iOSはAndroidと異なり、色々な制限があり、異なるふたつのアプリケーションと連携する方法もそのうちのひとつです。
AndroidではAIDLを使用したり、暗黙的ブロードキャストインテントを発行することでその実現は達成できますが、iOSの場合は、いくつかの課題が発生します。
本稿ではこのユースケース別に模索して試行した結果を記載します。
そのほかに、なにか良いアイデアがありましたらぜひ教えてください。
UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)を使用する
受信側のアプリケーションの実装例
Info.plist内の「URL Types」に任意のURLスキームを登録
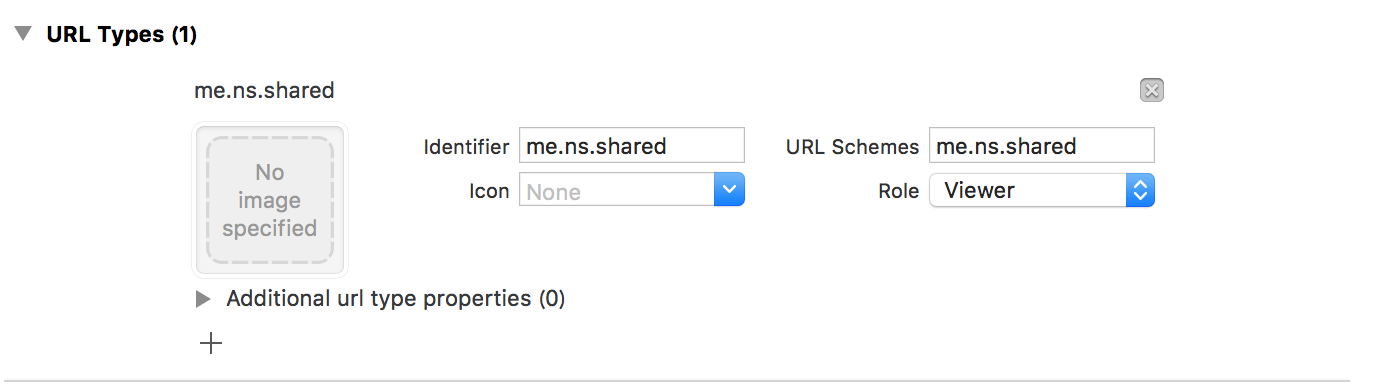
AppDelegateにapplication(_:open:options:)を実装、引き渡されるURL別の処理を実装
import UIKit
import UserNotifications
import AVFoundation
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
return true
}
func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey : Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
if let host = url.host, host == "PlaySound", let query = url.query, let systemSoundID:SystemSoundID = SystemSoundID(query) {
// host == PlaySound、queryを引き渡されるSystemSoundIDを再生する
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(systemSoundID)
}
return true
}
}
上記の実装では、登録したURLスキームでアプリが起動した場合、URLのhostがPlaySoundの場合、クエリパラメータに応じたシステムサウンドが再生します。
発信側のアプリケーションの実装例
アプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
まず、次のような実装でViewControllerのボタンタップイベントでUIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)を呼び出します
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var button: UIButton!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.tappedButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
}
func tappedButton(sender: UIButton) {
var urlComponents = URLComponents()
urlComponents.scheme = "me.ns.shared"
urlComponents.host = "PlaySound"
urlComponents.query = "1001"
UIApplication.shared.open(urlComponents.url!, options: [:]) { result in
NSLog(result.description)
}
}
}
上記の実装では、画面内の部品をユーザが操作した場合など、送信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合では正常に受信側のアプリケーションが起動し、システムサウンドが再生することがわかります。
![]() OK
OK
アプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがバックグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
結果からいうと、この場合はデータのやりとりができません。
まず、バックグラウンドからUIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)を呼び出すために、今回は位置情報の更新をバックグラウンドで実行するためにInfo.plist内の「Background Modes」をONにし、「Location updates」にチェックをいれます。

Info.plist内の「Privacy - Location Always Usage Description」も忘れずに追加します。
バックグラウンドでも動作するように「位置情報の利用の許可」は「常に許可」をアプリケーション内では要求します。

位置情報をバックグラウンドで実行するためのマネージャクラスを実装します。
import UIKit
import Foundation
import CoreLocation
class AppLocationManager: NSObject {
/// Shared instance
static let shared = AppLocationManager()
/// CLLocationManager
private var locationManager: CLLocationManager = CLLocationManager()
override init() {
super.init()
self.locationManager.delegate = self
}
/// 位置情報を常に許可する要求
public func requestAlwaysAuthorization() {
self.locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
}
/// 位置情報更新開始
public func startUpdate() {
self.locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation
self.locationManager.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
self.locationManager.pausesLocationUpdatesAutomatically = false
self.locationManager.distanceFilter = kCLDistanceFilterNone
self.locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
}
/// 位置情報更新停止
public func stopUpdate() {
self.locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation()
}
}
extension AppLocationManager: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
NSLog("didUpdateLocations")
var urlComponents = URLComponents()
urlComponents.scheme = "me.ns.shared"
urlComponents.host = "PlaySound"
urlComponents.query = "1001"
UIApplication.shared.open(urlComponents.url!, options: [:]) { result in
NSLog(result.description)
}
}
}
AppDelegateで位置情報を常に許可する要求を行います。
この例では位置情報の利用の許可の要求は前述のAppLocationManagerを通して行います。
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// 位置情報を常に許可する要求
