Firestoreのクエリでは、ドキュメント数を簡単にカウントする機能や何番目からというのを指定して取得(MongoDBのskipのような)するような機能が無いため、通常のページネーションを実装するのが難しく、下記のドキュメントのようにInfiniteScrollが前提とされています。
Firebase - クエリカーソルを使用したデータのページ設定
https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore/query-data/query-cursors?hl=ja
InfiniteScrollのメリット/デメリットについてはともかく、この記事ではあえて「前へ」/「次へ」ボタンのある通常のページネーションでFirestoreのコレクションを表示する例を実装してみます。
要件はざっくりと以下のような感じです。
- Web上の管理画面の実装を想定
- Reactを使用
- 複数のドキュメントフィールドに対してそれぞれ完全一致でクエリ指定して検索できるようにする
- ページ番号を含めたクエリパラメータをURLに保持(React Routerを使う)
- ページ番号のボタンやページ数は表示しない(次へ/前へのみ)
テストデータの作成
FirebaseAdminSDKを使ってテスト用のデータを一括で100件作成してみます。
Firebaseコンソールの[プロジェクトの設定]→[サービス アカウント]タブ内で取得した秘密鍵ファイルをfirebasekey.jsonとして置いておきます。
ソースはこんな感じにしました。
const admin = require('firebase-admin');
const serviceAccount = require('./key.json');
admin.initializeApp({
credential: admin.credential.cert(serviceAccount),
databaseURL: 'https://project-id.firebaseio.com',
});
const db = admin.firestore();
const batch = db.batch();
const length = 100; // ひとまず100件
const prefectures = ['茨城県', '栃木県', '群馬県', '埼玉県', '千葉県', '東京都', '神奈川県'];
const collectionPath = 'members';
(async () => {
try {
// データをクリア
const snapshot = await db.collection('members')
.get();
snapshot.docs.forEach((doc) => {
batch.delete(doc.ref);
});
// データを作成
for (let i = 1; i <= length; i++) {
const docId = db.collection(collectionPath).doc().id;
const memberId = (`000000000${i}`).slice(-10);
const name = `user${i}`;
const email = `user${i}@test.com`;
const age = Math.floor(Math.random() * 60) + 15;
const address = prefectures[Math.floor(Math.random() * prefectures.length)];
batch.set(db.collection(collectionPath).doc(docId), {
docId: docId,
memberId: memberId,
name: name,
email: email,
age: age,
address: address,
createdAt: admin.firestore.FieldValue.serverTimestamp(),
id: i
});
}
// バッチをコミット
await batch.commit();
console.log('success');
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
})();
SDKの初期化→バッチの作成→現在あるコレクション内のデータをクリア→データを作成→バッチをコミットという流れです。
各フィールドに関してはなんでもよいですが、何かしらソートに使えるような値を入れておく必要があります。ここでは、idとして連番をつけておきます。
$ yarn add --dev firebase-admin
$ node scripts/createTestData.js
実行してエラーがでなければ、テストデータが作成されているはずです。コンソールから確認してみてください。
ページを作成する
では、Reactでページを作成していきましょう。
複数のページがある管理画面の一つのリスト画面という想定で、react-router-domを使って単純にルーティングします。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { HashRouter as Router, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import List from './containers/List';
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="app-container">
<Route path="/" exact component={List} />
<Route path="/list" exact component={List} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
これからリスト画面として、containers/List.jsxを作成しますが、まず、React Routerはv4からクエリ文字列をパースしてくれなくなったので、クエリを扱いやすくするためにContainerの高階コンポーネントを作っておきます。
import { createElement, Component } from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import queryString from 'query-string';
import assign from 'lodash.assign';
import { QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS } from '../constants/common';
/**
* react-routerのlocationからクエリを取得して扱いやすくするためのラッパーコンポーネントを生成
* @param {Component} WrappedComponent
* @returns {ComponentWithQuery}
*/
export default (WrappedComponent) => {
class ComponentWithQuery extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.navigateWithQuery = this.navigateWithQuery.bind(this);
}
/**
* クエリを渡してハッシュ遷移
* @param {string} path
* @param {object} query
*/
navigateWithQuery(path = '', query) {
const { history, location } = this.props;
let qs = queryString.stringify(query, QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS);
if (qs) {
qs = `?${qs}`;
}
if (qs !== location.search) {
history.push(`${path ? `#${path}` : location.pathname}${qs}`);
}
}
render() {
const { location } = this.props;
const query = queryString.parse((location.search).split('?')[1], QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS);
return createElement(
WrappedComponent,
assign({}, this.props, { query, navigateWithQuery: this.navigateWithQuery }),
);
}
}
ComponentWithQuery.propTypes = {
location: PropTypes.shape({
hash: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
search: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
pathname: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
}).isRequired,
history: PropTypes.shape({
push: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
}).isRequired,
};
return ComponentWithQuery;
};
この関数を通して、React Routerからpropsで渡されるlocationとhistoryを使って、各Containerからクエリの読み書きが簡単にできるようにします。
QUERY_STRING_OPTIONSはquery-stringに渡すオプションですが、プロジェクト全体で合わせるために定数化しています。任意のものでいいと思いますが、skipNull: trueは入れたほうがよいかも。
さて、ではリスト画面を作成します。
const SEARCH_CONFIG = [ // 検索フォームの設定
{
key: 'email',
label: 'メールアドレス',
defaultValue: '',
props: {
type: 'text',
name: 'queryEmail',
placeholder: 'xxx@xxx.xxx',
},
},
{
key: 'address',
label: '都道府県',
defaultValue: '',
props: {
type: 'text',
name: 'queryAddress',
placeholder: 'ex) 東京',
},
},
];
class List extends Component {
...
