本記事はFortran Advent Calendar 2021の12日目の記事です。
はじめに
11月13日に開催された第2回並列計算勉強会で実施したdo concurrentを使用した並列化について、実施した内容を残すために書きます。
実行環境について
OS:Windows10
CPU:AMD Ryzen3
メモリ:32GB(1067MHz)
コンパイラ:MinGW-W64 GCC-8.1.0 x86_64-posix-seh
実行コードについて
こちらのコードを元に書き換えたものをベースとして使用した。
ベースのソースコード(通常のdoループ)
program HimenoBMTxp_F90
use, intrinsic :: iso_fortran_env
implicit none
!&<
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: p
!! pressure
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: a
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1), p(i,j,k)
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: b
!! coefficient matrix for cross derivative terms
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: c
!! coefficient matrix for p(i-1), p(j-1), p(k-1)
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: bnd
!! control variable for boundaries and objects. <br>
!! 1 in fluid and 0 on boundaries or in a object.
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: src
!! source term of Poisson equation
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: wrk
!! working area
!&>
integer(int32) :: mimax, mjmax, mkmax
integer(int32) :: imax, jmax, kmax !&
integer(int32) :: num_iteration
real(real32) :: flop, mflops, score, error
real(real64) :: time_begin_s, time_end_s, time_elapsed_s, dt
! Parameters related to performance measurments
real(real32), parameter :: FlopToMFlop = 1e-6
!! conversion coefficient from flops to mega flops
real(real32), parameter :: numFlopPerPoint = 34.0 ! [operations]
!! number of floating point number operations per grid point
real(real32), parameter :: MFlopsPenIII600 = 82.84 ! [MFLOPS]
!! reference performance (Mega flops) when using Pentium III 600 MHz
call read_grid_parameter(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, imax, jmax, kmax)
! Initializing matrixes
Initialize: block
integer(int32) :: k, num_points
!&<
allocate (p (mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (a (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 4), source=0.0) ! 4D for +x, +y, +z, and center
allocate (b (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 3), source=0.0) ! 3D for xy, yz, xz
allocate (c (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 3), source=0.0) ! 3D for -x, -y, -z
allocate (bnd(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (src(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (wrk(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
!&>
!&<
a (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, 1:3) = 1.0
a (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, 4) = 1.0/6.0
b (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, :) = 0.0
c (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, :) = 1.0
bnd(1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax) = 1.0
!&>
do k = 1, kmax
p(:, :, k) = real((k - 1)**2)/real((kmax - 1)**2)
end do
num_points = (kmax-2)*(jmax-2)*(imax-2) !& 2:imax-1 times 2:jmax-1 times 2:kmax-1
flop = real(num_points)*numFlopPerPoint
end block Initialize
print *, " mimax=", mimax, " mjmax=", mjmax, " mkmax=", mkmax
print *, " imax=", imax, " jmax=", jmax, " kmax=", kmax
dt = get_time_measurement_resolution()
print "(a,e12.5)", "Time measurement accuracy : ", dt
! Rehearsal measurment to estimate the number of iterations
Rehearsal: block
num_iteration = 3
print *, " Start rehearsal measurement process."
print *, " Measure the performance in 3 times."
! Jacobi iteration
time_begin_s = get_current_time()
call jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
time_end_s = get_current_time()
time_elapsed_s = time_end_s - time_begin_s
if (time_elapsed_s < dt) error stop "error : execution time is not correct. The grid size may be too small."
mflops = flop*FlopToMFlop/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration))
print *, " MFLOPS:", mflops, " time(s):", time_elapsed_s, error
end block Rehearsal
! end Rehearsal measurment
! Acatual measurment
Actual: block
! ExecTime specifys the measuring period in sec
! real(real32), parameter :: ExecTime = 60.0 !sec
real(real32), parameter :: ExecTime = 10.0 !sec
! set the number of Iterations so that the execution time is roughly ExecTime sec
num_iteration = int(ExecTime/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration)))
print *, "Now, start the actual measurement process."
print *, "The loop will be excuted in", num_iteration, " times."
print *, "This will take about one minute."
print *, "Wait for a while."
