問題
既存投稿一覧ページへのリンク
解法手順1
解法アプローチ
タイルの配置は交互に変わるため、始点と終点の座標の偶奇性を考慮する。
最短経路は、まず垂直方向に移動し、その後水平方向に移動することで求められる。
解法手順
-
入力として始点(Sx, Sy)と終点(Tx, Ty)の座標を受け取る。
-
始点と終点がそれぞれどのタイルにあるかを判定する。これは座標の偶奇性を利用して行う。
-
始点と終点を、それぞれのタイルの左端に調整する。これにより、水平方向の移動を簡単に計算できるようになる。
-
水平方向の距離(a)と垂直方向の距離(b)を計算する。
-
もし水平距離が垂直距離以下の場合、答えは垂直距離に等しい。
-
水平距離が垂直距離より大きい場合、垂直移動後に残りの水平距離の半分を追加で移動する必要がある。
-
計算された最小の通行料を出力する。
ACコード1
ac.py
def io_func():
# 始点の座標を入力として受け取る
Sx, Sy = map(int, input().split())
# 終点の座標を入力として受け取る
Tx, Ty = map(int, input().split())
return Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty
def solve(Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty):
# 始点と終点のタイルの左端判定用リスト
A = [1] * 2 # 初期値は1(右端)
# 始点のタイル判定
if (Sy % 2 == 0 and Sx % 2 == 0) or (Sy % 2 == 1 and Sx % 2 == 1):
A[0] = 0 # 左端
# 終点のタイル判定
if (Ty % 2 == 0 and Tx % 2 == 0) or (Ty % 2 == 1 and Tx % 2 == 1):
A[1] = 0 # 左端
# 始点と終点を左端に調整
Sx += 1 - A[0]
Tx += 1 - A[1]
# 始点が終点より右にある場合、座標を反転
if Sx > Tx:
Sx, Tx = -Sx, -Tx
# 水平方向の距離を計算
a = Tx - Sx
# 垂直方向の距離を計算
b = abs(Ty - Sy)
# 最小の通行料を計算
if a <= b:
answer = b
else:
answer = b + (a - b) // 2
return answer
# メイン処理
Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty = io_func()
result = solve(Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty)
print(result)
###
# Sx, Sy: 始点の座標
# Tx, Ty: 終点の座標
# A: 始点と終点のタイルが左端かどうかを示すリスト(0: 左端, 1: 右端)
# a: 水平方向の距離
# b: 垂直方向の距離
# answer: 最小の通行料
# 1. io_func関数で入力を受け取る
# 2. solve関数で以下の処理を行う:
# a. 始点と終点のタイルの位置(左端か右端か)を判定
# b. 始点と終点の座標を左端に調整
# c. 始点が終点より右にある場合、座標を反転
# d. 水平方向と垂直方向の距離を計算
# e. 最小の通行料を計算
# 3. 計算結果を出力する
オブジェクト指向版1
ac_object.py
import logging
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
def setup_logger(debug_mode):
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG if debug_mode else logging.INFO)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
file_handler = logging.FileHandler('program_trace.log')
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(file_handler)
return logger
class InputReader(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def read_input(self):
pass
class ConsoleInputReader(InputReader):
def read_input(self):
# 始点の座標を入力として受け取る
Sx, Sy = map(int, input().split())
# 終点の座標を入力として受け取る
Tx, Ty = map(int, input().split())
return Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty
class Coordinate:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
class TileSolver:
def __init__(self, debug_mode=False):
self.logger = setup_logger(debug_mode)
def solve(self, start: Coordinate, end: Coordinate):
self.logger.debug(f"開始: 始点({start.x}, {start.y}), 終点({end.x}, {end.y})")
# 始点と終点のタイルの左端判定
start_left = self._is_left_tile(start)
end_left = self._is_left_tile(end)
self.logger.debug(f"タイル判定: 始点左端={start_left}, 終点左端={end_left}")
# 始点と終点を左端に調整
start.x += 1 - int(start_left)
end.x += 1 - int(end_left)
