JavaScript 用のテスティングフレームワークである Jasmine の使い方のメモ。
Hello World
インストール
ここ からインストール。
zip を解凍すると以下のようになっている。
│ MIT.LICENSE
│ SpecRunner.html
│
├─lib
│ └─jasmine-2.0.0
│ boot.js
│ console.js
│ jasmine-html.js
│ jasmine.css
│ jasmine.js
│ jasmine_favicon.png
│
├─spec
│ PlayerSpec.js
│ SpecHelper.js
│
└─src
Player.js
Song.js
テスト対象の JS を書く
app.js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
テストコードを書く
app-test.js
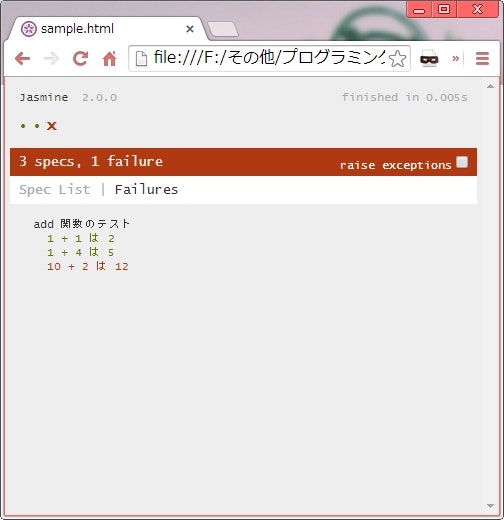
describe('add 関数のテスト', function() {
it('1 + 1 は 2', function() {
expect(add(1, 1)).toBe(2);
});
it('1 + 4 は 5', function() {
expect(add(1, 4)).toBe(5);
});
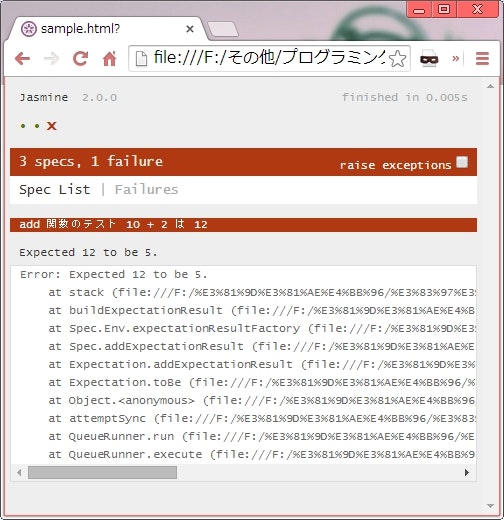
it('10 + 2 は 12', function() {
expect(add(10, 2)).toBe(5); // わざと失敗させている
});
});
HTML を作る
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<script src="jasmine.js"></script>
<script src="jasmine-html.js"></script>
<script src="boot.js"></script>
<script src="console.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="jasmine.css" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" type="image/png" href="jasmine_favicon.png" />
<script src="app.js"></script>
<script src="app-test.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
ブラウザで見る
説明
- Jasmine では、テストコードは Suite と Spec の2つで構成される。
- JUnit で言うと、 Suite はテストクラスで、 Spec はテストメソッド。
- Suite は
describe関数を使い、 Spec はit関数で宣言する。 - 値のチェックは
expect(actualValue).toBe(expectedValue);で実施する(toBe()以外にも色々メソッドが用意されている)。 - Jasmine のファイル・テスト対象のコード・テストコードを読み込んだ HTML をブラウザで表示することで、テストが実行され、結果が表示される。
-
boot.jsはjasmine.jsより後、かつテスト対象コードより前に読み込む必要がある。
テストの開始前後に処理を挟む
app-test.js
describe('test', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
console.log('before >>>');
});
afterEach(function() {
console.log("<<< after");
});
it('test1', function() {
console.log(" test1");
});
it('test2', function() {
console.log(" test2");
});
});
コンソール出力
before >>>
test1
<<< after
before >>>
test2
<<< after
-
beforeEach()関数とafterEach()関数で、各テストの前後に処理を挟むことができる。
this は spec ごとに初期化される
app-test.js
describe('test', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
console.log("[beforeEach]");
console.log("this.value = " + this.value);
this.value = 'before';
});
afterEach(function() {
console.log("[afterEach]");
console.log("this.value = " + this.value);
this.value = 'after';
});
it('test1', function() {
console.log("[test1]");
console.log("this.value = " + this.value);
this.value = 'test1';
});
it('test2', function() {
console.log("[test2]");
console.log("this.value = " + this.value);
this.value = 'test2';
});
});
コンソール出力
[beforeEach]
this.value = undefined
[test1]
this.value = before
[afterEach]
this.value = test1
[beforeEach]
this.value = undefined
[test2]
this.value = before
[afterEach]
this.value = test2
- 各 spec や