/**
* クエリの変更に対応してURLを変更するFunctionを返す
* @param {string | Array<string>} queryKey
* @returns {Function}
*/
handleChangeQuery(queryKey) {
const keys = Array.isArray(queryKey) ? queryKey : [queryKey];
return (...changedQuery) => {
const { query: currentQuery, navigateByQuery } = this.props;
const query = assign({}, currentQuery);
changedQuery.forEach((value, index) => {
query[keys[index]] = value;
});
if (queryKey !== 'page') {
query.page = 1;
}
if (!isEqual(currentQuery, query)) {
navigateByQuery('', query);
}
};
}
render() {
const { data, isLoading, pageLength } = this.state;
const { query } = this.props;
return (
<div className="container">
<SearchForm // 検索フォーム
inputs={SEARCH_CONFIG} // 表示する検索フィールドの設定を渡す
onSubmit={this.handleChangeQuery(SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (input.key)))}
defaultValues={SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (query[input.key]))} // デフォルトの値はページを開いたときのクエリを参照
/>
<SearchDetail // 検索内容を表示するコンポーネント
data={SEARCH_CONFIG
.map((input) => ({ label: input.label, value: query[input.key] }))
.filter((item) => (item.value))}
/>
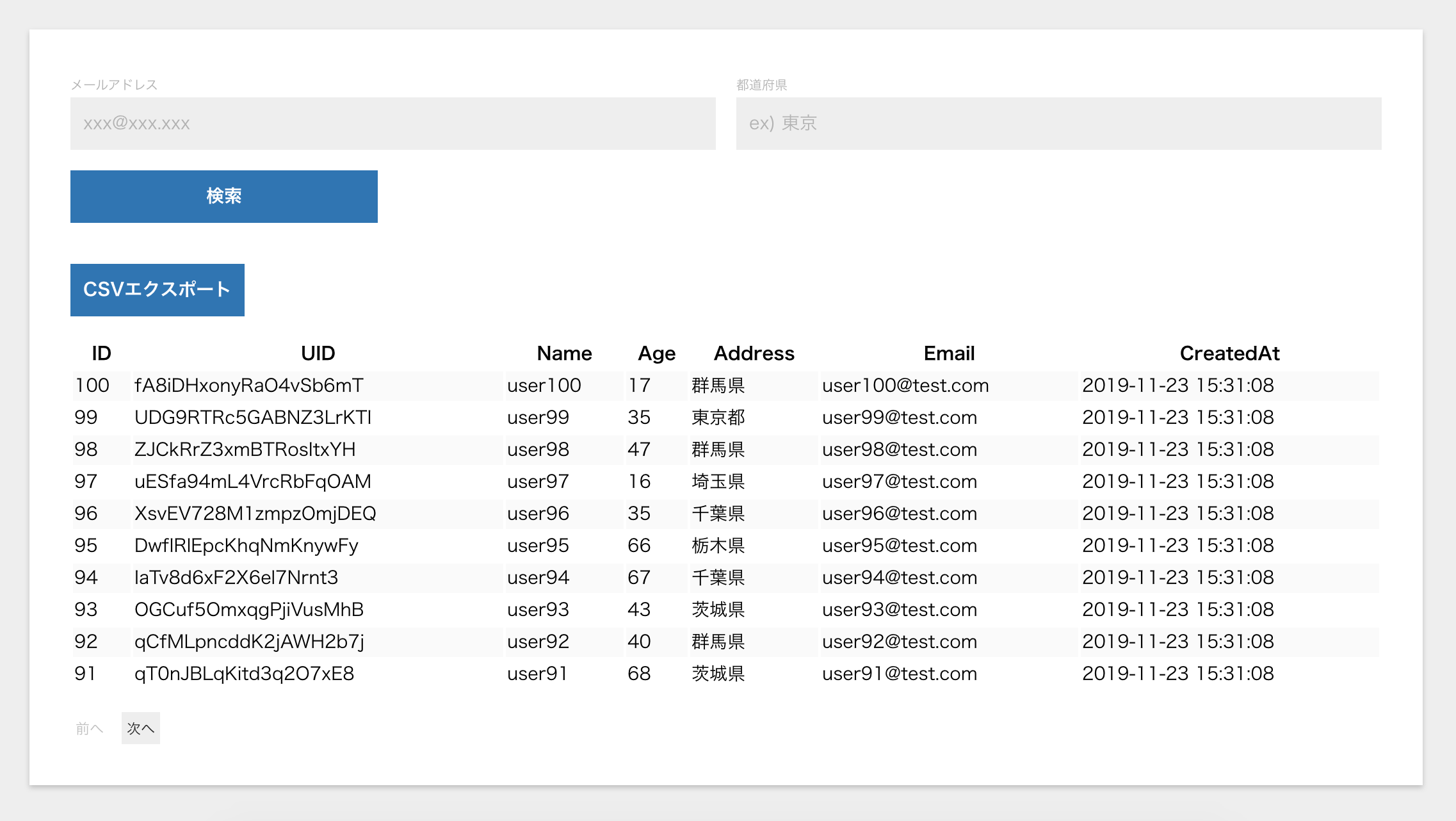
{data && ( // データ配列を渡したら一覧を描画してくれるコンポーネント
<UserList data={data} loading={isLoading} />
)}
{data ? ( // 前へ・次へボタンを含むUIコンポーネント(本当はページ番号ボタンも作りたかった)
<Pagination
length={pageLength}
current={query.page}
onSelect={this.handleChangeQuery('page')}
/>
) : null}
</div>
);
}
}
const queryShape = {};
SEARCH_CONFIG.forEach((input) => {
queryShape[input.key] = input.props.type === 'number' ? PropTypes.number : PropTypes.string;
});
List.propTypes = {
query: PropTypes.shape(queryShape).isRequired,
navigateByQuery: PropTypes.func.isRequired,
};
export default withQuery(List);
段階的に説明するとして、基本部分はこんな感じです。renderしている各コンポーネントについては単純なUIなので割愛しますが、要所としては
- 先ほどのwithQuery関数を使う(最後の行)
- 検索フォームの送信ボタンやページネーションボタンをクリックした時に値に応じてクエリ(
{ email: ..., address: ..., page: x })を作成しReact Routerでハッシュを変更(遷移) - その際、page以外のクエリが変更されたらpageを1に戻す
- 検索フィールドは柔軟に拡張できるようにした
という部分です。
データ取得処理の実装
これだけだとただハッシュが変わるだけなので、実際にデータ取得を開始する処理を追加します。
取得を開始するタイミングとしては1.初期表示、2.クエリが変わった時、なので、追加するところはcomponentDidMountとcomponentDidUpdateになります。
import isEqual from 'lodash.isequal';
...
componentDidMount() {
// 初期読み込み
const { query } = this.props;
this.fetch(query);
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
// クエリ変更時に読み込み
const { query: currentQuery } = this.props;
if (!isEqual(prevProps.query, currentQuery)) {
this.fetch(currentQuery);
}
}
...
では、上記のfetchメソッドでデータ取得を開始するのですが、その前にここで、Firestoreでクライアント側のページング処理をするためのクラスを用意し、Reactコンポーネントからはなるべく分離することにします。
例として、以下のようなクラスを作成してみました。
import queryString from 'querystring';
import flatten from 'lodash.flatten';
import { db } from '../Firebase'; // export const db = firebase.firestore();でexportしたもの
import { ITEM_PER_PAGE, QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS } from '../constants/common';
/**
* Firestoreでページング処理をするためのユーティリティ
*/
export default class FirestorePagination {
/**
* @param {string} baseCollectionPath
* @param {string} orderFieldPath
* @param {string} directionStr
*/
constructor(baseCollectionPath, orderFieldPath, directionStr = 'asc') {
this.baseRef = db.collection(baseCollectionPath);
this.orderFieldPath = orderFieldPath;
this.directionStr = directionStr;
this.map = {};
this.lastDocMap = {};
