はじめに
AWS Lambdaで構築したシステムってどうやってテストしていますか?私は最近までずっと、AWSのコンソールを使ってテストしていました。ある日、pytestとMotoの存在を知り、テストで試してみたら今までと全く違った世界が見えました。この発見を共有できればと思い、少し紹介させていただきます。
AWS Lambdaとは
サーバーレス(サーバーを導入したり、プログラム実行環境をセットアップしたりが全く不要です!)でアプリケーションを構築できるAWSのマネージドサービスです。「マネージド」とはAWSで管理されている状態を示し、利用者は環境管理の負担がとても小さく、アプリケーションロジック(コーディング)に集中できるというものです。また、コンピュータリソースを使った分だけ課金のタイプであるため、コストパフォーマンスが非常に良いです。
言語は、PythonやNode.js、Java、.NET、Rubyなどに対応しています。短い時間の処理に適しており、1回の実行時間は最大15分間という制約があります。長い処理に対しては、Step FunctionsやECS、AWS Batch、EC2などの他のサービスの利用を検討します。
AWS Lambdaのテスト
AWS Lambdaにはマネジメントコンソールから利用できるテストツールがあります。コード編集画面の上にある「Test」ボタンにより実行できます。
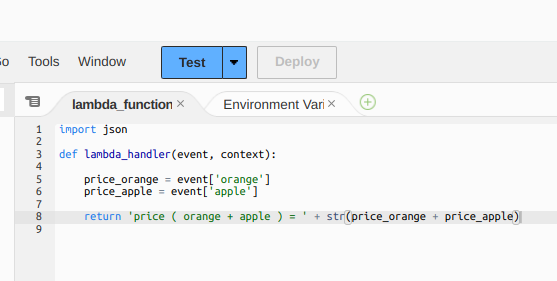
テストデータを変数eventにセットして引数として渡せます。
event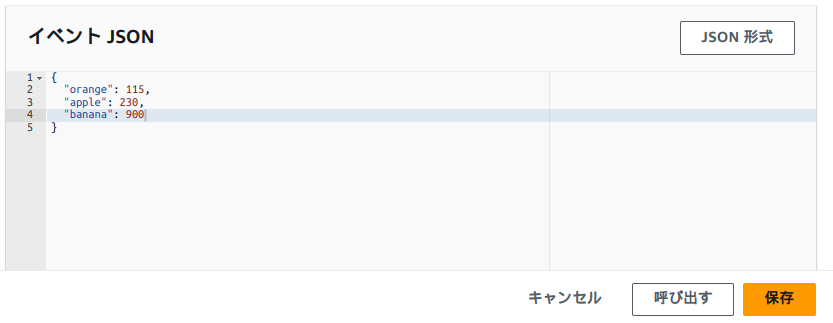
AWS Lmabdaのテストツールでテストする際の問題
とても使いやすいテストツールではありますが、AWS上で実行すると困ったことがおきます。以下の記事で紹介したシステム構成を例にして説明します。
テスト実行の度に、次のことが起こります。
データテーブルの内容が更新されてしまう
メールが送信されてしまう
では実際にAWSコンソールでテスト実行してみます。
テストデータですが、CloudWatch Logsから連携される実際のデータと同じ形式で作成する必要があります。以下のような形式となります。
{
"awslogs" : {
"data" : "{CloudTrailのイベントデータ(JSON)をgzipで圧縮し、base64でエンコードした値}"
}
}
少し煩雑ですが、テスト用のイベントデータをエンコードするpythonコードを作成します。
import base64
import gzip
import json
def json_to_encode(json_data):
json_str = json.dumps(json_data)
compressed_data = gzip.compress(json_str.encode('utf-8'))
encode_data = base64.b64encode(compressed_data)
return encode_data.decode('utf-8')
event_data = {ここにイベントデータを記入する}
logEvents = {"logEvents": [{"message": json.dumps(event_data)}]}
print(json_to_encode(logEvents))
CloudTrailの画面から、ConsoleLoginイベントのイベントレコードをコピーします。
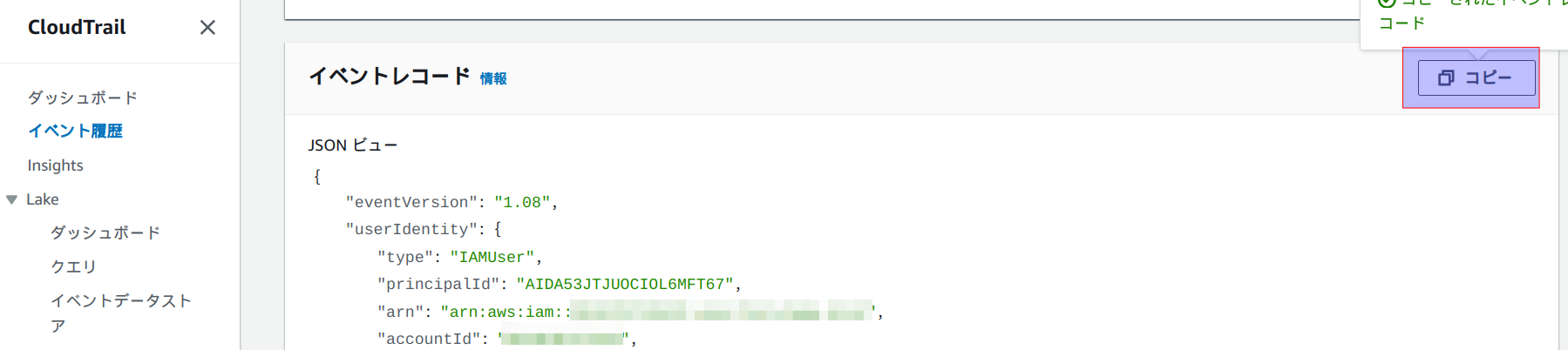
pythonコードにイベントデータを貼り付けし、テスト用にデータを変更します。その際以下の書き換えも一緒に行います。
null → None
false → False
true → True

コードを実行します。
python encode_testdata.py
出力されたbase64エンコードを使ってAWS Lambdaの画面より、テストデータを登録します。

ようやく、コンソールの「Test」をクリックする準備ができましたので、テスト実行します。

ここから、データテーブルを読みこんで、その内容をメール本文へ書き込むように機能を改善するケースを考えてみます。

結果を検証するためには、以下の点を考慮する必要があります。
テストを実行する前に、データテーブルの内容を初期化する
pytestとMotoを使用したテスト
ようやく本題に入っていきます。
pytestとは、Pythonの単体テスト用に設計されたテスト用フレームワークです。テストの作成と実行を効率的に行うことができると説明されています。Motoとは、単体テストにおいてAWSサービスをモックするためのライブラリです。例えばDynamoDBやS3をコード上で擬似的に再現してくれるため、テスト対象コードにAWSサービスを利用するboto3などの記述があったとしても、それをそのままローカル上で実行することができます。
今回のシステムの場合、データテーブルとSNSトピックはMotoでモックすることになります。入力データの作成やデータテーブルの初期化、テスト実行、テスト結果の比較はpytestで行います。

テストデモ
文章での説明ではピンと来ないと思いますので、デモでイメージを掴んで頂こうと思います。
環境セットアップ
Pythonランタイムが必要です。インストール手順は割愛します。
Pythonコードを編集、実行するエディターとしてはVScodeが便利です。無くても問題ありません。VScodeのインストール手順も割愛します。
pytestをインストールします。
pip install pytest
次にpytest.freezerをインストールします。これは、テスト実行時のシステム時間を固定させるために使用します。
pip install pytest.freezer
最後にMotoをインストールします。AWSサービス名を指定して、指定したサービスのみのライブラリをインストールすることも可能ですが、ここではすべてのサービスのライブラリをインストールします。
pip install moto[all]
テストコード解説
今回のテストでは、コード類を以下のように配置します。
作業フォルダ
├─ index.py # 今回のテスト対象のPythonコードです。
└─ tests
