glmnetパッケージでロジスティック回帰をしたときの回帰係数について調べてみた件。概ね下記のサイトのの翻訳になります。
Computing standardized logistic regression coefficients | Thinklab
Logisitic Regressions and regularization
glmnet()やcv.glmnet()を使ってロジスティック回帰を行う際、目的変数の予測値の精度だけを考えるなら説明変数の回帰係数はあまり気にしなくてもよい事なのですが、「どの変数が予測結果に一番寄与しているのか?」という検討をする場合は、どうしても標準回帰係数が必要になります。
引数standardize=TRUEにすると目的変数を標準化して計算してくれるのですが、計算された回帰係数の値の挙動がちょっと変だったのでいろいろと調べてみました。
データとしてbirthwtを使います(重量の列は削除)
require(MASS)
df <- birthwt[,-10]
説明変数に、生のデータと標準化したデータの2つを用意します。
# 目的変数
dy<-df[,1]
# 生データ
dx<-data.matrix(df[,-1])
# 標準化したデータ
dx_std<-data.matrix(scale(df[,-1]))
まず、生のデータを使い、glmnet()の中でデータを標準化standardize=TRUEさせた場合。
require(glmnet)
set.seed(123)
cvfit <- cv.glmnet(x = dx, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = TRUE)
coef(cvfit, s = "lambda.min")
9 x 1 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1
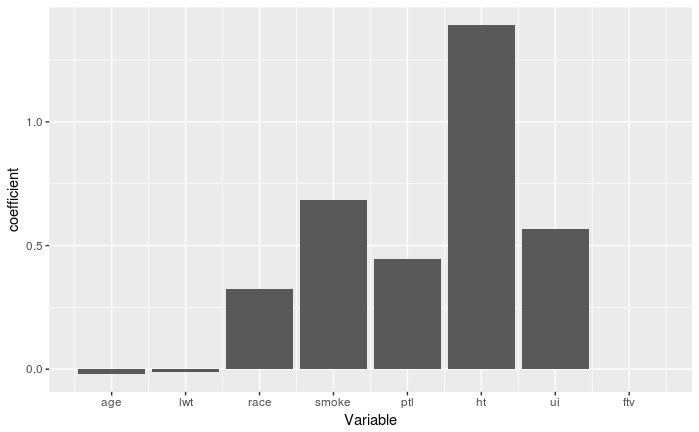
(Intercept) -0.305325527
age -0.020731964
lwt -0.009341129
race 0.322551584
smoke 0.685662074
ptl 0.443718755
ht 1.392601511
ui 0.566810926
ftv .
可視化してみると(切片は削除)
cf <- coef(cvfit, s = "lambda.min")
gg1 <- ggplot() +
geom_bar(aes(x = 1:length(cf[-1]), y = cf[-1]), stat = "identity") +
labs(x = "Variable", y = "coefficient") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 1:length(cf[-1]), labels = names(cf[-1]))
plot(gg1)
次に、説明変数を事前に標準化して、glmnet()の中でデータを標準化させないstandardize=FALSE場合
set.seed(123)
cvfit_std <- cv.glmnet(x = dx_std, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = FALSE)
coef(cvfit_std, s = "lambda.min")
9 x 1 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1
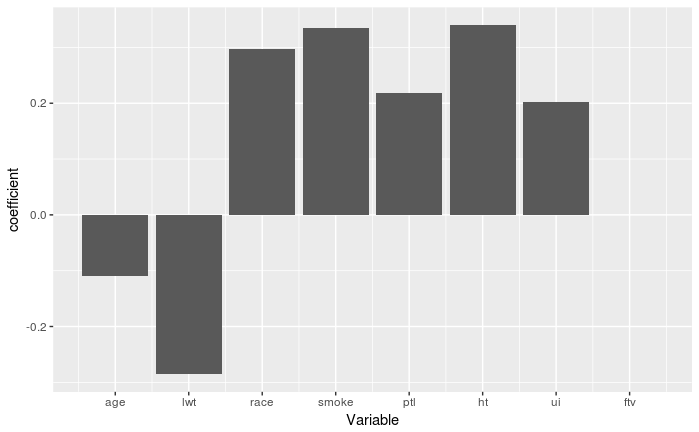
(Intercept) -0.8763857
age -0.1098520
lwt -0.2856459
race 0.2962127
smoke 0.3355561
ptl 0.2189051
ht 0.3404821
ui 0.2018926
ftv .