this.pageLengthMap = {};
}
/**
* Firestoreクエリを生成
* @param {object} query
* @param {string} directionStr
* @returns {firebase.firestore.Query}
* @private
*/
_getFSQuery(query, directionStr = this.directionStr) {
let fsQuery = this.baseRef.orderBy(this.orderFieldPath, directionStr);
Object.keys(query).forEach((key) => {
if (query[key] || query[key] === 0) {
fsQuery = fsQuery.where(key, '==', query[key]);
}
});
return fsQuery;
}
/**
* クエリから最後のドキュメントを取得
* @param {object} query
* @returns {Promise<firebase.firestore.QueryDocumentSnapshot>}
* @private
*/
async _getLastDoc(query) {
const snapshot = await this._getFSQuery(query, this.directionStr === 'asc' ? 'desc' : 'asc').limit(1).get();
return snapshot.docs[0];
}
/**
* 指定したページまでの全てのデータを同期的に取得
* @param {object} query
* @param {number} page
* @returns {Promise<void>}
* @private
*/
async _loadAllPageTo(query, page) {
for (let i = 1; i <= page; i += 1) {
await this.get(query, i);
}
}
/**
* 指定したページのデータを取得
* @param {object} query
* @param {number} page
* @param {number} itemPerPage
* @returns {Promise<{result: firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot, length: number}>}
*/
async get(query, page = 1, itemPerPage = ITEM_PER_PAGE) {
const pageIndex = page ? page - 1 : 0;
const fsQuery = this._getFSQuery(query);
const queryKey = queryString.stringify(query, QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS);
let current = this.map[queryKey];
let result = null;
if (current) { // すでに同じクエリで取得済み
if (current[pageIndex]) { // 同じページを取得済み
result = current[pageIndex];
} else if (current[pageIndex - 1]) { // 前のページを取得済み
const prevPageDocs = current[pageIndex - 1].docs;
const startAfter = prevPageDocs[prevPageDocs.length - 1];
result = await fsQuery.startAfter(startAfter).limit(itemPerPage).get();
} else if (current[pageIndex + 1]) { // 次のページを取得済み(発生しないはずだけど一応)
const endBefore = current[page].docs[0];
result = await fsQuery.endBefore(endBefore).limit(itemPerPage).get();
} else if (page <= this.pageLengthMap[queryKey]) { // ページを飛ばした場合
await this._loadAllPageTo(query, page);
result = current[pageIndex];
}
} else if (page === 1) { // 初めてのクエリで最初のページ
result = await fsQuery.limit(itemPerPage).get();
current = [];
this.map[queryKey] = current;
this.lastDocMap[queryKey] = await this._getLastDoc(query);
} else { // 初めてのクエリでページを飛ばした場合
await this._loadAllPageTo(query, page);
result = this.map[queryKey][pageIndex];
}
if (result && result.docs.length) {
this.map[queryKey][pageIndex] = result;
if (this.lastDocMap[queryKey]
&& result.docs[result.docs.length - 1].isEqual(this.lastDocMap[queryKey])) {
this.pageLengthMap[queryKey] = page;
}
} else if (page === 1) {
this.pageLengthMap[queryKey] = 0;
}
return {
result,
length: typeof this.pageLengthMap[queryKey] === 'number' ? this.pageLengthMap[queryKey] : Infinity,
};
}
}
こちらの要所としては
- 取得済みのデータ(QuerySnapshot)をクエリxページ番号ごとに作っておきインスタンス内にキャッシュしておく
- 通常の反対順のクエリで0番目のドキュメントを取得しておくことで、少なくとも取得したページが最後のページかどうか判定できる(その時最大ページ:lengthを返す)
- ページを指定したままリロードした時など、そのページまでまとめて取得する
といったところです。
クエリに関してはそれぞれインデックスを作成する必要があります。
(参考: https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore/query-data/indexing?hl=ja)
反対順のクエリの件はhackishな自覚はあり、こういった場合の柔軟なインデックス作成に関してまた別途調べようと思います。
では、先ほどのList.jsxで以下のようにコレクションのパス、ソートさせるフィールド名、ソート順(asc/desc)を指定して初期化し、fetchメソッドを追加します。
...
