はじめに
QGISに組み込まれた、Pythonコンソールを使って、GISデータをOBJファイルに書き出してみます。
※OBJファイルについては、Wikipediaのリンクを提示しておきます。テキストで書き出せる非常に単純なフォーマットなので、独自にエクスポートする場合に扱いやすいです。
切り抜き
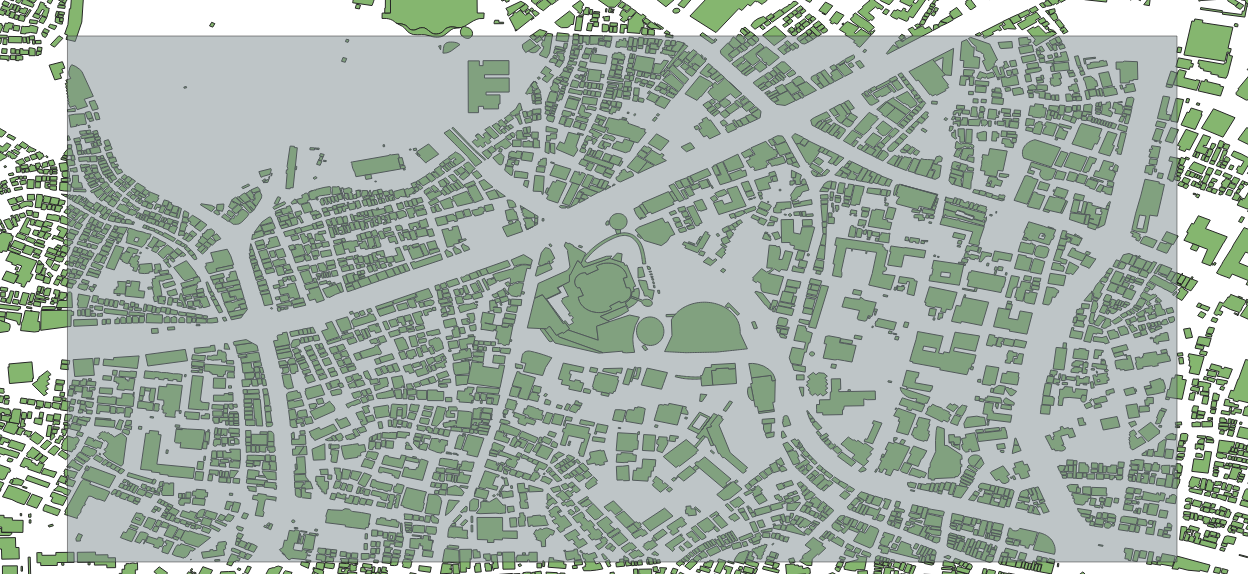
まず、対象範囲を切り抜きます。前回のデータをそのまま使うと、さすがに巨大になりすぎて、リアルタイムレンダリングでは対応できなくなるので、適当な範囲に切り抜いてみます。
今回は、六本木ヒルズ周辺を切り取ってみます。
まず、メニューから「レイヤ」-「レイヤの作成」-「新しい一時スクラッチレイヤ」を選び、ダイアログで、適当な名前とジオメトリタイプにポリゴンを選択します。
追加した新しいレイヤが編集モードになっていることを確認して、メニューから「編集」-「長方形の追加」-「領域範囲の長方形の追加」を行います。頂点と対角の頂点を左クリックで選択し、右クリックで追加終了になります。
図は分かりやすいように矩形の描画を半透明にしてあります。
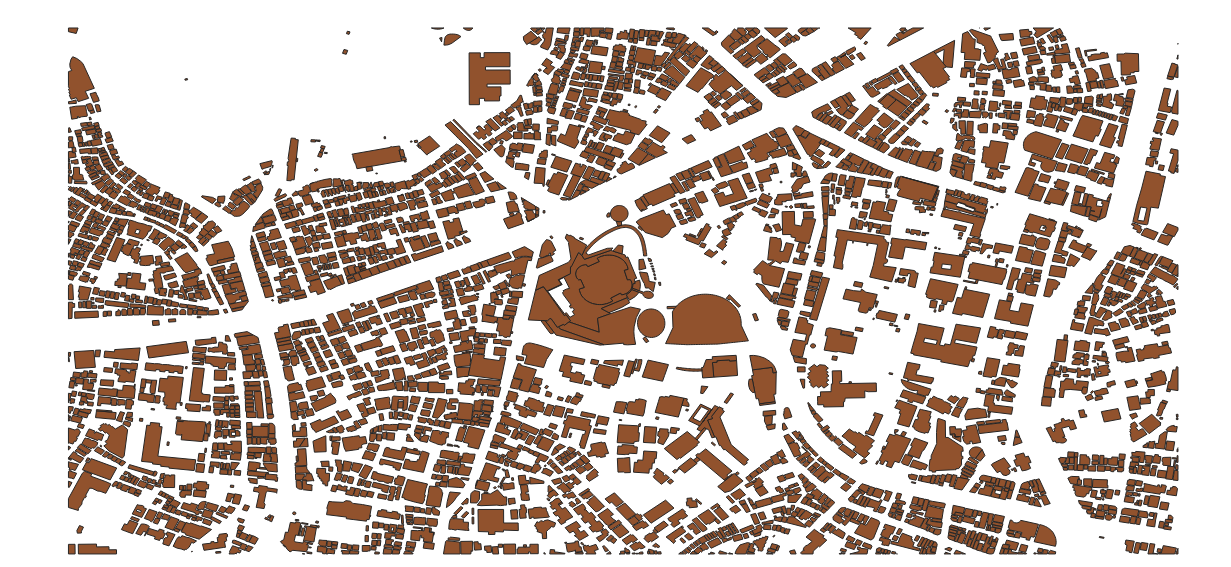
次に、「ベクタ」-「空間演算ツール」-「切り抜き」を選び、入力に建物データのレイヤ、オーバーレイに今作成した矩形領域を持つレイヤを選択して、実行します。
これで、エクスポートしたい領域が切り抜かれました。
ついでに、この矩形領域の重心を求めておきます。
「ベクタ」-「ジオメトリツール」-「重心」です。
できたポイントを地物情報表示ツールでクリックすれば、重心の緯度経度が分かります。
QGISのマクロ?Pythonコンソール
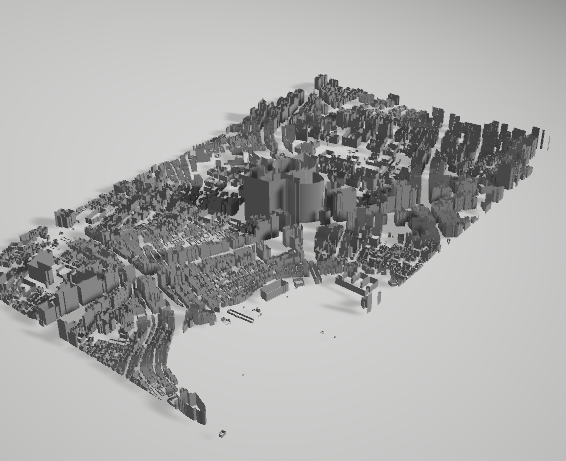
さて、Pythonコンソールを使って、このデータを3DのOBJファイルに書き出してみます。
Pythonコンソールはメニューから「プラグイン」-「Pythonコンソール」で呼び出すことができます。
座標変換
現在座標系はWGS84で(何も変えていなければたぶん)作業しています。座標系について細かいところを説明し始めると、ものすごい量になるので、ここでは割愛します。
WGS84では、座標は緯度経度で表されています。ここから、XYZの三次元直交座標系に変換します。以下のメソッドは、世界測地系と座標変換という本のプログラムを参考にして作成した座標変換のメソッドです。WGS84での地球の表し方に沿った極力正確な直交座標変換になっています。
なお、この計算では、少なくともdoubleの精度で行う必要があります。Pythonの浮動小数点はdoubleのはずなので、あまり気にしなくてもいいかと思いますが、UnityのVector3クラスなどはfloatで数値を持っているので、このプログラムを移植する場合は注意が必要です。