AppLocationManager.shared.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
return true
}
}
次のようなViewControllerのスイッチをONにした場合位置情報の更新を開始するような実装をします。
なお、以下の例ではパーミッションチェックなども含められていますが、単体の確認レベルでは割愛可能です。
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var button: UIButton!
@IBOutlet weak var updateLocationSwitch: UISwitch!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.tappedButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
updateLocationSwitch.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.changedLocationUpdateSwich(sender:)), for: .valueChanged)
}
override func viewDidAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidAppear(animated)
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(self.didEnterBackground(sender:)),
name: NSNotification.Name.UIApplicationDidEnterBackground, object: nil)
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(self, selector: #selector(self.willEnterForeground(sender:)),
name: NSNotification.Name.UIApplicationWillEnterForeground, object: nil)
// 位置情報更新開始/停止処理
self.locationUpdateIfPossible()
}
override func viewDidDisappear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewDidDisappear(animated)
NotificationCenter.default.removeObserver(self)
}
/// ボタン押下イベント
func tappedButton(sender: UIButton) {
var urlComponents = URLComponents()
urlComponents.scheme = "me.ns.shared"
urlComponents.host = "PlaySound"
urlComponents.query = "1001"
UIApplication.shared.open(urlComponents.url!, options: [:]) { result in
NSLog(result.description)
}
}
/// ボタン押下イベント
func changedLocationUpdateSwich(sender: UISwitch) {
// 位置情報更新開始/停止処理
self.locationUpdateIfPossible()
}
/// 位置情報更新開始/停止処理
private func locationUpdateIfPossible() {
if !updateLocationSwitch.isOn {
// 位置情報の更新停止
AppLocationManager.shared.stopUpdate()
return
}
// 位置情報常に許可リクエスト
switch CLLocationManager.authorizationStatus() {
case .authorizedAlways:
// 位置情報の更新開始
AppLocationManager.shared.startUpdate()
break
default:
self.updateLocationSwitch.setOn(false, animated: true)
// スマートタグサービス起動フラグ == ONの状態にも関わらず、
// 位置情報が許可されていない場合はスマートタグサービスは起動せず、
// 設定画面へ誘導する
showRequestLocation()
}
}
/// 位置情報要求 UIAlertController表示処理
/// - parameter peripheral: Peripheral
func showRequestLocation() {
let alert = UIAlertController(title: "位置情報の要求", message: "このアプリを使用するには位置情報を常に許可するに設定してください", preferredStyle: .alert)
alert.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "OK", style: .default) { action in
UIApplication.shared.open(URL(string:UIApplicationOpenSettingsURLString)!, options: [:], completionHandler: nil)
})
self.present(alert, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
/// アプリフォアグラウンド
func willEnterForeground(sender:Any) {
// 位置情報更新開始/停止処理
self.locationUpdateIfPossible()
}
/// アプリバックグラウンド
func didEnterBackground(sender:Any) {
// Do Nothing
}
}
さて、実際に動かしてみるとわかると思うのですが、位置情報の更新を開始するためのスイッチをONにすると、位置情報の更新が開始され、CLLocationManagerDelegate locationManager(_:didUpdateLocations:)内の処理により、UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)が呼び出され、受信側のアプリケーションが起動しますが、
受信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドになり、送信側のアプリケーションがバックグラウンドに移行した時点でUIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)
処理が失敗することがわかります。
これは、仕様的にあたりまえの話かもしれませんが、UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)はアプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合は失敗するためです。
以上のことから、発信側がバックグラウンドの状態でデータをやり取りしたい場合には、UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)は利用できなさそうです。
![]() NG
NG
Darwin Notificationsを使用する
まず、情報をブロードキャストする
NotificationCenterは異なるアプリへのブロードキャストはできないし、UNUserNotificationCenterはアプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合はアプリケーションがハンドリングできないため、そのまま通知センターに表示されるうえに、異なるアプリの場合はたとえフォアグラウンドだったとしてもUNUserNotificationCenterDelegate userNotificationCenter:willPresentNotification:withCompletionHandler:が呼ばれません。
