OpenAI Gym
インストール
git clone https://github.com/openai/gym.git
cd gym
pip install -e .
or
pip install gym
macの場合
brew install cmake boost boost-python sdl2 swig wget
ubuntuの場合
apt-get install -y python-numpy python-dev cmake zlib1g-dev libjpeg-dev xvfb libav-tools xorg-dev python-opengl libboost-all-dev libsdl2-dev swig
Supported systems
brew install boost-python --with-python3
Rendering on a server
X11.app xwindow system用DL
https://support.apple.com/ja-jp/HT201341
ランダムアクションで実行してみる
import gym
env = gym.make('CartPole-v0')
env.reset()
for _ in range(1000):
env.render()
env.step(env.action_space.sample()) # take a random action
chainerrl
インストール
git clone https://github.com/pfnet/chainerrl.git
cd chainerrl/examples/gym
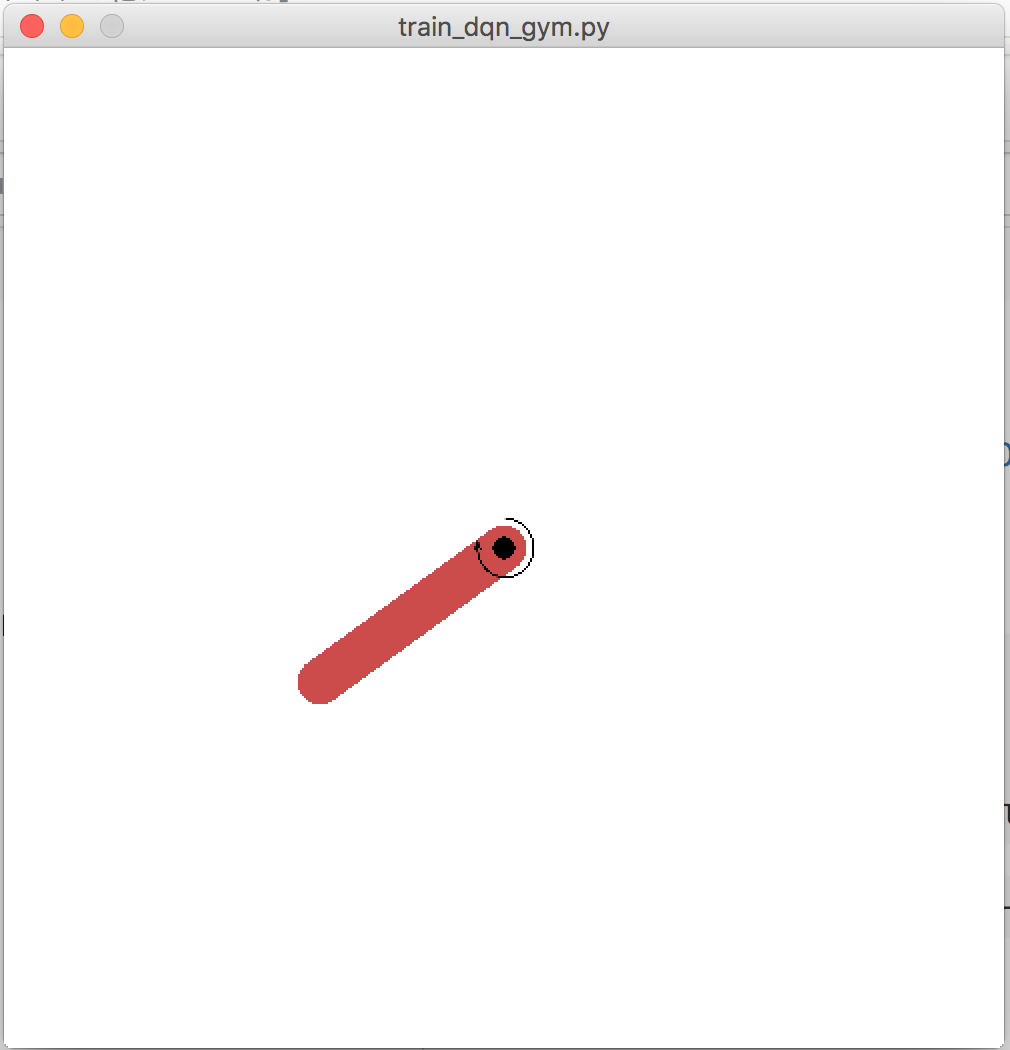
DQNを動かして見る
python train_dqn_gym.py --gpu -1 --monitor
環境
Observation
Type: Box(3)
| Num | Observation | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | cos(theta) | -1.0 | 1.0 |
| 1 | sin(theta) | -1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | theta dot | -8.0 | 8.0 |
Actions
Type: Box(1)
| Num | Observation | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Joint effort | -2.0 | 2.0 |
Reward
-(theta^2 + 0.1*theta_dt^2 + 0.001*action^2)
シータは-piとpiの間で正規化される。
Starting State
Piに-piからランダム角度、-1と1の間のランダムな速度
アルゴリズム(arxiv版)
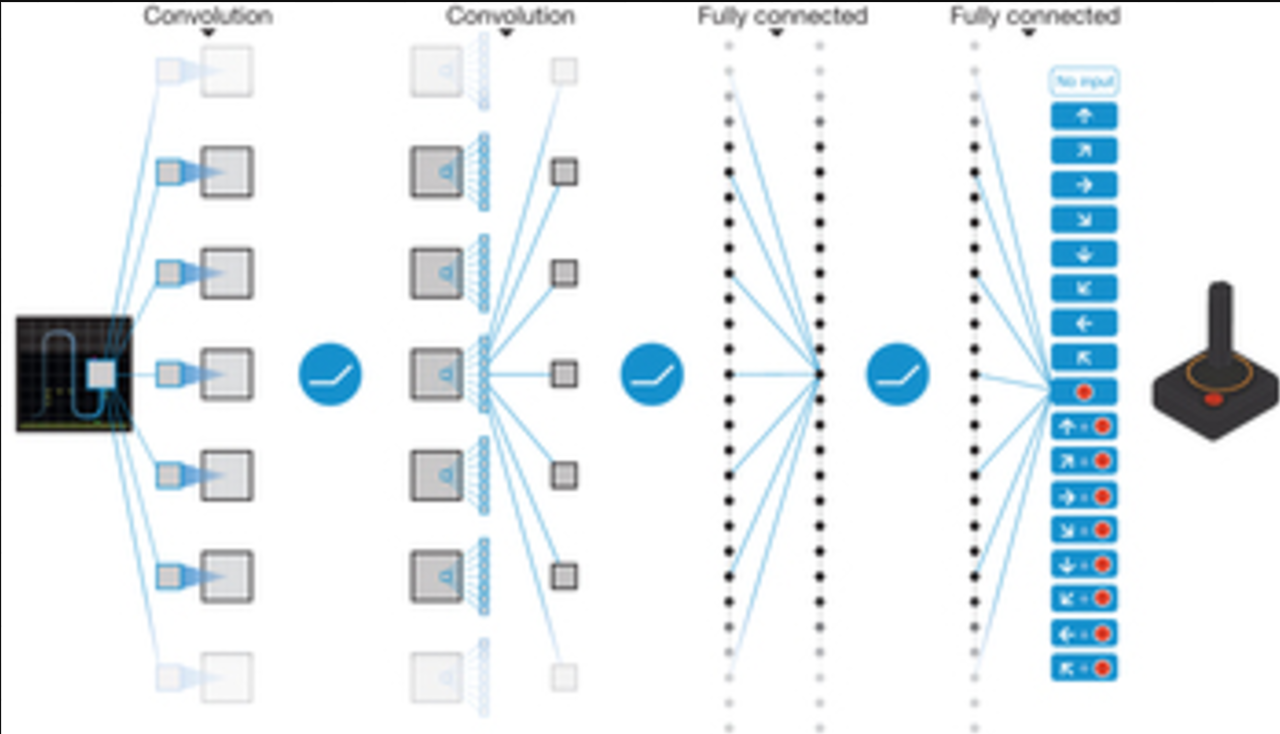
ニューラルネット部分
atari gameは210 × 160 pixel images with a 128 colorなので、 gray-scale and down-sampling it to a 110×84 imageした。そこからf 2D convolutionに入れるためにcropping an 84 × 84した。グレースケールなので84 84の行列。
the last 4 frames of a historyを溜め込んで、Q関数に突っ込む。
ネットワークφの構成を正確に書くと。
84 × 84 × 4 image produced by φ。1層目の隠れ層はconvolves 16で8 × 8 filters with stride 4です。2層目はconvolves 32 4 × 4 filters with stride 2。3層目は256ユニットで全結合。最終層はactionに全結合。
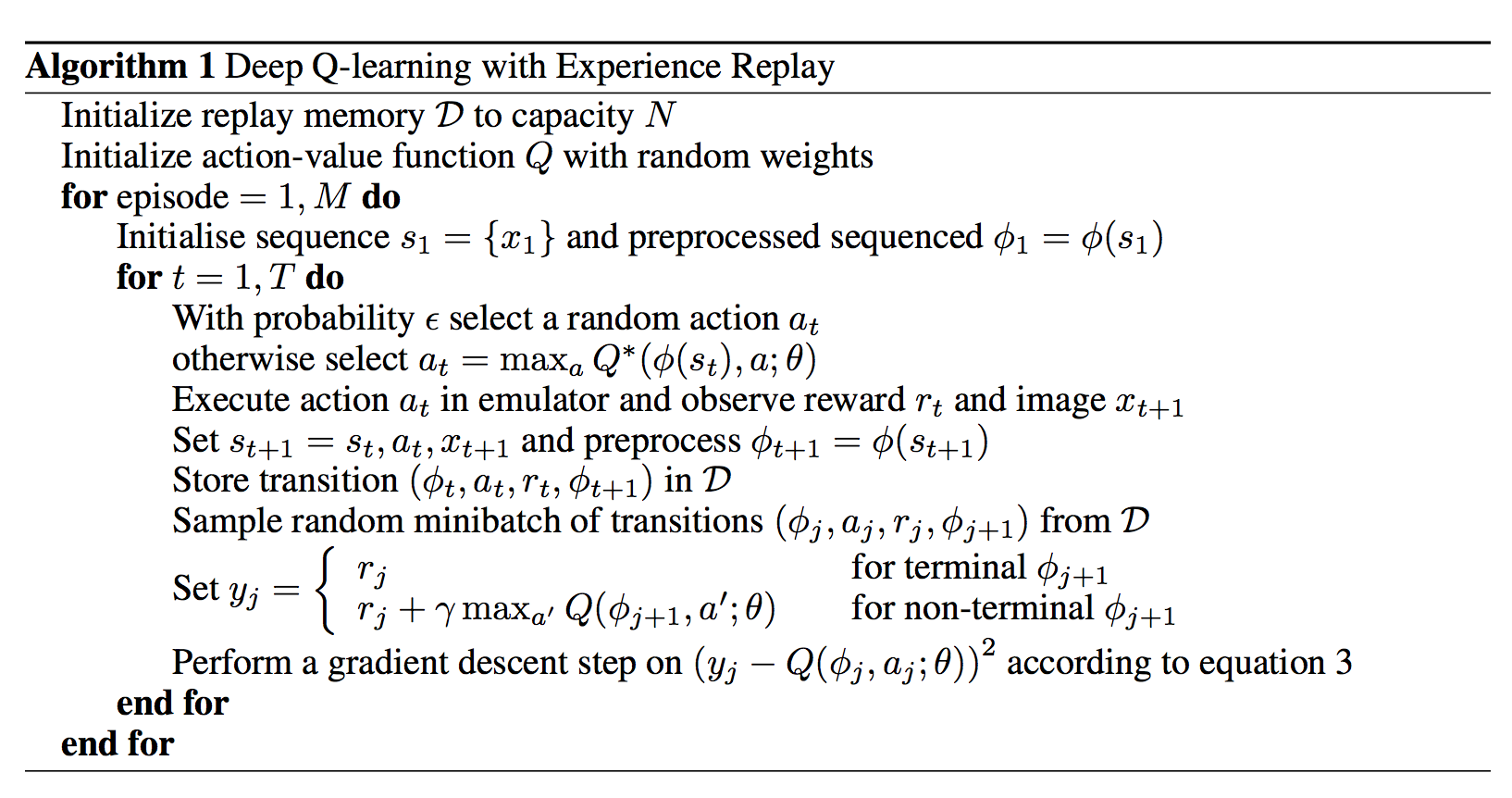
リプレイメモリーを初期化。行動価値関数Qの重みを初期化。
エピソードと時間ごとにループ。
ε確率で行動aを選択。
行動価値関数を最大化する。
行動atを実行。リワードrtを取得、image xt+1を取得。
...力尽きた
先人の方の資料をここへ
http://qiita.com/Ugo-Nama/items/08c6a5f6a571335972d5
論文
Nature版とarxiv版で少し違うようです。
・ V. Mnih et al., "Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning"
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1312.5602.pdf
・ V. Mnih et al., "Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning"