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChangeQuery = this.handleChangeQuery.bind(this);
this.export = this.export.bind(this);
this.dbPagination = new FirestorePagination('/members', 'id', 'desc');
this.state = {
data: null,
isLoading: false,
pageLength: Infinity,
};
}
...
/**
* DB読み込み
* @param {object} query
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async fetch(query = null) {
this.setState({
isLoading: true,
});
const { result, length } = await this.dbPagination
.get(assign({}, query, { page: null }), query.page || 1);
this.setState({
data: result ? result.docs.map((doc) => (doc.data())) : [],
isLoading: false,
pageLength: length,
});
}
...
これで一連の処理が完了しました。
デモ
こちらで動作を確認できます。
載せているソースは要所のみなので、詳しくはGithubの最新のソースを参照してください。
追記(2019/11/26)
汎用的なFirestoreのページネーション処理を作ったので、InfiniteScrollにするパターンでも使用してみることにします。
バリエーション2: やっぱりInfiniteScrollにする場合
デモはこちら
構造的な変化としては、ページ番号をURLではなくstateに持たせるという点になります。
...
class InfiniteList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.fetch = this.fetch.bind(this);
this.fetchNext = this.fetchNext.bind(this);
this.handleChangeQuery = this.handleChangeQuery.bind(this);
this.dbPagination = new FirestorePagination('/members', 'id', 'desc');
this.state = {
data: null,
isLoading: false,
page: 1, // stateにページ番号が入る
pageLength: Infinity,
};
}
componentDidMount() {
// 初期読み込み
this.fetch();
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
// クエリ変更時に読み込み
const { query: currentQuery } = this.props;
if (!isEqual(prevProps.query, currentQuery)) {
this.fetch();
}
}
/**
* DB読み込み
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async fetch() {
const { page, data } = this.state;
const { query } = this.props;
this.setState({ isLoading: true });
const { result, length } = await this.dbPagination.get(query, page);
const newData = result ? result.docs.map((doc) => (doc.data())) : [];
this.setState({
data: (data || []).concat(newData),
isLoading: false,
pageLength: length,
});
}
/**
* クエリの変更に対応してURLを変更するFunctionを返す
* @param {string | Array<string>} queryKey
* @returns {Function}
*/
handleChangeQuery(queryKey) {
const keys = Array.isArray(queryKey) ? queryKey : [queryKey];
return (...changedQuery) => {
const { query: currentQuery, navigateWithQuery } = this.props;
const query = assign({}, currentQuery);
changedQuery.forEach((value, index) => {
query[keys[index]] = value || value === 0 ? value : null;
});
this.setState({ data: [], page: 1 });
navigateWithQuery(null, query);
};
}
/**
* 追加読み込み
*/
fetchNext() {
const { page } = this.state;
this.setState({ page: page + 1 });
this.fetch();
}
render() {
const {
data,
page,
pageLength,
isLoading,
} = this.state;
const { query } = this.props;
return (
<div className="container">
<SearchForm
inputs={SEARCH_CONFIG}
onSubmit={this.handleChangeQuery(SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (input.key)))}
defaultValues={SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (query[input.key] || input.defaultValue))}
/>
<SearchDetail
data={SEARCH_CONFIG
.map((input) => ({ label: input.label, value: query[input.key] }))
.filter((item) => (item.value))}
/>
{data && (
<UserList
infinite
height={200}
data={data}
next={this.fetchNext}
hasMore={pageLength > page}
isLoading={isLoading}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}
}
...
