概要
- ここではコストマップについて基礎的な内容や処理の流れに焦点を当てて分析する。
前回 : move_baseの分析(1) -move_base本体-
次回 : move_baseの分析(3) -ローカルプランナー-
前提条件
- ROS distroはmelodic
- move_baseソースコード:https://github.com/ros-planning/navigation/tree/melodic-devel
- ソースコードから解析した内容を記す。
参考
- 産総研によるnavigationスタックの解説資料です。この記事を作った後に気づきました(汗)。
コストマップの基本知識
- hydro以降、ROSのコストマップは仕組みが変更された。
- 論文: "Layered Costmaps for Context-Sensitive Navigation", by Lu et. Al, IROS 2014.
- 論文では従来の仕組みをモノシリックコストマップ、提案手法をレイヤードコストマップと呼んでいる。
- モノシリックコストマップ
- 1つのコストマップで複数の情報(センサーで得た外界の情報、地図情報など)を管理する。
- レイヤードコストマップ
- 1つのマスターコストマップと各情報毎に定義したレイヤーを紐付けて管理する。
コストマップ本体の表現方法
- コストマップ本体は
Costmap2Dクラスで定義されている。- 1次元配列
costmap_にコストが格納される。- サイズは
size_x_×size_y_ - コード内でcellと呼ばれていたらこれを指す。
- サイズは
- 1次元配列
- Costmap2Dクラスで定義されているパラメータ
-
size_x_: コストマップの横サイズ[cell] -
size_y_: コストマップの縦サイズ[cell] -
resolution_: 1cellあたりの解像度[m] -
origin_x_: コストマップの左下原点x座標[m] -
origin_y_: コストマップの左下原点y座標[m]-
origin_x_,origin_y_はcostmap_を実空間(主にmapフレーム)のxy座標系と見た時の原点。 - 初期値は(0,0)だが、StaticLayerを使って2Dマップを読み込むとその原点が格納される。
- ローリングウィンドウが有効な場合、ロボットの位置によって常に更新される。
-
-
- 1 cellには0-255の値を格納できる。
- 予め定義されているコストは4種類
-
NO_INFORMATION: 255 -
LETHAL_OBSTACLE(致命的な障害物): 254 -
INSCRIBED_INFLATED_OBSTACLE(内接膨張障害物): 253 -
FREE_SPACE: 0 - その他の値はInflationLayerなどを使用した場合のみ設定される。
関連するクラス
- costmap_2d名前空間に属するクラスが全てコストマップに関わるクラスになるが、ここではその一部を紹介する。
- Costmap2D
- コストマップの本体クラス
- 実世界の座標とコストマップ上のセルに格納されたコスト間のマッピングを提供する。
- 実数座標とセルインデックスの相互変換など。
- Costmap2DROS
- Costmap2DクラスをROS経由で使えるようにしているラッパークラス。
- ROSでコストマップを使う場合はこのクラスを経由する。
- LayeredCostmap
- 各レイヤーをインスタンス化して管理し、1つのスコアに集約する管理を行う。
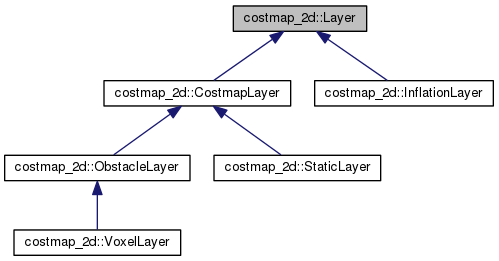
- Layer
- レイヤーを抽象化したクラス。
- レイヤーを作る場合はこのクラスを必ず継承する。
- CostmapLayer
- プライベートコストマップを持つレイヤーに対してコストマップを操作する汎用的な手法を提供する
- 例. レイヤーのコスト値をマスターコストマップに反映させる処理
- プライベートコストマップを持つ場合はこのクラスを必ず継承する。
- プライベートコストマップを持つレイヤーに対してコストマップを操作する汎用的な手法を提供する
- 各レイヤー(標準で用意されているもの)
- StaticLayer
- 2Dマップ画像の情報をコストに反映する場合に使用するレイヤー
- ObstacleLayer
- 2DLidarなどから得られた情報をコストに反映させる場合に使用するレイヤー
- VoxelLayer
- 3Dセンサー(3D Lidar, ToFカメラなど)から得られた情報をコストに反映させる場合に使用するレイヤー
- InflationLayer
- 登録された致命的なコストの周囲にロボットのサイズに応じて衝突の可能性をコストとして割り当てるレイヤー
- StaticLayer
- クラスの継承関係
コストマップの簡易フロー
- 前提
- move_baseの初期化処理でプランナー用に
Costmap2DROSクラスのインスタンスが生成された所から始まる。
- move_baseの初期化処理でプランナー用に
- 初期化処理
- tf受信処理
- レイヤードコストマップの構築
- その他
- パラメータ動的更新処理
- コストマップサイズ設定
- スレッド生成
- コストマップ更新処理
初期化処理
-
Costmap2DROSクラスのコンストラクタによる処理
tf受信処理
- robotフレーム(一般的にはbase_linkフレーム)とglobalフレーム(mapフレームやodomフレーム等)のtfが取得できるようになるまで待機する。
- 受信確認後、次の処理。
costmap_2d_ros.cpp
// we need to make sure that the transform between the robot base frame and the global frame is available
while (ros::ok() && !tf_.canTransform(global_frame_, robot_base_frame_, ros::Time(), ros::Duration(0.1), &tf_error))
{
ros::spinOnce();
if (last_error + ros::Duration(5.0) < ros::Time::now())
{
ROS_WARN("Timed out waiting for transform from %s to %s to become "
"available before running costmap, tf error: %s",
robot_base_frame_.c_str(), global_frame_.c_str(), tf_error.c_str());
last_error = ros::Time::now();
}
// The error string will accumulate and errors will typically be the same,
// so the last will do for the warning above. Reset the string here to avoid
// accumulation.
