はじめに
動作環境
- Windows 11 Home(23H2)
- .NET 8.0(SDK 8.0.204)
- Visual Studio 2022
- MySQL 8.4.2
前提
- Visual Studioインストール済み
手順
MySQL環境構築
インストール
以下サイトが分かりやすかったです。
こちらにある手順「MySQL Community Serverのインストール」では、管理者以外のユーザーの作成を後回しにしていますが、ここでやってしまっていいと思います。楽なので。
(飛ばしてしまった方は、同サイトの「ユーザーの作成」を参考にしてください)
データベースの作成
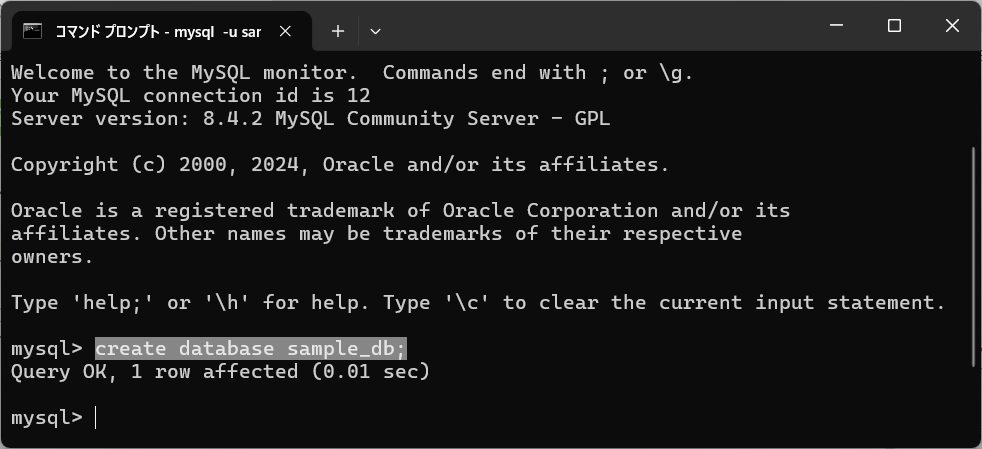
作成したユーザーでログインし、以下コマンドを実行します。
CREATE DATABASE データベース名
.NETアプリケーションの作成
今回は、「MySQLSample」という名前で、Razor Pagesアプリケーションを作成します。

パッケージのインストール
プロジェクト > NuGetパッケージの管理から、以下パッケージをインストールします。
- Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql(必須)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
それぞれのパッケージの役割について簡単にご説明します。
Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql
⇒MySQL用のDBプロバイダ。MySQLへの接続、および諸々操作するのに必要
今回はMySQLを使用するのでこちらのパッケージをインストールします。
このように、使用するDBエンジンに応じたプロバイダをインストールすることで、Entity Framework Core(EF Core)を利用できるようになります。
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
⇒EF Coreの便利機能が詰め込まれたツール。
こちらは必須ではないのですが、今回はテーブルの作成をDBマイグレーションで自動的に行うので、以下二つの機能を使用するためにインストールします。
- マイグレーションファイルの作成(Add-Migrationコマンド)
- マイグレーションの実行(Update-Databaseコマンド)
他にも便利な機能があるので、詳しくはこちらをご参照ください。
モデル作成
namespace MySQLSample.Models
{
public class Item
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = default!;
public int Price { get; set; }
}
}
DbContext作成
データベースと1対1で紐づく、DbContextの派生クラスを作成します。

using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace MySQLSample.Data
{
public class MySQLSampleContext : DbContext
{
public MySQLSampleContext(DbContextOptions<MySQLSampleContext> options) : base(options) { }
public DbSet<Models.Item> Item { get; set; } = default!;
}
}
DBとの接続設定
接続文字列の用意
今回は設定ファイルに定義しますが、「接続処理の実装」のタイミングで文字列をベタ書きでも問題ないです。
MySQLの接続文字列は以下の通りになります。
- server:DBサーバのホスト名(今回はlocalhost)
- port:MySQLが使用しているポート番号(デフォルトのままなら3306)
- database:作成したデータベース名
- userid:作成したユーザ名
- password:パスワード
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
+ "ConnectionStrings": {
+ "MySQLSampleContext": "server=127.0.0.1;port=3306;database=sample_db;userid=sample_user;password=sample_pass"
+ }
}
接続処理の実装
エントリポイントにて、上記の接続文字列を使ってMySQLに接続します。
+ using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
+ using MySQLSample.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
+ builder.Services.AddDbContext<MySQLSampleContext>(options => options.UseMySql(
+ builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("MySQLSampleContext"), new MySqlServerVersion(new Version(8, 4, 2))));
var app = builder.Build();
// 省略
DBマイグレーション
表示 > その他のウインドウ > パッケージマネジャーコンソールを開き、以下コマンドを実行します。
Add-Migration 任意のマイグレーション名
Update-Database

