全てのトラフィックをwwwなしの、SSL(https)にリダイレクトしたい
結論
長いので先に結論だけ書きます
-
SSL証明にACMを使い、ELBに証明書が適応されている状態を想定
-
ELB <-> EC2の接続がHTTP: 80の場合、NGINXはport 80でlistenする (ここの気付きが重要でした)
-
NGINXによるリダイレクトはwwwあり->wwwなしのみでよい
-
httpsリクエストをNGINXの80で受けるという設定に戸惑ったが、動作上これで良さそう
ELBでhttp -> httpsリダイレクトを行う方法も書いてみました
HTTP -> HTTPSのリダイレクトはELBで行う方がスマートかもしれない (Nginxでリダイレクトを行う方法あり) - Qiita
現状と目標
httpsかつ、wwwなしのドメインをリクエストしないとSSL接続されない
理想は以下の全ての条件でSSL接続にリダイレクトしたいが現状は
# wwwあり
http://www.mdclip.xyz -> http://mdclip.xyz (no SSL)
https://www.mdclip.xyz -> http://mdclip.xyz (no SSL)
# wwwなし
http://mdclip.xyz -> http://mdclip.xyz (no SSL)
https://mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)
環境
- DNS (Route 53) -> ELB -> EC2 (NGINX -> Puma)
- SSL証明: ACM
- Rails 6 (config/environments/production.rb: config.force_ssl = true)
NGINXの設定はnginx.confに書く?conf.d/*.confに書く
NGINXの設定はnginx.confに記述されているが
その中で/etc/nginx/conf.d/*.confがincludeされており
conf.d以下の内容が呼び出されるようになっている
記事によってこの辺りが曖昧でどのように使い分けるか把握しにくかったが
以下の記事をもとにイメージを掴むことができた
参考: nginx連載3回目: nginxの設定、その1 - インフラエンジニアway - Powered by HEARTBEATS
NGINXではserverディレクティブ(サーバー個別の設定、server {...}で記述される)で定義された
仮想サーバーを複数稼働させることができる
そして、このバーチャルサーバー毎の設定を置く場所がconf.d以下とのこと
なのでconf.d以下のfoo.confには単一のサーバーについての記述に留め
複数のserverディレクティブが記述されているような運用は良くないのかもしれない
ただし、今回conf.d以下の設定ファイルにドメイン間のリダイレクトを担う
serverディレクティブを複数配置してみたが、動作上は問題なさそうでした
全てのトラフィックをwwwなしの、SSL(https://)にリダイレクトしたい場合のNGINXの設定
結論
後述の内容から、以下のように書けば良いと理解した
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
もしくは
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
wwwなし -> wwwあり(その逆パターン)
# add 'www'
server {
listen 80; #非SSL
listen 443 ssl; #SSL こうやって2つ指定できる
server_name example.com; #wwwなしを
return 301 $scheme://www.example.com$request_uri; #wwwありへ
}
# 上記と同意
server {
listen 80; #非SSL
server_name example.com;
return 301 $scheme://www.example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl; #SSL
server_name example.com;
return 301 $scheme://www.example.com$request_uri;
}
# remove 'www'
server {
listen 80; #非SSL
listen 443 ssl; #SSL
server_name www.example.com; #wwwありを
return 301 $scheme://example.com$request_uri; #wwwなしへ
}
参考: How to Create NGINX Rewrite Rules | NGINX
Adding and Removing the www Prefix
These examples add and remove the www prefix:
# add 'www' server { listen 80; listen 443 ssl; server_name domain.com; return 301 $scheme://www.domain.com$request_uri; } # remove 'www' server { listen 80; listen 443 ssl; server_name www.domain.com; return 301 $scheme://domain.com$request_uri; }Again,
returnis preferable to the equivalentrewrite, which follows. Therewriterequires interpreting a regular expression –^(.*)$– and creating a custom variable ($1) that in fact is equivalent to the built‑in$request_urivariable.# NOT RECOMMENDED rewrite ^(.*)$ $scheme://www.domain.com$1 permanent;
http(非SSL) -> https(SSL)にリダイレクト
# http(非SSL) -> https(SSL)に転送
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://www.example.com$request_uri;
}
古いドメインから新しいドメインに移行する場合などは
敢えて$request_uriを省略することでホームページへ都度リダイレクトすることも可能
参考: How to Create NGINX Rewrite Rules | NGINX
Example – Forcing all Requests to Use SSL/TLS
This
serverblock forces all visitors to use a secured (SSL/TLS) connection to your site.server { listen 80; server_name www.domain.com; return 301 https://www.domain.com$request_uri; }Some other blogs about NGINX rewrite rules use an
iftest and therewritedirective for this use case, like this:# NOT RECOMMENDED if ($scheme != "https") { rewrite ^ https://www.mydomain.com$uri permanent; }But this method takes extra processing because NGINX must both evaluate the
ifcondition and process the regular expression in therewritedirective.
