【第1回】pySerialを使った顕微鏡用多波長LED光源の高速波長切り替えについて
【第2回】Pythonでカメラを制御する【研究用】
はじめに
自動ステージをPythonで制御する方法についてシェアしたいと思います。PythonでThorlabs Inc.の自動ステージを制御する方法について書かれている記事は探してもありませんでした。ですので、自分で書こうと思い、試行錯誤して得たノウハウのエッセンスを記事にしています。
今回使う自動ステージはThorlabs Inc.のステージです。このステージは同社顕微鏡に組み込むことができます。
自作顕微鏡は拡張性があるため、自由度が広がります。計測と解析を一元化することで、アナログな顕微鏡観察を自動化し、多変量データ解析をシームレスに導入できるでしょう。

開発環境
- Windows10 (x64)
- Python3.6
- Anaconda3
- MSL-Equipment
使用する機材
##インストール
Thorlabs自動ステージを動かすためには以下の2つが必要です。
- kinessis
- MSL-Equipmentモジュール
kinesis
こちらからkinesisをインストールします。
kinesisはローカルPC環境で動作するGUIベースのソフトウェア群およびDLL(Dynamic Link Library)ファイルを含むライブラリです。
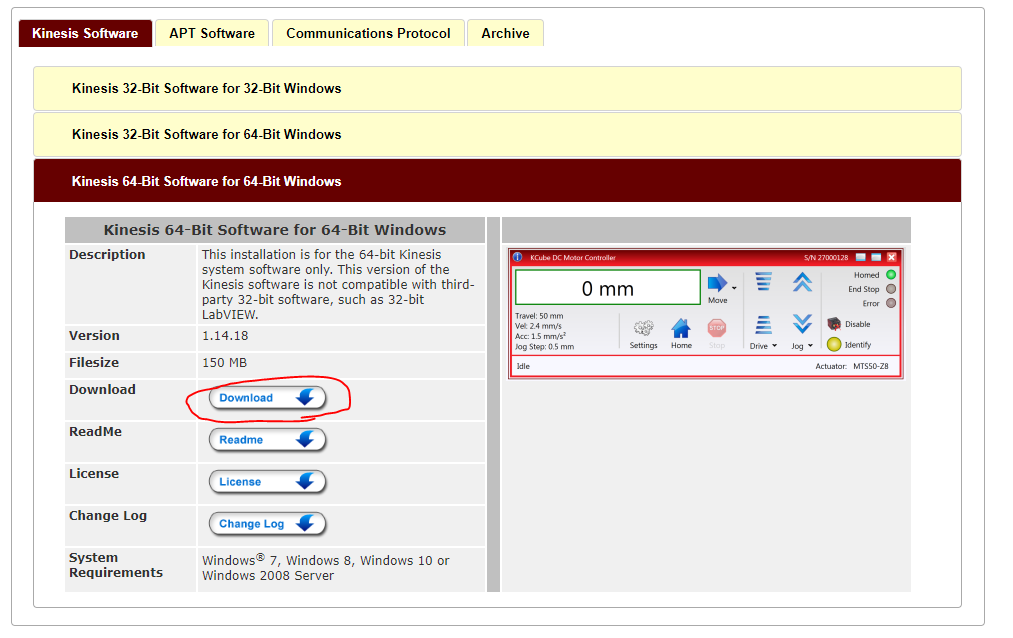
お使いのPC環境に合わせてバージョンを選んでください。GUIベースのアプリケーションがついてきますが、今回は使わずThorlabs.MotionControl.KCube.StepperMotor.dllが以下のディレクトリに保存されていれば問題ありません。
C:/Program Files/Thorlabs/Kinesis
今回はWindows10のx64なので、Kinesis 64-Bit Software for 64-Bit Windowsを選択します。Downloadをポチッ。
完了。
MSL-Equipmentモジュール
Thorlabas自動ステージを制御するためのモジュールMSL-Equipmentをインストールします。
このライブラリはニュージーランドの研究機関Measurement Standards Laboratory of New Zealandが無償で公開しています。
まず、以下のコマンドをコピペして実行しましょう。
condaコマンドで仮想環境thorlabs_demoを作ります。
conda create -n thorlabs_demo python=3.6
以下のコマンドでMSL-Equipmentをインストールします。
pip install https://github.com/MSLNZ/msl-equipment/archive/master.zip
例えば、次のようにAnaconda promptなどで実行してみましょう。
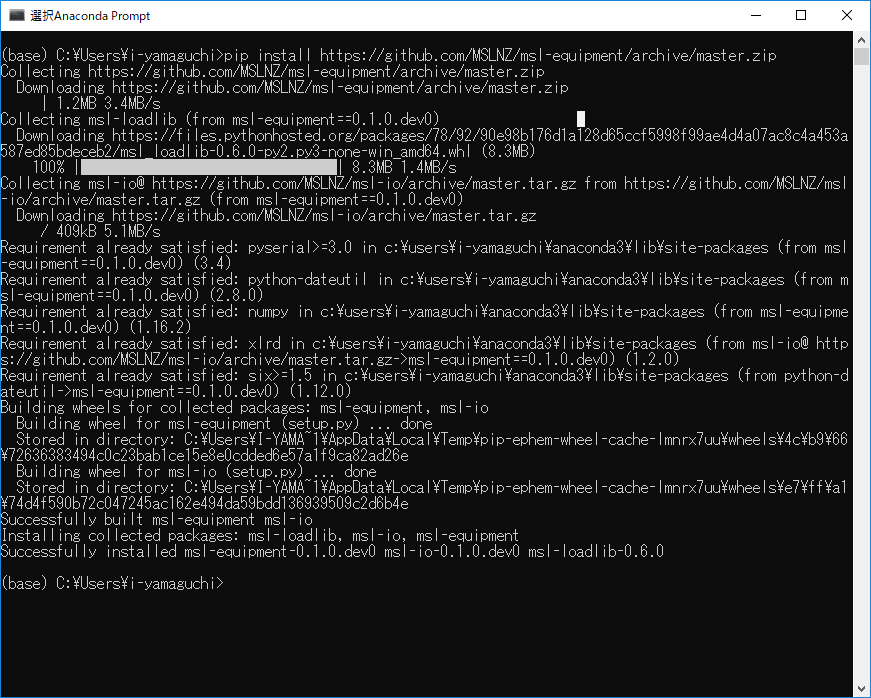
インストールが完了しました。準備完了ですね。
インストール手順(原文)
https://msl-equipment.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install.html
##動作確認
サンプルプログラムは以下のディレクトリからkst101.pyを探します。
C:\Users\あなたのユーザーネーム\anaconda3\Lib\site-packages\msl\examples\equipment\resources\thorlabs
下のプログラムをコピペしてもいいでしょう。
さて、サンプルプログラムを眺めてみます。
serial='26001809'の部分を自分が使っているデバイスのシリアル番号に変えるだけで動きそうですね。
"""
This example shows how to communicate with Thorlabs KST101, KCube Stepper Motor.
"""
# this "if" statement is used so that Sphinx does not execute this script when the docs are being built
if __name__ == '__main__':
import os
from pprint import pprint
from msl.equipment import EquipmentRecord, ConnectionRecord, Backend
from msl.equipment.resources.thorlabs import MotionControl