├─ __init__.py # テストコードを実行するために必要なファイル。空ファイル。
├─ test_1.py # テストコード (pytestの説明)
├─ test_2.py # テストコード (DynamoDB初期化)
├─ test_3.py # テストコード (テスト対象コードのテスト用)
└─ test_2_data.json # DynamoDB初期化用のテストデータ
test_1.py
関数の単体テストのサンプルです。index.pyモジュール内で定義している「Decode_event」関数と「create_inputData」関数にテストデータを入力し、結果を比較しています。
pytestでは、「test」から始まる関数名をテストコードとして実行します。assert文でテスト結果を比較して、合格か不合格かを判定します。
def testXXXXXXXXX():
・
・
assert 期待する結果 == テスト実行結果
pytestの実行は、作業フォルダにカレントを移動し、以下のようにします。
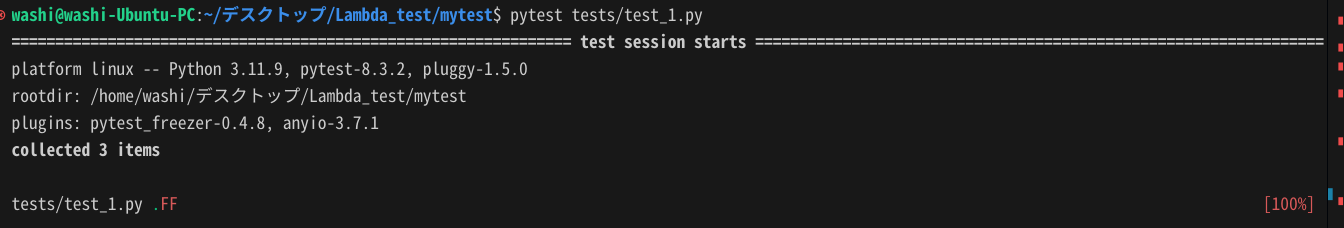
pytest tests/test_1.py
下図は、3つのテストコードを実行して、1つは合格、2つは不合格となった例です。

print文などのデバックログを表示したい場合は、オプション -sをつけます。
pytest tests/test_1.py -s
test_2.py
AWSサービスを使用するコードをテストするサンプルです。test_1.pyに比べて、@pytest.fixture(@で始まる記述部のことをデコレータと言います)、@aws_mockが登場しています。
@pytest.fixtureは、テストコードの実行前後で定形処理を実行させるために使用します。具体例としてテスト実行前に、データベースを初期化したり、環境のセットアップを行ったりします。各々のテストの実行前に呼び出すことができるので、連続したテストで効率よく実行できます。pytestを使用する目的はこのfixture機能を利用するためと言っても過言ではないと思います。
サンプルでは、init_databse関数内でDynamoDBテーブル「ConsoleLoginEventDataTable」を作成し、初期化用のデータを「test_2_data.json」からロードしています。with mock_aws()の内側の処理は、AWSのサービスをモックしています。したがって、DynamoDBに関する操作はすべて擬似的に行われます。
test_3.py
テスト対象であるindex.pyを本番同様に実行し、モックされたDynamoDBとSNSについて処理後の結果を確認しています。SNSトピックに発行されたメッセージを取り出して確認するためにSQSキューを使用しています。

テストコードを完成させて、index.pyを修正すれば、AWSを使用しなくても目的のコードが完成します。
※本記事では触れませんでしたが、おそらくDynamoDBテーブルのインデックス追加も同時に行うことになるはずで、これについてもテストコード上でテストできます。AWSへ反映する際は、Lambdaのコード展開と同時にDynamoDBテーブルの設定変更を行うことになります。
サンプルコード
本記事で使用したテストコードとテスト対象のプログラムコードです。
import json
def test_01_Decode_event():
# Decode_event関数の単体テスト
test_data = {"awslogs": {"data": "H4sIAHQ/vGYC/02OTQvCMAyG/4rkLLj5be9Dd9GLnqyHbCujsLVj"\
"7ZRR+t9N6WQGAm/yPvlw0Og6ewtlDbDF00ErjMFaUAGOAyJykhyKouCwJDEY0ecV8dKOwSLIjp2IlA4Rua6XqpQdNnkVvcvtnIWMNvYqtkkw"\
"/BgmsWUsSdeb7W5/OJ6SlIVLq7sw9kFimipLPSj7W/mPz99dsZ3emYe9B//yX74uF3ftAAAA"}}
test_event_data = {
"aaa": "bbb",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "ooooo",
"principalId": "HOGEHOGE",
"arn": "arn:aws:iam::012345678901:user/TestUser",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"userName": "TestUser"
}
}
expected = {"logEvents": [{"message": json.dumps(test_event_data) }]}
# テスト
from index import Decode_event
response = Decode_event(test_data)
assert expected == response
def test_02_create_inputData():
# create_inputData関数の単体テスト
test_data = json.dumps(
{
"userIdentity": {
"type": "IAMUser",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"userName": "TestUser"
},
"eventTime": "2024-08-13T07:24:58Z",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"sourceIPAddress": "123.124.29.13",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"eventID": "f386be0f-44c5-4f64-ab72-88fc0a899b2e"
}
)
expected = {"accountId": "012345678901",
"userName": "TestUser",
