0)
vis = visualizer.draw_dataset_dict(d)
cv2_imshow(vis.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])

実行すると、「Category ids in annotations are not in [1, #categories]! We'll apply a mapping for you.」という警告が出ますが、無視してよいです。カテゴリIDが1から始まってないと発生する警告です。詳しくはdetectron2のソースコード参照。
https://detectron2.readthedocs.io/en/latest/_modules/detectron2/data/datasets/coco.html
3. 学習
環境に対応するdetectron2をインストールして学習します。ほぼdetectron2のチュートリアルそのままのコードです。
!pip install pyyaml==5.1
import torch
TORCH_VERSION = ".".join(torch.__version__.split(".")[:2])
CUDA_VERSION = torch.__version__.split("+")[-1]
print("torch: ", TORCH_VERSION, "; cuda: ", CUDA_VERSION)
!pip install detectron2 -f https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/wheels/$CUDA_VERSION/torch$TORCH_VERSION/index.html
import detectron2
from detectron2.utils.logger import setup_logger
setup_logger()
import numpy as np
import os, json, cv2, random
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
from detectron2 import model_zoo
from detectron2.engine import DefaultPredictor, DefaultTrainer
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer, ColorMode
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog, DatasetCatalog
from detectron2.data.datasets import register_coco_instances
## データ準備
for data_type in ["train","val","test"]:
reg_name=f"mnist_detection_{data_type}"
register_coco_instances(reg_name, {}, f"coco_{data_type}.json", "")
## 学習
cfg = get_cfg()
cfg.merge_from_file(model_zoo.get_config_file("COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml"))
cfg.DATASETS.TRAIN = ("mnist_detection_train",)
cfg.DATASETS.TEST = ()
cfg.DATALOADER.NUM_WORKERS = 2
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = model_zoo.get_checkpoint_url("COCO-Detection/faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml")
cfg.SOLVER.IMS_PER_BATCH = 2
cfg.SOLVER.BASE_LR = 0.0004
cfg.SOLVER.MAX_ITER = (1000)
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.BATCH_SIZE_PER_IMAGE = (128)
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.NUM_CLASSES = 10
os.makedirs(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, exist_ok=True)
trainer = DefaultTrainer(cfg)
trainer.resume_or_load(resume=False)
trainer.train()
実行がおわったら、どれぐらい学習できているか確認します。
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, "model_final.pth")
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.6
predictor = DefaultPredictor(cfg)
mnist_detection_metadata = MetadataCatalog.get("mnist_detection_test")
from random import randint
for _ in range(3):
t = randint(1,2000)
print(f"images/test_{str(t).zfill(6)}.jpg")
im = cv2.imread(f"images/test_{str(t).zfill(6)}.jpg")
outputs = predictor(im)
v = Visualizer(im[:, :, ::-1],
metadata=mnist_detection_metadata,
scale=1.0
)
v = v.draw_instance_predictions(outputs["instances"].to("cpu"))
cv2_imshow(v.get_image()[:, :, ::-1])
モデルが予測した値が60%以上のものについてBBOXを出しています。
きちんと検知できているのもあれば、見逃しているのもあります。
3. 評価
COCO Evaluatorで評価してみます。
from detectron2.evaluation import COCOEvaluator, inference_on_dataset
from detectron2.data import build_detection_test_loader
evaluator = COCOEvaluator("mnist_detection_val", output_dir="./output")
val_loader = build_detection_test_loader(cfg, "mnist_detection_val")
print(inference_on_dataset(predictor.model, val_loader, evaluator))
# another equivalent way to evaluate the model is to use `trainer.test`
AP(Average Precision)とはざっくり言えばPrecision-Recall曲線のAUCのことです。
計算方法や対象の大きさで複数種類あります。
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APs | APm | APl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 46.885 | 62.038 | 60.541 | 46.895 | nan | nan |
| 用語 | |
|---|---|
| AP | IoUを0.5から0.95まで0.05刻みで動かして計算したAPの平均 |
| AP50 | IoU>0.5で計算したAP |
| AP75 | IoU>0.75で計算したAP |
| APs | 小さい物体に対するAP |
| APm | 中くらいの物体に対するAP |
| APl | 大きい物体に対するAP |
| IoU | 正解BBOXと予測BBOXのUnionに対するIntersectionの割合。正解と予測がぴったり重なれば1、重なりがなければ0。たとえば「IoU>0.5で計算したAP」とは、IoUが0.5を超える予測のみを正しい予測として計算したAPのこと |
今回の検出対象はすべて小さい物体に分類されるのでAPmとAPlはnanになっています。
クラスごとのAPは以下。
| category | AP | category | AP | category | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| zero | 67.623 | one | 47.831 | two | 38.955 |
| three | 0.000 | four | 72.527 | five | 23.396 |
| six | 51.118 | seven | 58.211 | eight | 48.638 |
| nine | 60.546 |
見ると、クラス3のAPが0になっています。他は2と5の精度が低いです。おそらく下の画像のように、「3を5と認識している」「2と5の見分けが難しい」が原因だと思います。
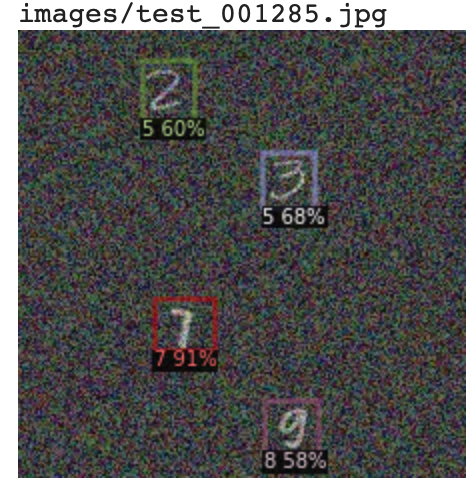
気が向けば改善したいと思います。
参考
・COCOフォーマットについて
・APについて
https://jonathan-hui.medium.com/map-mean-average-precision-for-object-detection-45c121a31173
・detectron2チュートリアル
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/16jcaJoc6bCFAQ96jDe2HwtXj7BMD_-m5