ここで試したのがDarwin Notificationsになりますが、様々な通知を受けられるこのAPIを組み込んだ場合のリジェクトのリスクや、幾つかの制限があり、なかなか効果的に利用できるつくりを思いうかべられませんでした。
以下に試した実装例をあげます。
受信側のアプリケーションの実装例
AppDelegateにapplication:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:にCFNotificationCenterGetDarwinNotifyCenterのObserverを登録します。
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
CFNotificationCenterAddObserver(CFNotificationCenterGetDarwinNotifyCenter(), nil, { _, _, name, _, _ in
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(1001)
}, "me.ns.shared" as CFString, nil, CFNotificationSuspensionBehavior.deliverImmediately)
return true
}
}
上記の実装では、Darwin Notification Centerから通知が来た場合にシステムサウンドが再生します。
Darwin Notificationの場合、とくに通知の権限の要求を確認することなく利用できるようです。(なかなかおそろしい)
発信側のアプリケーションの実装例
アプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
まず、次のような実装でViewControllerのボタンタップイベントで受信側のアプリケーションが登録している通知名でDarwin NotificationをPostします。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var button: UIButton!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.tappedButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
}
/// ボタン押下イベント
func tappedButton(sender: UIButton) {
CFNotificationCenterPostNotification(CFNotificationCenterGetDarwinNotifyCenter(),
CFNotificationName("me.ns.shared" as CFString), nil, nil, true)
}
}
実際にためしてみるとわかりますが、上記の実装では、送信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合だと、受信側のCFNotificationCallbackが呼ばれず、システムサウンドが再生されません。
これは、CFNotificationCenterAddObserverにあるとおりにバックグラウンドにあるときに通知を処理するsuspensionBehaviorがDarwin Notification Centerの場合は無視される、とあります。
Flag indicating how notifications should be handled when the application is in the background. See CFNotificationSuspensionBehavior for the list of available values.
If center is a Darwin notification center, this value is ignored.
このため、一度受信側のアプリケーションをフォアグラウンドにしてあげる必要があるため、ボタン押下イベントでは次のような対処をしました。
なお、UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)の実装例は「UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)を使用する」のセクションをご確認ください。
/// ボタン押下イベント
func tappedButton(sender: UIButton) {
switch UIApplication.shared.applicationState {
case .active:
var urlComponents = URLComponents()
urlComponents.scheme = "me.ns.shared"
UIApplication.shared.open(urlComponents.url!, options: [:]) { result in
NSLog(result.description)
}
break
default:
CFNotificationCenterPostNotification(CFNotificationCenterGetDarwinNotifyCenter(),
CFNotificationName("me.ns.shared" as CFString), nil, nil, true)
}
}
さて、確認される前に気が付かれたかと思いますが、このような実装だと、UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)で受信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドとなりますので、送信側のアプリケーションはバックグラウンドになります。つまり、ボタンが押せません。
本末転倒である。
![]() NG
NG
アプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがバックグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
バックグラウンドでのDarwin NotificationをPostには、「UIApplication open(_:options:completionHandler:)を使用する」のセクションで使用したAppLocationManagerを利用します。
このAppLocationManagerのCLLocationManagerDelegate locationManager(_:didUpdateLocations:)内で次のようにDarwin NotificationをPostします。
extension AppLocationManager: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
NSLog("didUpdateLocations")
CFNotificationCenterPostNotification(CFNotificationCenterGetDarwinNotifyCenter(),
CFNotificationName("me.ns.shared" as CFString), nil, nil, true)
}
}
上記の実装では、位置情報の更新を開始するためのスイッチをONにすると、位置情報の更新が開始され、CLLocationManagerDelegate locationManager(_:didUpdateLocations:)内の処理により、受信側のアプリケーションが登録している通知名でDarwin NotificationをPostしますが、受信側がフォアグラウンドでない場合は通知を受けられません。
このため、リジェクトの可能性も考慮すると使い所が限られてくるかと思います。
![]() NG?