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v518/n7540/abs/nature14236.html
コードを上から見て見る
引数もろもろ
def main():
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--outdir', type=str, default='dqn_out')
parser.add_argument('--env', type=str, default='Pendulum-v0')
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=None)
parser.add_argument('--gpu', type=int, default=0)
parser.add_argument('--final-exploration-steps',
type=int, default=10 ** 4)
parser.add_argument('--start-epsilon', type=float, default=1.0)
parser.add_argument('--end-epsilon', type=float, default=0.1)
parser.add_argument('--demo', action='store_true', default=False)
parser.add_argument('--load', type=str, default=None)
parser.add_argument('--steps', type=int, default=10 ** 5)
parser.add_argument('--prioritized-replay', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--episodic-replay', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--replay-start-size', type=int, default=None)
parser.add_argument('--target-update-frequency', type=int, default=10 ** 2)
parser.add_argument('--target-update-method', type=str, default='hard')
parser.add_argument('--soft-update-tau', type=float, default=1e-2)
parser.add_argument('--update-frequency', type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument('--eval-n-runs', type=int, default=100)
parser.add_argument('--eval-frequency', type=int, default=10 ** 4)
parser.add_argument('--n-hidden-channels', type=int, default=100)
parser.add_argument('--n-hidden-layers', type=int, default=2)
parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.99)
parser.add_argument('--minibatch-size', type=int, default=None)
parser.add_argument('--render-train', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--render-eval', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--monitor', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--reward-scale-factor', type=float, default=1e-3)
args = parser.parse_args()
args.outdir = experiments.prepare_output_dir(
args, args.outdir, argv=sys.argv)
print('Output files are saved in {}'.format(args.outdir))
if args.seed is not None:
misc.set_random_seed(args.seed)
np.clip(arr, 0.0, 1.0)はarrの行列内のデータを0~1の間に抑えると言う意味なので
clip_action_filterで環境ごとにアクションを制限している。