! Jacobi iteration
time_begin_s = get_current_time()
call jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
time_end_s = get_current_time()
! compute benchmark results
time_elapsed_s = time_end_s - time_begin_s
mflops = flop*FlopToMFlop/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration))
score = mflops/MFlopsPenIII600
print *, " Loop executed for ", num_iteration, " times"
print *, " Error :", error
print *, " MFLOPS:", mflops, " time(s):", time_elapsed_s
print *, " Score based on Pentium III 600MHz :", score
end block Actual
Finalize: block
deallocate (p)
deallocate (a)
deallocate (b)
deallocate (c)
deallocate (bnd)
deallocate (src)
deallocate (wrk)
end block Finalize
contains
!| get time measurement resolution of the system
function get_time_measurement_resolution() result(time_interval)
implicit none
integer(int32) :: count, count_rate, count_max
real(real64) :: time_interval
call system_clock(count, count_rate, count_max)
time_interval = 1.0/dble(count_rate)
end function get_time_measurement_resolution
!| get elapsed time in second from the reference time
! function get_current_time() result(current_time_s)
! implicit none
! integer(int32) :: count, count_rate, count_max
! real(real64) :: current_time_s
! call system_clock(count, count_rate, count_max)
! current_time_s = dble(count)/dble(count_rate)
! end function get_current_time
function get_current_time() result(current_time_s)
use omp_lib
implicit none
real(real64) :: current_time_s
current_time_s = omp_get_wtime()
end function get_current_time
!| read problem (grid size) from standard input and set the number of grid points according to the grid size
subroutine read_grid_parameter(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, imax, jmax, kmax)
implicit none
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mimax
!! number of grid points in x direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mjmax
!! number of grid points in y direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mkmax
!! number of grid points in z direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: imax
!! number of grid points in x direction
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: jmax
!! number of grid points in y direction
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: kmax
!! number of grid points in z direction
character(10) :: size
print *, "Select Grid-size:"
print *, " XS (64x32x32)"
print *, " S (128x64x64)"
print *, " M (256x128x128)"
print *, " L (512x256x256)"
print *, " XL (1024x512x512)"
print "(A,$)", " Grid-size = "
! read (*, *) size
size = "L"
call set_grid_size(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, size)
imax = mimax - 1
jmax = mjmax - 1
kmax = mkmax - 1
end subroutine read_grid_parameter
!| set the number of grid points according to the grid size
subroutine set_grid_size(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, size)
implicit none
!&<
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mimax
!! number of grid points in x direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mjmax
!! number of grid points in y direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mkmax
!! number of grid points in z direction (with padding)
character(*), intent(in) :: size
!! grid size
!&>
select case (size)
case ("XS", "xs")
mimax = 64 + 1