NG?
App Groupsを使用する
App Groupsというのは、同じ開発者がリリースしたアプリ間でデータを共有できる機能です。
このため、開発元が異なれば使うことができないため、別の会社などがリリースしているアプリとではデータの共有ができません。
受信側のアプリケーションの実装例
XcodeでApp Groupsを設定します。

AppDelegateにapplication(_:open:options:)に登録した「group.me.ns」のUserDefaultsにおける指定キーの監視を追加、observeValue(forKeyPath:of:change:context:)で変更があった場合に変更があった値をもとにシステムサウンドが再生されます。
import UIKit
import AVFoundation
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
UserDefaults(suiteName: "group.me.ns")?.addObserver(self, forKeyPath: "TEST", options: [.new], context: nil)
return true
}
override func observeValue(forKeyPath keyPath: String?, of object: Any?, change: [NSKeyValueChangeKey : Any]?, context: UnsafeMutableRawPointer?) {
if keyPath == "TEST", let value:SystemSoundID = change?[.newKey] as? SystemSoundID {
AudioServicesPlaySystemSound(value)
}
}
}
発信側のアプリケーションの実装例
XcodeでApp Groupsを設定します。

アプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
まず、次のような実装でViewControllerのボタンタップイベントで、登録した「group.me.ns」のUserDefaultsに受信側のアプリケーションが監視しているキーで値を保存します。
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var button: UIButton!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(self.tappedButton(sender:)), for: .touchUpInside)
}
/// ボタン押下イベント
func tappedButton(sender: UIButton) {
let value = 1000 + arc4random_uniform(100)
UserDefaults(suiteName: "group.me.ns")?.set(value, forKey: "TEST")
}
}
上記の実装では、画面内の部品をユーザが操作した場合など、送信側のアプリケーションがフォアグラウンドの場合では正常に受信側のアプリケーションが起動し、システムサウンドが再生することがわかります。
ただし、受信側のアプリケーションがSuspendedの状態の場合は呼び出しが行われず、受信側のアプリケーションのプロセス発火のトリガーとしては利用できません。
このため、App Groupsの利用は、基本的に自社開発したリリースしたアプリ間でデータを共有するくらいに限定され、別のアプリに命令を出すといったユニキャストなデータのやり取りには不向きかと思われます。
![]() NG?
NG?
アプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合
次にあげるのは発信側のアプリケーションがバックグラウンドであることを前提の実装例です。
App Groupsを利用したバックグラウンド処理での命令ですが、「Darwin Notificationsを使用する」「アプリケーションがバックグラウンドの場合」セクションと同様にAppLocationManagerのCLLocationManagerDelegate locationManager(_:didUpdateLocations:)内で登録した「group.me.ns」のUserDefaultsに受信側のアプリケーションが監視しているキーで値を保存します。
extension AppLocationManager: CLLocationManagerDelegate {
public func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
NSLog("didUpdateLocations")
let value = 1000 + arc4random_uniform(100)
UserDefaults(suiteName: "group.me.ns")?.set(value, forKey: "TEST")
}
}
そうすると、位置情報の更新を開始するためのスイッチをONにすると、位置情報の更新が開始され、CLLocationManagerDelegate locationManager(_:didUpdateLocations:)内の処理により、「group.me.ns」のUserDefaultsに値が書き込まれるたびにシステムサウンドが再生することがわかります。
ただし、フォアグラウンドでの処理と同じように受信側のアプリケーションがSuspendedの状態の場合は呼び出しが行われず、受信側のアプリケーションのプロセス発火のトリガーとしては利用できません。
![]() NG?
NG?