全てのトラフィックを特定のドメインにリダイレクト
server {
listen 80 default_server; # http://
listen 443 ssl default_server; # https://
server_name _; # "_"全一致
return 301 $scheme://www.example.com;
}
参考: How to Create NGINX Rewrite Rules | NGINX
Redirecting All Traffic to the Correct Domain Name
Here’s a special case that redirects incoming traffic to the website’s home page when the request URL doesn’t match any
serverandlocationblocks, perhaps because the domain name is misspelled. It works by combining thedefault_serverparameter to thelistendirective and the underscore as the parameter to theserver_namedirective.server { listen 80 default_server; listen 443 ssl default_server; server_name _; return 301 $scheme://www.domain.com; }We use the underscore as the parameter to
server_nameto avoid inadvertently matching a real domain name – it’s safe to assume that no site will ever have the underscore as its domain name. Requests that don’t match any otherserverblocks in the configuration end up here, though, and thedefault_serverparameter tolistentells NGINX to use this block for them. By omitting the$request_urivariable from the rewritten URL, we redirect all requests to the home page, a good idea because requests with the wrong domain name are particularly likely to use URIs that don’t exist on the website.
rewriteよりもreturnを用いることが望ましい理由
-
if...処理を都度行うことは効率的でない. -
rewriteを用いるとNGINXが正規表現を処理する必要があり効率的でない. - ヒトにとってもNGINXが301コードを返すことが明示的で解釈しやすい.
以上を踏まえたNGINXの設定(NG)
nginx.conf
いずれのバーチャルサーバーにも該当しない場合のトラフィックを受ける
default_serverについての記述のみ残しました
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
conf.d/app.conf
error_log /var/www/myapp/shared/log/nginx.error.log;
access_log /var/www/myapp/shared/log/nginx.access.log;
upstream myapp {
server unix://var/www/myapp/shared/tmp/sockets/puma.sock;
}
## #1 以下の2つのserverディレクティブで, wwwなしのhttpsにリダイレクト
# http > https
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
# www > no_www
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl; # #2 httpsで受ける
client_max_body_size 4G;
server_name example.com;
keepalive_timeout 5;
# Location of our static files
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
location ~ ^/assets/ {
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
if (!-f $request_filename) {
proxy_pass http://myapp;
break;
}
