はじめに
Rで最適化問題を解くことができるらしいので,学部レベル(初級)のミクロ経済学の序盤で習う,「予算制約の中で効用(満足感)を最大化する購買量の探索」という効用最大化問題(最適消費計画問題)を例にとり,Rで簡単な制約付き最適化問題を解いたりイロイロしてみます。
◇2018年1月20日追記
ここに載せたことをshinyで作動させてみました。
シンプルな効用最大化問題計算機という感じです。
https://nigimitama.shinyapps.io/MicroEconomics_01_UtilityMaximizationProblem/
中身のコードはこのページの下部(おまけ2)にあります。よろしければ御覧ください。
問題
2財モデルのこんな問題があるとします。
第1財の消費量を$x_1$,第2財の消費量を$x_2$と表す。ある家計の効用関数が$U(x_1,x_2)=x_1^{\frac{2}{5}}x_2^{\frac{3}{5}}$で表されるとする。予算が$100$,第1財の価格が$4$,第2財の価格が$6$のとき,効用を最大化する最適消費量はそれぞれいくらか?
$$\max_{x_1,x_2} \hspace{1em} x_1^{\frac{2}{5}}x_2^{\frac{3}{5}}$$
$$s.t. \hspace{1em} 100 = 4x_1+6x_2$$
ラグランジュの未定乗数法で解ける問題ですが,Rで解いてみます。
Rで解く
{Rsolnp}パッケージを使います。
library(Rsolnp)
ObjFunc = function(x) return( - x[1]^(2/5) * x[2]^(3/5) ) #目的関数
# solnp()は最小化をするようになっているので,目的関数にマイナスを掛ける
ConstFunc = function(x) return( x[1]* 4 + x[2] * 6 ) #制約式の右辺
eq.value <- c(100) #制約式の左辺
x0 <- c(1,1) #決定変数を初期化
solution <- solnp(x0, fun = ObjFunc, eqfun = ConstFunc, eqB = eq.value )
# 最適な「x_1」と「x_2」の値
solution$pars
[1] 10 10
最適な消費量$x_1^* , x_2^* $ は $x_1^* = 10, \ x_2^* = 10$であることが示された
(おまけ1)図示
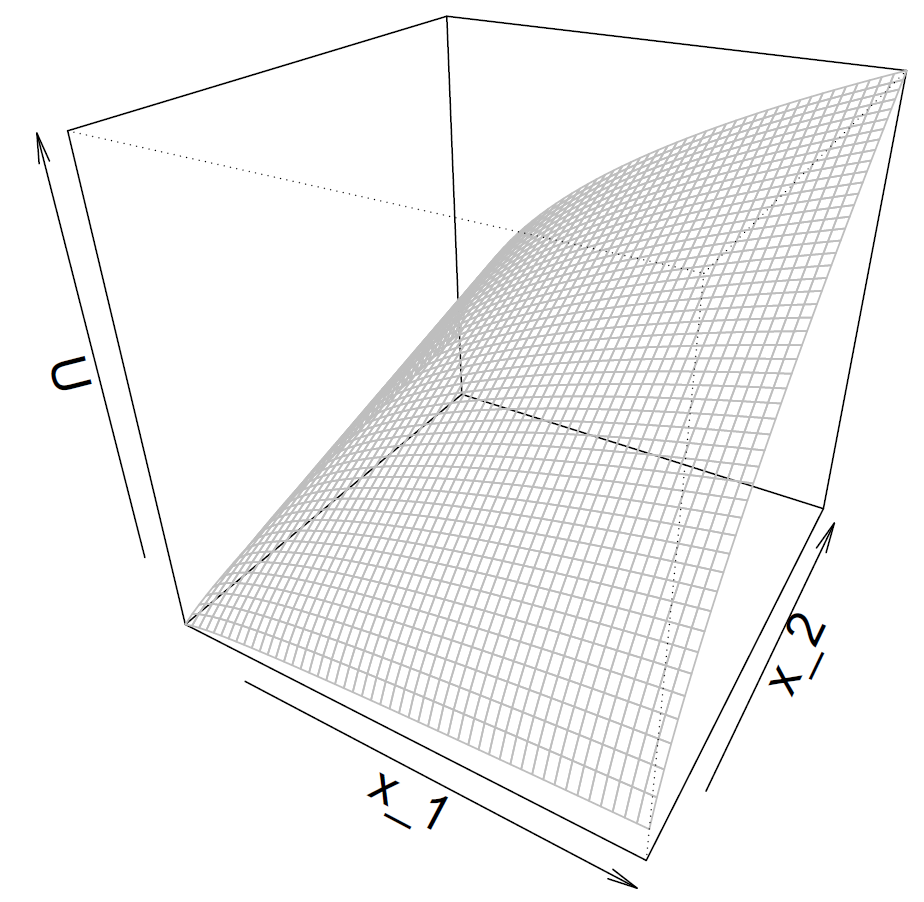
■効用関数の図示
モノ($x_1,x_2$)をたくさん買うほど効用$U$は上がる
# 3次元プロット:persp()
x_1 <- 1:50
x_2 <- 1:50
u <- function(x_1,x_2) {x_1^(2/5) * x_2^(3/5)} #効用関数を定義
U <- outer(x_1, x_2, u) #outer()はx_1,x_2に対応したf(x_1,x_2)の値を行列で返す
persp(x_1, x_2, U,
theta = 30, # 横回転の角度
phi = 30, # 縦回転の角度
ticktype = "simple", # 線の種類
lwd = 0.5, # 線の太さ
col = F,
border = 8)
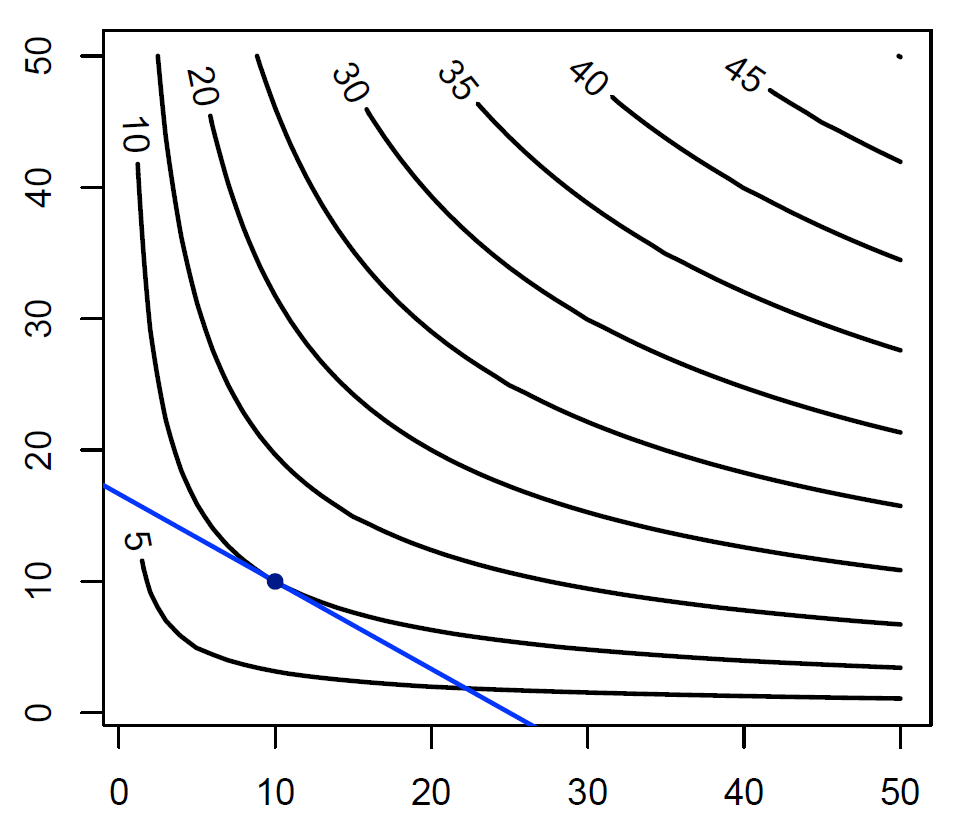
■等高線(無差別曲線)と予算制約線と最適消費点
効用関数の曲面を真上から見て等高線にした図。経済学ではこの等高線を無差別曲線という。
予算制約線(青い直線)と最適消費点(藍色の点)も記しておいた。
無差別曲線と予算制約線が接する点が最適消費点となる。
# 等高線:contour()
contour(x_1, x_2, U, method = "edge", labcex = 1,lwd = 2)