# ensure that the Kinesis folder is available on PATH
os.environ['PATH'] += os.pathsep + 'C:/Program Files/Thorlabs/Kinesis'
# rather than reading the EquipmentRecord from a database we can create it manually
record = EquipmentRecord(
manufacturer='Thorlabs',
model='KST101',
serial='26002319', # update the serial number for your KST101
connection=ConnectionRecord(
backend=Backend.MSL,
address='SDK::Thorlabs.MotionControl.KCube.StepperMotor.dll',
),
)
def wait():
motor.clear_message_queue()
while True:
status = motor.convert_message(*motor.wait_for_message())['id']
if status == 'Homed' or status == 'Moved':
break
position = motor.get_position()
real = motor.get_real_value_from_device_unit(position, 'DISTANCE')
print(' at position {} [device units] {:.3f} [real-world units]'.format(position, real))
# avoid the FT_DeviceNotFound error
MotionControl.build_device_list()
# connect to the KCube Stepper Motor
motor = record.connect()
print('Connected to {}'.format(motor))
# load the configuration settings (so that we can use the get_real_value_from_device_unit() method)
motor.load_settings()
# start polling at 200 ms
motor.start_polling(200)
# home the device
print('Homing...')
motor.home()
wait()
print('Homing done. At position {} [device units]'.format(motor.get_position()))
# move to position 100000
print('Moving to 100000...')
motor.move_to_position(100000)
wait()
print('Moving done. At position {} [device units]'.format(motor.get_position()))
# move by a relative amount of -5000
print('Moving by -5000...')
motor.move_relative(-5000)
wait()
print('Moving done. At position {} [device units]'.format(motor.get_position()))
# jog forwards
print('Jogging forwards by {} [device units]'.format(motor.get_jog_step_size()))
motor.move_jog('Forwards')
wait()
print('Jogging done. At position {} [device units]'.format(motor.get_position()))
# stop polling and close the connection
motor.stop_polling()
motor.disconnect()
# you can access the default settings for the motor to pass to the set_*() methods
print('\nThe default motor settings are:')
pprint(motor.settings)
上のプログラムのserial='26001809'をserial='26002319'に変更します。
プログラムを実行して動作したら完成です。