mjmax = 32 + 1
mkmax = 32 + 1
case ("S", "s")
mimax = 128 + 1
mjmax = 64 + 1
mkmax = 64 + 1
case ("M", "m")
mimax = 256 + 1
mjmax = 128 + 1
mkmax = 128 + 1
case ("L", "l")
mimax = 512 + 1
mjmax = 256 + 1
mkmax = 256 + 1
case ("XL", "xl")
mimax = 1024 + 1
mjmax = 512 + 1
mkmax = 512 + 1
case default
error stop "Unexpected Grid-size"
end select
end subroutine set_grid_size
!| solve Poisson equation using Jacobi method
subroutine jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
implicit none
!&<
real(real32), intent(inout) :: p(:, :, :)
!! pressure
real(real32), intent(inout) :: error
!! squared error
real(real32), intent(in) :: a(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1), p(i,j,k)
real(real32), intent(in) :: b(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for cross derivative term
real(real32), intent(in) :: c(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1)
real(real32), intent(in) :: bnd(:, :, :)
!! control variable for boundaries and objects
real(real32), intent(in) :: src(:, :, :)
!! source term of Poisson equation
real(real32), intent(inout) :: wrk(:, :, :)
!! working area
integer(int32), intent(in) :: num_iteration
!! number of Jacobi iteration
!&>
integer(int32) :: loop
integer(int32) :: i, j, k
real(real32) :: p_new, dp
real(real32), parameter :: rlx = 0.8 !relaxation parameter
integer(int32), parameter :: x = 1
integer(int32), parameter :: y = 2
integer(int32), parameter :: z = 3
integer(int32), parameter :: center = 4
integer(int32), parameter :: xy = 1
integer(int32), parameter :: yz = 2
integer(int32), parameter :: zx = 3
integer(int32) :: imax
integer(int32) :: jmax
integer(int32) :: kmax
imax = ubound(p, x) - 1
jmax = ubound(p, y) - 1
kmax = ubound(p, z) - 1
!&<
Jacobi_iteration: do loop = 1, num_iteration
error = 0.0
do k = 2, kmax-1
do j = 2, jmax-1
do i = 2, imax-1
p_new = a(i, j, k, x )*p(i+1, j , k ) &
+ a(i, j, k, y )*p(i , j+1, k ) &
+ a(i, j, k, z )*p(i , j , k+1) &
+ b(i, j, k, xy)*( p(i+1, j+1, k ) - p(i+1, j-1, k ) &
- p(i-1, j+1, k ) + p(i-1, j-1, k )) &
+ b(i, j, k, yz)*( p(i , j+1, k+1) - p(i , j-1, k+1) &
- p(i , j+1, k-1) + p(i , j-1, k-1)) &
+ b(i, j, k, zx)*( p(i+1, j , k+1) - p(i-1, j , k+1) &
- p(i+1, j , k-1) + p(i-1, j , k-1)) &
+ c(i, j, k, x)*p(i-1, j , k ) &
+ c(i, j, k, y)*p(i , j-1, k ) &
+ c(i, j, k, z)*p(i , j , k-1) &
+ src(i, j, k)
dp = (p_new*a(i, j, k, center) - p(i, j, k))*bnd(i, j, k)
! error = error + dp*dp
wrk(i, j, k) = p(i, j, k) + rlx*dp
end do
end do
end do
p(2:imax-1, 2:jmax-1, 2:kmax-1) = wrk(2:imax-1, 2:jmax-1, 2:kmax-1)
end do Jacobi_iteration
!&>
end subroutine jacobi
end program HimenoBMTxp_F90
do concurrentを使うように書き換えたもの。
program HimenoBMTxp_F90
use, intrinsic :: iso_fortran_env
implicit none
!&<
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: p
!! pressure
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: a
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1), p(i,j,k)
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: b
!! coefficient matrix for cross derivative terms
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :, :), allocatable :: c
!! coefficient matrix for p(i-1), p(j-1), p(k-1)
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: bnd
!! control variable for boundaries and objects. <br>
!! 1 in fluid and 0 on boundaries or in a object.