コードの変更点の要所を説明するとこのような感じです。
- リストの一番下まで見たらページ数をインクリメントしデータを取得
- 取得したデータは配列に追加していく(
Array.concat) - クエリパラメータが変わるときにデータ配列をクリア
一覧を表示する部分では、基本的には一番下までスクロールした時に指定した関数を呼べばいいだけなのでそれほど複雑なことは必要ありませんが、今回はreact-infinite-scroll-componentを使用してみます。
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react';
import InfiniteScroll from 'react-infinite-scroll-component';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
import classNames from 'classnames';
class UserList extends PureComponent {
renderItems() {
const { data } = this.props;
return data.length ? (
<table className="user-list__table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>UID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>CreatedAt</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{data.map((item) => (
<tr key={item.id} className="user-list__item">
<td className="user-list__value">{item.id}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{item.docId}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{item.name}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{item.age}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{item.address ? item.address : '-'}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{item.email || '-'}</td>
<td className="user-list__value">{new Date(item.createdAt.seconds * 1000).toLocaleString()}</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
) : null;
}
render() {
const {
infinite,
height,
data,
loading,
hasMore,
next,
} = this.props;
return (
<div
style={infinite ? null : { height }}
className={classNames('user-list', {
'user-list--loading': loading,
'user-list--empty': data.length === 0,
})}
>
{infinite ? (
<InfiniteScroll
height={height}
dataLength={data.length}
next={next}
hasMore={hasMore}
loader={<p>LOADING...</p>}
scrollThreshold={1}
>
{this.renderItems()}
</InfiniteScroll>
) : (this.renderItems())}
</div>
);
}
}
UserList.defaultProps = {
loading: false,
height: null,
infinite: false,
hasMore: true,
next: null,
};
UserList.propTypes = {
height: PropTypes.number,
loading: PropTypes.bool,
data: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.shape({
id: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
email: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
address: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
})).isRequired,
// infinite scroll options
infinite: PropTypes.bool,
hasMore: PropTypes.bool,
next: PropTypes.func,
};
export default UserList;
このライブラリ、PropsオプションがREADMEに記載しているものと現在のバージョンとで違っているので、うまく動作しない場合は元ソースのProps定義部分あたりをみればわかります。
ページの一部分でスクロールさせたい場合は、heightを入れるとスクロールイベントをハンドリングする要素がwindowではなくコンポーネントの親要素になるようです。
バリエーション3: InfiniteScroll+リアルタイム検索
検索フォームの入力に合わせてリアルタイムで検索結果を表示するようにしてみます。
デモはこちら
...
const DURATION = 300;
class InfiniteRealtimeSearchList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.fetch = this.fetch.bind(this);
this.fetchNext = this.fetchNext.bind(this);
this.handleChangeQuery = this.handleChangeQuery.bind(this);
this.dbPagination = new FirestorePagination('/members', 'id', 'desc');
this.state = {
data: null,
isLoading: false,
page: 1,
pageLength: Infinity,
query: {},
};
}
componentDidMount() {
// 初期読み込み
this.fetch();
}
/**
* DB読み込み
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async fetch() {
const {
page,
data,
isLoading,
query,
} = this.state;
if (!isLoading) {
this.setState({ isLoading: true });
}
const { result, length } = await this.dbPagination.get(query, page);
const newData = result ? result.docs.map((doc) => (doc.data())) : [];
this.setState({
data: (data || []).concat(newData),
isLoading: false,
pageLength: length,
});
}
/**
* クエリの変更に対応してURLを変更するFunctionを返す
* @param {string | Array<string>} queryKey
* @returns {Function}
*/
handleChangeQuery(queryKey) {
const keys = Array.isArray(queryKey) ? queryKey : [queryKey];
