当記事ではAtCoder、ABCのB問題ならびにC問題(時々D問題も)のKotlinでの解法を超初心者向けに詳細に解説します。
B - Nice Grid
やりたいこと
行(r)と列(r)を入力値から受け取って、その座標の色が白なのか黒なのかを求めたい。
まず、入力値の座標が縦棒エリアに属するのか、横棒エリアに属するのかを判定しよう。
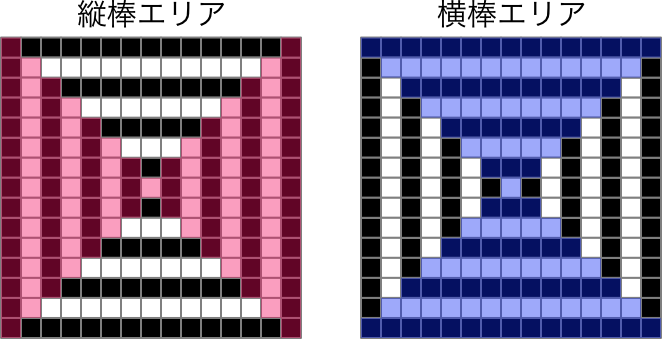
入力された座標がどちらのエリアに属するのかは行(r)と列(c)を中央の白いマスの行・列との差の絶対値の大小で決まる。
Math.abs(8 - r) < Math.abs(8 - c)
ならば縦棒エリアに属し、
Math.abs(8 - r) > Math.abs(8 - c)
ならば横棒エリアに属する
Math.abs(8 - r) == Math.abs(8 - c)
の場合は両方(縦棒と横棒がぶつかる角の部分)に属することになる。
入力された座標が縦棒エリアに属する場合はcの値と中央のマスの列の差が偶数である場合は白、奇数である場合は黒となる。
入力された座標が横棒エリアに属する場合はrの値と中央のマスの行の差が偶数である場合は白、奇数である場合は黒となる。
これをコードにすると以下のようになる。
if (Math.max(Math.abs(8 - r), Math.abs(8 - c)) % 2 == 0) "white" else "black"
入力値の取得
// 入力値の取得
val (r, c) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
サンプルコード
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
// 入力値の取得
val (r, c) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
println(if (Math.max(Math.abs(8 - r), Math.abs(8 - c)) % 2 == 0) "white" else "black")
}
C - Matrix Reducing
やりたいこと
行列Aの各行・列がとりうる状態は「残っている」「削除された」の2種類。行・列の最大値は10なので、全ての組み合わせについて行列Bと同じものが存在するかどうかを調べよう。
各行・列の状態を0,1に割り当てて、N桁の二進数として 0から $2^n-1$ までビットフラグを処理しよう。
ビットフラグについての詳細はこちらを参照してください。
AtCoder B,C問題をKotlinで解こう - ABC249 C - Just K
入力値の取得
// 入力値の取得
val (h1, w1) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val a = (1..h1).map { readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() } }
val (h2, w2) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val b = (1..h2).map { readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() } }
サンプルコード
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println(if (getAns()) "Yes" else "No")
}
private fun getAns(): Boolean {
// 入力値の取得
val (h1, w1) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val a = (1..h1).map { readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() } }
val (h2, w2) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val b = (1..h2).map { readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() } }
for (i in (1 until (1 shl h1))) {
// フラグに合致する行のインデックス(削除されていない行)のリストを作る
val rowIndex = (0 until h1).filter { (1 shl it) and i != 0 }
// 行の数が数列Bの行の数と不一致の場合は処理をスキップする
if (rowIndex.size != h2) {
continue
}
for (j in (1 until (1 shl w1))) {
// フラグに合致する列のインデックス(削除されていない列)のリストを作る
val colIndex = (0 until w1).filter { (1 shl it) and j != 0 }
// 列の数が数列Bの列の数と不一致の場合は処理をスキップする
if (colIndex.size != w2) {
continue
}
// 行列Aからフラグに合致しない行・列を削除した新しい行列を作成する
val map = mutableListOf<MutableList<Int>>()
for (k in rowIndex) {
val row = mutableListOf<Int>()
for (l in colIndex) {
row.add(a[k][l])
}
map.add(row)
}
// 新しい行列が行列Bと一致するかどうかを判定する
var isMatch = true
for (k in map.indices) {
for (l in map[k].indices) {
if (b[k][l] != map[k][l]) {
isMatch = false
break
}
}
if (!isMatch) {
break
}
}
if (isMatch) {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}