def clip_action_filter(a):
return np.clip(a, action_space.low, action_space.high)
make_envで環境を作成。
エピソードという単位で学習を回すためにtimestep_limit等を設定。
def make_env(for_eval):
env = gym.make(args.env)
if args.monitor:
env = gym.wrappers.Monitor(env, args.outdir)
if isinstance(env.action_space, spaces.Box):
misc.env_modifiers.make_action_filtered(env, clip_action_filter)
if not for_eval:
misc.env_modifiers.make_reward_filtered(
env, lambda x: x * args.reward_scale_factor)
if ((args.render_eval and for_eval) or
(args.render_train and not for_eval)):
misc.env_modifiers.make_rendered(env)
return env
env = make_env(for_eval=False)
timestep_limit = env.spec.tags.get(
'wrapper_config.TimeLimit.max_episode_steps')
obs_size = env.observation_space.low.size
action_space = env.action_space
Qネットワークの定義。
if isinstance(action_space, spaces.Box):
action_size = action_space.low.size
# Use NAF to apply DQN to continuous action spaces
q_func = q_functions.FCQuadraticStateQFunction(
obs_size, action_size,
n_hidden_channels=args.n_hidden_channels,
n_hidden_layers=args.n_hidden_layers,
action_space=action_space)
# Use the Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process for exploration
ou_sigma = (action_space.high - action_space.low) * 0.2
explorer = explorers.AdditiveOU(sigma=ou_sigma)
else:
n_actions = action_space.n
q_func = q_functions.FCStateQFunctionWithDiscreteAction(
obs_size, n_actions,
n_hidden_channels=args.n_hidden_channels,
n_hidden_layers=args.n_hidden_layers)
# Use epsilon-greedy for exploration
explorer = explorers.LinearDecayEpsilonGreedy(
args.start_epsilon, args.end_epsilon, args.final_exploration_steps,
action_space.sample)
値の更新
opt = optimizers.Adam()
opt.setup(q_func)
rbuf_capacity = 5 * 10 ** 5
if args.episodic_replay:
if args.minibatch_size is None:
args.minibatch_size = 4
if args.replay_start_size is None:
args.replay_start_size = 10
if args.prioritized_replay:
betasteps = \
(args.steps - timestep_limit * args.replay_start_size) \
// args.update_frequency
rbuf = replay_buffer.PrioritizedEpisodicReplayBuffer(
rbuf_capacity, betasteps=betasteps)
else:
rbuf = replay_buffer.EpisodicReplayBuffer(rbuf_capacity)
else:
if args.minibatch_size is None:
args.minibatch_size = 32