self.logger.debug(f"左端調整後: 始点({start.x}, {start.y}), 終点({end.x}, {end.y})")
# 始点が終点より右にある場合、座標を反転
if start.x > end.x:
start.x, end.x = -start.x, -end.x
self.logger.debug("座標反転実行")
# 水平方向と垂直方向の距離を計算
horizontal_distance = end.x - start.x
vertical_distance = abs(end.y - start.y)
self.logger.debug(f"距離計算: 水平={horizontal_distance}, 垂直={vertical_distance}")
# 最小の通行料を計算
if horizontal_distance <= vertical_distance:
answer = vertical_distance
else:
answer = vertical_distance + (horizontal_distance - vertical_distance) // 2
self.logger.debug(f"最小通行料計算結果: {answer}")
return answer
def _is_left_tile(self, coord: Coordinate):
if (coord.y % 2 == 0 and coord.x % 2 == 0) or (coord.y % 2 == 1 and coord.x % 2 == 1):
return 0
else:
return 1
class TileGame:
def __init__(self, input_reader: InputReader, solver: TileSolver):
self.input_reader = input_reader
self.solver = solver
def play(self):
Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty = self.input_reader.read_input()
start = Coordinate(Sx, Sy)
end = Coordinate(Tx, Ty)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
debug_mode = False # デバッグモードを有効にする場合はTrueに設定
input_reader = ConsoleInputReader()
solver = TileSolver(debug_mode)
game = TileGame(input_reader, solver)
game.play()
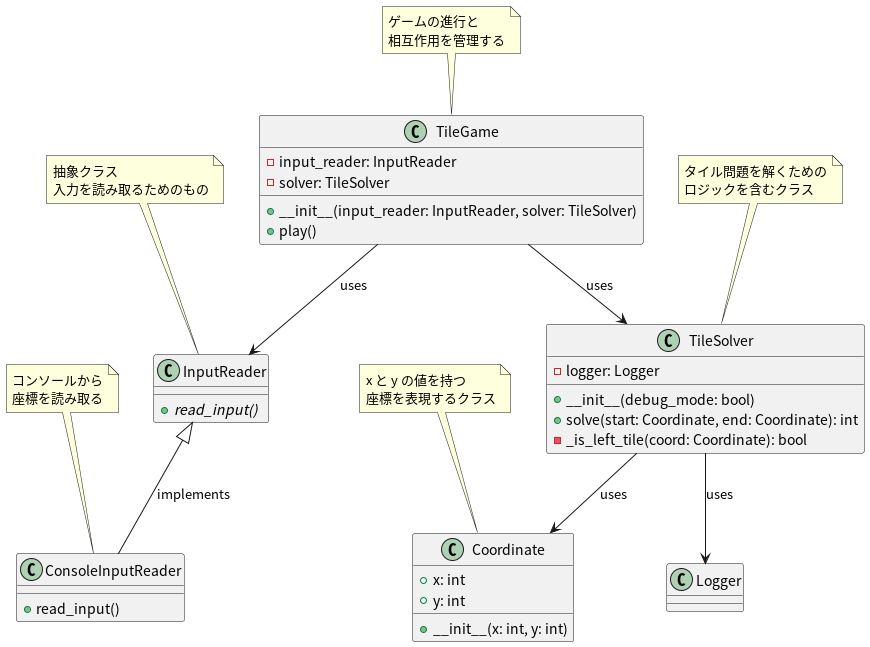
オブジェクト図
オブジェクト指向版1で書くメリット
拡張性と再利用性
ac_object.py
class FileInputReader(InputReader):
def __init__(self, filename):
self.filename = filename
def read_input(self):
with open(self.filename, 'r') as file:
Sx, Sy = map(int, file.readline().split())
Tx, Ty = map(int, file.readline().split())
return Sx, Sy, Tx, Ty
# メイン処理を以下のように変更
if __name__ == "__main__":
debug_mode = True
input_reader = FileInputReader('input.txt') # ファイルから入力を読み込む
path_solver = TileSolver(debug_mode)
executor = ProgramExecutor(input_reader, path_solver)
executor.execute()
テスト容易性
ac_object.py
import unittest
class TestPathSolver(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
self.solver = TileSolver(debug_mode=True)
def test_solve_same_point(self):
start = Coordinate(0, 0)
end = Coordinate(0, 0)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
self.assertEqual(result, 0)
def test_solve_horizontal_movement(self):
start = Coordinate(0, 0)
end = Coordinate(4, 0)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
self.assertEqual(result, 2)
def test_solve_vertical_movement(self):
start = Coordinate(0, 0)
end = Coordinate(0, 5)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
self.assertEqual(result, 5)
def test_solve_diagonal_movement(self):
start = Coordinate(0, 0)
end = Coordinate(3, 3)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
self.assertEqual(result, 3)
def test_solve_complex_movement(self):
start = Coordinate(1, 1)
end = Coordinate(5, 3)
result = self.solver.solve(start, end)
self.assertEqual(result, 3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()