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: src
!! source term of Poisson equation
real(real32), dimension(:, :, :), allocatable :: wrk
!! working area
!&>
integer(int32) :: mimax, mjmax, mkmax
integer(int32) :: imax, jmax, kmax !&
integer(int32) :: num_iteration
real(real32) :: flop, mflops, score, error
real(real64) :: time_begin_s, time_end_s, time_elapsed_s, dt
! Parameters related to performance measurments
real(real32), parameter :: FlopToMFlop = 1e-6
!! conversion coefficient from flops to mega flops
real(real32), parameter :: numFlopPerPoint = 34.0 ! [operations]
!! number of floating point number operations per grid point
real(real32), parameter :: MFlopsPenIII600 = 82.84 ! [MFLOPS]
!! reference performance (Mega flops) when using Pentium III 600 MHz
call read_grid_parameter(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, imax, jmax, kmax)
! Initializing matrixes
Initialize: block
integer(int32) :: k, num_points
!&<
allocate (p (mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (a (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 4), source=0.0) ! 4D for +x, +y, +z, and center
allocate (b (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 3), source=0.0) ! 3D for xy, yz, xz
allocate (c (mimax, mjmax, mkmax, 3), source=0.0) ! 3D for -x, -y, -z
allocate (bnd(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (src(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
allocate (wrk(mimax, mjmax, mkmax), source=0.0)
!&>
!&<
a (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, 1:3) = 1.0
a (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, 4) = 1.0/6.0
b (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, :) = 0.0
c (1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax, :) = 1.0
bnd(1:imax, 1:jmax, 1:kmax) = 1.0
!&>
do k = 1, kmax
p(:, :, k) = real((k - 1)**2)/real((kmax - 1)**2)
end do
num_points = (kmax-2)*(jmax-2)*(imax-2) !& 2:imax-1 times 2:jmax-1 times 2:kmax-1
flop = real(num_points)*numFlopPerPoint
end block Initialize
print *, " mimax=", mimax, " mjmax=", mjmax, " mkmax=", mkmax
print *, " imax=", imax, " jmax=", jmax, " kmax=", kmax
dt = get_time_measurement_resolution()
print "(a,e12.5)", "Time measurement accuracy : ", dt
! Rehearsal measurment to estimate the number of iterations
Rehearsal: block
num_iteration = 3
print *, " Start rehearsal measurement process."
print *, " Measure the performance in 3 times."
! Jacobi iteration
time_begin_s = get_current_time()
call jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
time_end_s = get_current_time()
time_elapsed_s = time_end_s - time_begin_s
if (time_elapsed_s < dt) error stop "error : execution time is not correct. The grid size may be too small."
mflops = flop*FlopToMFlop/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration))
print *, " MFLOPS:", mflops, " time(s):", time_elapsed_s, error
end block Rehearsal
! end Rehearsal measurment
! Acatual measurment
Actual: block
! ExecTime specifys the measuring period in sec
! real(real32), parameter :: ExecTime = 60.0 !sec
real(real32), parameter :: ExecTime = 10.0 !sec
! set the number of Iterations so that the execution time is roughly ExecTime sec
num_iteration = int(ExecTime/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration)))
print *, "Now, start the actual measurement process."
print *, "The loop will be excuted in", num_iteration, " times."
print *, "This will take about one minute."
print *, "Wait for a while."
! Jacobi iteration
time_begin_s = get_current_time()
call jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
time_end_s = get_current_time()
! compute benchmark results
time_elapsed_s = time_end_s - time_begin_s
mflops = flop*FlopToMFlop/(time_elapsed_s/dble(num_iteration))
score = mflops/MFlopsPenIII600
print *, " Loop executed for ", num_iteration, " times"
print *, " Error :", error
print *, " MFLOPS:", mflops, " time(s):", time_elapsed_s
print *, " Score based on Pentium III 600MHz :", score
end block Actual
Finalize: block
deallocate (p)
deallocate (a)
deallocate (b)
deallocate (c)
deallocate (bnd)
deallocate (src)
deallocate (wrk)
end block Finalize
contains
!| get time measurement resolution of the system
function get_time_measurement_resolution() result(time_interval)