if args.replay_start_size is None:
args.replay_start_size = 1000
if args.prioritized_replay:
betasteps = (args.steps - args.replay_start_size) \
// args.update_frequency
rbuf = replay_buffer.PrioritizedReplayBuffer(
rbuf_capacity, betasteps=betasteps)
else:
rbuf = replay_buffer.ReplayBuffer(rbuf_capacity)
def phi(obs):
return obs.astype(np.float32)
エージェント定義
agent = DQN(q_func, opt, rbuf, gpu=args.gpu, gamma=args.gamma,
explorer=explorer, replay_start_size=args.replay_start_size,
target_update_frequency=args.target_update_frequency,
update_frequency=args.update_frequency,
phi=phi, minibatch_size=args.minibatch_size,
target_update_method=args.target_update_method,
soft_update_tau=args.soft_update_tau,
episodic_update=args.episodic_replay, episodic_update_len=16)
if args.load:
agent.load(args.load)
eval_env = make_env(for_eval=True)
デモモードの場合の実行
あるいは学習評価モードでの実行
if args.demo:
mean, median, stdev = experiments.eval_performance(
env=eval_env,
agent=agent,
n_runs=args.eval_n_runs,
max_episode_len=timestep_limit)
print('n_runs: {} mean: {} median: {} stdev'.format(
args.eval_n_runs, mean, median, stdev))
else:
experiments.train_agent_with_evaluation(
agent=agent, env=env, steps=args.steps,
eval_n_runs=args.eval_n_runs, eval_frequency=args.eval_frequency,
outdir=args.outdir, eval_env=eval_env,
max_episode_len=timestep_limit)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
もう少し細かく見て見る
ほぼ抽象化されてる。
Qネットワークを見て見る。
FCQuadraticStateQFunctionは Normalized Advantage FunctionsをDQNに適応してる。
https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.00748
FCStateQFunctionWithDiscreteActionの方がDQNの方。
FCStateQFunctionWithDiscreteActionにQネットワーク、LinearDecayEpsilonGreedyにεグリーディが実装されてるのであろう。
ここでは定義だけで何もしてない。これをagentに渡す。
n_actions = action_space.n
q_func = q_functions.FCStateQFunctionWithDiscreteAction(
obs_size, n_actions,
n_hidden_channels=args.n_hidden_channels,
n_hidden_layers=args.n_hidden_layers)
# Use epsilon-greedy for exploration
explorer = explorers.LinearDecayEpsilonGreedy(
args.start_epsilon, args.end_epsilon, args.final_exploration_steps,
action_space.sample)
さらにMLPを呼び出してる。
class FCStateQFunctionWithDiscreteAction(
SingleModelStateQFunctionWithDiscreteAction):
"""Fully-connected state-input Q-function with discrete actions.