abline(a = 100/6, b = -4/6, lwd = 2, col = "blue") #予算制約線
points(x = 10, y = 10, lwd = 3, col = "darkblue", pch = 16) #最適消費点
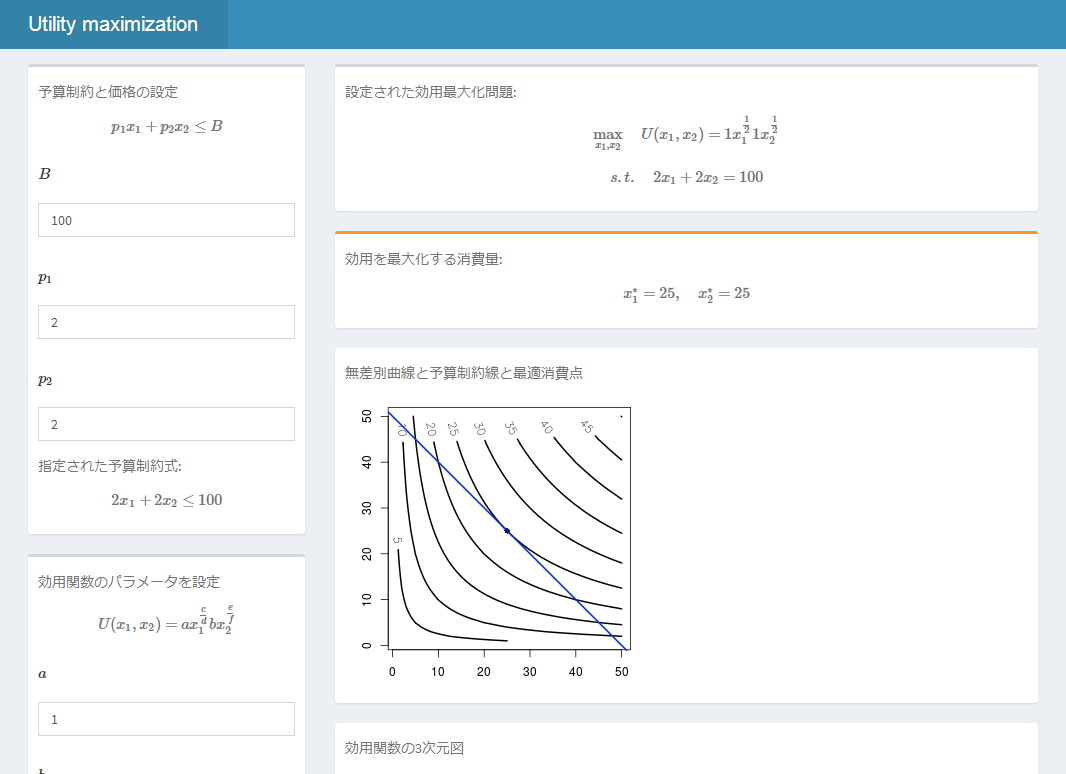
(おまけ2)Shinyで効用最大化問題計算機を作る
以上の制約付き最適化問題を解く{Rsolnp}の処理や関数の図示などをshinyで行わせてみる。
# 日本語の文字列が本文中にあるとdeployできないみたい
# server側のRenderUI内の日本語は問題ないのでコレを利用
library(shinydashboard)
library(shiny)
library(Rsolnp)
header <- dashboardHeader(
title = "Utility maximization problem"
)
body <- dashboardBody(
column(width = 3,
#予算制約
box(width = NULL,
uiOutput('budgettext'),
numericInput("budget",
label = "$$B$$",
value = 100),
numericInput("p_1",
label = "$$p_1$$",
value = 2),
numericInput("p_2",
label = "$$p_2$$",
value = 2),
uiOutput("budgetform")
),
box(width = NULL,
#効用関数モジュール
uiOutput('utilityfunctiontext'),
withMathJax(), #TeX表記有効化
numericInput("a",
label = "$$a$$",
value = 1),
numericInput("b",
label = "$$b$$",
value = 1),
numericInput("c",
label = "$$c$$",
value = 1),
numericInput("d",
label = "$$d$$",
value = 2),
numericInput("e",
label = "$$e$$",
value = 1),
numericInput("f",
label = "$$f$$",
value = 2),
uiOutput("utilityfunction")
),
box(width = NULL,
#p("変数の範囲(描画範囲)"),
numericInput("range",
label = "range of graph",
value = 50)
)
),
fluidRow(
column(width = 7,
#設定された効用最大化問題
box(width = NULL,
uiOutput("Utilitymaximizationproblem")
),
#効用最大化問題の解
box(width = NULL, status = "warning",
uiOutput("maxutility")
),
#無差別曲線
box(width = NULL, solidHeader = TRUE,
uiOutput('indifferencecurve'),
plotOutput("Plot2D", width = 300, height = 300)
),
box(width = NULL, solidHeader = TRUE,
uiOutput('Plot3Dtext'),
plotOutput("Plot3D",height = 300)
)
)
)
)
dashboardPage(
header,
dashboardSidebar(disable = TRUE),
body
)
library(shinydashboard)
library(shiny)
library(Rsolnp)