beforeEach,afterEach関数の中で使用するthisは、テストごとに初期化されたオブジェクトが渡される。 -
thisは1つの spec の中で共有される。
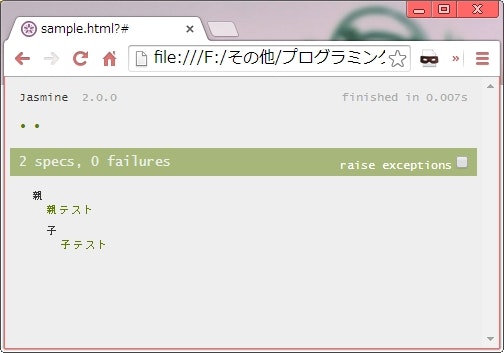
suite を入れ子にする
app-test.js
describe('親', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
console.log("親 beforeEach");
});
afterEach(function() {
console.log("親 afterEach");
});
it('親テスト', function() {
console.log(" 親テスト");
});
describe('子', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
console.log(" 子 beforeEach");
});
afterEach(function() {
console.log(" 子 afterEach");
});
it('子テスト', function() {
console.log(" 子テスト");
});
});
});
ブラウザ
コンソール出力
親 beforeEach
親テスト
親 afterEach
親 beforeEach
子 beforeEach
子テスト
子 afterEach
親 afterEach
-
describeは入れ子にできる。
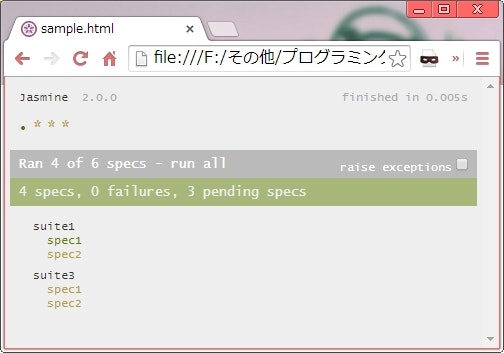
特定の suite または spec を実行しないようにする
app-test.js
describe('suite1', function() {
it('spec1', function() {
console.log("suite1 spec1");
});
xit('spec2', function() {
console.log("suite1 spec2");
});
});
xdescribe('suite2', function() {
it('spec1', function() {
console.log("suite2 spec1");
});
xit('spec2', function() {
console.log("suite2 spec2");
});
});
describe('suite3', function() {
it('spec1', function() {
console.log("suite3 spec1");
pending();
});
it('spec2');
});
ブラウザ
コンソール出力
suite1 spec1
suite3 spec1
- 関数の名前の先頭に
xを付けると(xdescribe(),xit())、その suite または spec は実行されなくなる。 - spec の場合は、さらに以下の2つの方法がある。
-
it関数にテストコードの関数を渡さず、 spec 名だけを渡す。 -
it関数に渡したテストコードの中でpending()関数を実行する。※この場合、テストは実行されるがエラーになっても無視される。
-
Matcher
組み込みの Matcher
完全に一致することをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect(10).toBe(10);
});
});
-
toBe()は===で値を比較する。
否定する
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect(10).not.toBe(13);
});
});
-
expect()の後ろに.notを挟むことで、その後の比較内容を否定できる。
オブジェクトや配列の各要素が同じであることをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var obj1 = {
name: 'Hoge',
age: 14
};
var obj2 = {
name: 'Hoge',
age: 14
};
expect(obj1).toEqual(obj2);
var array1 = [1, 2, 3];
var array2 = [1, 2, 3];
expect(array1).toEqual(array2);
});
});
-
toEqual()は、オブジェクトや配列の各要素をそれぞれ比較して、すべて同じであることをチェックする。
正規表現でチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect('Hello Jasmine!!').toMatch(/^[a-zA-Z! ]+$/);
});
});
-
toMatch()で正規表現によるチェックができる。 - 正規表現で指定したパターンにマッチする箇所が、
expect()で渡した文字列の中に一つでも存在すればテストは通る。
undefined でないことをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var a = 'aaa';
var u = undefined;
expect(a).toBeDefined(); // テスト OK
expect(u).toBeDefined(); // テスト NG
});
});
-
toBeDefined()で、expect()で指定した値が undefined でないことをチェックできる。
undefined であることをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var a = 'aaa';
var u = undefined;
expect(a).toBeUndefined(); // テスト NG
expect(u).toBeUndefined(); // テスト OK
});
});
-
toBeUndefined()で、expect()で指定した値が undefined であることをチェックできる。
null であることをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect(null).toBeNull();
});
});
-
toBeNull()で、expect()で指定した値が null であることをチェックできる。
真と評価される値かどうかチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// テスト OK
expect(1).toBeTruthy();
expect('a').toBeTruthy();
// テスト NG
expect(0).toBeTruthy();
expect('').toBeTruthy();
});
});
-
toBeTruthy()で、expect()で指定した値が真と評価される値かどうかをチェックできる。
偽と評価される値かどうかをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// テスト NG
expect(1).toBeFalsy();
expect('a').toBeFalsy();
// テスト OK
expect(0).toBeFalsy();
expect('').toBeFalsy();
});
});
-
toBeFalsy()で、expect()で指定した値が偽と評価される値かどうかをチェックできる。
配列に指定した要素が含まれることをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect([1, 2, 3]).toContain(3);
});
});
-
toContain()で指定した値が、expect()で指定した配列に要素として存在するかをチェックできる。
数値の大小比較をする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
expect(1).toBeLessThan(2);
expect(4).toBeGreaterThan(3);
});
});
-
toBeLessThan()で小なり、toBeGreaterThan()で大なり比較ができる。
何らかの例外がスローされることをチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var func = function() {
throw 'test';
};
expect(func).toThrow();
});
});
-
toThrow()で、expect()で指定した関数が何かしらの例外をスローすることをチェックできる。
スローされた例外をチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var func = function() {
throw 'test';
};
expect(func).toThrow('test');
});
});
-
toThrow()の値を渡したものと同じものがスローされることをチェックできる。
指定したクラスのインスタンスであることを確認する
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
function MyClass() {}
var myClass = new MyClass();
// verify
expect(myClass).toEqual(jasmine.any(MyClass));
expect({}).toEqual(jasmine.any(Object));
expect([]).toEqual(jasmine.any(Array));
expect(11).toEqual(jasmine.any(Number));
expect('').toEqual(jasmine.any(String));
expect(true).toEqual(jasmine.any(Boolean));
});
});
- あるインスタンスと
jasmine.any(コンストラクタ関数)をtoEqual()で比較することで、指定したクラスインスタンスであることをチェックできる。
オブジェクトの一部のプロパティだけ値をチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
var obj = {
hoge: 'HOGE',
fuga: 'FUGA'
};
expect(obj).toEqual(jasmine.objectContaining({fuga: 'FUGA'}));
});
});
-
jasmine.objectContaining()をtoEqual()に渡すことで、一部のプロパティの存在だけをチェックできる。 - 後述する
toHaveBeenCalledWith()の引数に渡すことも可能。
カスタムマッチャー
基本
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
jasmine.addMatchers({
myMatcher: function(util, customEqualityTesters) {
return {
compare: function(actual, expected) {
return {
pass: actual === expected
};
}
};
}
});
expect(10).myMatcher(10);
});
});
-
jasmine.addMatchers()で自作のマッチャーを追加する。 -
jasmine.addMatchers()に渡すオブジェクトには、自作マッチャーごとにファクトリ関数をセットする。 - マッチャーのファクトリ関数は、
compare()関数を持つオブジェクトを return するようにする。 -
compare()関数は、expect()に渡された値(actual)と、この自作マッチャーの引数に渡された値(expected)が渡される。 -
compare()関数は、passプロパティを持つオブジェクトを return するようにする。 -
passプロパティには、比較結果を boolean で設定する。
任意のエラーメッセージを設定する