implicit none
integer(int32) :: count, count_rate, count_max
real(real64) :: time_interval
call system_clock(count, count_rate, count_max)
time_interval = 1.0/dble(count_rate)
end function get_time_measurement_resolution
!| get elapsed time in second from the reference time
! function get_current_time() result(current_time_s)
! implicit none
! integer(int32) :: count, count_rate, count_max
! real(real64) :: current_time_s
! call system_clock(count, count_rate, count_max)
! current_time_s = dble(count)/dble(count_rate)
! end function get_current_time
function get_current_time() result(current_time_s)
use omp_lib
implicit none
real(real64) :: current_time_s
current_time_s = omp_get_wtime()
end function get_current_time
!| read problem (grid size) from standard input and set the number of grid points according to the grid size
subroutine read_grid_parameter(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, imax, jmax, kmax)
implicit none
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mimax
!! number of grid points in x direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mjmax
!! number of grid points in y direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mkmax
!! number of grid points in z direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: imax
!! number of grid points in x direction
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: jmax
!! number of grid points in y direction
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: kmax
!! number of grid points in z direction
character(10) :: size
print *, "Select Grid-size:"
print *, " XS (64x32x32)"
print *, " S (128x64x64)"
print *, " M (256x128x128)"
print *, " L (512x256x256)"
print *, " XL (1024x512x512)"
print "(A,$)", " Grid-size = "
! read (*, *) size
size = "L"
call set_grid_size(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, size)
imax = mimax - 1
jmax = mjmax - 1
kmax = mkmax - 1
end subroutine read_grid_parameter
!| set the number of grid points according to the grid size
subroutine set_grid_size(mimax, mjmax, mkmax, size)
implicit none
!&<
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mimax
!! number of grid points in x direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mjmax
!! number of grid points in y direction (with padding)
integer(int32), intent(inout) :: mkmax
!! number of grid points in z direction (with padding)
character(*), intent(in) :: size
!! grid size
!&>
select case (size)
case ("XS", "xs")
mimax = 64 + 1
mjmax = 32 + 1
mkmax = 32 + 1
case ("S", "s")
mimax = 128 + 1
mjmax = 64 + 1
mkmax = 64 + 1
case ("M", "m")
mimax = 256 + 1
mjmax = 128 + 1
mkmax = 128 + 1
case ("L", "l")
mimax = 512 + 1
mjmax = 256 + 1
mkmax = 256 + 1
case ("XL", "xl")
mimax = 1024 + 1
mjmax = 512 + 1
mkmax = 512 + 1
case default
error stop "Unexpected Grid-size"
end select
end subroutine set_grid_size
!| solve Poisson equation using Jacobi method
subroutine jacobi(p, error, a, b, c, bnd, src, wrk, num_iteration)
implicit none
!&<
real(real32), intent(inout) :: p(:, :, :)
!! pressure
real(real32), intent(inout) :: error
!! squared error
real(real32), intent(in) :: a(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1), p(i,j,k)
real(real32), intent(in) :: b(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for cross derivative term
real(real32), intent(in) :: c(:, :, :, :)
!! coefficient matrix for p(i+1), p(j+1), p(k+1)
real(real32), intent(in) :: bnd(:, :, :)
!! control variable for boundaries and objects
real(real32), intent(in) :: src(:, :, :)
!! source term of Poisson equation
real(real32), intent(inout) :: wrk(:, :, :)
!! working area
integer(int32), intent(in) :: num_iteration
!! number of Jacobi iteration
!&>
integer(int32) :: loop
integer(int32) :: i, j, k
real(real32) :: p_new, dp
real(real32), parameter :: rlx = 0.8 !relaxation parameter
integer(int32), parameter :: x = 1
integer(int32), parameter :: y = 2
integer(int32), parameter :: z = 3
integer(int32), parameter :: center = 4
integer(int32), parameter :: xy = 1
integer(int32), parameter :: yz = 2
integer(int32), parameter :: zx = 3
integer(int32) :: imax
integer(int32) :: jmax
integer(int32) :: kmax
imax = ubound(p, x) - 1
jmax = ubound(p, y) - 1
kmax = ubound(p, z) - 1
!&<
!