tf_error.clear();
}
レイヤードコストマップの構築
- 初めに
LayeredCostmapクラスのインスタンスlayered_costmap_を生成する。- このインスタンスはマスターコストマップである
costmap_インスタンスと、レイヤーを格納するplugins_配列を持つ。
- このインスタンスはマスターコストマップである
- パラメータサーバーに
pluginsがある場合、各レイヤーの生成と初期化処理を行う。-
pluginsパラメータがない場合は古い形式でパラメータを読み込む。
-
- 各レイヤーはClassLoaderでインスタンスを生成し
layered_costmap_のplugins_配列に追加していく。 - 最後に各レイヤーを初期化する。
- まず
Layerクラスのinitialize関数が呼び出され、その後各レイヤーのonInitialize関数が呼ばれる。 - この時
layered_costmap_のアドレスを渡して各レイヤー内で生成されるlayered_costmap_と一致するようにする。 - この処理により、各レイヤーからマスターコストマップへアクセスすることができるようになる。
- まず
costmap_2d_ros.cpp
layered_costmap_ = new LayeredCostmap(global_frame_, rolling_window, track_unknown_space);
...
if (private_nh.hasParam("plugins"))
{
XmlRpc::XmlRpcValue my_list;
private_nh.getParam("plugins", my_list);
for (int32_t i = 0; i < my_list.size(); ++i)
{
std::string pname = static_cast<std::string>(my_list[i]["name"]);
std::string type = static_cast<std::string>(my_list[i]["type"]);
copyParentParameters(pname, type, private_nh);
// ClassLoaderでレイヤーのインスタンスを生成
boost::shared_ptr<Layer> plugin = plugin_loader_.createInstance(type);
// レイヤーをplugins_配列に追加
layered_costmap_->addPlugin(plugin);
// レイヤーの初期化
plugin->initialize(layered_costmap_, name + "/" + pname, &tf_);
}
}
layer.cpp
void Layer::initialize(LayeredCostmap *parent, std::string name, tf2_ros::Buffer *tf)
{
// 各レイヤーのlayered_costmap_とマスターコストマップのlayered_costmap_が同じ物を指すようにしている。
layered_costmap_ = parent;
name_ = name;
tf_ = tf;
onInitialize();
}
その他
- フットプリントの設定など
パラメータ動的更新処理
コストマップサイズ設定
- コストマップのサイズがロックされていない場合、設定ファイルから読み込んだ値でコストマップマップのサイズを更新する。
- コストマップのサイズがロックされるのは、StaticLayerで2Dマップを読み込んだ場合。
costmap_2d_ros.cpp
// find size parameters
double map_width_meters = config.width, map_height_meters = config.height, resolution = config.resolution,
origin_x = config.origin_x, origin_y = config.origin_y;
// ロックされていなければマスターコストマップのサイズをパラメータで更新
if (!layered_costmap_->isSizeLocked())
{
layered_costmap_->resizeMap((unsigned int)(map_width_meters / resolution),
(unsigned int)(map_height_meters / resolution), resolution, origin_x, origin_y);
}
スレッド生成
- コストマップ更新用スレッドを生成する。
- スレッドで動作させる関数に
mapUpdateLoop関数を登録。 - 引数にコストマップの更新周期を渡す。
- スレッドで動作させる関数に
costmap_2d_ros.cpp
map_update_thread_ = new boost::thread(boost::bind(&Costmap2DROS::mapUpdateLoop, this, map_update_frequency));
コストマップ更新処理
- スレッドが起動し
mapUpdateLoop関数内でupdateMap関数が呼び出されてコストマップの更新処理が定期的に実行される。 -
updateMap関数では初めにロボットのグローバルフレーム上での位置(x,y,yaw)を取得し、それをLayeredCostmapクラスのUpdateMap関数に渡して更新処理が行われる。
costmap_2d_ros.cpp
void Costmap2DROS::updateMap()
{
if (!stop_updates_)
{
// get global pose
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped pose;
if (getRobotPose(pose))
{
double x = pose.pose.position.x, y = pose.pose.position.y, yaw = tf2::getYaw(pose.pose.orientation);
layered_costmap_->updateMap(x, y, yaw);
geometry_msgs::PolygonStamped footprint;
footprint.header.frame_id = global_frame_;