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
jasmine.addMatchers({
myMatcher: function(util, customEqualityTesters) {
return {
compare: function(actual, expected) {
return {
pass: actual === expected,
message: 'hoge'
};
}
};
}
});
expect(10).myMatcher(101);
});
});
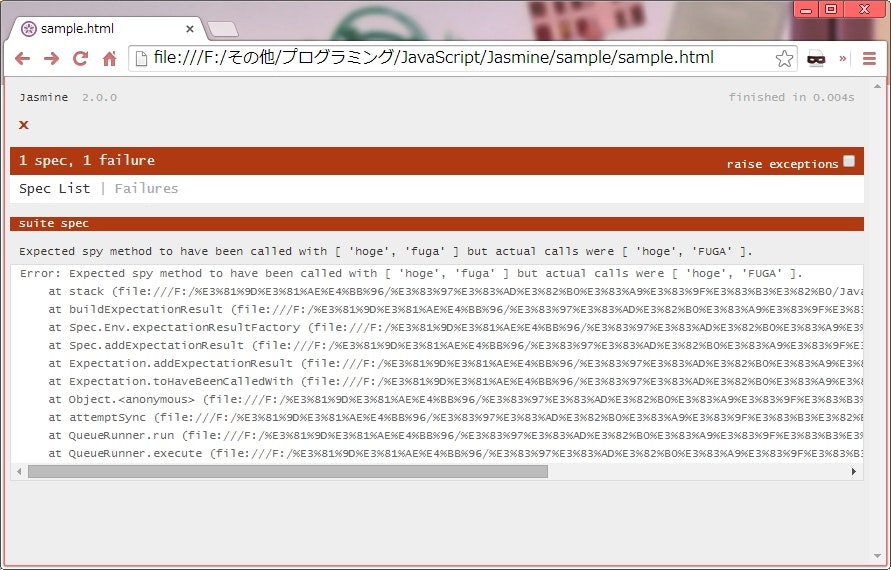
ブラウザ表示
-
compare()関数が返すオブジェクトにmessageプロパティを設定すると、エラー時にそのメッセージが出力される。
スパイ
特定のオブジェクトのメソッドが実行されたかどうかをチェックする
app-test.js
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method();
// verify
expect(obj.method).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
コンソール出力
何も出力されない。
-
spyOn(オブジェクト, 'メソッド名')関数でオブジェクトを監視できるようになる。 -
toHaveBeanCalled()でメソッドが実行されたかどうかをチェックできる。 - 監視対象になったメソッドは、本来の実装は実行されなくなる。
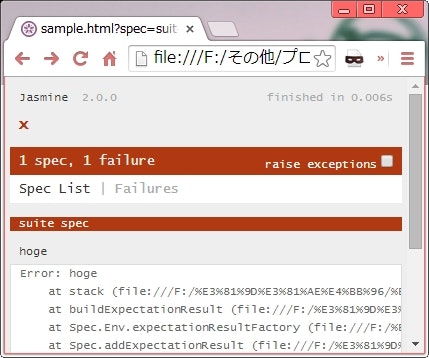
テストを失敗させたときのブラウザ表示
引数も含めてメソッドが実行されたことをチェックする
app-test.js
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method('hoge', 'fuga');
// verify
expect(obj.method).toHaveBeenCalledWith('hoge', 'fuga');
});
});
-
toHaveBeenCalledWith()で引数を含めてメソッドが実行されたことをチェックできる。
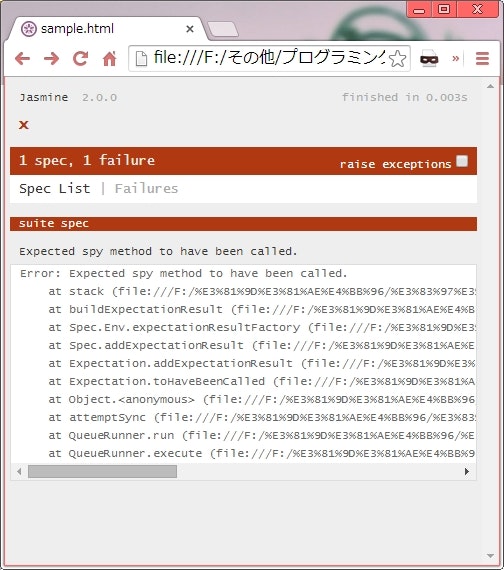
テストを失敗させたときのブラウザ表示
引数のマッチングを緩める
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method('any string');
// verify
expect(obj.method).toHaveBeenCalledWith(jasmine.any(String));
});
});
-
jasmine.any(コンストラクタ関数)をtoHaveBeenCalledWith()の引数に渡すことで、 任意の String 値 という風にマッチングの精度を緩めることができる。
監視対象にしたメソッドを実行したときに、本来の実装も実行されるようにする
app-test.js
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method').and.callThrough();
// exercise
obj.method();
// verify
expect(obj.method).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
コンソール出力
obj#method()
-
spyOnの後に、and.callThrough()と続けることで、メソッドが実行されたときに本来の実装も呼ばれるようになる。
メソッドの戻り値を任意の値に差し替える
app-test.js
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method').and.returnValue("stub");
// exercise
var result = obj.method();
// verify
expect(result).toBe('stub');
});
});
-
spyOn()の後にand.returnValue(戻り値)と続けることで、メソッドを実行したときの戻り値を任意の値に差し替えることができる。
メソッドを実行したときの処理を、任意の関数に差し替える
app-test.js
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method').and.callFake(function(param) {
console.log("fake param = " + param);
return "fake";
});
// exercise
var result = obj.method('hoge');
// verify
expect(result).toBe('fake');
});
});
コンソール出力
fake param = hoge
-
spyOn()の後にand.callFake(フェイクの関数)と続けることで、メソッドを実行した時の処理を任意の関数に差し替えることができる。
メソッドを実行したときに例外をスローさせる
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method').and.throwError('mock exception');
// verify
expect(obj.method).toThrowError('mock exception');
});
});
-
spyOn()の後にand.toThrowError(スローする例外)と続けることで、メソッドを実行した時に例外をスローさせることができる。
メソッドが実行された回数をチェックする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method();
obj.method();
// verify
expect(obj.method.calls.count()).toBe(2);