往々にして地理座標を扱うときは、doubleで扱うようにしておいた方が余計な失敗をしないで済みます。
def BLH2XYZ(b,l,h):
# WGS84
a = 6378137.0
f = 1.0 / 298.257223563
b = math.radians(b)
l = math.radians(l)
e2 = f * (2.0 - f)
N = a / math.sqrt(1.0 - e2 * math.pow(math.sin(b), 2.0))
X = (N + h) * math.cos(b) * math.cos(l);
Y = (N + h) * math.cos(b) * math.sin(l);
Z = (N * (1 - e2) + h) * math.sin(b);
return (X,Y,Z)
OBJ書き出し
そして、上の座標変換メソッドを組み込んだ形で、OBJ書き出しのプログラムを作成します。
def BLH2XYZ(b,l,h):
# WGS84
a = 6378137.0
f = 1.0 / 298.257223563
b = math.radians(b)
l = math.radians(l)
e2 = f * (2.0 - f)
N = a / math.sqrt(1.0 - e2 * math.pow(math.sin(b), 2.0))
X = (N + h) * math.cos(b) * math.cos(l);
Y = (N + h) * math.cos(b) * math.sin(l);
Z = (N * (1 - e2) + h) * math.sin(b);
return (X,Y,Z)
layer = iface.activeLayer()
features = layer.getFeatures()
i = 0
j = 0
fp = open("test.obj",mode='w')
fp.write("g "+str(i)+"\n")
# ※前に取得しておいた矩形領域の重心に変える
cx = 139.72957
cy = 35.66021
ox,oy,oz = BLH2XYZ(cy,cx,0)
for feature in features:
# print(feature.id())
mp = feature.geometry().asMultiPolygon()
try:
height = int(feature['height'])*2
if height < 1:
height = 2
except:
height = 5
for polygon in mp:
for polyline in polygon:
i=i+1
prev_p_index = j