"eventTime": "2024/08/13 16:24:58",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"sourceIPAddress": "123.124.29.13",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"eventID": "f386be0f-44c5-4f64-ab72-88fc0a899b2e",
"unixtime": 1739085898}
# テスト
from index import create_inputData
response = create_inputData(test_data)
assert expected == response
def test_03_create_inputData():
# create_inputData関数の単体テスト
test_data = json.dumps(
{
"userIdentity": {
"type": "Root",
"accountId": "012345678901"
},
"eventTime": "2024-08-13T07:24:58Z",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"sourceIPAddress": "123.124.29.13",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"eventID": "f386be0f-44c5-4f64-ab72-88fc0a899b2e"
}
)
expected = {"accountId": "012345678901",
"userName": "Root",
"eventTime": "2024/08/13 16:24:58",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"sourceIPAddress": "123.124.29.13",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"eventID": "f386be0f-44c5-4f64-ab72-88fc0a899b2e",
"unixtime": 1739085898}
# テスト
from index import create_inputData
response = create_inputData(test_data)
assert expected == response
import boto3
import pytest
import json
from boto3.dynamodb.conditions import Key
from moto import mock_aws
@pytest.fixture()
def init_database():
with mock_aws():
with open('tests/test_2_data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
test_data = json.load(fp)['DynamoDB']
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.create_table(
TableName='ConsoleLoginEventDataTable',
KeySchema=[{'AttributeName':'eventID','KeyType':'HASH'}],
AttributeDefinitions=[{'AttributeName':'eventID','AttributeType':'S'}],
ProvisionedThroughput={'ReadCapacityUnits':1,'WriteCapacityUnits':1}
)
with table.batch_writer() as batch:
for item in test_data['ConsoleLoginEventDataTable']:
batch.put_item(Item=item)
yield table
@mock_aws
def test_02_db(init_database):
# DyandmoDBのモックのサンプル
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table('ConsoleLoginEventDataTable')
response = table.scan()
print(response)
# テスト
assert 2 == response['Count']
expected1 = {
"eventID": "16866c0f-a39d-4600-b4d7-de52a46738b4",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventTime": "2024/08/12 23:55:07",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"unixtime": 1739026507,
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"userName": "Root"
}
response1 = table.get_item(
Key={'eventID': '16866c0f-a39d-4600-b4d7-de52a46738b4'}
)
assert expected1 == response1['Item']
expected2 = {
"eventID": "22b54d23-e41f-47c1-84ca-d9b53c76f7d4",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventTime": "2024/08/14 13:27:45",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"unixtime": 1739161665,
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"userName": "dummyUser"
