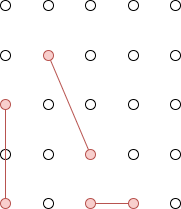
問題
入力例01のイメージ
既存投稿一覧ページへのリンク
Before
AtCoder Beginner Contest 374_C 問題
Next
AtCoder Beginner Contest 374_E 問題
解法手順1
- 入力を受け取り、各線分の座標を保存する。
- 各線分の長さを計算し、印字時間(長さ / 印字速度T)を求める。
- 全ての線分の印字時間の合計を計算する。
- 線分の数Nに対して、2^N通りの方向の組み合わせを生成する(ビット全探索)。
- 各方向の組み合わせに対して、N!通りの順序の順列を生成する。
- 各組み合わせ(方向と順序)に対して:
a. 現在位置を(0,0)に初期化する。
b. 各線分について:- 現在位置から線分の開始点までの移動時間を計算する。
- 現在位置を線分の終点に更新する。
c. 総移動時間を計算し、最小値を更新する。
- 最小の総移動時間と総印字時間を合計して最終的な答えを出力する。
ACコード1
ac.py
import itertools
def io_func():
# 入力を受け取る
n, s, t = map(int, input().split())
lines = []
for _ in range(n):
lines.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
return n, s, t, lines
def calculate_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2):
# 2点間の距離を計算する
return ((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2) ** 0.5
def calculate_move_time(x1, y1, x2, y2, speed):
# 2点間の移動時間を計算する
return calculate_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) / speed
def solve(n, s, t, lines):
# 各線分の印字時間を計算し、合計する
print_times = []
for line in lines:
length = calculate_distance(line[0], line[1], line[2], line[3])
print_times.append(length / t)
total_print_time = sum(print_times)
# 全ての可能な順序と方向を考慮し、最小の移動時間を求める
min_move_time = float('inf')
for direction_bits in range(2**n):
directions = [bool(direction_bits & (1 << i)) for i in range(n)]
for order in itertools.permutations(range(n)):
current_x, current_y = 0, 0
move_time = 0
for i in order:
start_x, start_y = lines[i][2:] if directions[i] else lines[i][:2]
end_x, end_y = lines[i][:2] if directions[i] else lines[i][2:]
move_time += calculate_move_time(current_x, current_y, start_x, start_y, s)
current_x, current_y = end_x, end_y
min_move_time = min(min_move_time, move_time)
# 最小の総移動時間と総印字時間を合計して結果を返す
return min_move_time + total_print_time
def main():
n, s, t, lines = io_func()
result = solve(n, s, t, lines)
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# ###
# n: 線分の数
# s: レーザーの移動速度
# t: レーザーの印字速度
# lines: 各線分の座標 (x1, y1, x2, y2)
# print_times: 各線分の印字時間
# total_print_time: 全線分の印字時間の合計
# min_move_time: 最小の移動時間
# direction_bits: 各線分の方向を表すビット列
# directions: 各線分の方向(True: 逆方向、False: 順方向)
# order: 線分を描く順序
# current_x, current_y: レーザーの現在位置
# move_time: 現在の組み合わせにおける移動時間
# 1. io_func(): 入力を受け取り、必要なデータを返す
# 2. calculate_distance(): 2点間の距離を計算する
# 3. calculate_move_time(): 2点間の移動時間を計算する
# 4. solve(): メインの解法ロジックを実装
# a. 各線分の印字時間を計算し、合計する
# b. 全ての可能な順序と方向の組み合わせを生成
# c. 各組み合わせに対して移動時間を計算し、最小値を更新
# d. 最小の移動時間と総印字時間を合計して結果を返す
# 5. main(): プログラムのエントリーポイント。入力を受け取り、solve()を呼び出し、結果を出力する
オブジェクト指向版1
ac_object.py
import itertools
import logging
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
def setup_logger(debug_mode):
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
if not logger.handlers: # ハンドラが存在しない場合のみ追加
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG if debug_mode else logging.INFO)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
file_handler = logging.FileHandler('program_trace.log', encoding="utf8")
file_handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(file_handler)
return logger
class InputHandler(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def get_input(self):
pass
class OutputHandler(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def output_result(self, result):
pass
class StandardInputHandler(InputHandler):
def get_input(self):
# 入力を受け取る
n, s, t = map(int, input().split())
lines = []
for _ in range(n):
lines.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
return n, s, t, lines
class StandardOutputHandler(OutputHandler):
def output_result(self, result):
print(result)
class GeometryCalculator:
@staticmethod
def calculate_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2):
# 2点間の距離を計算する
return ((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2) ** 0.5
@staticmethod
def calculate_move_time(x1, y1, x2, y2, speed):
# 2点間の移動時間を計算する
return GeometryCalculator.calculate_distance(x1, y1, x2, y2) / speed
class LaserPrinter:
def __init__(self, n, s, t, lines, debug_mode=False):
self.n = n
self.s = s
self.t = t
self.lines = lines
self.logger = setup_logger(debug_mode)
def solve(self):
self.logger.debug("解法の開始")
self.logger.debug(f"n(={self.n}), s(={self.s}), t(={self.t}), lines(={self.lines})")
# 各線分の印字時間を計算し、合計する
print_times = []
for line in self.lines:
length = GeometryCalculator.calculate_distance(line[0], line[1], line[2], line[3])
self.logger.debug(f"({line[0]},{line[1]}),({line[2]},{line[3]})")
self.logger.debug(f"{length / self.t}")
print_times.append(length / self.t)
total_print_time = sum(print_times)
self.logger.debug(f"総印字時間: {total_print_time}")
# 全ての可能な順序と方向を考慮し、最小の移動時間を求める
min_move_time = float('inf')
for direction_bits in range(2**self.n):
directions = [bool(direction_bits & (1 << i)) for i in range(self.n)]
for order in itertools.permutations(range(self.n)):
current_x, current_y = 0, 0
move_time = 0
for i in order:
start_x, start_y = self.lines[i][2:] if directions[i] else self.lines[i][:2]
end_x, end_y = self.lines[i][:2] if directions[i] else self.lines[i][2:]
self.logger.debug(f"({current_x},{current_y}) -> ({start_x},{start_y})")
move_time += GeometryCalculator.calculate_move_time(current_x, current_y, start_x, start_y, self.s)
self.logger.debug(f"move_time: {GeometryCalculator.calculate_move_time(current_x, current_y, start_x, start_y, self.s)}")
current_x, current_y = end_x, end_y
min_move_time = min(min_move_time, move_time)
self.logger.debug(f"現在の最小移動時間: {min_move_time}")
# 最小の総移動時間と総印字時間を合計して結果を返す
result = min_move_time + total_print_time
self.logger.debug(f"最終結果: {result}")
return result
class LaserPrinterController:
def __init__(self, input_handler: InputHandler, output_handler: OutputHandler, debug_mode=False):
self.input_handler = input_handler
self.output_handler = output_handler
self.debug_mode = debug_mode
def run(self):
n, s, t, lines = self.input_handler.get_input()
printer = LaserPrinter(n, s, t, lines, self.debug_mode)
result = printer.solve()
self.output_handler.output_result(result)
def main():
input_handler = StandardInputHandler()
output_handler = StandardOutputHandler()
controller = LaserPrinterController(input_handler, output_handler, debug_mode=True)
controller.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()