# サーバロジックの定義
shinyServer(function(input, output) {
# 予算制約式box見出し
output$budgettext <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText("予算制約と価格の設定$$p_1 x_1 + p_2 x_2 \\leq B$$"))
})
#指定された予算をTeXでUIに表示
output$budgetform <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText(paste0('指定された予算制約式:$$',
input$p_1,'x_1 + ', input$p_2,'x_2',
'\\leq',input$budget,'$$')))
})
# 効用関数box見出し
output$utilityfunctiontext <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText('効用関数のパラメータを設定$$U(x_1,x_2)=a x_1^ \\frac{c}{d} b x_2^ \\frac{e}{f}$$'))
})
#指定された効用関数をTeXでUIに表示
output$utilityfunction <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText(paste0('指定された効用関数:$$U(x_1,x_2)=',
input$a,'x_1','^\\frac{',input$c,'}','{',input$d,'}', input$b,'x_2','^\\frac{',input$e,'}','{',input$f,'}','$$')))
})
#設定された効用最大化問題
output$Utilitymaximizationproblem <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText(paste0(
'設定された効用最大化問題:',
'$$ \\max_{x_1,x_2} \\hspace{1em} U(x_1,x_2)=',input$a,'x_1','^\\frac{',input$c,'}','{',input$d,'}', input$b,'x_2','^\\frac{',input$e,'}','{',input$f,'}$$',
'$$s.t. \\hspace{1em} ', input$p_1,'x_1 + ', input$p_2,'x_2 \\leq',input$budget,'$$'
)))
})
#最適消費計画の解
output$maxutility <- renderUI({
ObjFunc = function(x) return( - input$a * x[1]^(input$c/input$d) * input$b * x[2]^(input$e/input$f) ) #目的関数
#solnp()は最小化をするようになっているので,目的関数にマイナスを掛ける
ConstFunc = function(x) return( x[1]* input$p_1 + x[2] * input$p_2 ) #制約式の右辺
eq.value <- c(input$budget) #制約式の左辺
x0 <- c(1,1) #決定変数を初期化
solution <- solnp(x0, fun = ObjFunc, eqfun = ConstFunc, eqB = eq.value )
#return
withMathJax(helpText(paste0("効用を最大化する消費量:",
'$$x_{1}^*=',solution$pars[1],', \\hspace{1em} x_{2}^*=',solution$pars[2],'$$')))