その他ためしたこと
サイレントPushを利用する
細かい内容は割愛しますが、次のような方法も試しました。
- 受信側アプリケーションがAPNsにデバイストークンを要求、APNsからデバイストークンが返却される
- 取得したデバイストークンをWeb Serverに登録する
- 送信側アプリケーションが任意のコマンドをWeb Serverに要求する
- Web Serverは受信側アプリケーションに向けてAPNsにプッシュ通知を要求
- 受信側アプリケーションはAPNsから受信したPush通知の内容に応じた処理を実施する
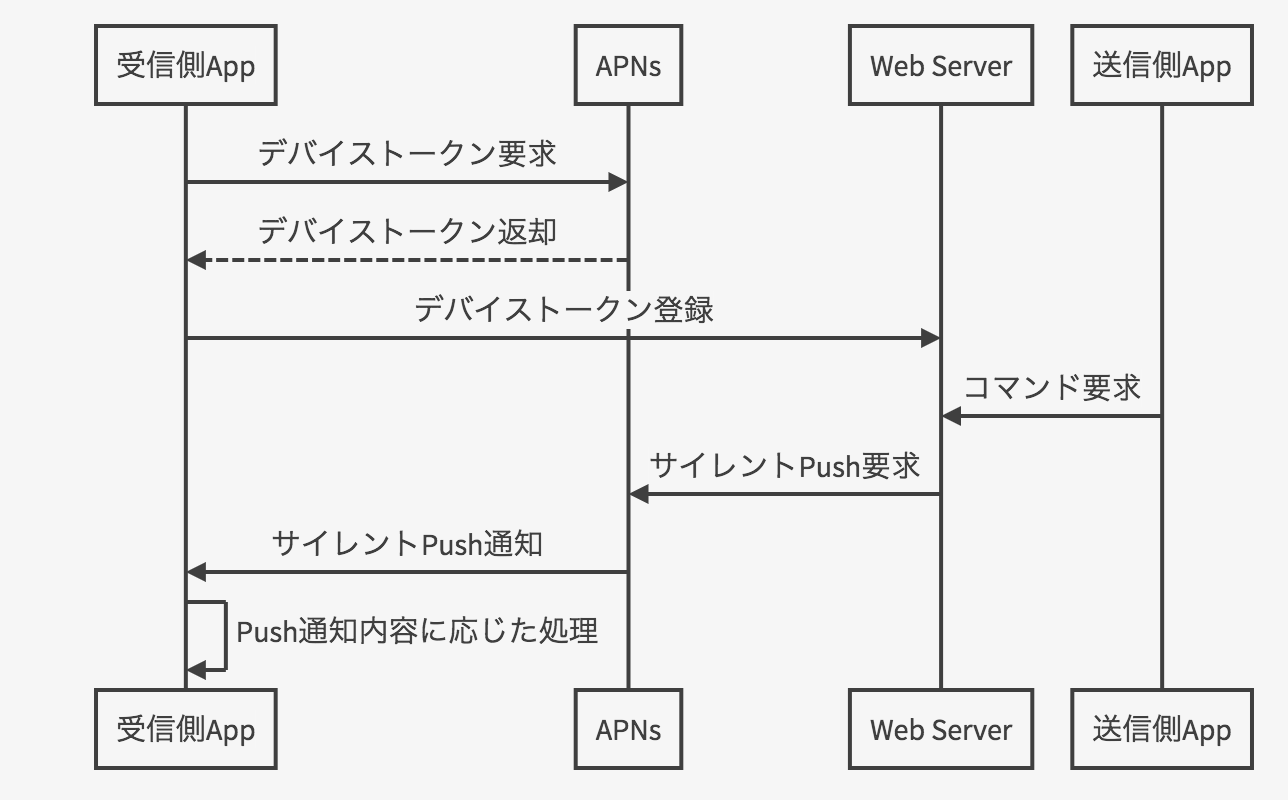
これを利用すると、送信側のアプリケーションの状態を特に気にすることなく、また、受信側のアプリケーションのプロセスがSuspendedの状態でもapplication(_:didReceiveRemoteNotification:fetchCompletionHandler:)で発火し、任意の処理を行うことができます。
ただし、APNSがメッセージの配信の成功を保証しておらず、たとえば送信側のアプリケーションがコマンドを要求した後に通信が遮断された場合はPush通知がこない可能性もありますし、速度に対して期待値は得られないかもしれません。
![]() OK?
OK?
NSDistributedNotificationCenterというものがあるらしい
iOSではサポートしていないようです。
![]() NG
NG