});
});
-
メソッド.calls.count()で、そのメソッドが実行された回数が取得できる。
メソッドが実行されたときの引数をキャプチャする
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method();
obj.method(11);
obj.method('hoge', 'fuga');
// verify
expect(obj.method.calls.argsFor(0)).toEqual([]);
expect(obj.method.calls.argsFor(1)).toEqual([11]);
expect(obj.method.calls.argsFor(2)).toEqual(['hoge', 'fuga']);
});
});
-
メソッド.calls.argsFor(n)でメソッドが実行されたときに渡された引数を取得できる。 - 引数は配列で取得できる。
- すべての引数を一回で取得する場合は
allArgs()を使う。
最初 or 最後に実行されたメソッドの情報を取得する
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var obj = {
method: function() {
console.log('obj#method()');
}
};
spyOn(obj, 'method');
// exercise
obj.method('first');
obj.method(11);
obj.method('last');
// verify
expect(obj.method.calls.first()).toEqual({object: obj, args: ['first']});
expect(obj.method.calls.mostRecent()).toEqual({object: obj, args: ['last']});
});
});
-
first()で最初に実行されたメソッドに関する情報が、mostRecent()で最後に実行されたメソッドの情報が取得できる。
裸のスパイ関数を作る
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var spyFunction = jasmine.createSpy();
// exercise
spyFunction();
// verify
expect(spyFunction).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
-
jasmine.createSpy()で裸のスパイ関数を生成できる。 - 生成したスパイ関数は、これまでのスパイと同じように呼び出しなどをチェックできる。
裸のスパイオブジェクトを作る
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var spyObj = jasmine.createSpyObj('spyName', ['hoge', 'fuga', 'piyo']);
// exercise
spyObj.hoge();
spyObj.piyo();
// verify
expect(spyObj.hoge).toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(spyObj.fuga).not.toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(spyObj.piyo).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
-
jasmine.createSpyObj(名前, [定義するプロパティ名のリスト])で裸のスパイオブジェクトを生成できる。
時間を操る
setTimeout などの動作を制御する
- 1 秒経つ前に verify が実行されるので、下記テストは必ず失敗する。
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
var spy = jasmine.createSpy();
// exercise
setTimeout(function() {
spy();
}, 1000);
// verify
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
- 1 秒経過してから
spy()が確かに実行されていることをチェックしたい場合は、 clock の仕組みを使用する。
describe('suite', function() {
it('spec', function() {
// setup
jasmine.clock().install();
var spy = jasmine.createSpy();
// exercise
setTimeout(function() {
spy();
}, 100);
jasmine.clock().tick(101); // 時は加速する
// verify
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalled();
// teardown
jasmine.clock().uninstall();
});
});
- これを実行すると、テストは必ず成功する。
- 何が起こっているかというと、
jasmine.clock().tick(101)の時点で、時間が 101ms 強制的に進められている。 - その結果、 verify が実行される前に
spy()が実行され、テストが成功する。 -
jasmine.clock().install()とjasmine.clock().uninstall()は、処理の前後に必ず実行する。 - 要はメイド・イン・ヘブン。
非同期処理がある場合、それが終了してから次のテストに移るようにする
describe('suite', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('beforeEach');