})
#無差別曲線と予算制約線と最適消費点
output$indifferencecurve <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText('無差別曲線と予算制約線と最適消費点'))
})
output$Plot2D <- renderPlot({
#以下のreactiveな要素をrenderPlotに入れれば使えるっぽい
#効用関数をfunctionの形で定義
u <- function(x_1,x_2) {input$a * x_1 ^ (input$c/input$d) * input$b * x_2 ^ (input$e/input$f)} #効用関数を定義
#xの範囲指定
x_1 <- 1:input$range
x_2 <- 1:input$range
U <- outer(x_1, x_2, u) #outer()はx_1,x_2に対応したf(x_1,x_2)の値を行列で返す
#plot
par(mar=c(3,3,1,1))
contour(x_1, x_2, U, method = "edge", labcex = 1,lwd = 2)
abline(a = input$budget/input$p_2, b = -input$p_1/input$p_2, lwd = 2, col = "blue") #予算制約線 x_2 = ...
#最適消費点
ObjFunc = function(x) return( - input$a * x[1]^(input$c/input$d) * input$b * x[2]^(input$e/input$f) ) #目的関数
#solnp()は最小化をするようになっているので,目的関数にマイナスを掛ける
ConstFunc = function(x) return( x[1]* input$p_1 + x[2] * input$p_2 ) #制約式の右辺
eq.value <- c(input$budget) #制約式の左辺
x0 <- c(1,1) #決定変数を初期化
solution <- solnp(x0, fun = ObjFunc, eqfun = ConstFunc, eqB = eq.value )
points(x = solution$pars[1], y = solution$pars[2], lwd = 3, col = "darkblue", pch = 16) #最適消費点
})
#3D plot of utility function 効用関数の3次元図
output$Plot3Dtext <- renderUI({
withMathJax(helpText('効用関数の3次元図'))
})
output$Plot3D <- renderPlot({
#以下のreactiveな要素をrenderPlotに入れれば使えるっぽい
#効用関数をfunctionの形で定義
u <- function(x_1,x_2) {input$a * x_1 ^ (input$c/input$d) * input$b * x_2 ^ (input$e/input$f)} #効用関数を定義
#xの範囲指定
x_1 <- 1:input$range
x_2 <- 1:input$range
U <- outer(x_1, x_2, u) #outer()はx_1,x_2に対応したf(x_1,x_2)の値を行列で返す
persp(x_1, x_2, U,
theta = 30, # 横回転の角度。ここをいじって表示のアングルを変える。
phi = 20, # 縦回転の角度。ここをいじって表示のアングルを変える。
ticktype = "simple", # 線の種類
lwd = 0.5, # 線が太いと見づらかったりするので0.5にしておいた。
col = F, #塗りつぶしなし
border = 8 #枠線灰色
)
})
})