}
response2 = table.get_item(
Key={'eventID': '22b54d23-e41f-47c1-84ca-d9b53c76f7d4'}
)
assert expected2 == response2['Item']
import boto3
import pytest
import os
import json
import base64
import gzip
from boto3.dynamodb.conditions import Key
from moto import mock_aws
# テスト用Queueはテストコードでも利用するため、グローバル変数にする
pytest.test_queue_url = ""
@pytest.fixture()
def init_aws():
with mock_aws():
# モックするAWS AccountIDの固定
os.environ['MOTO_ACCOUNT_ID'] = '111122223333'
os.environ['TOPIC_ARN'] = 'arn:aws:sns:ap-northeast-1:111122223333:test-topic' # Lambda関数が利用する環境変数
# SNSトピックを作成
client_sns = boto3.client('sns', region_name='ap-northeast-1')
response = client_sns.create_topic(Name='test-topic')
topic_arn = response['TopicArn']
# SQSキューを作成
client_sqs = boto3.client('sqs', region_name='ap-northeast-1')
response = client_sqs.create_queue(
QueueName='test-queue'
)
queue_url = response['QueueUrl']
queue_arn = client_sqs.get_queue_attributes(
QueueUrl=queue_url,
AttributeNames=['QueueArn']
)['Attributes']['QueueArn']
pytest.test_queue_url = queue_url
# SNSトピックにSQSキューをサブスクライブする
response = client_sns.subscribe(
TopicArn=topic_arn,
Protocol='sqs',
Endpoint=queue_arn
)
#データベースの初期化
with open('tests/test_2_data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
test_data = json.load(fp)['DynamoDB']
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.create_table(
TableName='ConsoleLoginEventDataTable',
KeySchema=[{'AttributeName':'eventID','KeyType':'HASH'}],
AttributeDefinitions=[{'AttributeName':'eventID','AttributeType':'S'}],
ProvisionedThroughput={'ReadCapacityUnits':1,'WriteCapacityUnits':1}
)
with table.batch_writer() as batch:
for item in test_data['ConsoleLoginEventDataTable']:
batch.put_item(Item=item)
yield table
@mock_aws
def test_03_main(init_aws):
# index.pyに連携するテスト用のイベントデータを作成する
test_event_data = {
"eventVersion": "1.08",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "IAMUser",
"principalId": "AIDA53JTJUOCIOL6MFT67",
"arn": "arn:aws:iam::012345678901:user/TestUser",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"userName": "TestUser999"
},
"eventTime": "2024-08-15T07:30:12Z",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"requestParameters": None,
"responseElements": {
"ConsoleLogin": "Success"
},
"additionalEventData": {
"LoginTo": "https://console.aws.amazon.com/console/home?testestestestestest",
"MobileVersion": "No",
"MFAIdentifier": "arn:aws:iam::012345678901:mfa/TestUser999",
"MFAUsed": "Yes"
},
"eventID": "test-eventID-99999999999",
"readOnly": False,
"eventType": "AwsConsoleSignIn",
"managementEvent": True,
"recipientAccountId": "012345678901",
"eventCategory": "Management",
"tlsDetails": {
"tlsVersion": "TLSv1.3",
"cipherSuite": "TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256",