Args:
n_dim_obs: number of dimensions of observation space
n_dim_action: number of dimensions of action space
n_hidden_channels: number of hidden channels
n_hidden_layers: number of hidden layers
"""
def __init__(self, ndim_obs, n_actions, n_hidden_channels,
n_hidden_layers, nonlinearity=F.relu,
last_wscale=1.0):
super().__init__(model=MLP(
in_size=ndim_obs, out_size=n_actions,
hidden_sizes=[n_hidden_channels] * n_hidden_layers,
nonlinearity=nonlinearity,
last_wscale=last_wscale))
__init__はネットワーク定義で、__call__は実行時(update)に呼び出される。
hidden_sizesにいっぱい格納されてるとzipで回されてhidden_layersに何層も定義できそう。*は可変引数。
class MLP(chainer.Chain):
"""Multi-Layer Perceptron"""
def __init__(self, in_size, out_size, hidden_sizes, nonlinearity=F.relu,
last_wscale=1):
self.in_size = in_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.hidden_sizes = hidden_sizes
self.nonlinearity = nonlinearity
layers = {}
if hidden_sizes:
hidden_layers = []
hidden_layers.append(L.Linear(in_size, hidden_sizes[0]))
for hin, hout in zip(hidden_sizes, hidden_sizes[1:]):
hidden_layers.append(L.Linear(hin, hout))
layers['hidden_layers'] = chainer.ChainList(*hidden_layers)
layers['output'] = L.Linear(hidden_sizes[-1], out_size,
wscale=last_wscale)
else:
layers['output'] = L.Linear(in_size, out_size, wscale=last_wscale)
super().__init__(**layers)
def __call__(self, x, test=False):
h = x
if self.hidden_sizes:
for l in self.hidden_layers:
h = self.nonlinearity(l(h))
return self.output(h)
学習の部分であろうtrain_agent_with_evaluationを追って見る。
Evaluatorで評価オブジェクトを生成。train_agentで学習用のオブジェクトを実行。
ここも抽象化されてるので深堀する。
def train_agent_with_evaluation(
agent, env, steps, eval_n_runs, eval_frequency,
outdir, max_episode_len=None, step_offset=0, eval_explorer=None,
eval_max_episode_len=None, eval_env=None, successful_score=None,
render=False, logger=None):
"""Run a DQN-like agent.
Args:
agent: Agent.
env: Environment.
steps (int): Number of total time steps for training.
eval_n_runs (int): Number of runs for each time of evaluation.
eval_frequency (int): Interval of evaluation.
outdir (str): Path to the directory to output things.
max_episode_len (int): Maximum episode length.
step_offset (int): Time step from which training starts.
eval_explorer: Explorer used for evaluation.
eval_env: Environment used for evaluation.
successful_score (float): Finish training if the mean score is greater
or equal to this value if not None
"""
logger = logger or logging.getLogger(__name__)
makedirs(outdir, exist_ok=True)
if eval_env is None:
eval_env = env
if eval_max_episode_len is None:
eval_max_episode_len = max_episode_len
evaluator = Evaluator(agent=agent,
n_runs=eval_n_runs,
eval_frequency=eval_frequency, outdir=outdir,
max_episode_len=eval_max_episode_len,
explorer=eval_explorer,
env=eval_env,
step_offset=step_offset,
logger=logger)
train_agent(
agent, env, steps, outdir, max_episode_len=max_episode_len,
step_offset=step_offset, evaluator=evaluator,
successful_score=successful_score, logger=logger)
評価用のEvaluatorの中身。openaiに渡す用の評価ファイルを生成してそう。
class Evaluator(object):
def __init__(self, agent, env, n_runs, eval_frequency,
outdir, max_episode_len=None, explorer=None,
step_offset=0, logger=None):
self.agent = agent
self.env = env
self.max_score = np.finfo(np.float32).min
self.start_time = time.time()
self.n_runs = n_runs
self.eval_frequency = eval_frequency
self.outdir = outdir
self.max_episode_len = max_episode_len
self.explorer = explorer
self.step_offset = step_offset
self.prev_eval_t = (self.step_offset -
self.step_offset % self.eval_frequency)
self.logger = logger or logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Write a header line first
with open(os.path.join(self.outdir, 'scores.txt'), 'w') as f:
custom_columns = tuple(t[0] for t in self.agent.get_statistics())
column_names = (('steps', 'elapsed', 'mean', 'median', 'stdev') +
custom_columns)
print('\t'.join(column_names), file=f)
def evaluate_and_update_max_score(self, t):
mean, median, stdev = eval_performance(
self.env, self.agent, self.n_runs,
max_episode_len=self.max_episode_len, explorer=self.explorer,
logger=self.logger)
elapsed = time.time() - self.start_time
custom_values = tuple(tup[1] for tup in self.agent.get_statistics())
values = (t, elapsed, mean, median, stdev) + custom_values
record_stats(self.outdir, values)
if mean > self.max_score:
update_best_model(self.agent, self.outdir, t, self.max_score, mean,
logger=self.logger)
self.max_score = mean
return mean
学習部分のtrain_agentを見てみる。
dqnの処理はdqn.pyに書いてる。
ここで呼び出されてるのはact_and_train、stop_episode_and_train。
def train_agent(agent, env, steps, outdir, max_episode_len=None,
step_offset=0, evaluator=None, successful_score=None,
logger=None):
logger = logger or logging.getLogger(__name__)
episode_r = 0
episode_idx = 0
# o_0, r_0
obs = env.reset()
r = 0
done = False
t = step_offset
agent.t = step_offset
episode_len = 0
try:
while t < steps:
# a_t
action = agent.act_and_train(obs, r)
# o_{t+1}, r_{t+1}
obs, r, done, info = env.step(action)
t += 1
episode_r += r
episode_len += 1
if done or episode_len == max_episode_len or t == steps:
agent.stop_episode_and_train(obs, r, done=done)
logger.info('outdir:%s step:%s episode:%s R:%s',
outdir, t, episode_idx, episode_r)
logger.info('statistics:%s', agent.get_statistics())
if evaluator is not None:
evaluator.evaluate_if_necessary(t)
if (successful_score is not None and
evaluator.max_score >= successful_score):
break
if t == steps:
break
# Start a new episode
episode_r = 0
episode_idx += 1
episode_len = 0
obs = env.reset()
r = 0
done = False
except Exception:
# Save the current model before being killed
save_agent(agent, t, outdir, logger, suffix='_except')
raise
# Save the final model
save_agent(agent, t, outdir, logger, suffix='_finish')
act_and_trainの中身を見る。
self.model = q_functionでinit時にQネットワークを取得している。画像分類をしたいわけではないのでno_backprop_modeをつけてバックプロップしないで、そのままネットワークを通してaction_valueを出力。q値が最大のものを返す。って何個actionが返って来てるのか?