return (...changedQuery) => {
window.clearTimeout(this.changeTimer);
this.changeTimer = window.setTimeout(() => {
const { query: currentQuery } = this.state;
const query = assign({}, currentQuery);
changedQuery.forEach((value, index) => {
query[keys[index]] = value || value === 0 ? value : null;
});
Object.keys(query).forEach((key) => {
if (query[key] === null) {
delete query[key];
}
});
this.setState({
data: [],
page: 1,
query,
isLoading: true,
}, this.fetch);
}, DURATION);
};
}
/**
* 追加読み込み
*/
fetchNext() {
const { page } = this.state;
this.setState({ page: page + 1 });
this.fetch();
}
render() {
const {
data,
page,
pageLength,
isLoading,
query,
} = this.state;
return (
<div className="container">
<SearchForm
inputs={SEARCH_CONFIG}
onChange={this.handleChangeQuery(SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (input.key)))}
defaultValues={SEARCH_CONFIG.map((input) => (query[input.key] || input.defaultValue))}
/>
<button
className="button"
type="button"
onClick={this.export}
>
CSVエクスポート
</button>
{data && (
<UserList
infinite
height={200}
data={data}
next={this.fetchNext}
hasMore={pageLength > page}
isLoading={isLoading}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}
}
export default InfiniteRealtimeSearchList;
前述のwithQuery関数も使用せず、検索クエリを完全にstateに持たせるようになりました。
ここは任意ですが、例として検索フォームの最後の変更から300msの間隔をあけて多少負荷を軽減するようにしています。
追記(2019/12/5) リアルタイムに変更を反映する
ページネーションパターンよりもおもにInfiniteスクロールのパターンですが、例えばタイムラインやチャット画面などではリアルタイムでの変更を反映することが求められます。追加で、ページ内のドキュメントが変更された時に画面に反映する流れを作ってみたいと思います。
FirestoreのCollectionReference、Query、DocumentSnapshotにはonSnapshotというメソッドが用意されており、ドキュメントの変更を監視することができます。
db.collection('/members').onSnapshot(snapshot => {
console.log('Current documents: ', snapshot.docs);
});
しかし例によってfirestore.Queryは取得するドキュメントの位置を簡単には指定できないため、ドキュメントの追加・削除に対応するのはなかなかややこしい問題です。
そこで、ここまでに作ったページネーション用の処理をさらに整理して、最終的に以下のような3つの階層でクラスを作成してみることにします。
- FirestorePage 特定の検索クエリの1つのページを取得し、変更を監視する
- FirestorePageManager 特定の検索クエリに対応して全てのFirestorePageをまとめる
- FirestoreQueryPagination 複数の検索クエリに対応して全てのFirestorePageManagerをまとめる
それぞれの役割はだいたい想像が着くと思うのですが、順に見ていくと、
/**
* Firestoreでページング処理をするためのユーティリティ
* ページ単位を扱う
*/
export default class FirestorePage {
/**
*
* @param {firebase.firestore.Query} baseFsQuery
* @param {firebase.firestore.QueryDocumentSnapshot} startAfter
* @param {number} itemsPerPage
*/
constructor(baseFsQuery, startAfter, itemsPerPage) {
this.hasInitialized = false;
this.baseFsQuery = baseFsQuery;
this.itemsPerPage = itemsPerPage;
this.fsQuery = (startAfter ? baseFsQuery.startAfter(startAfter) : baseFsQuery)
.limit(itemsPerPage);
}
/**
* データの取得
* 監視を開始する
* @returns {Promise<firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot>}
*/
async load() {
this._unsubscribe = this.fsQuery.onSnapshot(this._onSnapshot.bind(this));
this.snapshot = await this.fsQuery.get();
return this.snapshot;
}
/**
* startAfterを変更しデータを取得
* 監視を開始する
* @param {firebase.firestore.QueryDocumentSnapshot} startAfter
* @returns {Promise<firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot>}
*/
async resetStartAfter(startAfter) {
this.hasInitialized = false;
delete this.snapshot;
this.fsQuery = (startAfter ? this.baseFsQuery.startAfter(startAfter) : this.baseFsQuery)
.limit(this.itemsPerPage);
if (this._unsubscribe) {
this._unsubscribe();
}
return this.load();
}
/**
* スナップショットをハンドリング
* @param {firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot} snapshot
*/
_onSnapshot(snapshot) {
if (!this.hasInitialized || !this.snapshot) {
this.hasInitialized = true;
} else {
const prevLastDoc = this.lastDoc;
this.snapshot = snapshot;
const currentLastDoc = this.lastDoc;
let lastDocChanged = false;
if (prevLastDoc) {
lastDocChanged = !prevLastDoc.isEqual(currentLastDoc);
} else if (currentLastDoc) {
