背景
「前から見てるものをBird Eye View(上からの視点)に変換するってどういうこと?」 「上にもう一個カメラがついてるんじゃなくて?」最近まで数学的に全くイメージ出来なかった。
BEVの考え方をツラツラと書いていく。
アルゴリズム
どうやったら上からの視点になるの?
上から見た道路の写真って白線が直線になっていると思います。
*線がカーブでなければ
*平行な直線であれば何でもokay
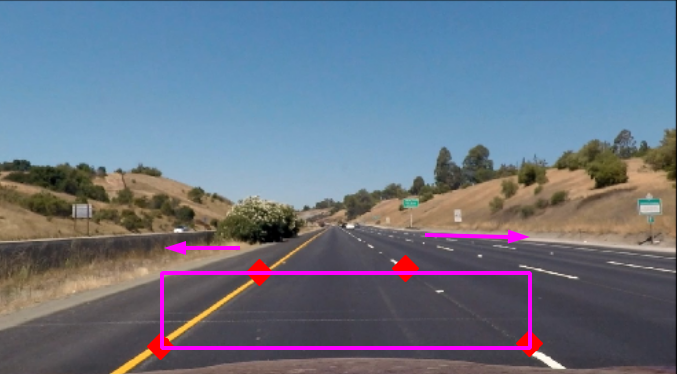
しかし、前から見ると八の時型になっていますね。これは遠いものが小さく見える事から起きます。
実際は直線である4点を選び、直線であるという事実から、直線になるように引き伸ばすイメージで変換すると、BEVになります。
opencvで実際やってみたので見てください。
設定
必要な事は直線である4点を選ぶだけlane_shape = [(584, 458), (701, 458), (295, 665), (1022, 665)]
top_left, top_right, bottom_left, bottom_right = lane_shape
source = np.float32([top_left, top_right, bottom_right, bottom_left])
destination = np.float32([(bottom_left[0], 0), (bottom_right[0], 0),
(bottom_right[0], self.img_height - 1), (bottom_left[0], self.img_height - 1)])
self.overhead_transform = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(source,
destination)
bird eye view変換
def warp_to_overhead(self, undistorted_img):
"""
Transforms this camera's images from the dashboard perspective to an overhead perspective.
Note: Make sure to undistort first.
"""
return cv2.warpPerspective(undistorted_img, self.overhead_transform, dsize=(self.img_width, self.img_height))
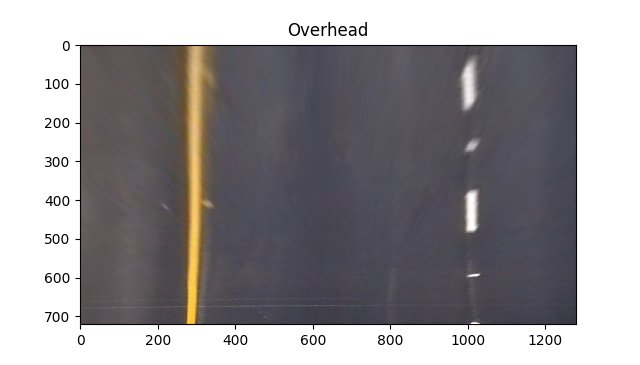
結果
before 結論
・平行な直線という事実から4点を選ぶと変換するためのParameterが得られる。 ・このメソッドだと地面に対するカメラの傾きや地面が平らでない場合などは使えない。距離の情報を持ってるのかな〜とか期待したのでがなかったです。