def act_and_train(self, state, reward):
with chainer.no_backprop_mode():
action_value = self.model(
self.batch_states([state], self.xp, self.phi), test=True)
q = float(action_value.max.data)
greedy_action = cuda.to_cpu(action_value.greedy_actions.data)[0]
batch_statesは状態をバッチで返す。
def batch_states(states, xp, phi):
states = [phi(s) for s in states]
return xp.asarray(states)
q値の平均に減衰を掛けて新しいq値を加算する。
# Update stats
self.average_q *= self.average_q_decay
self.average_q += (1 - self.average_q_decay) * q
select_actionの中身はないので上で求めた最大の値が入る。
action = self.explorer.select_action(
self.t, lambda: greedy_action, action_value=action_value)
self.t += 1
最新の状態をreplay_bufferに格納する。
if self.last_state is not None:
assert self.last_action is not None
# Add a transition to the replay buffer
self.replay_buffer.append(
state=self.last_state,
action=self.last_action,
reward=reward,
next_state=state,
next_action=action,
is_state_terminal=False)
self.last_state = state
self.last_action = action
update_if_necessaryで必要に応じてネットワークを更新してる。
self.replay_updater.update_if_necessary(self.t)
self.logger.debug('t:%s r:%s a:%s', self.t, reward, action)
return self.last_action
長くなるのでupdateの方だけ見ていく。
def update_if_necessary(self, iteration):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.replay_start_size:
return
if iteration % self.update_frequency != 0:
return
for _ in range(self.n_times_update):
if self.episodic_update:
episodes = self.replay_buffer.sample_episodes(
self.batchsize, self.episodic_update_len)
self.update_func(episodes)
else:
transitions = self.replay_buffer.sample(self.batchsize)
self.update_func(transitions)
batch_experiencesでexpriencesをバッチにしてexp_batchに格納。
experiencesに重みを持ってればexp_batch['weights']に重みを格納。
def update(self, experiences, errors_out=None):
"""Update the model from experiences
This function is thread-safe.
Args:
experiences (list): list of dict that contains
state: cupy.ndarray or numpy.ndarray
action: int [0, n_action_types)
reward: float32
next_state: cupy.ndarray or numpy.ndarray
next_legal_actions: list of booleans; True means legal
gamma (float): discount factor
Returns:
None
"""
has_weight = 'weight' in experiences[0]
exp_batch = batch_experiences(experiences, xp=self.xp, phi=self.phi,
batch_states=self.batch_states)
if has_weight:
exp_batch['weights'] = self.xp.asarray(
[elem['weight'] for elem in experiences],
dtype=self.xp.float32)
if errors_out is None:
errors_out = []
_compute_lossでネットワークの計算。
loss = self._compute_loss(
exp_batch, self.gamma, errors_out=errors_out)
if has_weight:
self.replay_buffer.update_errors(errors_out)
# Update stats
self.average_loss *= self.average_loss_decay
self.average_loss += (1 - self.average_loss_decay) * float(loss.data)
self._compute_y_and_tは値の推定を再度やってる。
誤差について詳しくは_compute_lossの中。
def _compute_loss(self, exp_batch, gamma, errors_out=None):
"""Compute the Q-learning loss for a batch of experiences
Args:
experiences (list): see update()'s docstring
gamma (float): discount factor
Returns:
loss
"""
y, t = self._compute_y_and_t(exp_batch, gamma)
if errors_out is not None:
del errors_out[:]
delta = F.sum(F.basic_math.absolute(y - t), axis=1)
delta = cuda.to_cpu(delta.data)
for e in delta:
errors_out.append(e)
if 'weights' in exp_batch:
return compute_weighted_value_loss(
y, t, exp_batch['weights'],
clip_delta=self.clip_delta,
batch_accumulator=self.batch_accumulator)
else:
return compute_value_loss(y, t, clip_delta=self.clip_delta,
batch_accumulator=self.batch_accumulator)
二乗誤差の親戚のF.huber_lossで誤差を出してる。
def compute_weighted_value_loss(y, t, weights,
clip_delta=True, batch_accumulator='mean'):
"""Compute a loss for value prediction problem.