"clientProvidedHostHeader": "ap-southeast-2.signin.aws.amazon.com"
}
}
logEvents = {"logEvents": [{"message": json.dumps(test_event_data)}]}
event = {"awslogs":{"data": base64.b64encode(gzip.compress(json.dumps(logEvents).encode('utf-8')))}}
# index.pyを実行する
from index import lambda_handler
response = lambda_handler(event, "")
# SNSトピックにPulishされたメッセージをSQSから取り出して確認
client_sqs = boto3.client('sqs', region_name='ap-northeast-1')
response = client_sqs.receive_message(QueueUrl=pytest.test_queue_url)
print("SQSで受信したメッセージ:")
mail_message = json.loads(response["Messages"][0]["Body"])
print(mail_message['Subject'])
print(mail_message['Message'])
expected_subject = "AWSコンソールログイン"
assert expected_subject == mail_message['Subject']
expected_message = '''\
AWSコンソールへのログインがありました。
日時: yyyy/mm/dd hh:MM:dd
AWSアカウント: 012345678901
ユーザー: xxxxxxxx
アクセス元IP:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
ブラウザ情報:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
前回のログインは以下の通りです。
日時: yyyy/mm/dd hh:MM:dd
AWSアカウント: 012345678901
ユーザー: xxxxxxxx
アクセス元IP:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
ブラウザ情報:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
今月(yyyy/mm)のログイン回数合計: xxx
前月(yyyy/mm)のログイン回数合計: xxx
'''
# assert expeteced_message = mail_message['Message']
# DyandmoDBに追加されたレコードを確認する
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table('ConsoleLoginEventDataTable')
# 1件追加されるので合計3になるはず
response = table.scan()
assert 3 == response['Count']
expected = {
"eventID": "test-eventID-99999999999",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventTime": "2024/08/15 07:30:12",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"unixtime": 1739226612,
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"userName": "TestUser999"
}
response = table.get_item(
Key={'eventID': 'test-eventID-99999999999'}
)
assert expected == response['Item']
{
"DynamoDB": {
"ConsoleLoginEventDataTable": [
{
"eventID": "16866c0f-a39d-4600-b4d7-de52a46738b4",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventTime": "2024/08/12 23:55:07",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"unixtime": 1739026507,
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"userName": "Root"
},
{
"eventID": "22b54d23-e41f-47c1-84ca-d9b53c76f7d4",
"accountId": "012345678901",
"awsRegion": "ap-southeast-2",
"eventName": "ConsoleLogin",
"eventSource": "signin.amazonaws.com",
"eventTime": "2024/08/14 13:27:45",
"sourceIPAddress": "12.234.156.78",
"unixtime": 1739161665,
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"userName": "dummyUser"
}
]
}
}
# coding: utf-8
import json
import base64
import gzip
import os
import boto3
import datetime
from dateutil import tz
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
