目的
センサ評価用の基板を使ってアプリとか作るなら、やっぱり無線がいいですよね。
でも、だいたい評価用の基板にはbluetooothとかwifiなんてついていません。
最近は無線モジュール側はけっこうすぐに使えたりするのですが、(僕にとっては)Androidアプリが難しかったりします。
サンプルコードもjavaしか見つけられなくて、手こずりました。
ここらへんを簡単にできるようにメモしておきます✌
環境
テストには以下のものを用いました。
- Nexus 6P (Android 8.1.0)
- Android Studio 3.5.3
- Kotlin
- ESP32-DevKitC ESP-WROOM-32開発ボード
- Arduino 1.8.13
- Tera Term
ソリューションの提案
下図の上のようにセンサとスマホで通信したいけど、できないというのが今回解決したい課題です。
図の下側のように、センサとスマホの間に ESP32 を挟むだけで、センサからはUARTでデータを送信するだけで、スマホ側に届くんです!
(もうこれ便利すぎなんですが、もっと便利なBluetooth+Wifiのモジュールがあれば教えてください。)
たいていUARTはついていると思いますが、そうじゃない場合はESP側のソフトを適宜変えましょう。
ESP32編
無線モジュール側はとても簡単です。
まずはArduinoのボードマネージャでESP32用のライブラリたちをダウンロードしましょう。
ダウンロード方法については、ESP32とBluetoothSerialで文字列を送受信する を参考にしてみてください。
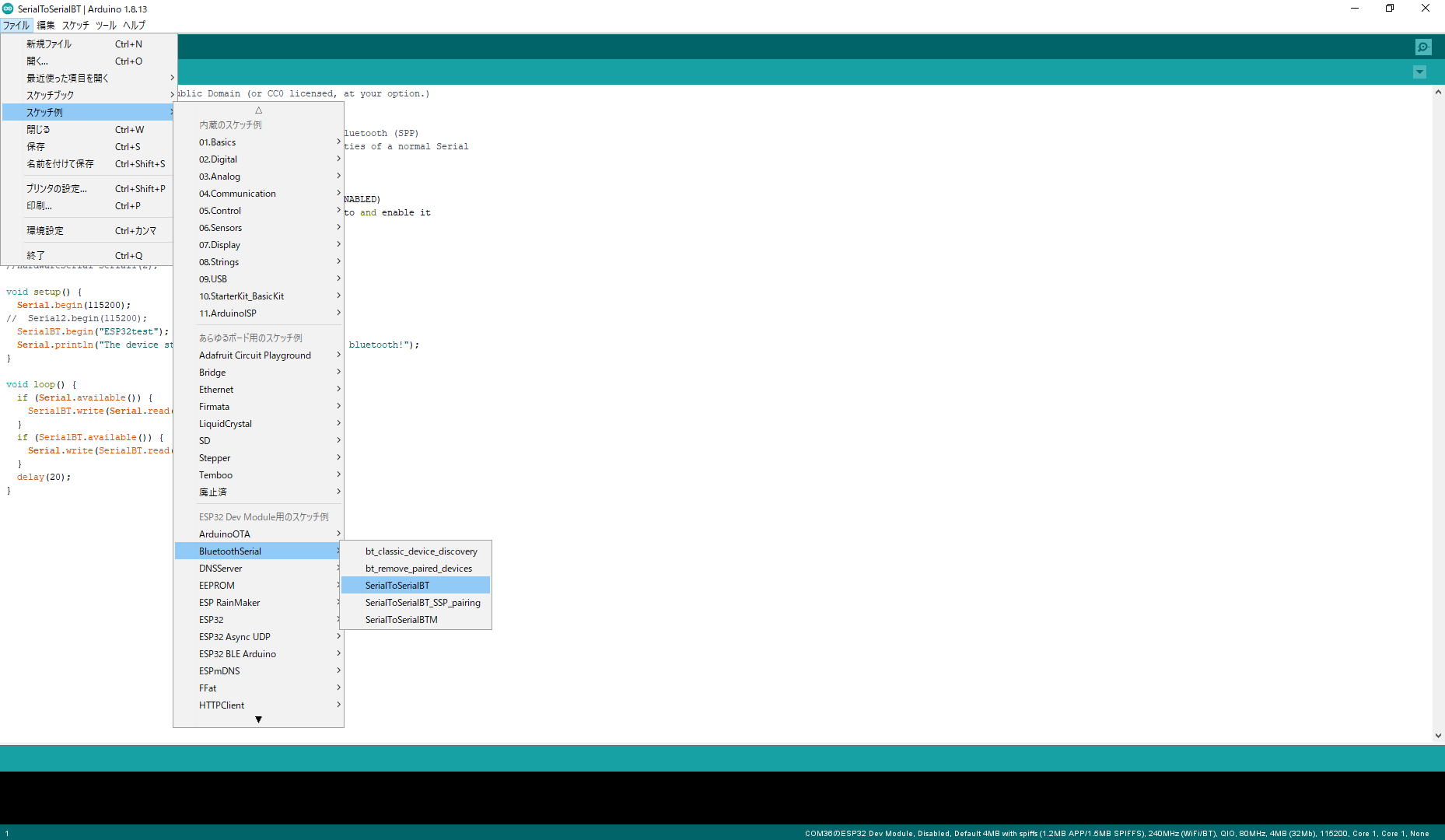
ダウンロード出来たら、サンプルコードを開きます。
以下の画像にある通り、SerialToSerialBTを選択しましょう。
PCやスマホからはESP32testという名前のデバイスとして見つけることができます。スマホとペアリングをしておきましょう。
このソースコードを使えば、ちゃんと動いているかどうかをUSB-UART経由でテストすることが可能です。
ですがここで使われているUART0はUSB-UARTに使われており通信できないため、センサ基板からデータを受け取るという目的が果たせません。
そこで、IO16,IO17にあるUART2を使います。
参考: Arduino-ESP32 Serial通信
以下のソースコードはほぼサンプルコードそのままですが、UART2を使用できるように変更してあります。
Serial.begin(115200)を残しているのは、これをなくすと、デバッグメッセージが出せないから(?)かESP32が動かなくなるからです。
//This example code is in the Public Domain (or CC0 licensed, at your option.)
//By Evandro Copercini - 2018
//
//This example creates a bridge between Serial and Classical Bluetooth (SPP)
//and also demonstrate that SerialBT have the same functionalities of a normal Serial
# include "BluetoothSerial.h"
# if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
# error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
# endif
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial2.begin(115200); // これがUART2