同様に可視化してみると(切片は削除)
cf_std <- coef(cvfit_std, s = "lambda.min")
gg2 <- ggplot() +
geom_bar(aes(x = 1:length(cf_std[-1]), y = cf_std[-1]), stat = "identity") +
labs(x = "Variable", y = "coefficient") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = 1:length(cf_std[-1]), labels = names(cf_std[-1]))
plot(gg2)
あれれ?答えがちがう??glmnet()の計算時に標準化するか、説明変数を先に標準化させてglmnet()で計算させるかの違いだけで結果は同じだと思っていたのですが・・・
改めてglmnet()のhelpの引数standardizeを読むと
Logical flag for x variable standardization, prior to fitting the model sequence. The coefficients are always returned on the original scale. (以下略)
と「回帰係数は常に元の単位に戻されます」って書いてありました・・・orz
試しに標準化したデータを使って、glmnet()の中でデータを標準化standardize=TRUEさせても
set.seed(123)
cvfit_std2 <- cv.glmnet(x = dx_std, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = TRUE)
coef(cvfit_std2, s = "lambda.min")
9 x 1 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1
(Intercept) -0.8763857
age -0.1098520
lwt -0.2856459
race 0.2962127
smoke 0.3355561
ptl 0.2189051
ht 0.3404821
ui 0.2018926
ftv .
と、standardize=FALSEと同じ結果に。説明変数はすでに標準化しているので、glmnet()の中で標準化をしてもしなくても答えは同じ、ということですね。
ということで、glmnet()を使って標準回帰係数を計算するには事前に元のデータをscale()とかで標準化して計算すればよいのですが、データによっては標準化が出来ない場合があります。それは、変数が同じ値を持つときで、変数の標準偏差が0となりscale()の結果がNaNとなってしまうためglmnet()でエラーが発生します。
# 説明変数に値が同じ変数wを追加
dx2<-data.matrix(cbind(df[,-1],w=1))
# 標準化した説明変数
dx2_std<-data.matrix(scale(cbind(df[,-1],w=1)))
# 目的変数
dy<-df[,1]
set.seed(123)
cvfit_std <- cv.glmnet(x = dx2_std, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = FALSE)
lognet(x, is.sparse, ix, jx, y, weights, offset, alpha, nobs, でエラー: 外部関数の呼び出し (引数 5) 中に NA/NaN/Inf があります
事前にデータから標準化できない変数列を削除することで回避できるのですが、できれば元のデータフレームの構造を弄りたくないって時もあります。実はglmnet()はこういった標準化出来ない変数があっても、内部処理で回避してちゃんと計算してくれます。(古いバージョンではエラーになりましたが)
set.seed(123)
cvfit <- cv.glmnet(x = dx2, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = T)
coef(cvfit, s = "lambda.min")
10 x 1 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix"
1
(Intercept) -0.305325527
age -0.020731964
lwt -0.009341129
race 0.322551584
smoke 0.685662074
ptl 0.443718755
ht 1.392601511
ui 0.566810926
ftv .
w .
そこで、元データを弄ることなくglmnet()で標準回帰係数を得たいときはどうすればよいか?ということを調べてみた結果が一番上のリンクで、そこにその答えがありました。詳細は読んでもらうとして、結論から述べると
-
glmnet()内部ではデフォルトstandardize=TRUEで説明変数を標準化して標準回帰係数を計算した後に、agresti変換の逆変換を行い、元のデータの次元に回帰係数に戻している
ということのこと。このagresti変換についてはよくわからないのですが、
\begin{eqnarray}
b_x^* & =& b_x \cdot \sigma _x \\
b_0^* & = & b_0 + \sum b_x \cdot \mu_x
\end{eqnarray}
とすることでglmnet()で得られた回帰係数を標準回帰係数に変換することができるようです。(glmnet()のソース(FORTRAN)でも確認しているみたいです)
ということでglmnet()による回帰係数の計算結果から標準回帰係数に逆変換(?)するコードがこちら。
set.seed(123)
cvfit <- cv.glmnet(x = dx, y = dy, family = "binomial", standardize = TRUE)
# 標準化されていない回帰係数
cf <- coef(cvfit, s = "lambda.min")[,1]
# 各変数の標準偏差
sds <- sapply(as.data.frame(dx), sd)
# 各変数の平均
mus <- sapply(as.data.frame(dx), mean)
# 回帰係数を標準化する
cf_std <- cf * c(1, c(sds[names(cf)][-1]))
# 切片を標準化する
cf_std[1] <- cf[1] + sum(cf[-1] * mus[names(cf)][-1])
as.data.frame(cf_std)
cf_std
(Intercept) -0.8763857
age -0.1098520
lwt -0.2856459
race 0.2962127
smoke 0.3355561
ptl 0.2189051
ht 0.3404821
ui 0.2018926
ftv 0.0000000
と、標準化したデータによる回帰係数と同じ値になりました。
glmnet()の結果を用いて説明変数の寄与する度合いを検討する場合は注意が必要です。