Itemクラスの情報に応じて、itemテーブルが作られました。

使用例
MySQLSampleContextを通じてDBからデータを取得し、フィールドのオブジェクトに格納しています。
public class IndexModel : PageModel
{
+ private readonly MySQLSampleContext _context;
+ public IList<Item> Items { get; set; } = default!;
public IndexModel(MySQLSampleContext context)
{
+ _context = context;
}
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
+ Items = await _context.Item.ToListAsync();
}
}
あとは各アプリケーションのやり方に応じて、データを参照します。
@page
@model IndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home page";
}
+ <table class="table">
+ <thead>
+ <tr>
+ <th>
+ @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Items[0].Name)
+ </th>
+ <th>
+ @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Items[0].Price)
+ </th>
+ </tr>
+ </thead>
+ <tbody>
+ @foreach (var item in Model.Items)
+ {
+ <tr>
+ <td>
+ @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)
+ </td>
+ <td>
+ @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Price)
+ </td>
+ </tr>
+ }
+ </tbody>
+ </table>
動作確認
動かしてみると、
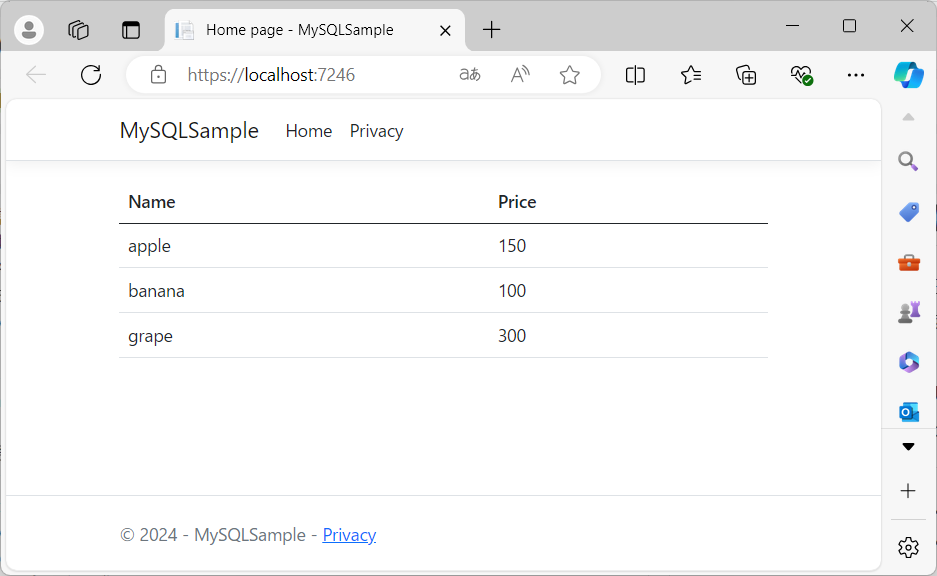
無事MySQLからデータを取得することができました。
余談(コマンドによるDbContextの作成)
今回は手でDbContextの派生クラスを作成しましたが、Scaffold-DbContextコマンドを使用すれば簡単に作成できそうなことに気づきました。
(こちらもAdd-Migration, Update-Databaseと並び、Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Toolsに含まれる機能です)
おわりに
ここでは省略しましたが、スキャフォールディングを使えば簡単にCRUD処理が実装できたり、データアノテーションを使用してカラム定義を行ったり、Seedでサンプルデータを突っ込めたりと便利な機能は多々あります。
詳しくは参考リンクを参考にしてみてください!
参考
- EF Core の概要
- Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql(MySQLプロバイダ)
- 移行の概要(DBマイグレーション)