SerialBT.begin("ESP32test"); //Bluetooth device name
Serial.println("The device started, now you can pair it with bluetooth!");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial2.available()) {
SerialBT.write(Serial2.read());
}
if (SerialBT.available()) {
Serial2.write(SerialBT.read());
}
delay(20);
}
Android編
Androidは基本的にはサンプルソースを読むのが大変だったので、Bluetooth の概要を参考にしました。
ここのソースコードを全部コピーしただけでは動かなかったのですが、動かないポイントとしてはクライアント側の接続にありました。
connectしたsocketを使って通信をするのですが、useという関数が最後まで行くとsocket.closeが呼ばれてしまい、通信が終わってしまいます。これがなんかうまくいかない原因だったようです。
private inner class ConnectThread(device: BluetoothDevice) : Thread() {
・・・
// ここから問題のコード
mmSocket?.use { socket ->
// Connect to the remote device through the socket. This call blocks
// until it succeeds or throws an exception.
socket.connect()
// The connection attempt succeeded. Perform work associated with
// the connection in a separate thread.
manageMyConnectedSocket(socket)
// この関数の後にsocket.close()が自動で呼ばれる
}
// ここまで問題のコード
}
・・・
}
もう一つ、SPPを使う場合に注意するべきは、UUIDです。
bluetoothのSPPを使う場合にはもともと用意されているUUIDをdevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID)のMY_UUIDのところに入れてやる必要があります。以下はSPPのUUIDです。
00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB
以下のソースコードはAndroidStudioのEmptyActivityをベースにして、Bluetooth の概要をコピーしてきたものです。
ここではonCreateの中で、ペアリング済みのbluetoothデバイスを探して、ESP32testというデバイスを見つけたらそれに接続するというプログラムになっています。
途中のdevice.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(device.uuids[0].uuid)でペアリングした際に取得したUUID(これはSPPと一致する)を入れているところがポイントです。
const val TAG = "MainActivity"
const val TARGET_DEVICE_NAME = "ESP32test"
const val REQUEST_ENABLE_BLUETOOTH = 1
// Defines several constants used when transmitting messages between the
// service and the UI.