footprint.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
transformFootprint(x, y, yaw, padded_footprint_, footprint);
footprint_pub_.publish(footprint);
initialized_ = true;
}
}
}
-
LayeredCostmapクラスのupdateMap関数は少し込み入っているのでもう少し詳細を記す。 - 初めにローリングウィンドウが有効な場合、
Costmap2DクラスのupdateOrigin関数でコストマップの原点を更新する処理を行う。- ローリングウィンドウは現在のロボットの位置を中心にしたコストマップを指す。
- そのため更新周期毎にロボットが移動していたら原点の更新が必要になる。
- 次に各レイヤー毎に
updateBound関数を実行しバウンディングボックスの更新を行う。- バウンディングボックス=新たにコスト値を更新する必要がある領域。
- 例. ObstacleLayerの場合、ある閾値の距離以内でなおかつ新しい障害物が生じた範囲。
- 各レイヤーがプライベートコストマップを持っている場合、同時に更新が行われる。
- バウンディングボックスの算出終了後、マスターコストマップのバウンディングボックスに該当する範囲をクリアし、各レイヤーごとに
updateCosts関数でマスターコストマップの値をレイヤーの値で更新する。- この時使用されるバウンディングボックスは全レイヤーの中で一番大きな物が使用される。
layered_costmap.cpp
PPvoid LayeredCostmap::updateMap(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw)
{
// Lock for the remainder of this function, some plugins (e.g. VoxelLayer)
// implement thread unsafe updateBounds() functions.
boost::unique_lock<Costmap2D::mutex_t> lock(*(costmap_.getMutex()));
// if we're using a rolling buffer costmap... we need to update the origin using the robot's position
if (rolling_window_)
{
// 現在のロボットの位置からみて、コストマップの左下原点を再計算。
double new_origin_x = robot_x - costmap_.getSizeInMetersX() / 2;
double new_origin_y = robot_y - costmap_.getSizeInMetersY() / 2;
// コストマップの原点を更新
costmap_.updateOrigin(new_origin_x, new_origin_y);
}
if (plugins_.size() == 0)
return;
minx_ = miny_ = 1e30;
maxx_ = maxy_ = -1e30;
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer>>::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end(); ++plugin)
{
double prev_minx = minx_;
double prev_miny = miny_;
double prev_maxx = maxx_;
double prev_maxy = maxy_;
// バウンディングボックスとプライベートコストマップの更新
(*plugin)->updateBounds(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, &minx_, &miny_, &maxx_, &maxy_);
if (minx_ > prev_minx || miny_ > prev_miny || maxx_ < prev_maxx || maxy_ < prev_maxy)
{
ROS_WARN_THROTTLE(1.0,
"Illegal bounds change, was [tl: (%f, %f), br: (%f, %f)], but "
"is now [tl: (%f, %f), br: (%f, %f)]. The offending layer is %s",
prev_minx, prev_miny, prev_maxx, prev_maxy, minx_, miny_, maxx_, maxy_,
(*plugin)->getName().c_str());
}
}
int x0, xn, y0, yn;
costmap_.worldToMapEnforceBounds(minx_, miny_, x0, y0);
costmap_.worldToMapEnforceBounds(maxx_, maxy_, xn, yn);
x0 = std::max(0, x0);
xn = std::min(int(costmap_.getSizeInCellsX()), xn + 1);
y0 = std::max(0, y0);
yn = std::min(int(costmap_.getSizeInCellsY()), yn + 1);
ROS_DEBUG("Updating area x: [%d, %d] y: [%d, %d]", x0, xn, y0, yn);
if (xn < x0 || yn < y0)
return;
costmap_.resetMap(x0, y0, xn, yn);
for (vector<boost::shared_ptr<Layer>>::iterator plugin = plugins_.begin(); plugin != plugins_.end(); ++plugin)
{
// マスターコストマップを更新
(*plugin)->updateCosts(costmap_, x0, y0, xn, yn);
}
bx0_ = x0;
bxn_ = xn;
by0_ = y0;
byn_ = yn;
initialized_ = true;
}