Args:
y (Variable or ndarray): Predicted values.
t (Variable or ndarray): Target values.
weights (ndarray): Weights for y, t.
clip_delta (bool): Use the Huber loss function if set True.
batch_accumulator (str): 'mean' will devide loss by batchsize
Returns:
(Variable) scalar loss
"""
assert batch_accumulator in ('mean', 'sum')
y = F.reshape(y, (-1, 1))
t = F.reshape(t, (-1, 1))
if clip_delta:
losses = F.huber_loss(y, t, delta=1.0)
else:
losses = F.square(y - t) / 2
losses = F.reshape(losses, (-1,))
loss_sum = F.sum(losses * weights)
if batch_accumulator == 'mean':
loss = loss_sum / y.shape[0]
elif batch_accumulator == 'sum':
loss = loss_sum
return loss
backwardとupdateで勾配より重みの更新。
self.optimizer.zero_grads()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.update()
dqn.pyに戻ってエピソードと学習を止めるstop_episode_and_train。
def stop_episode_and_train(self, state, reward, done=False):
"""Observe a terminal state and a reward.
This function must be called once when an episode terminates.
"""
assert self.last_state is not None
assert self.last_action is not None
# Add a transition to the replay buffer
self.replay_buffer.append(
state=self.last_state,
action=self.last_action,
reward=reward,
next_state=state,
next_action=self.last_action,
is_state_terminal=done)
self.stop_episode()
最後にsave_agent。
def save_agent(agent, t, outdir, logger, suffix=''):
dirname = os.path.join(outdir, '{}{}'.format(t, suffix))
agent.save(dirname)
logger.info('Saved the agent to %s', dirname)
強化学習豆知識
LEM(Learning from Easy Missions)
実世界で動くエージェントを作成したい。その時に学習コストを減らすためにシミュレータでの事前学習と簡単なタスクから学習をさせて転移学習を繰り返すという手法が有効。
Q学習のおすすめサイト
http://www.jonki.net/entry/2016/05/05/174519
ソース
https://github.com/jojonki/reinforcement-practice/blob/master/simple-q-learning.py
経路探索問題をQ学習で解く。
0からスタートし、5番がゴール。
学習時はランダムの場所から学習する。
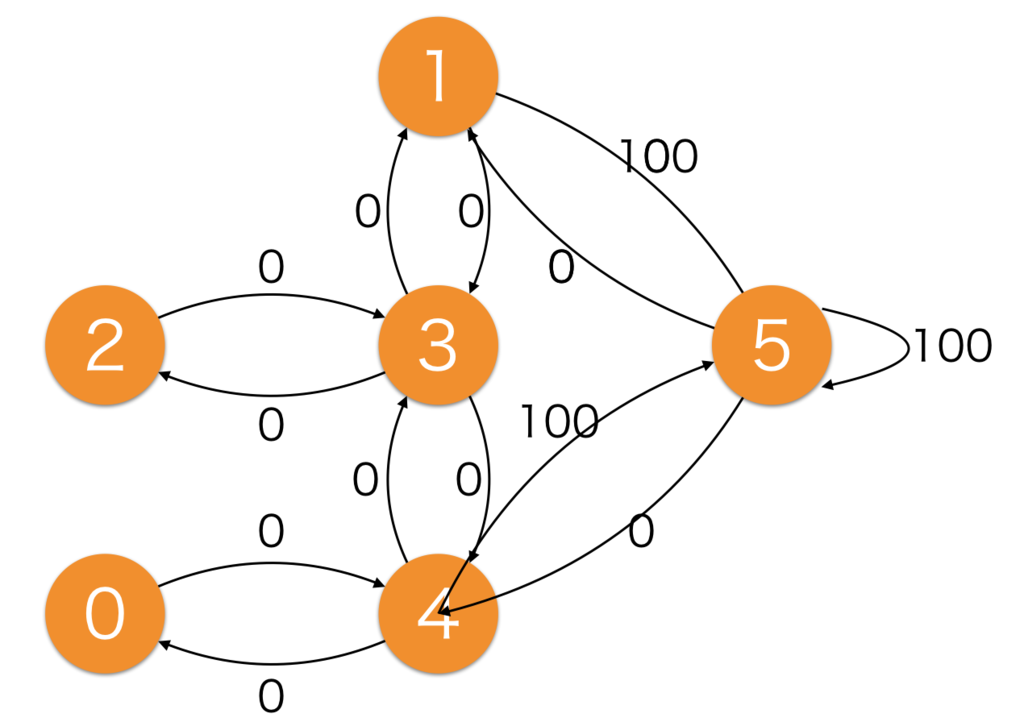
縦軸が移動元で横軸が移動先。縦軸であれば上から0,1,2,3,4,5というふうに決まっている。
行けない場所には-1を入れている。
例で4から5の移動の場合は100の報酬が与えられている。(縦が上から5個目で横が左から6個目)
# Reward matrix
R = np.array([
[-1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1],
[-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, 100],
[-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1],
[-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, -1],
[ 0, -1, -1, 0, -1, 100],
[-1, 0, -1, -1, 0, 100]
])
Qテーブル用の行列を用意。
# Initial Q-value
Q = np.zeros((6,6))
LEARNING_COUNT = 1000
GAMMA = 0.8
GOAL_STATE = 5
先にQクラスを定義して学習メソッドと行動するメソッドが定義しておき、
下記のようなアルゴリズムで実行する。
if __name__ == "__main__":
QL = QLearning()
QL.learn()
QL.dumpQvalue()
for s in range(R.shape[0]-1):
QL.runGreedy(s)
クラスの生成時は何もないので、QL.learn()の中を見ていく。
初めは_getRandomStateでランダムの場所でスタート。
LEARNING_COUNT回分実行する。
def learn(self):
# set a start state randomly
state = self._getRandomState()
for i in range(LEARNING_COUNT):
_getPossibleActionsFromStateは可能な移動のstateが返ってくる。
# extract possible actions in state
possible_actions = self._getPossibleActionsFromState(state)
_getPossibleActionsFromStateの中身をみる。
-1以外の場所のstateインデックスをlistで返してる。
def _getPossibleActionsFromState(self, state):
if state < 0 or state >= R.shape[0]: sys.exit("invaid state: %d" % state)