const val MESSAGE_READ: Int = 0
const val MESSAGE_WRITE: Int = 1
const val MESSAGE_TOAST: Int = 2
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val bluetoothAdapter: BluetoothAdapter? = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter()
private var connectedThread: ConnectedThread? = null
private var connectThread: ConnectThread? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
if (bluetoothAdapter == null) {
Log.d(TAG, "bluetooth is not supported.")
return
}
if (!bluetoothAdapter.isEnabled) {
val enableBluetoothIntent = Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE)
startActivityForResult(enableBluetoothIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BLUETOOTH)
}
val pairedDevices: Set<BluetoothDevice>? = bluetoothAdapter.bondedDevices
pairedDevices?.forEach { device ->
val deviceName = device.name
val deviceHardwareAddress = device.address // MAC address
if (device.name == TARGET_DEVICE_NAME) {
Log.d(TAG, "name = %s, MAC <%s>".format(deviceName, deviceHardwareAddress))
device.uuids.forEach { uuid ->
Log.d(TAG, "uuid is %s".format(uuid.uuid))
}
connectThread = ConnectThread(device)
connectThread?.start()
return
}
}
}
fun manageMyConnectedSocket(socket: BluetoothSocket) {
connectedThread = ConnectedThread(socket)
connectedThread?.start()
}
private inner class ConnectThread(device: BluetoothDevice) : Thread() {
private val mmSocket: BluetoothSocket? by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.NONE) {
device.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(device.uuids[0].uuid)
// SPPのUUIDは決まっているけどほかのUUIDだったり、そもそもUUIDを打たなくていいから便利
}
public override fun run() {
// Cancel discovery because it otherwise slows down the connection.
bluetoothAdapter?.cancelDiscovery()
if (mmSocket == null) {
return
}
val socket = mmSocket
socket ?: return
socket.connect()
// The connection attempt succeeded. Perform work associated with
// the connection in a separate thread.
manageMyConnectedSocket(socket)
// ここではないどこかでcloseの処理は入れないといけない
// socket.close()
// mmSocket?.use { socket ->
// // Connect to the remote device through the socket. This call blocks
// // until it succeeds or throws an exception.
// socket.connect()
// // The connection attempt succeeded. Perform work associated with
// // the connection in a separate thread.
// manageMyConnectedSocket(socket)
// }
}
// Closes the client socket and causes the thread to finish.
fun cancel() {
try {
mmSocket?.close()
} catch (e: IOException) {
Log.e(TAG, "Could not close the client socket", e)
}
}
}
private inner class ConnectedThread(private val mmSocket: BluetoothSocket) : Thread() {
private val mmInStream: InputStream = mmSocket.inputStream
private val mmOutStream: OutputStream = mmSocket.outputStream
private val mmBuffer: ByteArray = ByteArray(1024) // mmBuffer store for the stream
override fun run() {
var numBytes: Int // bytes returned from read()
Log.d(TAG, "connect start!")
// Keep listening to the InputStream until an exception occurs.
while (true) {
// Read from the InputStream.
numBytes = try {
mmInStream.read(mmBuffer)
} catch (e: IOException) {
Log.d(TAG, "Input stream was disconnected", e)
break
}
Log.d(TAG, mmBuffer[0].toString())
// // Send the obtained bytes to the UI activity.
// val readMsg = handler.obtainMessage(
// MESSAGE_READ, numBytes, -1,
// mmBuffer)
// readMsg.sendToTarget()
}
}
// // Call this from the main activity to send data to the remote device.
// fun write(bytes: ByteArray) {
// try {
// mmOutStream.write(bytes)
// } catch (e: IOException) {
// Log.e(TAG, "Error occurred when sending data", e)
//
// // Send a failure message back to the activity.
// val writeErrorMsg = handler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_TOAST)
// val bundle = Bundle().apply {
// putString("toast", "Couldn't send data to the other device")
// }
// writeErrorMsg.data = bundle
// handler.sendMessage(writeErrorMsg)
// return
// }
//
// // Share the sent message with the UI activity.
// val writtenMsg = handler.obtainMessage(
// MESSAGE_WRITE, -1, -1, mmBuffer)
// writtenMsg.sendToTarget()
// }
// Call this method from the main activity to shut down the connection.
fun cancel() {
try {
mmSocket.close()
} catch (e: IOException) {
Log.e(TAG, "Could not close the connect socket", e)
}
}
}
}
結果
AndroidStudioのlogcatで確認できました!
abと入力したら97,98とlogcat上で表示されています。