}, 1000);
});
it('spec', function() {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('spec');
}, 500);
});
afterEach(function() {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('afterEach');
}, 200);
});
});
コンソール出力
afterEach
spec
beforeEach
-
beforeEach,afterEachおよび各 Spec で非同期処理がある場合、終了を待つこと無く次の処理へ移ってしまう。 - 非同期処理が終わってから次の処理に移って欲しい場合は次のようにする。
describe('suite', function() {
beforeEach(function(done) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('beforeEach');
done();
}, 1000);
});
it('spec', function(done) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('spec');
done();
}, 500);
});
afterEach(function(done) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('afterEach');
done();
}, 200);
});
});
コンソール出力
beforeEach
spec
afterEach
-
beforeEach,afterEach, Spec に渡している関数で引数(done)を受け取るようにする。 - 次に、その受け取った引数を、非同期処理が終了した後で実行する。
- すると、
done()が実行されるまで、次の処理に移らずに待機してくれるようになる。- 引数を受け取る用にした時点で Jasmine は処理を待機するようになる。
- なので、引数は宣言したけど
done()し忘れると、テストが停止してしまう上にしばらくしてからタイムアウトでエラーになる。
- デフォルトでは、 5 秒まで待機してくれるが、それ以上待機するとタイムアウトエラーになる。
- タイムアウトの時間を長くしたい場合は以下のようにする。
describe('suite', function() {
var originalTimeout;
beforeEach(function() {
originalTimeout = jasmine.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_INTERVAL;
jasmine.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_INTERVAL = 10000;
});
it('spec', function(done) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('spec');
done();
}, 6000);
});
afterEach(function() {
jasmine.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_INTERVAL = originalTimeout;
});
});
-
jasmine.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT_INTERVALにタイムアウト時間が設定されているので、この値をテストの前後で切り替える。
Grunt で動かす
-
gruntとgrunt-contrib-jasmineはインストール済みの前提。
フォルダ構成
|-node_modules
|-Gruntfile.js
`src
|-main
| `-js
| `-app.js
`-test
`-js
`-test.js
各ファイル
Gruntfile.js
module.exports = function(grunt) {
grunt.initConfig({
jasmine: {
build: {
src: 'src/main/js/**/*.js',
options: {
specs: 'src/test/js/**/*.js',
keepRunner: true,
junit: {
path: 'build/jasmine-test/'
}
}
}
}
});
grunt.loadNpmTasks('grunt-contrib-jasmine');
grunt.registerTask('default', ['jasmine']);
};
-
srcがテスト対象コードのファイルの場所。 -
options.specsがテストコードの場所。 -
options.keepRunnerを true にしておくと、 Jasmine を実行するときの HTML ファイル(_SpecRunner.html)が出力されたままになる(デフォルトは削除される)。 -
options.junit.pathで、テスト結果が xml ファイルで出力される(Jenkins で CI するときに使うやつ)。
app.js
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
test.js
describe("suite", function() {
it("spec", function (){
expect(add(1, 3)).toBe(4);
});
});
jasmine タスクを実行する
>grunt jasmine
Running "jasmine:build" (jasmine) task
Testing jasmine specs via PhantomJS
suite
√ spec
1 spec in 0.004s.
>> 0 failures
Done, without errors.
- PhantomJS 上でテストが実行される。