for point in polyline:
x,y,z = BLH2XYZ(point.y(),point.x(),0)
x2,y2,z2 = BLH2XYZ(point.y(),point.x(),height)
x = x - ox
y = y - oy
z = z - oz
x2 = x2 - ox
y2 = y2 - oy
z2 = z2 - oz
s = math.radians(-cx)
rx = x * math.cos(s) - y * math.sin(s)
ry = x * math.sin(s) + y * math.cos(s)
s = math.radians(-cy)
rxx = rx * math.cos(s) - z * math.sin(s)
rz = rx * math.sin(s) + z * math.cos(s)
s = math.radians(-cx)
rx2 = x2 * math.cos(s) - y2 * math.sin(s)
ry2 = x2 * math.sin(s) + y2 * math.cos(s)
s = math.radians(-cy)
rxx2 = rx2 * math.cos(s) - z2 * math.sin(s)
rz2 = rx2 * math.sin(s) + z2 * math.cos(s)
fp.write("v "+str(ry)+" "+str(rxx)+" "+str(rz)+"\n")
fp.write("v "+str(ry2)+" "+str(rxx2)+" "+str(rz2)+"\n")
j=j+1
current = j - prev_p_index
for num in range(current):
p1 = (2*num+1)
p2 = (2*num+2)
p3 = (2*num+3)
p4 = (2*num+4)
if p3 > current*2:
p3 = p3 - current*2
if p4 > current*2:
p4 = p4 - current*2
p1 = p1 + prev_p_index*2
p2 = p2 + prev_p_index*2
p3 = p3 + prev_p_index*2
p4 = p4 + prev_p_index*2
fp.write("f "+str(p1)+" "+str(p2)+" "+str(p3)+" "+str(p1)+"\n")
fp.write("f "+str(p4)+" "+str(p3)+" "+str(p2)+" "+str(p4)+"\n")
fp.close()
print("Done")
このプログラム内で、処理としては先ほどの地理座標から直交座標への座標変換と、原点の移動と全体の回転、OBJへの書き出しを行っています。