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /500.html;
location = /500.html {
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
}
}
ところがこの時点での結果は、
# wwwあり
http://www.mdclip.xyz -> http://www.mdclip.xyz (no SSL)
https://www.mdclip.xyz -> https://www.mdclip.xyz (SSL)
# wwwなし
http://mdclip.xyz -> http://mdclip.xyz (no SSL)
https://mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)

しかも全てのトラフィックがPumaではなくdefault_serverに到達してしまった
以下再度検証へ...
最終検証・解決
AWS Route 53
example.comだけでなく、www.example.comのAレコードについても
ルーティング先にELBのエイリアスを指定する必要がありました
これがないとWWWありのリクエストがNGINXまで到達せず
”サーバーが見つからない”エラーが出ます
ELBの設定を確認
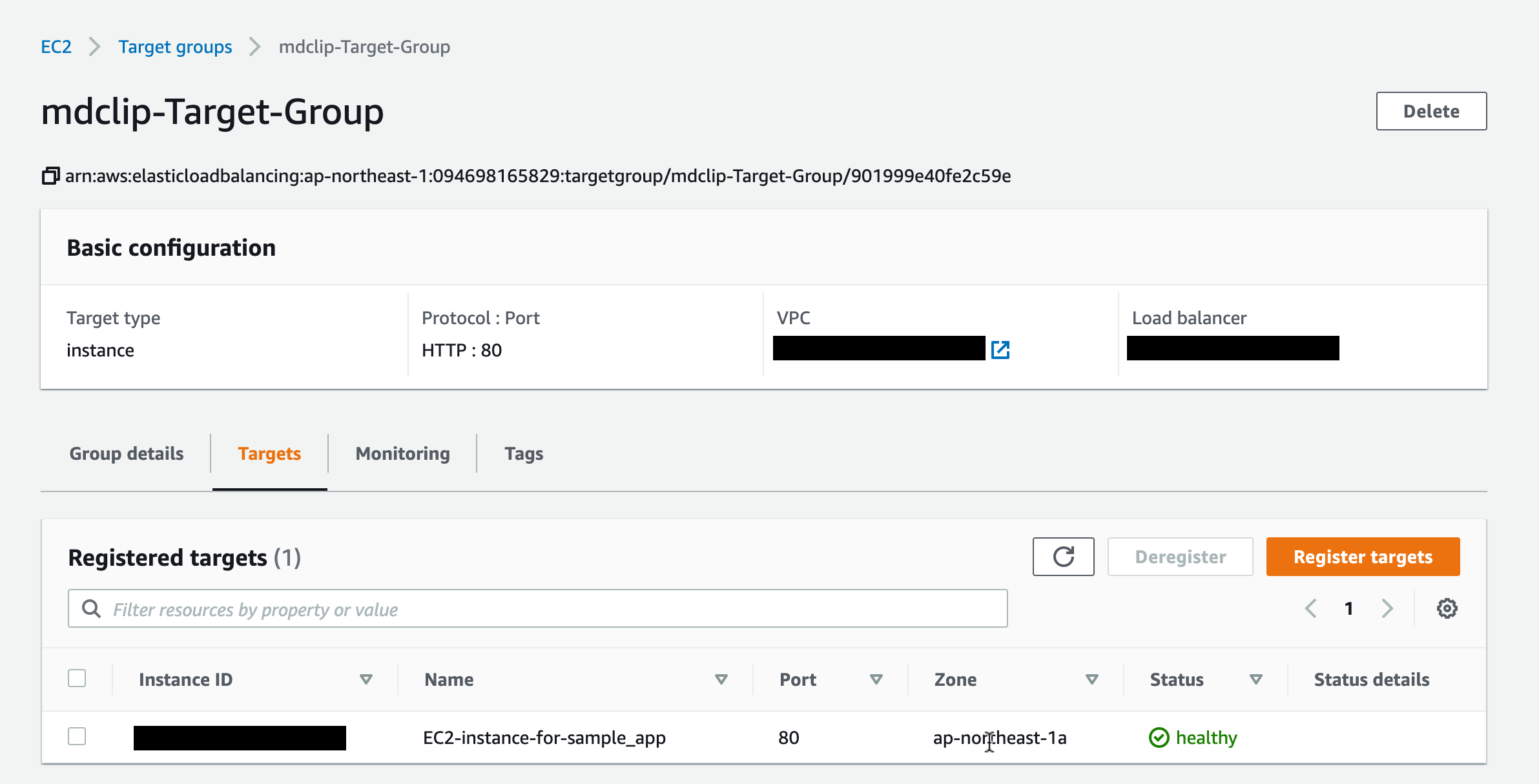
Target groupの設定はEC2インスタンスにHTTP: 80で接続するようになっていました
(ここもHTTPS: 443に変更する方法もあるようです)
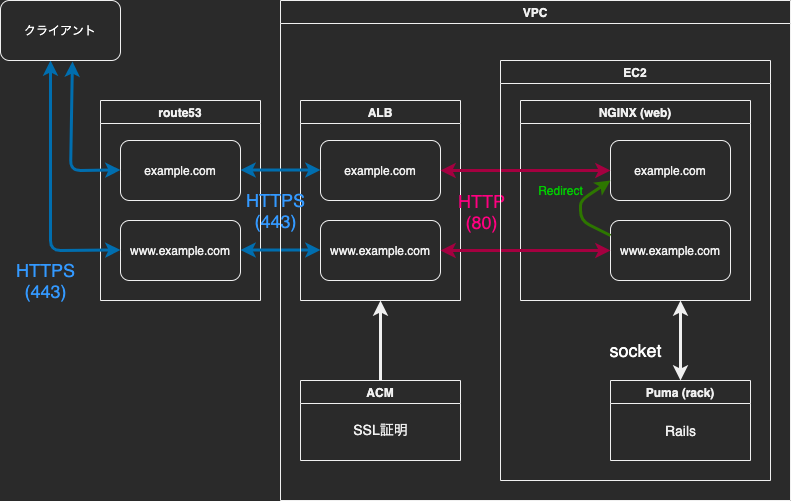
この状況を図にすると
(これがやりたかった!)
重要なのはHTTPSリクエストに対しても
EC2は80ポートでELBと接続されているということ
(言葉が不適切でしたら訂正願います)
だから
- NGINX側は443ではなく80でlistenする必要がある
- 443 > 80へのリダイレクトはNGINXで設定不要(上図の緑の部分のみでいい)
NGINXの設定(再・OK)
nginx.conf
ここは変わりなし
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
conf.d/app.conf
error_log /var/www/myapp/shared/log/nginx.error.log;
access_log /var/www/myapp/shared/log/nginx.access.log;
upstream myapp {
server unix://var/www/myapp/shared/tmp/sockets/puma.sock;
}
# www > no_www
server {
listen 80; #443は不要
server_name www.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 80; #80でlisten
client_max_body_size 4G;
server_name example.com;
keepalive_timeout 5;
# Location of our static files
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
location ~ ^/assets/ {
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_redirect off;
if (!-f $request_filename) {
proxy_pass http://myapp;
break;
}
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /500.html;
location = /500.html {
root /var/www/myapp/current/public;
}
}
これで以下のように目標が達成されました
# wwwあり
http://www.mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)
https://www.mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)
# wwwなし
http://mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)
https://mdclip.xyz -> https://mdclip.xyz (SSL)
おまけ
AmazonLinux環境でのNGINX関連コマンド
設定をリロード
sudo systemctl reload nginx
再起動
sudo systemctl restart nginx
起動
sudo systemctl start nginx
終了
sudo systemctl stop nginx
NGINXのプロセスを確認 (残ったプロセスをkillするときなど)
sudo lsof -i | grep nginx