lastDocChanged = true;
}
if (this.onUpdateCallback) {
this.onUpdateCallback(snapshot, lastDocChanged);
}
}
}
/**
* データの変更時に呼ばれる関数をセットする
* @param {function} callback
*/
onUpdate(callback) {
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
this.onUpdateCallback = callback;
}
}
/**
* ページにドキュメントが含まれるかどうかを返す
* @returns {boolean}
*/
get hasDocs() {
return !this.snapshot.empty;
}
/**
* ページの最後のドキュメントを返す
* @returns {firebase.firestore.QueryDocumentSnapshot | null}
*/
get lastDoc() {
return this.hasDocs ? this.snapshot.docs[this.snapshot.docs.length - 1] : null;
}
}
まずページ単位を扱うクラスには、指定されたベースとなるfirestore.Queryインスタンス、startAfterに指定するドキュメント、1ページに含まれる最大のドキュメント数から実際にドキュメントの取得・監視を行い、親クラス(FirestorePageManager)に変更を伝える役割を持たせます。
ここがややこしくなる所以でもありますが、ページに対してstartAfterに指定するドキュメントはコレクション内のドキュメントの追加・削除によって変わることが想定されるので、親クラスからリセットできるようにします。
リセットする際は、onSnapshotで指定したリスナーをデタッチします。onSnapshotメソッドの返り値自体がデタッチするための関数になっています。
onSnapshotに渡したリスナーは初期ロード時にも呼ばれますが、別途getメソッドで取得するようにしているため、初期ロードを無視するようにしています。
続いて、一つの検索クエリに対して全てのページをまとめるクラスを作成します。
import flatten from 'lodash.flatten';
import FirestorePage from './FirestorePage';
/**
* Firestoreでページング処理をするためのユーティリティ
* 一つの検索クエリでの全てのページを扱う
*/
export default class FirestorePageManager {
/**
*
* @param {firebase.firestore.Query | firebase.firestore.CollectionReference} fsQueryOrCollectionRef
* @param {number} itemsPerPage
*/
constructor(fsQueryOrCollectionRef, itemsPerPage) {
this.fsQuery = fsQueryOrCollectionRef;
this.itemsPerPage = itemsPerPage;
this.pages = [];
}
/**
* ページ番号を指定してFirestorePageインスタンスを返す
* @param {number} page
* @returns {FirestorePage}
*/
get(page) {
return this.pages[page - 1];
}
/**
* データの変更時に呼ばれる関数をセットする
* @param {function} callback
*/
onUpdate(callback) {
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
this.onUpdateCallback = callback;
}
}
/**
* ページ番号を指定してFirebasePageを初期化
* あるいはstartAfterを更新する
* @param {number} page
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async _setPage(page) {
const index = page - 1;
const startAfter = index === 0 ? null : this.pages[index - 1].lastDoc;
if (this.pages[index]) {
await this.pages[index].resetStartAfter(startAfter);
} else {
const fsPage = new FirestorePage(this.fsQuery, index === 0
? null : startAfter, this.itemsPerPage);
fsPage
.onUpdate((snapshot, lastDocChanged) => this.onUpdatePage(page, snapshot, lastDocChanged));
await fsPage.load();
this.pages[index] = fsPage;
}
}
/**
* 最大のページ数をチェックして更新する
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async _checkLength() {
this.pages = this.pages.filter((fsPage) => (fsPage.hasDocs));
const currentLength = this.pages.length;
const nextDocQuerySnapshot = await this.fsQuery
.startAfter(this.pages[currentLength - 1].lastDoc)
.limit(1).get();
if (!nextDocQuerySnapshot.docs.length) {
this.length = currentLength;
} else if (typeof this.length === 'number') {
delete this.length;
}
}
/**
* ページのデータ更新時に呼ばれる
* そのページの最後のドキュメントが変わったらそれ以降のページも更新する
* @param {number} page
* @param {firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot} snapshot
* @param {boolean} lastDocChanged
* @returns {Promise<void>}
*/
async onUpdatePage(page, snapshot, lastDocChanged) {
const index = page - 1;
if (this.onUpdateCallback) {
this.onUpdateCallback({ page, snapshot, length: this.length });
if (lastDocChanged && this.pages[index + 1]) {
for (let i = page + 1; i <= this.pages.length; i += 1) {
await this._setPage(i);
if (i === this.pages.length) {
await this._checkLength();
}
this.onUpdateCallback({
page: i,
snapshot: this.pages[i - 1] ? this.pages[i - 1].snapshot : null,
length: typeof this.length === 'number' ? this.length : Infinity,
});
}
}
}
}
/**
* ページ番号を指定してデータを取得
* @param {number} page
* @returns {Promise<FirestorePage | null>}
*/
async load(page) {
const index = page - 1;