! Jacobi_iteration: do loop = 1, num_iteration
do concurrent (loop = 1:num_iteration)
error = 0.0
do concurrent (k = 2:kmax-1)
! do k = 2, kmax-1
do concurrent (j = 2:jmax-1)
! do j = 2, jmax-1
do concurrent (i = 2:imax-1)
! do i = 2, imax-1
p_new = a(i, j, k, x )*p(i+1, j , k ) &
+ a(i, j, k, y )*p(i , j+1, k ) &
+ a(i, j, k, z )*p(i , j , k+1) &
+ b(i, j, k, xy)*( p(i+1, j+1, k ) - p(i+1, j-1, k ) &
- p(i-1, j+1, k ) + p(i-1, j-1, k )) &
+ b(i, j, k, yz)*( p(i , j+1, k+1) - p(i , j-1, k+1) &
- p(i , j+1, k-1) + p(i , j-1, k-1)) &
+ b(i, j, k, zx)*( p(i+1, j , k+1) - p(i-1, j , k+1) &
- p(i+1, j , k-1) + p(i-1, j , k-1)) &
+ c(i, j, k, x)*p(i-1, j , k ) &
+ c(i, j, k, y)*p(i , j-1, k ) &
+ c(i, j, k, z)*p(i , j , k-1) &
+ src(i, j, k)
dp = (p_new*a(i, j, k, center) - p(i, j, k))*bnd(i, j, k)
! error = error + dp*dp
wrk(i, j, k) = p(i, j, k) + rlx*dp
end do
end do
end do
p(2:imax-1, 2:jmax-1, 2:kmax-1) = wrk(2:imax-1, 2:jmax-1, 2:kmax-1)
! end do Jacobi_iteration
end do
!&>
end subroutine jacobi
end program HimenoBMTxp_F90
テスト条件について
今回は並列コア数とコンパイル時の最適化オプションを振って並列性能が上がるか検討した。
- コア数:1、2、4
- コンパイルオプション:-O1、-O2、-O3、-Ofast、-Og
- 複数コア計算時の共通コンパイルオプション:-floop-parallelize-all、-ftree-parallelize-loops(1コアの場合は使用していない)
マトリックスのサイズはLを使用した。
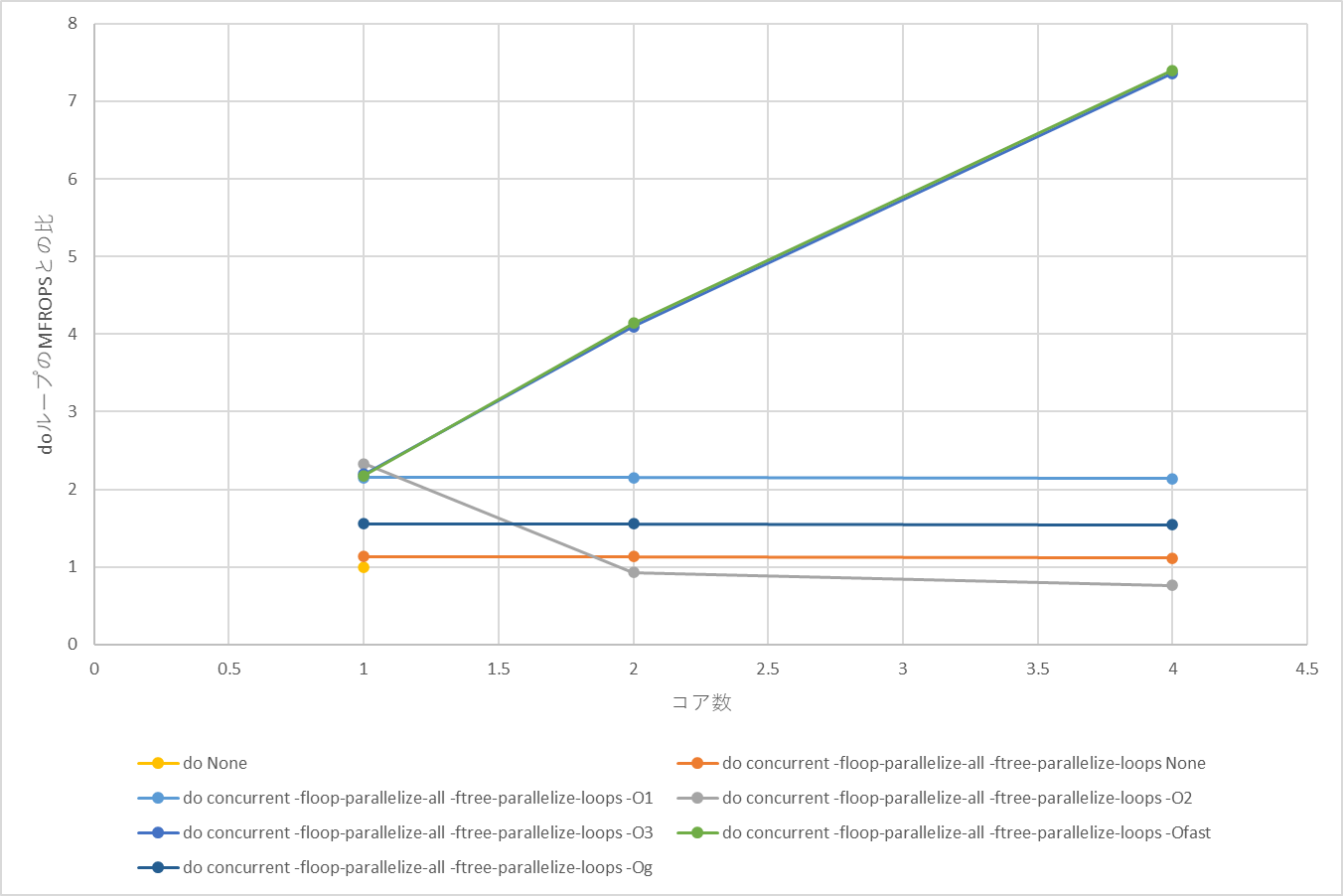
実行結果
比較対象にする通常のdoループ
gfortran .\himenoBMT.f90 -o himenoBMT.exe -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 791.631592 | 1 |
do concurrent + コンパイルオプションによるMFROPS。コンパイルコマンドと結果を順に示す。
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc.exe -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 895.503235 | 1.131212099 |
| 2 | 897.748962 | 1.134048933 |
| 4 | 884.753357 | 1.117632704 |
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_o1.exe -O1 -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2_o1.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -O1 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4_o1.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -O1 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1704.48059 | 2.153123507 |
