ElasticsearchとKibana、形態素解析エンジンとしてSudachiをインストールしたログです。
以下を参考にしました。
- [Elasticsearch で Sudachi 使う] (https://whitech0c0late.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/05/13/235137)
- Elasticsearchのための新しい形態素解析器 「Sudachi」
- [Install Elasticsearch with RPM]
(https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/rpm.html)
※お試し環境なので可用性・セキュリティは考慮していません。
使用した環境
[インスタンスを作成する - Oracle Cloud Infrastructureを使ってみよう(その3)]
(https://community.oracle.com/docs/DOC-1019204) を参考に、VCN(仮想クラウドネットワーク)を作成し、VM(Computeインスタンス)を作成。
OS:Oracle Linux 7.x (最新のもの) を選択
インスタンス作成後、Public IPアドレスと、Private IPアドレスを確認しておく。
(Compute >> Instances >> Instance Details)
インストール
Javaのインストール。rpmを別途ダウンロードして以下を実行
# mkdir /usr/java
# cd /usr/java/
# rpm -ivh jre-8u191-linux-x64.rpm
/etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo を以下の内容で作成
[elasticsearch-6.x]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 6.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md
Elasticsearch 6.2.0をインストール
(Sudachiプラグインが、最新バージョンのElasticsearchには対応していないようでインストールに失敗したので、Elasticsearchのバージョンを明示的に指定してyum install)
# yum --showduplicates search elasticsearch (※install可能なバージョンを確認)
# yum install elasticsearch-6.2.0-1.noarch
Sudachiプラグインインストール
# yum install maven
# yum install git
# git clone https://github.com/WorksApplications/elasticsearch-sudachi.git
# cd elasticsearch-sudachi/
# mvn package
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install file:///root/elasticsearch-sudachi/target/releases/analysis-sudachi-elasticsearch6.2-1.1.0-SNAPSHOT.zip
Kibanaインストール(バージョンを6.2.0に合わせる)
# yum --showduplicates search kibana
# yum install kibana-6.2.0-1.x86_64
起動
以下の確認により、systemctlを使用して起動する
$ ps -p 1
PID TTY TIME CMD
1 ? 00:00:02 systemd
Elasticsearch起動
# /bin/systemctl daemon-reload
# /bin/systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/elasticsearch.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service.
# systemctl start elasticsearch.service
Kibana起動
# /bin/systemctl daemon-reload
# /bin/systemctl enable kibana.service
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kibana.service to /etc/systemd/system/kibana.service.
# systemctl start kibana.service
動作確認
Elasticsearch起動確認
# curl -X GET "localhost:9200/"
{
"name" : "RTk9yAi",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "PtV0gqoQQsGjMa-fBZ1Uhw",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.2.0",
"build_hash" : "37cdac1",
"build_date" : "2018-02-01T17:31:12.527918Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.2.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Sudachiプラグイン確認
# curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200/_nodes/plugins?pretty'
{
"_nodes" : {
"total" : 1,
..(中略)..
"plugins" : [ {
"name" : "analysis-sudachi",
"version" : "1.1.0-SNAPSHOT",
"description" : "The Japanese (Sudachi) Analysis plugin integrates Lucene Sudachi analysis module into elasticsearch.",
"classname" : "com.worksap.nlp.elasticsearch.sudachi.plugin.AnalysisSudachiPlugin",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"requires_keystore" : false
}
],
Sudachiの辞書ファイルのダウンロードと配置
# wget https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/com/worksap/nlp/sudachi/0.1.1-SNAPSHOT/sudachi-0.1.1-20181108.091011-45-dictionary-core.zip
# mkdir /etc/elasticsearch/sudachi_tokenizer/
# unzip sudachi-0.1.1-20181108.091011-45-dictionary-core.zip
# mv system_core.dic /etc/elasticsearch/sudachi_tokenizer/
sudachi_testという名前のindex作成 (まずは以下の内容でsudachi.json作成)
