はじめに
交差テーブルを利用したマッピングには毎回、頭を悩まされます。
今回は、交差テーブルに複合キー以外を持った場合の登録方法をご紹介します。
複合キーのみの登録
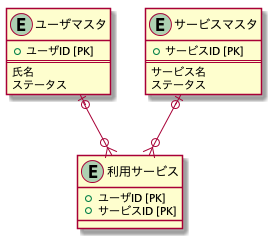
まず、以下のような関係をもったエンティティがあるとします。
この場合の保存方法は以下のようになります。
ユーザマスタ
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = {"id"})
@Entity
@Table
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String status;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name = "user_service",joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name="user_id"), referencedColumnName="id"
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name="service_id", referencedColumnName="id"))
private List<Service> services = new ArrayList<>();
public User(String name,String status){
this.name = name;
this.status = status;
}
// 利用するサービスを追加します
public void addService(Service service){
services.add(service);
}
}
サービスマスタ
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = {"id"})
@Entity
@Table
public class Service implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String status;
public Service(String name,String status) {
this.name = name;
this.status = status;
}
}
登録処理
User user = entityManager.find(User.class,<ユーザID>);
Service service = entityManager.find(Service.class,<利用するサービスID>);
user.addService(service);
entityManager.persist(user);
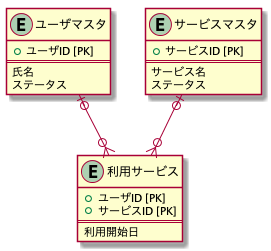
複合キー以外の項目がある場合の登録
利用サービステーブルに「利用開始日」を追加します。
この場合、@JoinTableのみでは利用開始日の保存ができないので、利用サービスとしてエンティティクラスを作成することになります。
利用サービス
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = {"id"})
@Entity
@Table(name = "user_service")
public class UserService implements Serializable {
@EmbeddedId
private PrimaryKey pk;
@Column(name = "begin_date")
private LocalDate beginDate;
@ManyToOne
@MapsId("userId")
private User user;
@ManyToOne
@MapsId("serviceId")
private Service service;
public UserService(User user, Service service,LocalDate beginDate) {
this.user = user;
this.service = service;
this.beginDate = beginDate;
}
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Embeddable
public static class PrimaryKey implements Serializable {
@Column(name = "user_id")
private Long userId;
@Column(name = "service_id")
private Long serviceId;
}
}
ここで重要なのは@MapsIdです。引数にマッピングしたいPrimaryKeyクラスで定義したフィールド名を指定します。これによって、エンティティクラスと複合キーが関連づけられます。
ユーザマスタも修正します。元々、ユーザマスタから利用しているサービスを取得できたのですが、
利用サービスクラス経由で取得するようにします。
ユーザマスタ
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode(of = {"id"})
@Entity
@Table
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String status;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user")
private List<UserService> services = new ArrayList<>();
public User(String name,String status){
this.name = name;
this.status = status;
}
// 利用するサービスを追加します
public void addService(Service service){
services.add(new UserService(this, service, LocalDate.now()));
}
// 交差テーブルのリストではなく、サービスのリストを返却してあげる
public List<Service> getServices(){
return services.stream().map(UserService::getService).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
登録処理サンプル
User user = entityManager.find(User.class,<ユーザID>);
Service service = entityManager.find(Service.class,<利用するサービスID>);
user.addServices(service);
entityManager.persist(user);