decoded_data = Decode_event(event)
logEvents = decoded_data['logEvents']
for logEvent in logEvents:
inputData = create_inputData(logEvent['message'])
response = Store_Data(inputData)
# proccess email
if response['statusCode'] == 200:
subject = 'AWSコンソールログイン'
message = json.dumps(inputData)
try:
response = Publish_sns(subject, message)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print(response)
return{
'statusCode': 500,
'body': 'Error Publishing event!'
}
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Console Login Event Published successfully.'
}
def create_inputData(strevent):
print(strevent)
event = json.loads(strevent)
utcTime = datetime.datetime.strptime(event['eventTime'], '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ')
ttlTime = utcTime + datetime.timedelta(days=180)
japanTime = utcTime.astimezone(tz.gettz('Asia/Tokyo'))
inputData = {}
inputData['eventID'] = event['eventID']
inputData['accountId'] = event['userIdentity']['accountId']
match event['userIdentity']['type']:
case 'IAMUser':
inputData['userName'] = event['userIdentity']['userName']
case 'Root':
inputData['userName'] = 'Root'
inputData['eventTime'] = japanTime.strftime('%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S')
inputData['eventSource'] = event['eventSource']
inputData['eventName'] = event['eventName']
inputData['awsRegion'] = event['awsRegion']
inputData['sourceIPAddress'] = event['sourceIPAddress']
inputData['userAgent'] = event['userAgent']
inputData['unixtime'] = int(datetime.datetime.timestamp(ttlTime))
return inputData
def Store_Data(inputData):
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
ConsoleLoginEventDataTable = dynamodb.Table('ConsoleLoginEventDataTable')
try:
response = ConsoleLoginEventDataTable.put_item(Item=inputData)
#
# response = ConsoleLoginEventDataTable.put_item(
# Item=inputData,
# conditionExpression=Attr('eventID').not_exists()
# )
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': 'Console Login Event stored successfully.'
}
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print(inputData)
return{
'statusCode': 500,
'body': 'Error storing event!'
}
def Publish_sns(subject, message):
sns = boto3.client('sns')
topicArn = os.environ['TOPIC_ARN']
response = sns.publish(
TopicArn=topicArn,
Subject=subject,
Message=message
)
return response
def Decode_event(event):
decode_data = base64.b64decode(event['awslogs']['data'])
json_data = json.loads(gzip.decompress(decode_data))
return json_data
そのうち作成するかも
まとめ
今回、pytestとMotoを使用してAWS LambdaのテストをローカルPC上で実施できました。また、テストをコード化できたため、テスト工程の作業を一部自動的に行うことができるようになりました。修正されたコードをAWSへ反映させる前に自動でテストを実行し、テストに合格したら検証済みのコードを自動的に反映させるのようなことが実現できるかもしれません。過去に作成したテストコードを活用して、レグレッションテストが素早くできるようになるかもしれません。たぶん、CI/CD(継続的インテグレーション/継続的デリバリー)を実現する最初のステップではないかと私は思います。