return list(np.where(np.array(R[state] != -1)))[0]
ランダムでアクションを選択。
# choise an action from possible actions randomly
action = random.choice(possible_actions)
これで次のstateとactionが確定したのでQ関数に突っ込む。
出た値をQテーブルに格納。Qテーブルは縦軸state、横軸actionでQ値を保持し行動する時に指標にする。
# Update Q-value
# Q(s,a) = r(s,a) + Gamma * max[Q(next_s, possible_actions)]
next_state = action # in this example, action value is same as next state
next_possible_actions = self._getPossibleActionsFromState(next_state)
max_Q_next_s_a = self._getMaxQvalueFromStateAndPossibleActions(next_state, next_possible_actions)
Q[state, action] = R[state, action] + GAMMA * max_Q_next_s_a
state = next_state
# If an agent reached a goal state, restart an episode from a random start state
if state == GOAL_STATE:
state = self._getRandomState()
Greedyでの行動。
maxの価値の方向のみに行動する。
for s in range(R.shape[0]-1):
QL.runGreedy(s)
Qテーブルができているので、今いるstateを入れるとmaxのactionがわかる。
best_action_candidatesにmaxのQ値のstateを入れる。
def runGreedy(self, start_state = 0):
print "===== START ====="
state = start_state
while state != GOAL_STATE:
print "current state: %d" % state
possible_actions = self._getPossibleActionsFromState(state)
# get best action which maximaizes Q-value(s, a)
max_Q = 0
best_action_candidates = []
for a in possible_actions:
if Q[state][a] > max_Q:
best_action_candidates = [a,]
max_Q = Q[state][a]
elif Q[state][a] == max_Q:
best_action_candidates.append(a)
# get a best action from candidates randomly
best_action = random.choice(best_action_candidates)
print "-> choose action: %d" % best_action
state = best_action # in this example, action value is same as next state
print "state is %d, GOAL!!" % state
初めに出てるのは学習後のQテーブルで、
これを使ってグリーディ方策で実行した。
[[ 0 0 0 0 378 0]
[ 0 0 0 302 0 472]
[ 0 0 0 302 0 0]
[ 0 378 241 0 378 0]
[302 0 0 302 0 472]
[ 0 378 0 0 372 465]]
('s ', 0)
('env is ', (6, 6))
===== START =====
current state: 0
('best_action_candidates:', [4])
-> choose action: 4
current state: 4
('best_action_candidates:', [5])
-> choose action: 5
state is 5, GOAL!!
('s ', 1)
('env is ', (6, 6))
===== START =====
current state: 1
('best_action_candidates:', [5])
-> choose action: 5
state is 5, GOAL!!
('s ', 2)
('env is ', (6, 6))
===== START =====
current state: 2
('best_action_candidates:', [3])
-> choose action: 3
current state: 3
('best_action_candidates:', [1, 4])
-> choose action: 1
current state: 1
('best_action_candidates:', [5])
-> choose action: 5
state is 5, GOAL!!
('s ', 3)
('env is ', (6, 6))
===== START =====
current state: 3
('best_action_candidates:', [1, 4])
-> choose action: 4
current state: 4
('best_action_candidates:', [5])
-> choose action: 5
state is 5, GOAL!!
('s ', 4)
('env is ', (6, 6))
===== START =====
current state: 4
('best_action_candidates:', [5])
-> choose action: 5
state is 5, GOAL!!
ロケットシミュレータ
動かそうとライブラリを入れてる段階で環境がぶっ壊れた。
壊れてもいいタイミングでやったほうがいいかもしれない。
https://github.com/pyjbooks/PyRockSim
https://github.com/Lageos/pyrocket
参考
openai gymインストールについて
https://recordnotfound.com/gym-openai-119096
dqn実行
https://github.com/elix-tech/dqn
http://qiita.com/Ugo-Nama/items/08c6a5f6a571335972d5