if (!this.pages[index] && (typeof this.length !== 'number' || this.length >= page)) {
if (index === 0 || this.pages[index - 1]) {
await this._setPage(page);
} else {
for (let i = 1; i <= page; i += 1) {
await this.load(i);
}
}
}
if (!this.pages[index + 1]) {
await this._checkLength();
}
return this.pages[index] || null;
}
}
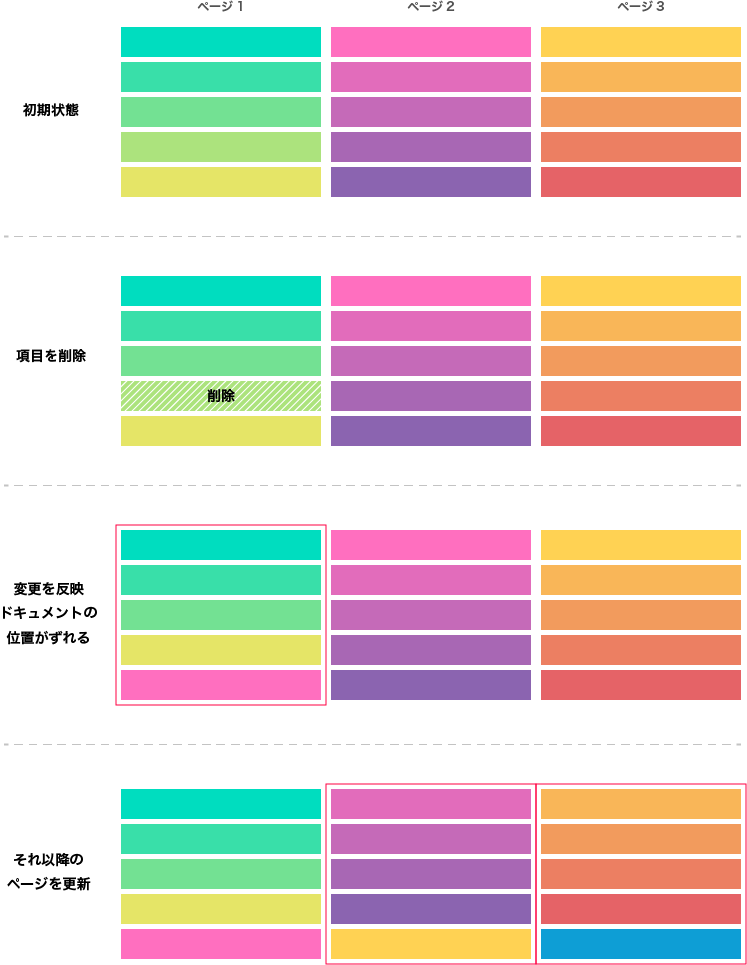
先ほどのFirestorePageの配列を持ち、変更を監視します。変更があった場合通常そのまま親クラスに変更を伝えるだけですが、変更があったページの最後のドキュメントが変更(ドキュメント自体が違うものになった)されている場合にはそれ以降のすでに読み込んでいるページを読み込み直すようにすることで、ページの位置を常に最新の状態に保つようにします。
このようなイメージです。
また_checkLengthの部分では、それが最後のページかどうかを判定するために以前は逆の順番のfirestore.Queryを使用することで最後のドキュメントを取得していましたが、「少なくとも次のドキュメントが一つあるかどうか」で判定するように変更しました。
そして複数の検索クエリを取りまとめるクラスとして以前作ったFirestorePaginationを修正します。こちらは大分シンプルになりました。
import queryString from 'querystring';
import { db } from '../Firebase';
import { ITEM_PER_PAGE, QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS } from '../constants/common';
import FirestorePageManager from './FirestorePageManager';
/**
* Firestoreでページング処理をするためのユーティリティ
*/
export default class FirestoreQueryPagination {
/**
* @param {string} baseCollectionPath
* @param {string} orderFieldPath
* @param {string} directionStr
*/
constructor(baseCollectionPath, orderFieldPath, directionStr = 'asc') {
this.baseRef = db.collection(baseCollectionPath);
this.orderFieldPath = orderFieldPath;
this.directionStr = directionStr;
this.map = {};
}
/**
* Firestoreクエリを生成
* @param {object} query
* @param {string} directionStr
* @returns {firebase.firestore.Query}
* @private
*/
_getFSQuery(query, directionStr = this.directionStr) {
let fsQuery = this.baseRef.orderBy(this.orderFieldPath, directionStr);
Object.keys(query).forEach((key) => {
if (query[key] || query[key] === 0) {
fsQuery = fsQuery.where(key, '==', query[key]);
}
});
return fsQuery;
}
/**
* Firestoreクエリに対して変更を監視
* @param {FirestorePageManager} fsPageManager
* @param {object} query
* @private
*/
_listenSnapshot(fsPageManager, query) {
fsPageManager.onUpdate(({ snapshot, page, length }) => {
if (this.onUpdateCallback) {
this.onUpdateCallback({
query,
page,
snapshot,
length,
});
}
});
}
/**
* 変更に対するリスナー関数を登録
* @param {function} callback
*/
onUpdate(callback) {
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
this.onUpdateCallback = callback;
}
}
/**
* 指定したページのデータを取得
* @param {object} query
* @param {number} page
* @param {number} itemsPerPage
* @returns {Promise<{result: firebase.firestore.QuerySnapshot, length: number}>}
*/
async get(query, page = 1, itemsPerPage = ITEM_PER_PAGE) {
const queryKey = queryString.stringify(query, QUERY_STRING_OPTIONS);
let fsPageManager = this.map[queryKey];
let fsPage = null;
if (fsPageManager) { // すでに同じクエリで取得済み
fsPage = await fsPageManager.load(page);
} else { // 初めてのクエリ
fsPageManager = new FirestorePageManager(this._getFSQuery(query), itemsPerPage);
fsPage = await fsPageManager.load(page);
this.map[queryKey] = fsPageManager;
this._listenSnapshot(fsPageManager, query);
}
return {
result: fsPage && fsPage.snapshot,
length: typeof fsPageManager.length === 'number' ? fsPageManager.length : Infinity,
};
}
}
最後に、Reactコンポーネントの方でこのonUpdateにリスナー関数を渡して変更を反映してみます。
画面コンポーネントのconstructorでonUpdateリスナーを登録します。
this.dbPagination = new FirestoreQueryPagination('/members', 'id', 'desc');
this.dbPagination.onUpdate(this.onUpdate.bind(this));
onUpdate({
query,
page,
snapshot,
length,
}) {
const { query: currentQuery } = this.props;
const currentPage = typeof currentQuery.page === 'number' ? currentQuery.page : 1;
if (page === currentPage && !isEqual(currentQuery, query)) {
this.setState({
data: snapshot ? snapshot.docs.map((doc) => (doc.data())) : [],
pageLength: length,
});
}
}
変更されたのが現在表示しているページであればデータを反映します。
ページを読み込んでからFirebaseコンソールでドキュメントを削除してみると、うまくページ変更が反映できたのが確認できました。