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"analysis": {
"tokenizer": {
"sudachi_tokenizer": {
"type": "sudachi_tokenizer",
"mode": "search",
"discard_punctuation": true
}
},
"analyzer": {
"sudachi_analyzer": {
"filter": [
],
"tokenizer": "sudachi_tokenizer",
"type": "custom"
}
}
}
}
}
}
sudachi_testという名前のindex作成
$ curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:9200/sudachi_test/ -d @sudachi.json
{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"sudachi_test"}
Sudachiの動作を見てみる
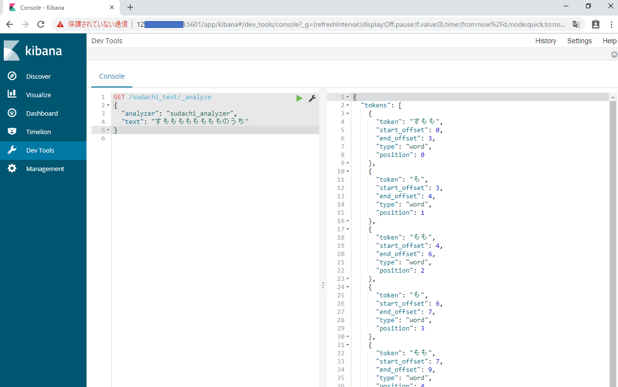
「すももももももももものうち」という文字列を入力
Sudachiを使う場合
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'localhost:9200/sudachi_test/_analyze?pretty' -d '{"analyzer": "sudachi_analyzer", "text": "すもももももももものうち"}'
結果
完璧♪
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "すもも",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "もも",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "もも",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 9,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "の",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "うち",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 6
}
]
}
Sudachiを使わない場合(stadardアナライザの利用)
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" 'localhost:9200/sudachi_test/_analyze?pretty' -d '{"analyzer": "standard", "text": "すもももももももものうち"}'
結果
1文字ずつ分割されている
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "す",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 9,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "も",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 10,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "の",
"start_offset" : 10,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 10
},
{
"token" : "う",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 11
},
{
"token" : "ち",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 13,
"type" : "<HIRAGANA>",
"position" : 12
}
]
}
リモートからもつながるように設定変更
Elasticsearch(PORT:9200)は、localhostにバインドして起動する設定のため、localhostからしか接続できないようになっていました。
Kibana(PORT:5601)も、最初の設定ではlocalhostからしか接続できないようになっていました。
Elasticsearch, Kibanaの設定ファイル変更し再起動
設定ファイルを変更(必要に応じて元のファイルをcpしてオリジナル版を残しておく)
network.host: 0.0.0.0
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
elasticsearch.url: "http://<PUBLIC_IP_ADDRESS>:9200"
# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
# systemctl restart kibana.service
このクラウド環境固有の設定変更
ComputeインスタンスのFirewallの設定
デフォルトではSSHサービス以外は全て閉じられているので使用するポートを許可する
# firewall-cmd --list-ports (※現状確認:何も無い)
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5601/tcp
success
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=9200/tcp
success
# firewall-cmd --reload
success
# firewall-cmd --list-ports
5601/tcp 9200/tcp
Oracle CloudのVCNの設定で、特定PORTへのアクセスを許可
- KibanaへのPORT(5601)を開放
- ElasticsearchのPORT(9200)も一緒に開放
Networking >> Virtual Cloud Networks >> Virtual Cloud Network Details より
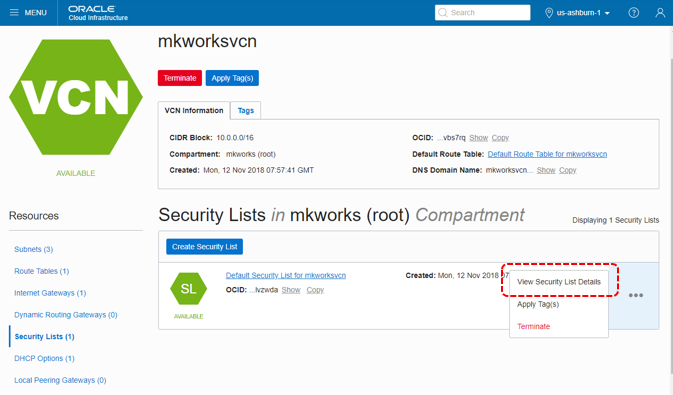
「Security Lists」をクリックし、以下の画面に。
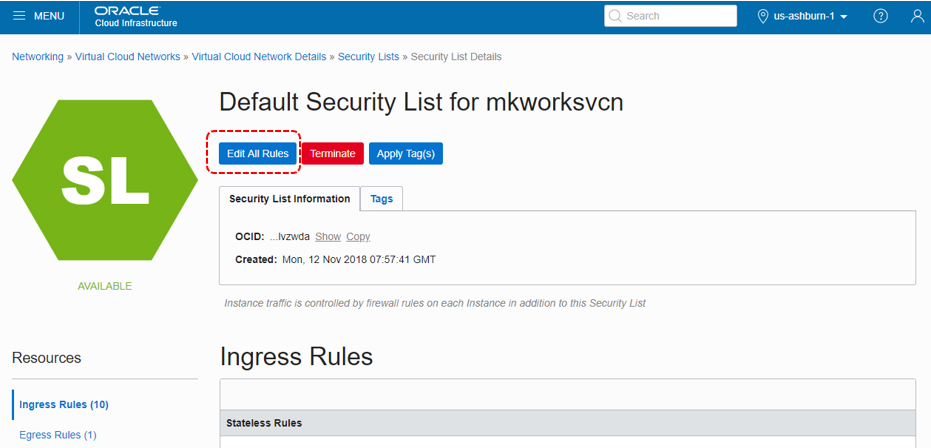
「View Security List Details」をクリック
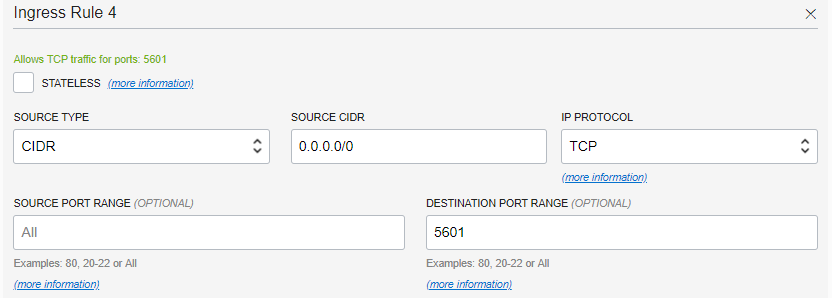
「Edit All Rules」をクリックし、Ingressルールの一番下にある「+ Another Ingress Rules」をクリックし、以下のように全IPアドレス(0.0.0.0)からPORT:5601を追加。
(※アクセスするIPアドレスがわかっている場合は絞って指定)
PORT:9200 も同様に追加する。
最後に、一番下にある「Save Security List Rules」を忘れずにクリックし保存。
Kibanaにリモートからアクセス
手元のPCから、http://PUBLIC_IP_ADDRESS:5601/
アクセス成功。
Dev Tools → 「すもももももももものうち」を入力してみたところ。
追記
設定の続き。
Elasticsearch + Logstash + Kibana + SudachiプラグインでTwitterを可視化したときのtemplate