| 2 | 1705.00012 | 2.153779785 |
| 4 | 1693.13 | 2.138785285 |
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_o2.exe -O2 -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2_o2.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -O2 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4_o2.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -O2 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1846.24219 | 2.332198726 |
| 2 | 736.637878 | 0.930531178 |
| 4 | 604.445312 | 0.763543696 |
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_o3.exe -O3 -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2_o3.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -O3 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4_o3.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -O3 -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1740.00525 | 2.19799875 |
| 2 | 3242.29468 | 4.095711582 |
| 4 | 5825.41113 | 7.358740087 |
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_ofast.exe -Ofast -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2_ofast.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -Ofast -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4_ofast.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -Ofast -floop-parallelize-all -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1723.20935 | 2.176781937 |
| 2 | 3276.69116 | 4.139161692 |
| 4 | 5855.90527 | 7.397260707 |
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_og.exe -Og -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl2_og.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=2 -Og -fopenmp
gfortran .\himenoBMT_dc.f90 -o himenoBMT_dc_fpl4_og.exe -ftree-parallelize-loops=4 -Og -fopenmp
| スレッド数 | MFROPS | doループのMFROPSとの比 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1232.59961 | 1.557036913 |
| 2 | 1229.75427 | 1.55344264 |
| 4 | 1228.80859 | 1.552248044 |
グラフで見るとこんな感じになる。
おわりに
do concurrentでフロップスの変化を確認した。
最適化オプションによって顕著に傾向が異なる様子が見えた。